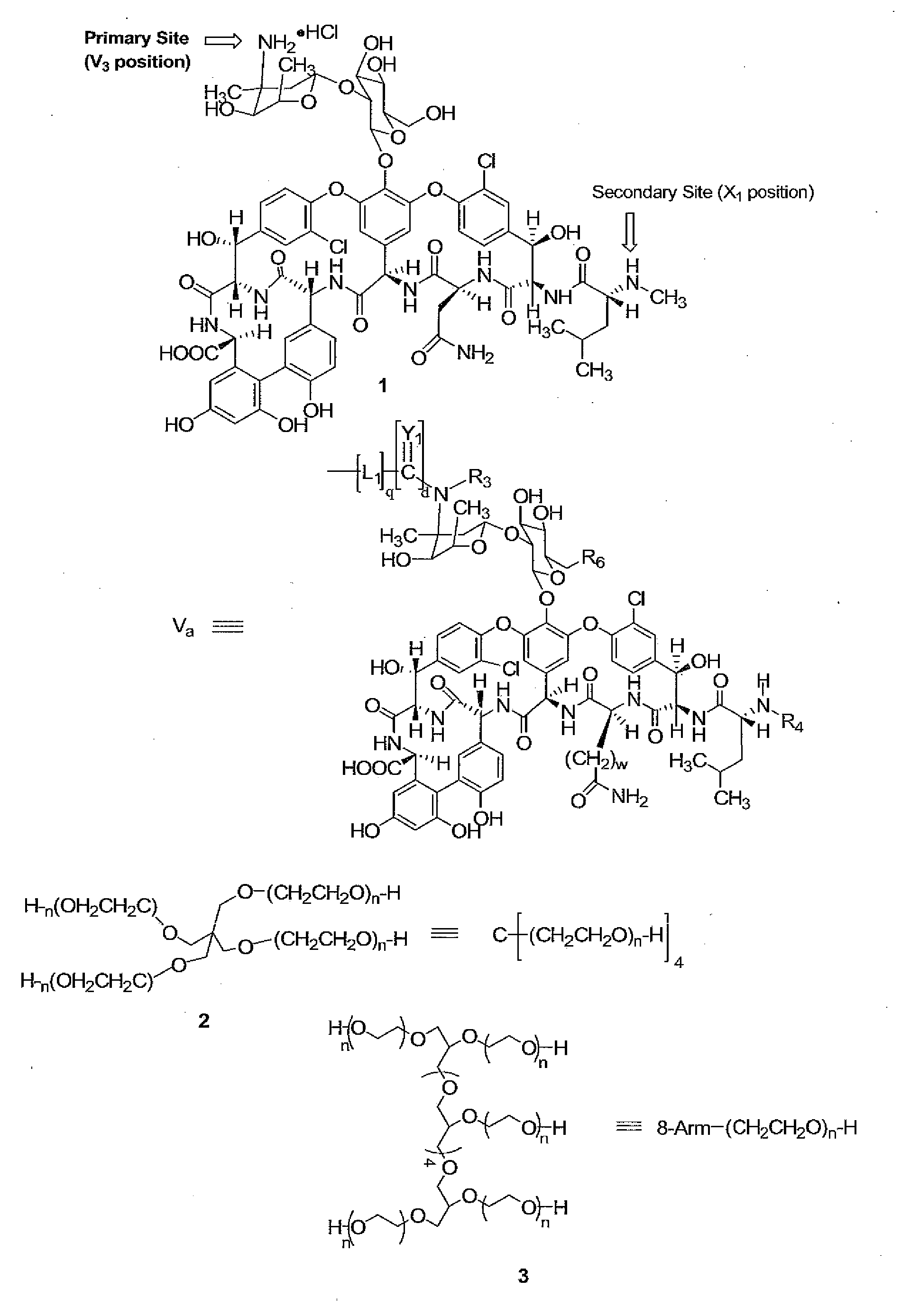
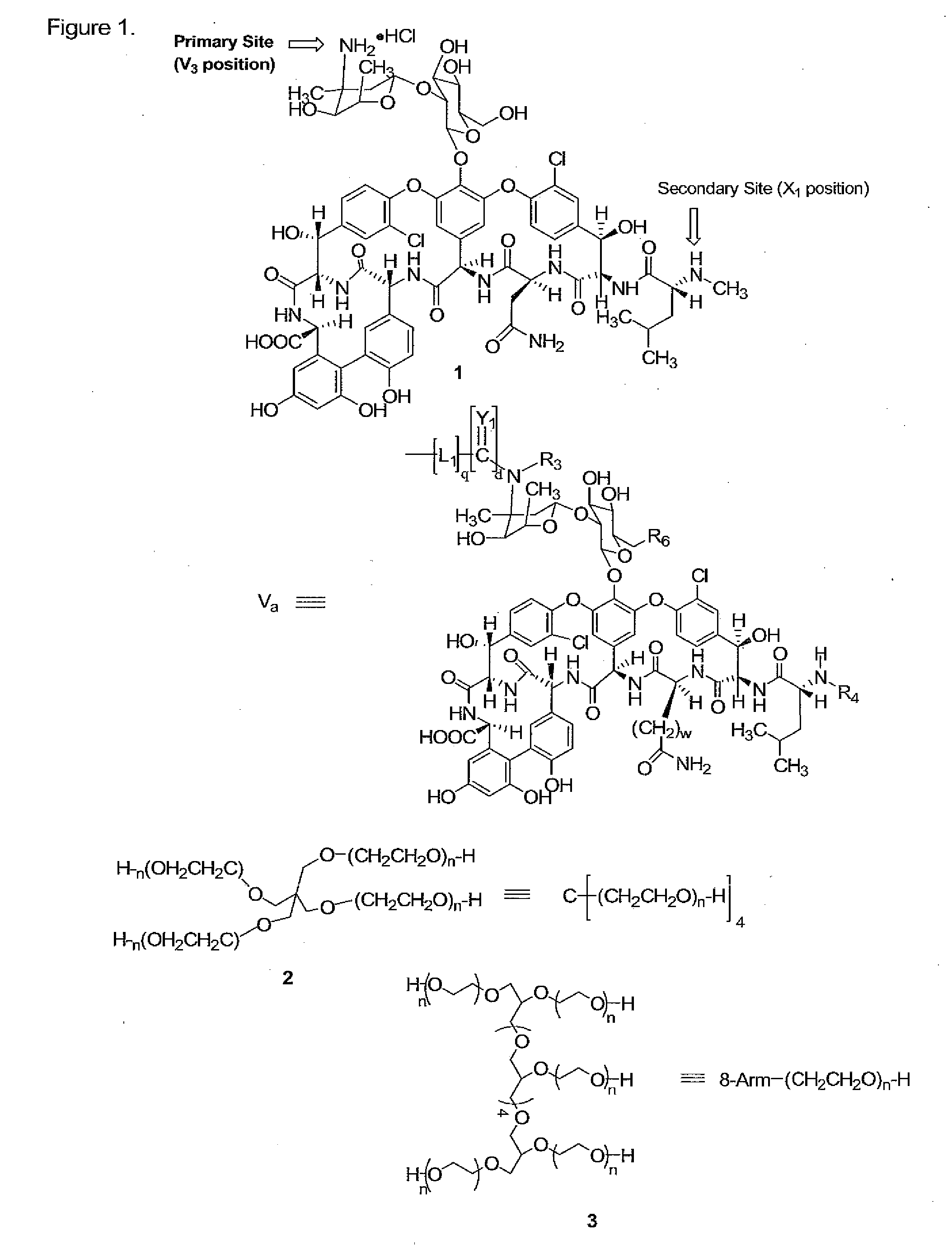
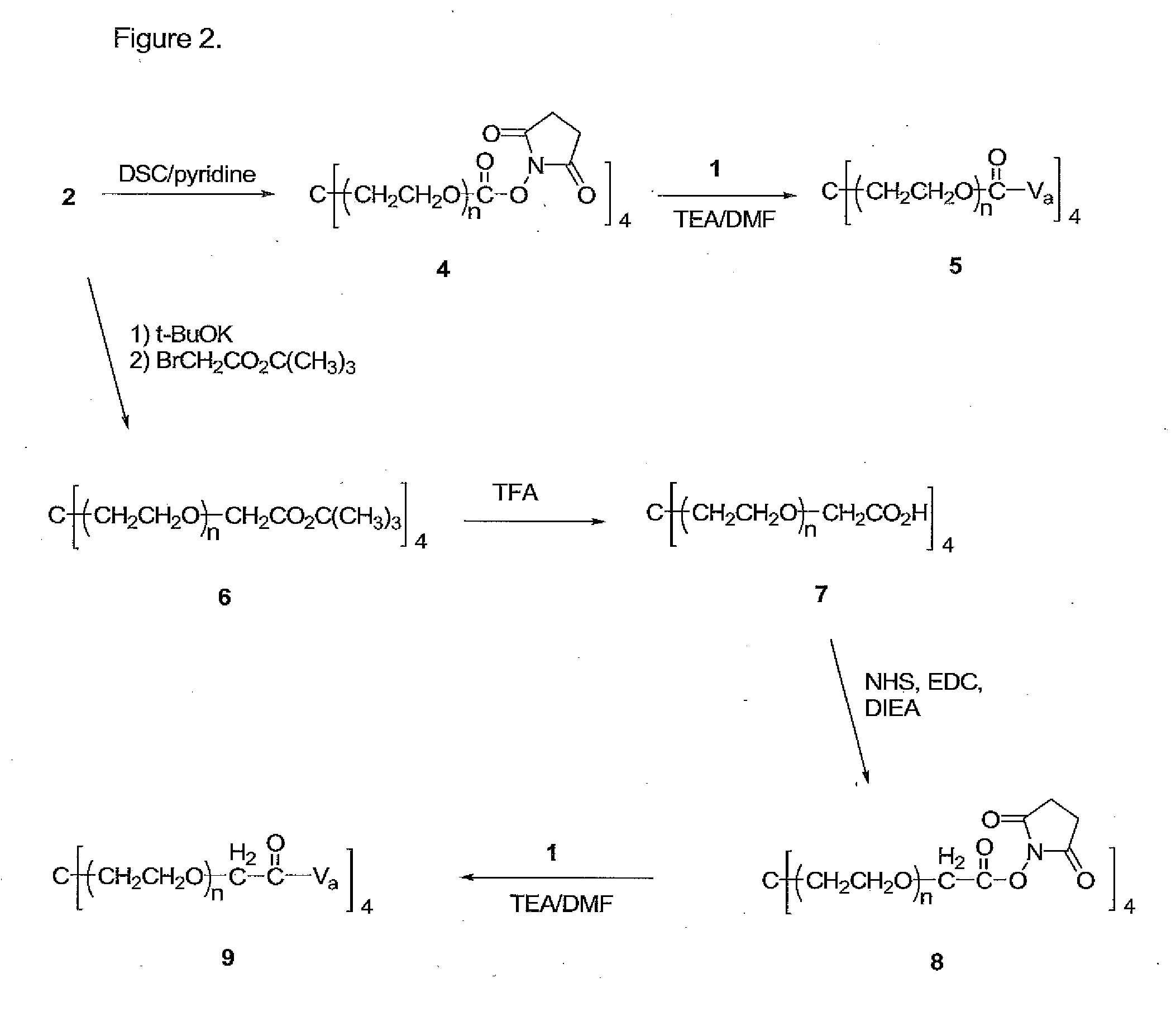Prodrugs of vancomycin with hydrolysis resistant polymer linkages
a vancomycin and hydrolysis resistant technology, applied in the field of prodrugs, can solve the problems of not providing sufficient active compounds, and achieve the effects of prolonging the circulating life, reducing dose frequency and its related medical costs, and maintaining serum levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0148]Compound 4. A solution of 2 (mw 40 kDa, 23 g, 0.575 mmol) and disuccinimidyl carbonate (DSC, 2.36 g, 9.2 mmol) in methylene chloride (DCM, 230 mL) and dimethylformamide (DMF, 23 mL) was cooled to 0° C., followed by the addition of pyridine (0.75 mL, 9.2 mmol). This mixture was allowed to warm to room temperature overnight, followed by filtration through Celite® and partial removal of the solvent from the filtrate by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure. The crude product was precipitated with ether and collected by filtration, and crystallized from 20% DMF / isopropanol (IPA) to yield 4 (20.1 g, 0.496 mmol, 86%). 13C NMR (67.8 MHz, C5D5N) δ 168.2, 151.1, 70.7-69.6 (PEG), 68.0, 45.2, 25.2.
example 2
[0149]Compound 5. To a solution of 1 (0.550 g, 0.37 mmol) and triethylamine (TEA, 2.06 mL, 14.8 mmol) in DMF (50 mL) was added 4 (3 g, 0.074 mmol) and 5.5 g molecular sieves (4 Å) and the mixture stirred at 30° C. for 5 hrs. The reaction mixture was filtered through celite, the PEG conjugate precipitated with ether, filtered, and crystallized from DMF / ethanol (50:50) three times to give 5 (2.0 g, 0.0436 mmol, 59%).
example 3
[0150]Compound 6. A solution of 2 (10 g, 0.025 mmol) in toluene (150 mL) was azeotroped for 2 hrs with the removal of 50 mL of distillate. The reaction mixture was then cooled to 30° C., followed by the addition of a 1.0 M solution potassium t-butoxide in t-butanol (1.7 ml, 1.7 mmol). The resulting mixture was stirred for 1 hr at 45° C., cooled to 30° C., followed by the addition of t-butyl bromoacetate (0.4 g, 2.0 mmol). The resulting mixture was refluxed for 18 hrs, followed by filtration through Celite and partial removal of the solvent from the filtrate by rotary evaporation under reduced pressure. The crude product was precipitated with ether, collected by filtration, and crystallized from IPA to yield 6 (8.1 g, 0.20 mmol, 80%). 13C NMR (67.8 MHz, C5D5N) δ 169.1, 81.1, 72.2-69.6 (PEG), 68.7, 45.2, 27.9.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com