Light-emitting device, electronic equipment, and process of producing light-emitting device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
A: First Embodiment
A-1 Structure of Light-Emitting Device
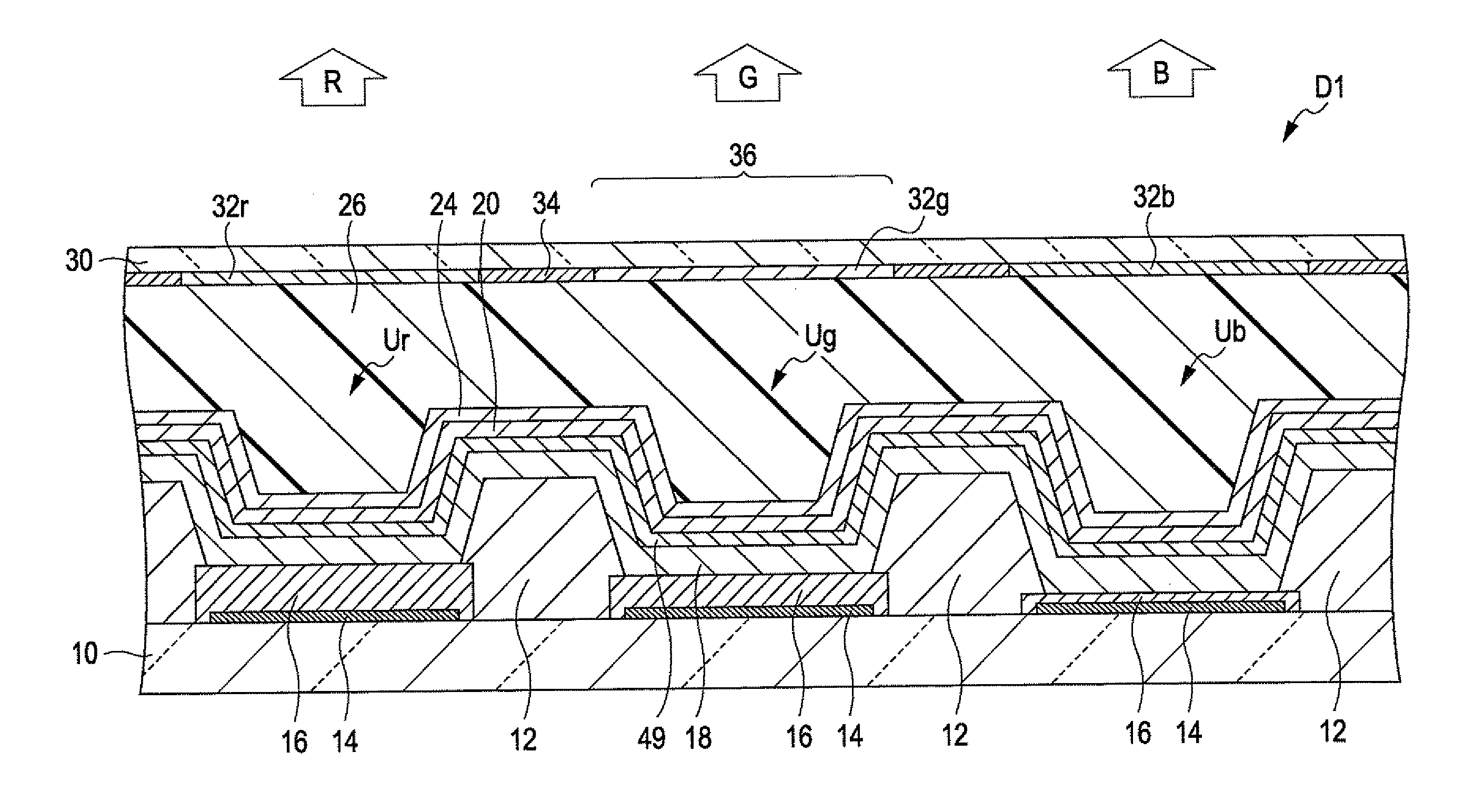
[0088]FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a structure of a light-emitting device D1 according to a first embodiment of the invention. As shown in FIG. 1, the light-emitting device D1 is configured such that a plurality of light-emitting elements U (Ur, Ug, and Ub) is arrayed on a surface of a first substrate 10. Each of the light-emitting elements U is an element generating light with a wavelength corresponding to any of a plurality of colors (red, green, and blue). In these elements, a single light-emitting function layer is common to the plurality of elements, and emission light with a wavelength corresponding to the respective light-emitting elements is extracted by controlling the optical length between the below-described reflecting layer and semi-reflective opposite electrode in each light-emitting element for optimizing resonance. In the first embodiment, by the resonance effect, the light-emitting element Ur ...
second embodiment
B: Second Embodiment
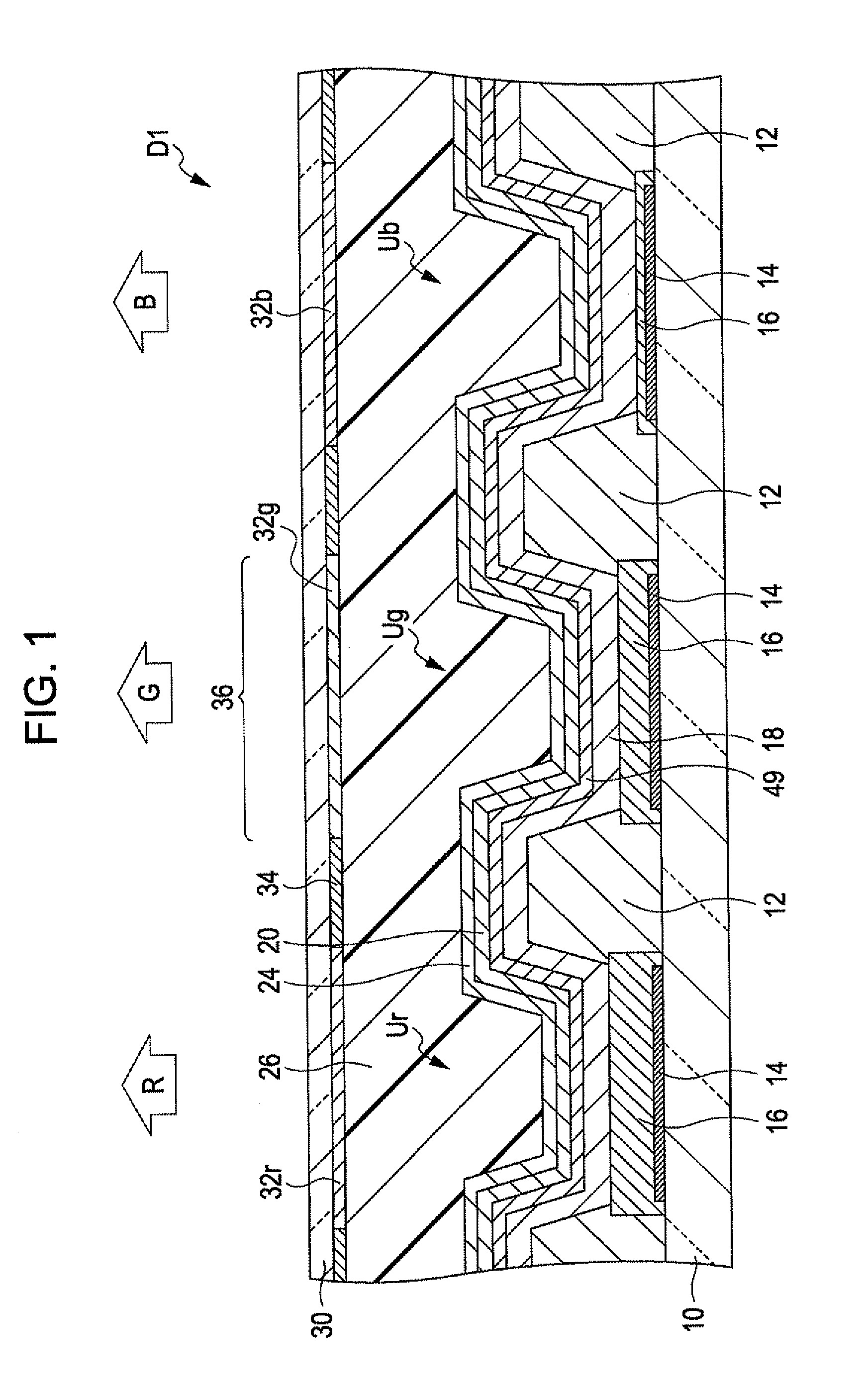
[0130]In a second embodiment, the deposition rate ratio of Mg and Ag for forming the opposite electrode 20 is set to 1:9. Since the other configuration is the same as that of the first embodiment, the description thereof is omitted,
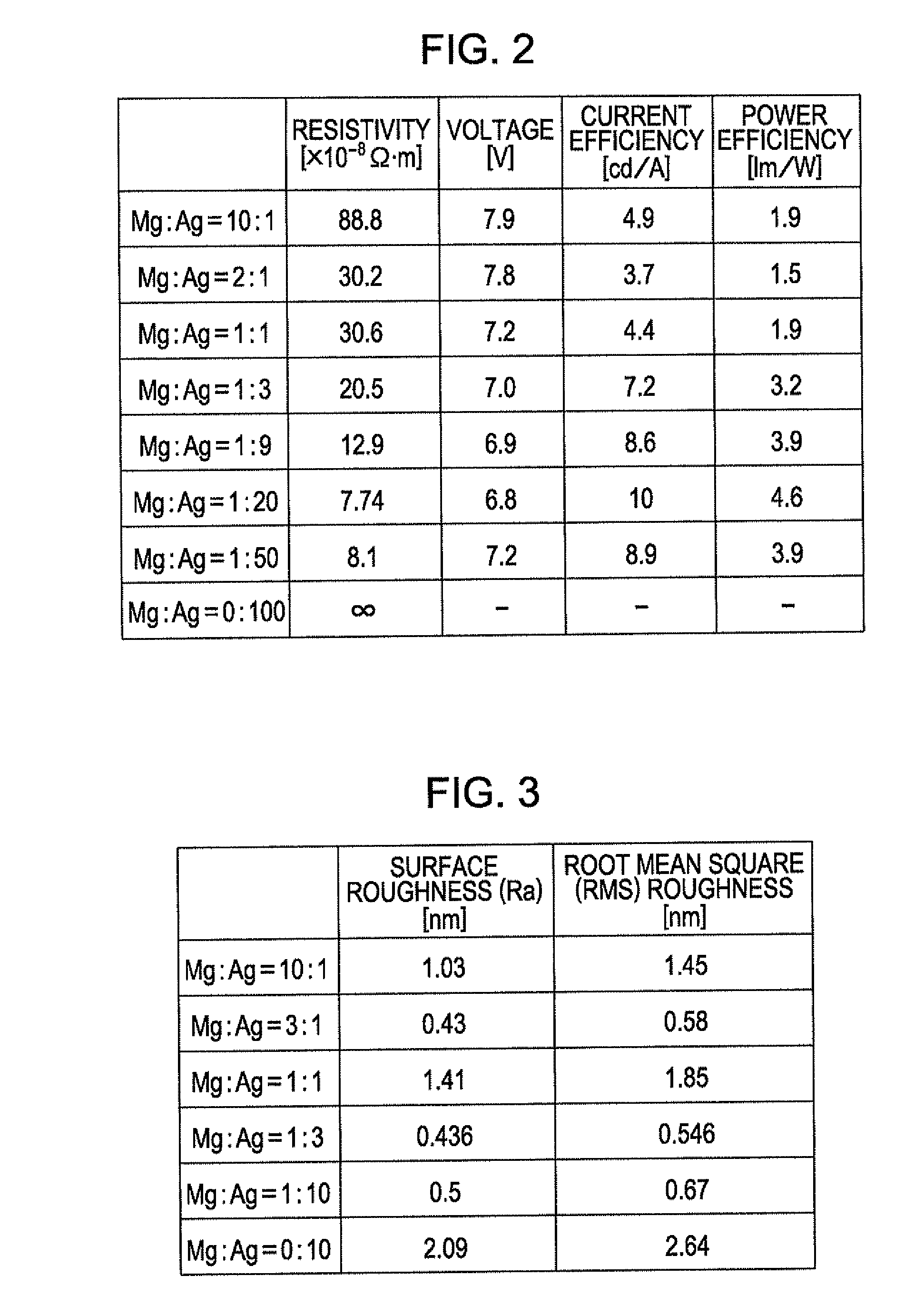
[0131]FIG. 11 is a diagram showing measurement results of various factors in each case that the thickness of the opposite electrode 20 of the light-emitting element Ug according to the second embodiment is 10 nm, 13 nm, or 16 nm, The sheet resistance values shown in FIG. 11 are those of the opposite electrode 20, and the values of voltage, current efficiency, and power efficiency are those when the density of current flowing in the opposite electrode 20 is set to 17.5 mA / cm2. In addition, though it is not shown in the drawing, the values of the various factors when the thickness of the opposite electrode 20 is 20 nm are equivalent to those when the thickness is 16 nm.
[0132]As shown in FIG. 11, it is confirmed that the sheet resistance ...
third embodiment
C: Third Embodiment
[0133]FIG. 12 is a cross-sectional view illustrating a structure of a light-emitting device D2 according to a third embodiment of the invention. In the above-described embodiments, the light-emitting function layer 18 is common to all the light-emitting elements U, but in the third embodiment, the light-emitting function layer 18 is independently formed for each emission color of the light-emitting elements U.
[0134]As shown in FIG. 12, the light-emitting function layers 18 (18r, 18g, and 18b) each include a hole-injection layer 41 disposed on the pixel electrode 16, a hole-transporting layer 43 disposed on the hole-injection layer 41, a light-emitting layer 45 (45r, 45g, or 45b) disposed on the hole-transporting layer 43, and an electron-transporting layer 47 disposed on the light-emitting layer 45. The light-emitting function layer 18r of the light-emitting element Ur contains the light-emitting layer 45r made of an organic EL material that generates light of an ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com