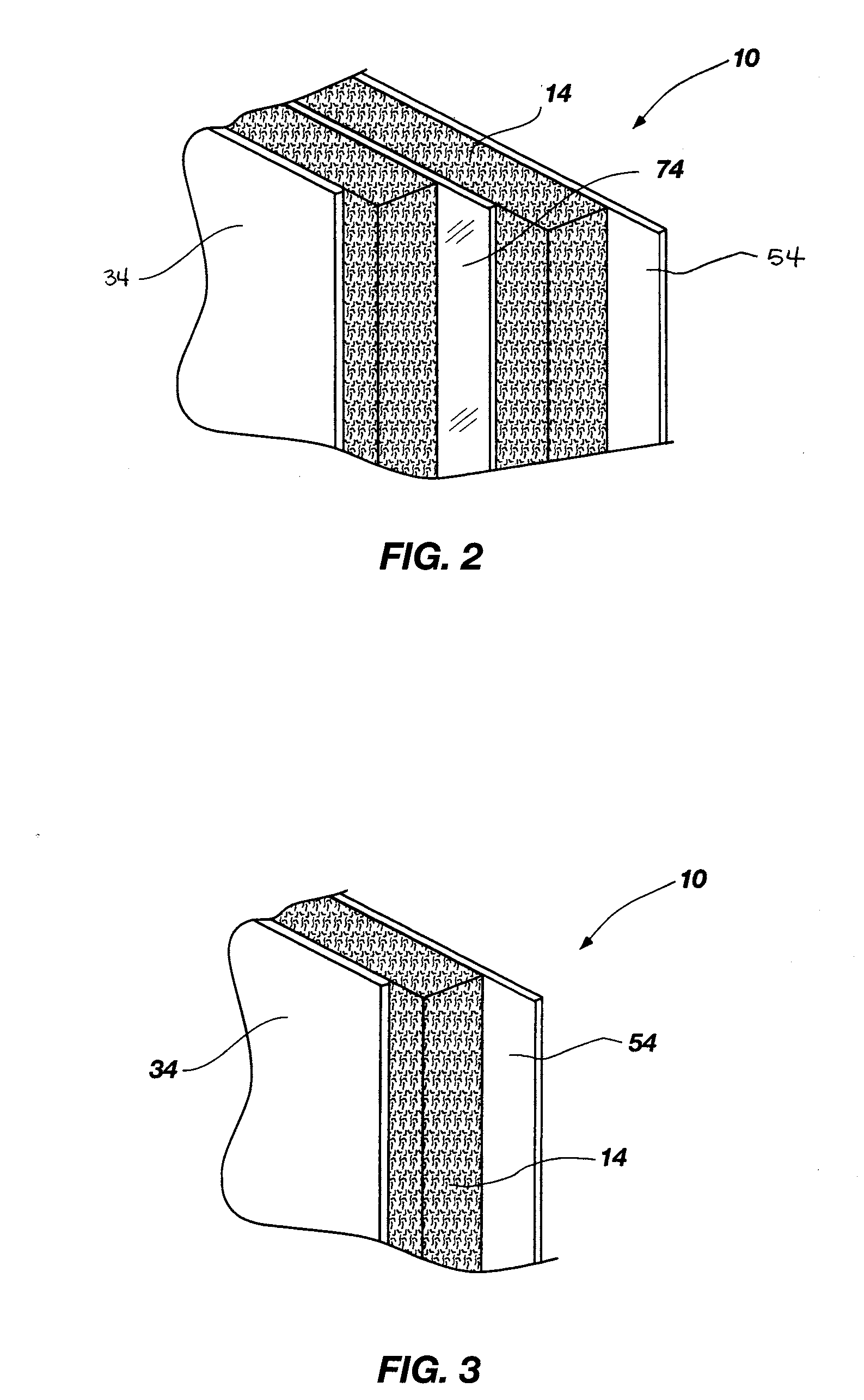
Sound Attenuation Building Material And System
a sound attenuation and building material technology, applied in the field of building materials, can solve the problems of poor noise reduction properties, conventional types of shear panels, poor sound attenuators, etc., and achieve the effect of adding strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Testing of Utility Material of Cenospheres and Sodium Silicate
[0104]A mixture of cenospheres of the form of Extendospheres™ and sodium silicate were combined and allowed to dry and form a fire-resistant insulating material Extendospheres™ of a 300-600 micron diameter size range were combined with sodium silicate solution (O type from PQ corporation) in a 1:1 weight ratio. The wet slurry was poured into a cavity around the turbine and allowed to dry. It formed a hardened mass of Extendospheres™ and sodium silicate. The material was tested with an Ipro-Tek single spool gas turbine. The tests showed that the material has a high insulation capacity, and the ability to withstand heat. The insulation was exposed to temperatures of up to 1200° C. However, it was found that when the material is exposed directly to flames for periods of more than a few minutes, it cracks and blisters and begins to lose physical strength.
example 2
Formation of Mold to Form Wallboard
[0105]In one aspect, the utility material can be wallboard panels. The panels can optionally be formed by exposing an uncured wallboard to microwaves. Such formation, as well as general wallboard formation, can utilize a mold. An example of a mold can be made up of a vinylester resin mold having top and bottom pieces. To form the vinylester resin mold, a wood mold is first constructed. The wood mold can be formed according to the shape and dimensions as illustrated in FIG. 9.
[0106]To form the vinylester resin mold, an outer mold of wood is attached to the base of the wood mold using double sided tape. Any releasable binder or means of attaching can be alternatively used. A resin mixture is formed of 97.5 wt % vinylester resin mixed with 2.5 wt % methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP) catalyst. Microspheres of the form of Extendospheres and the resin mixture are added in a 1:1 ratio to form a core mixture. The core mixture is mixed well using a stirrin...
example 3
Preparation of Wallboard Using Mold
[0107]As noted, the utility material can be in the form of wallboard panels. The panels can optionally be formed by using the porous vinylester resin mold. First, a wallboard backing paper is cut using a backing paper template as shown in FIG. 10. Although a particular backing paper shape is illustrated, it should be understood that the backing paper can be of any shape or size sufficient to form a segment of wallboard. Facing paper is cut to a rectangle sized just smaller than the greater dimensions of the backing paper. In the present embodiment, the facing paper is cut to an 11.625 inch by 15.25 inch rectangle. The backing paper is folded and placed in the porous mold. A wallboard mixture may be formed using:
700 to 900 g microspheres
1100 to 1300 g sodium silicate solution, such as that sold by “O”
300 to 500 g latex binder
20 to 30 cc foaming agent
[0108]Specifically, the foaming agent is added first to the sodium silicate solution and mixed using ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequencies | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com