Multi parametric classification of cardiovascular sounds
a multi-parameter, heart sound technology, applied in the field of heart sound classification, can solve the problems of difficult to provide an automated device for diagnosing coronary stenosis using auscultatory sounds, complicated and expensive use of the above-mentioned techniques, and severe defects in the blood supply
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
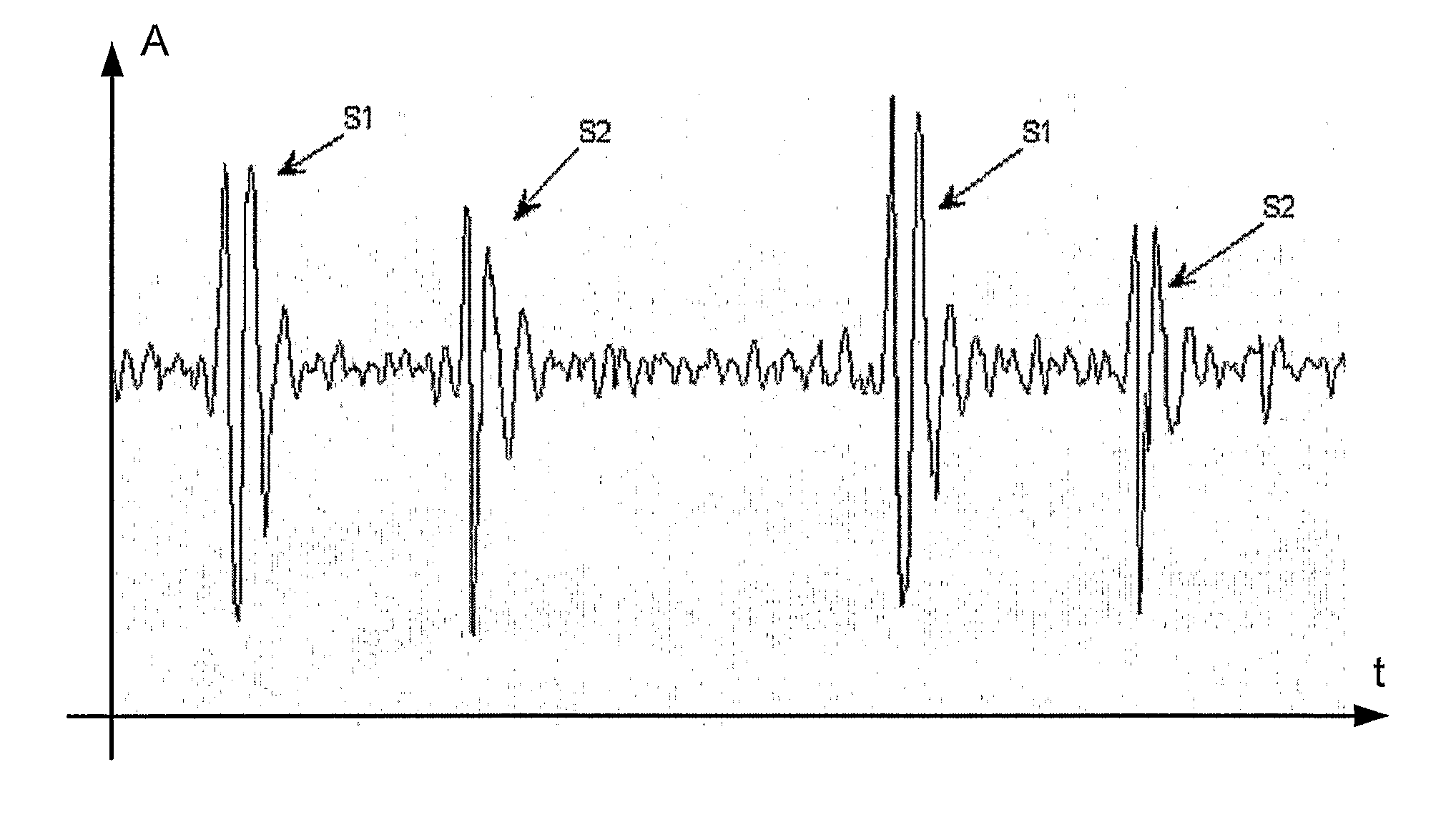
[0043]FIG. 1 illustrates a graph of a typical heart sound recorded by a stethoscope and shows the amplitude (A) of the sound pressure at the y-axis and time (t) at the x-axis. The heart sounds reflect events in the cardiac cycle: the deceleration of blood, turbulence of the blood flow and the closing of valves. The closing of the valves is typically represented by two different heart sounds, the first (S1) and the second (S2) heart sound. The first and second heart sounds are illustrated in the figure, and S1 marks the beginning of systole which is the part of the cardiac cycle in which the heart muscle contracts, forcing the blood into the main blood vessels, and the end of the diastole which is the part of the heart cycle during which the heart muscle relaxes and expands. During diastole, blood fills the heart chambers. The duration of systolic segments is nearly constant around 300 ms for healthy subjects. Given a pulse of 60 beats per minute the duration of a cardiac cycle will ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com