Kraft-Pulping of Hot Water Extracted Woodchips
a hot water extraction and pulping technology, applied in the field of kraft pulping of hot water extracted wood chips, can solve the problems of high energy cost and damage to lignocellulosic fibers, and limiting the number of pulp applications, so as to reduce the weight of pulp, increase the bulk, and reduce the effect of pulp weigh
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0055]In all of the following examples, the lignocellulosic material used was Eucalyptus wood chips, unless otherwise noted. Although Eucalyptus wood chips were used as the lignocellulosic source, any lignocellulosic material could be used.
[0056]A liquor (water) to lignocellulosic material ratio of 4:1 was added to a vessel capable of holding pressure, for example a high pressure laboratory M / K circulation digester and brought from about room temperature to about a temperature of 160° C. over about a 40 minute period. During this hot water contacting time, acetic acid was produced through an auto-hydrolysis reaction to reach a concentration of about 0.06M.
[0057]The vessel was maintained at this temperature for about 30 minutes to about 80 minutes. The extracted lignocellulosic material was then thoroughly washed with water to remove dissolved substances. The remaining liquor in the vessel was then separated into its constituents.
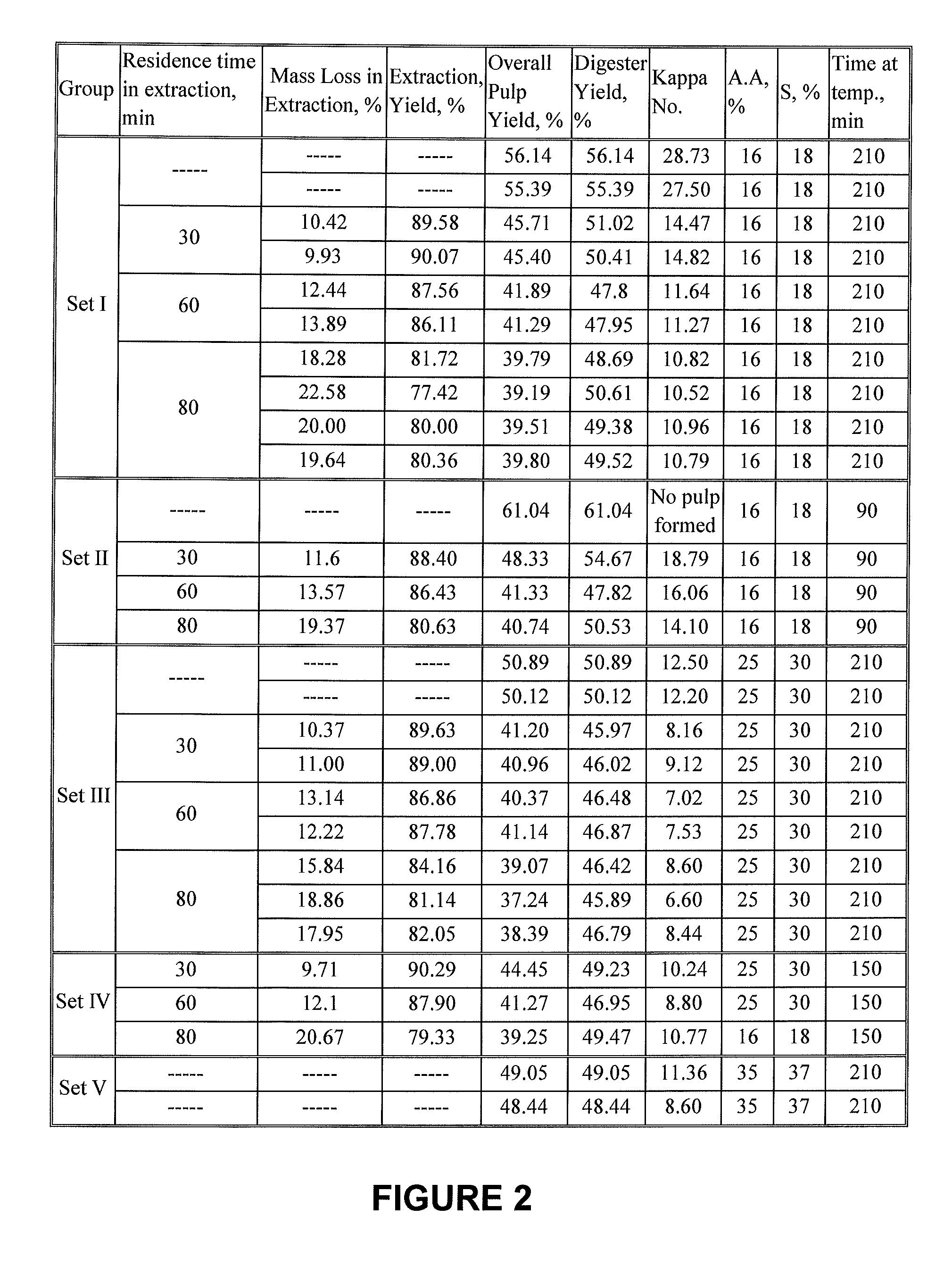
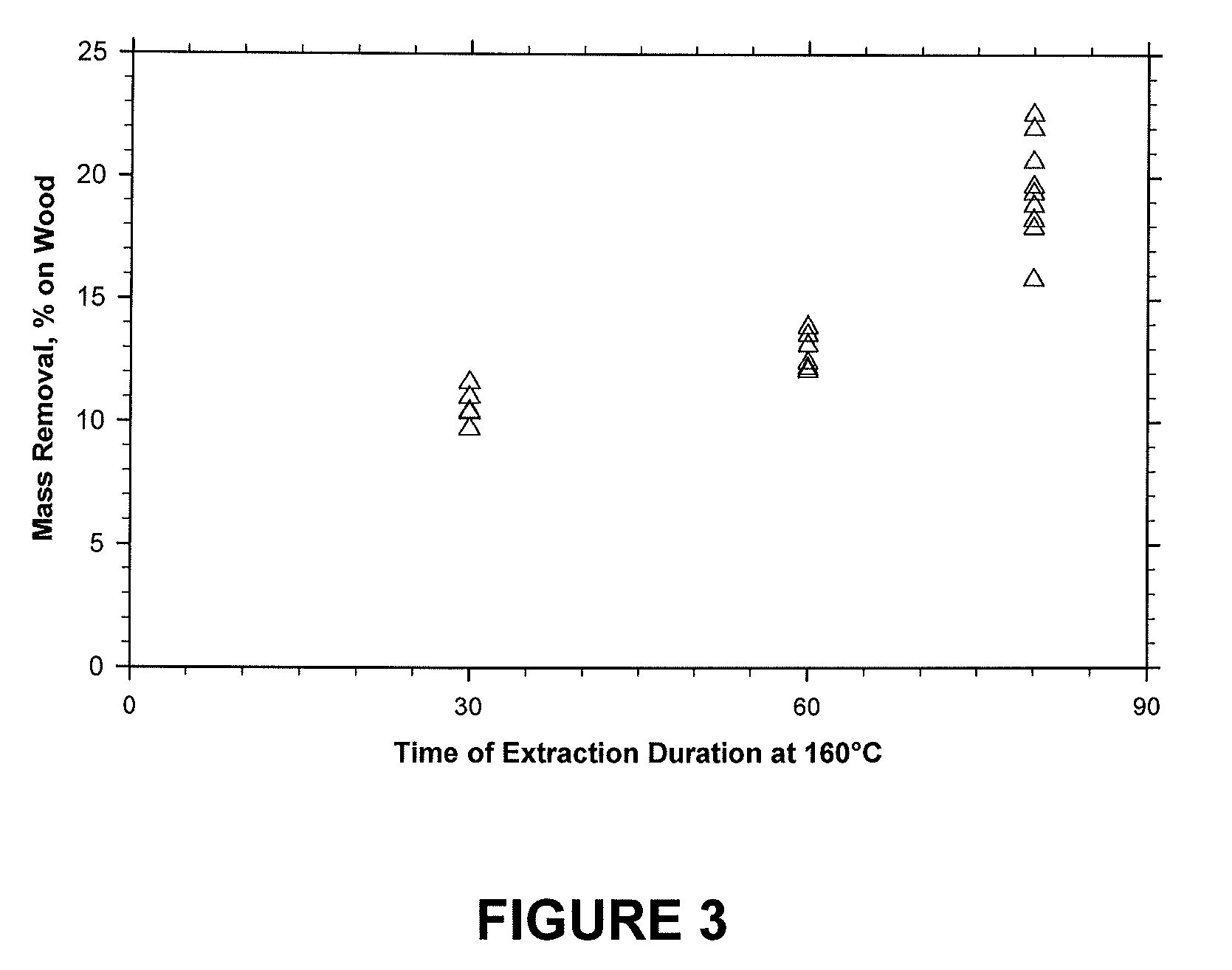
[0058]The mass which was removed during hot water cont...
example 2
[0060]FIG. 5 shows the UV light absorptivities of the liquid, or black liquor, within the pulping reactor during the pulping process at 280 nm during the kraft pulping of hot-water extracted wood chips and control woodchips. Time zero represents when the reactor contents, including woodchips, water and an initial concentration of active alkali at 16% and sulfide at 18%, have been mixed for 15 minutes at room temperature, with the temperature about to be raised. The active alkali is the percentage of equivalent Na2O in the solution and the sulfidity is the ratio of Na2S (or specifically its equivalent in Na2O) to the total Na2O. The temperature reached 150° C. in about 30 minutes, and was maintained at that temperature. Based on FIG. 5, there is a noticeable increase in UV light absorptivities at 280 nm during the initial de-lignification periods (from the start of the temperature raise to around 70 minutes), after which the absorptivity increased more slowly and leveled off towards ...
example 3
[0061]FIG. 6 shows the sodium hydroxide concentration in the black liquor as a function of time during chemical pulping for control and hot-water extracted wood chips. Initially sodium hydroxide was added to water in the pulping reactor at a concentration of about 0.956 Molar, followed by the addition of woodchips. The contents of the pulping reactor were mixed for 15 minutes at room temperature. The temperature was increased to about 150° C. over about 30 minutes. As can be seen in FIG. 6, during the first 30 minutes, the drop in alkali concentration in the black liquor was very rapid for hot-water extracted woodchips. More alkali was consumed at a faster rate for the pulping of hot-water extracted woodchips as compared to the control chips, and the residual concentration of alkali was much higher in the control wood chips as compared to the hot-water extracted wood chips.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| kappa number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com