Semiconductor device production method and semiconductor production apparatus
a semiconductor and production method technology, applied in the direction of electrolysis process, electrolysis components, cells, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to fill a metal in the wiring region, difficult in the prior art electroplating method and electroplating apparatus to measure, and difficult to create any voids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0028]A first embodiment of the present invention is described hereafter with reference to FIG. 1.
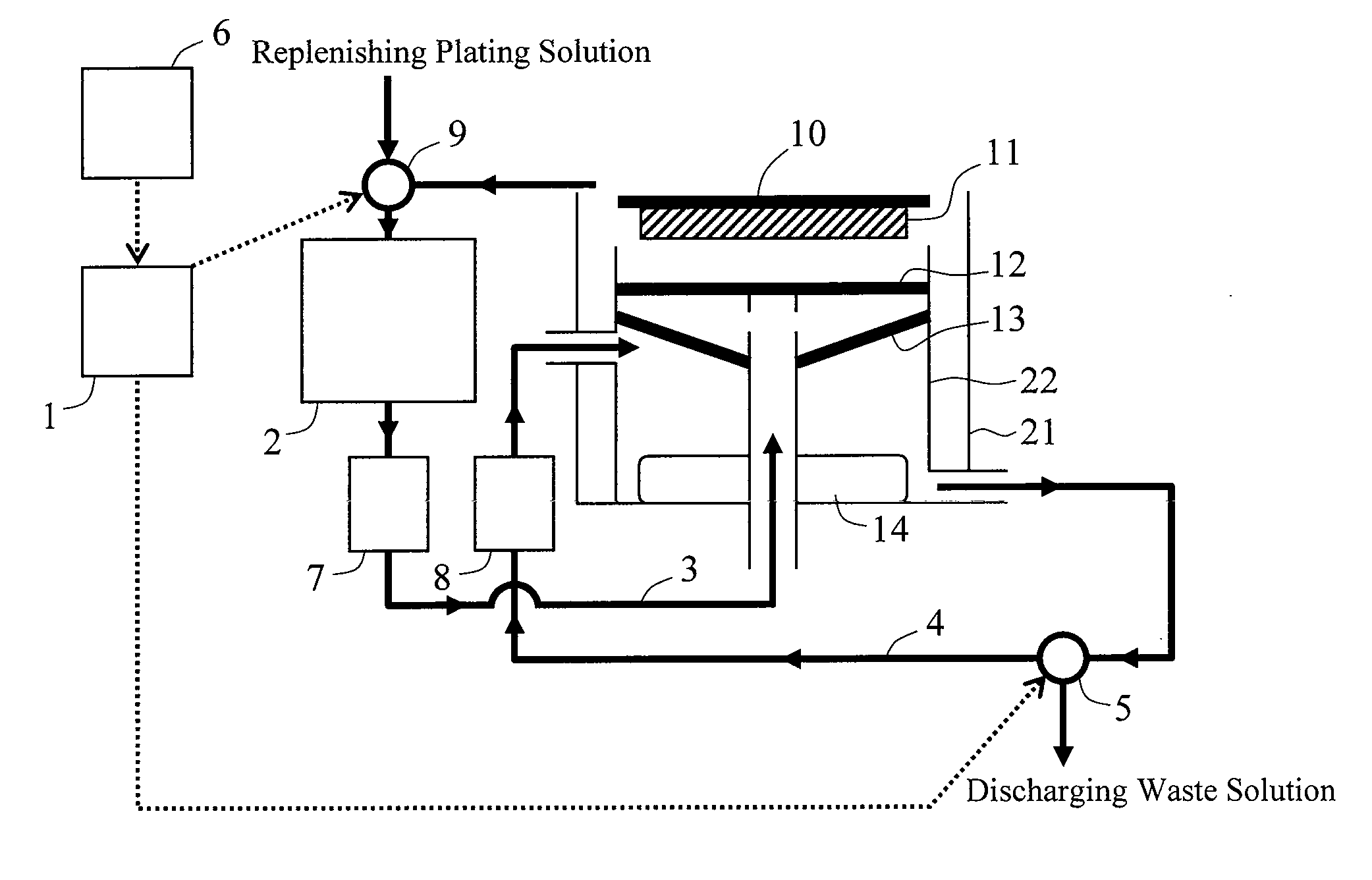
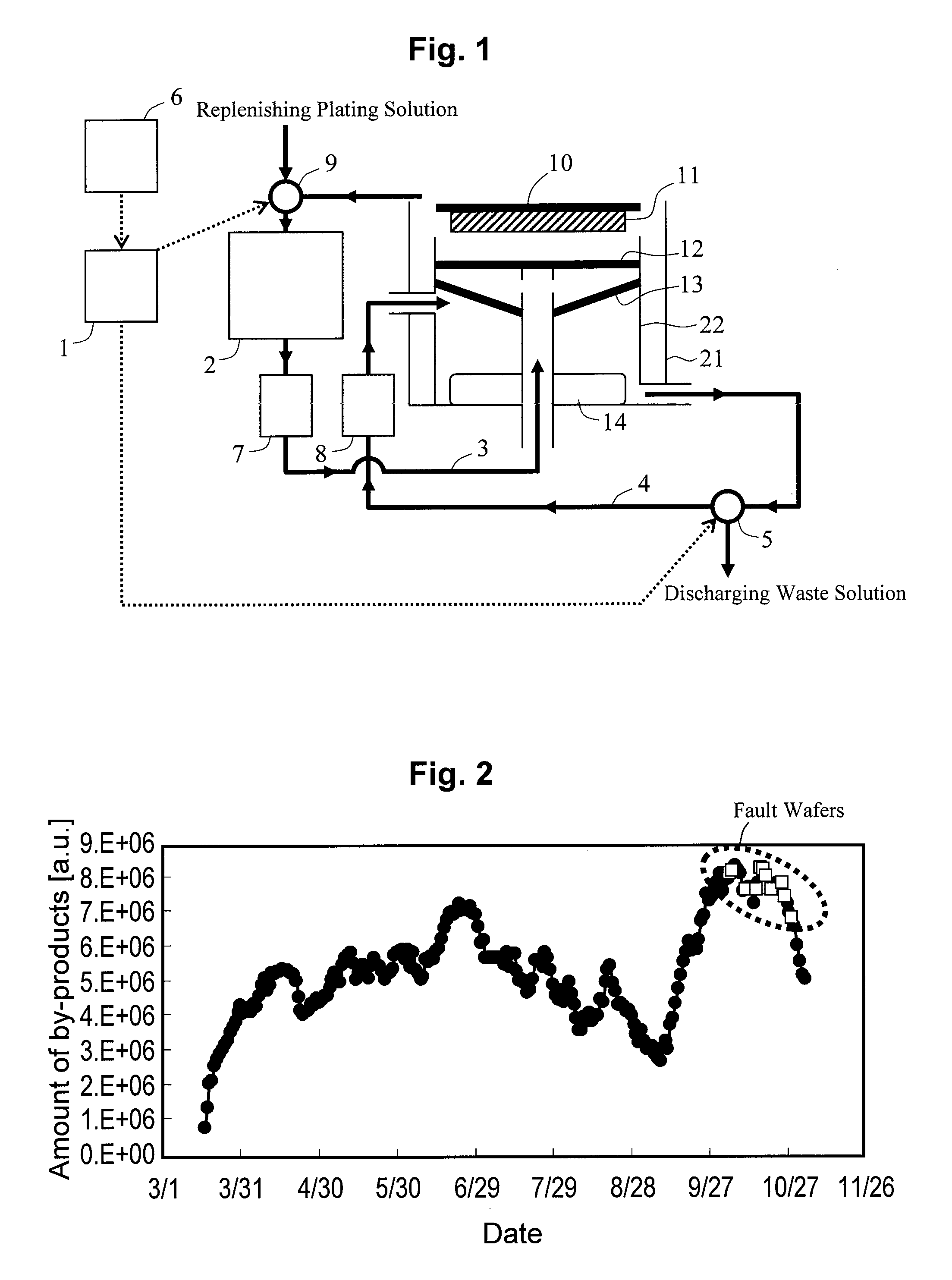
[0029]FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the structure of an electroplating apparatus relating to the first embodiment. The electroplating apparatus comprises a plating chamber 21 having a partition 22. An anode 14 is placed at the bottom of the plating chamber 21. Facing the anode 14, a cathode 10 holds a wafer 11 in a manner such that the surface to be treated is oriented toward the anode 14. A filter 13 and a diffusion plate 12 are provided between the anode 14 and cathode 10 in this order from the anode 14. The electroplating apparatus of this embodiment further comprises a circulation line 3 and a sub-circulation line 4 as the plating solution circulation path. The circulation line 3 is a circulation path allowing the plating solution from the top end of the plating chamber 21 to re-enter between the diffusion plate 12 and filter 13 via a plating tank 2 and a filter 7. The sub-c...
second embodiment
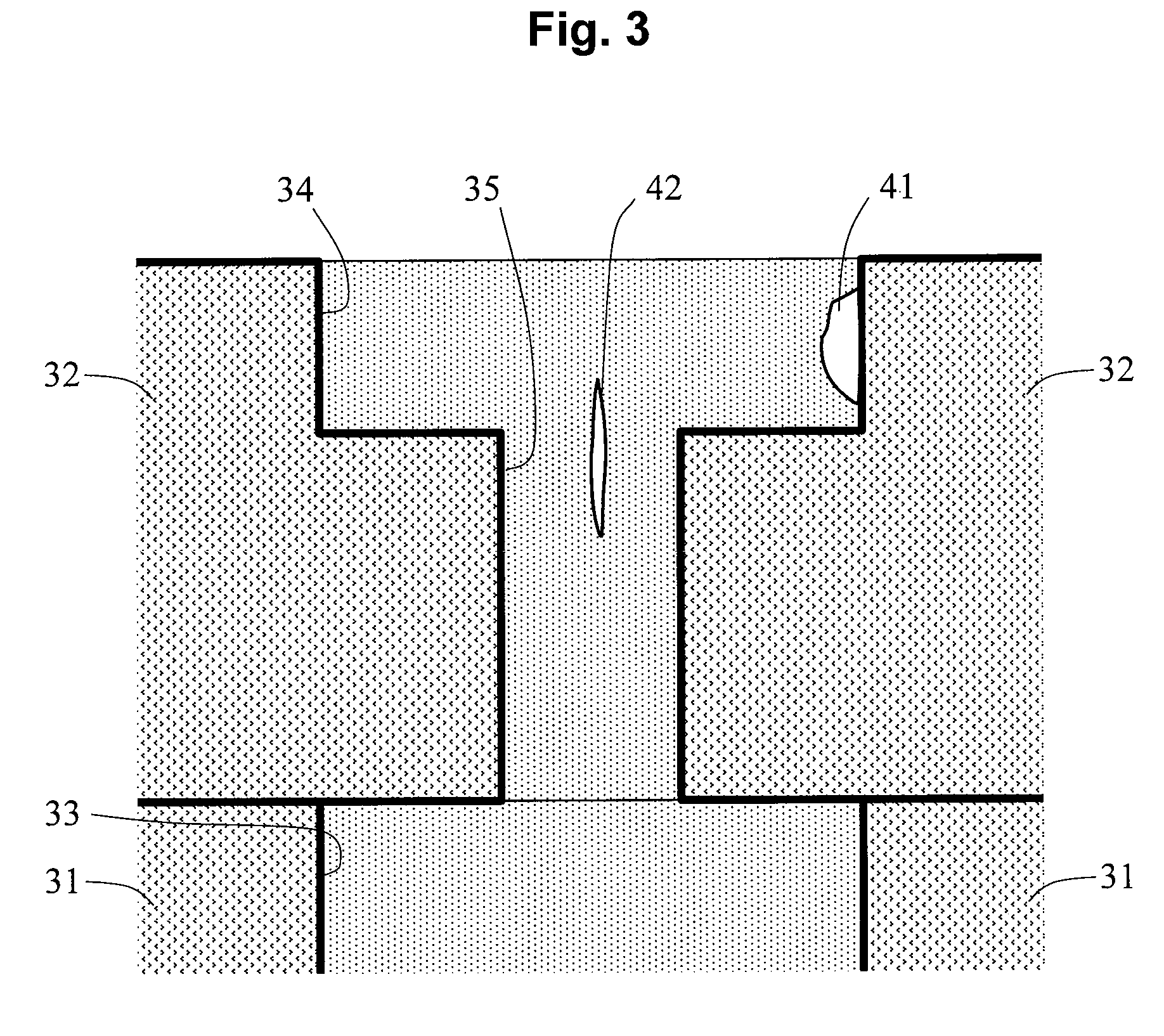
[0046]A second embodiment provides a filling method creating no defects such as voids and seams based on the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0047]FIG. 6 is a flowchart of a plating process presenting the second embodiment. When the electroplating apparatus starts a recipe for plating, first, the monitoring unit 6 measures the concentrations of the three additives (S1). The monitoring unit 6 orders the control unit 1 to replenish plating solution in the case of NG in which the measurements are outside predetermined value ranges. The control unit 1 being ordered opens the supply valve 9 and replenishes a predetermined volume of plating solution (S1NG, S2). When the replenishment is completed, the monitoring unit 6 measures the concentrations of the additives once again (S1). The replenishment of plating solution is repeated until the concentrations of the additives are within the above predetermined ranges. When the replenished volume exceeds the total volume of plating sol...
third embodiment
[0050]A third embodiment of the present invention will be described hereafter. The third embodiment of the present invention relates to an electroplating method in which the optimum volume of waste solution is determined. The plating solution is expensive and it is preferable that the volume of waste solution is minimized. Then, in this embodiment, a technique of determining the optimum volume of waste solution based on the quantity of wafers to be processed, namely the amount of by-products to be produced, total volume of plating solution, and volume of waste solution, will be described.
[0051]FIG. 7 is a graphical representation showing results of simulating the amount of by-products in the plating solution in relation to the number of times of discharging waste solution. Here, the amounts of by-products were calculated for the cases when volume ratios of waste solution to the total volume of plating solution (hereafter, referred to as a waste solution ratio) were 8% and 29% with t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com