Cells genetically modified to comprise pancreatic islet glucokinase and uses thereof
a technology of pancreatic islet and cell, which is applied in the field of genetically modified cell population to produce insulin, can solve the problems of diabetes, rapid rise of glucose level, and inability of the human body to properly metabolise glucose, and achieve the effects of reducing the risk of diabetes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Generation and Testing of Melligen Cells
Materials and Methods
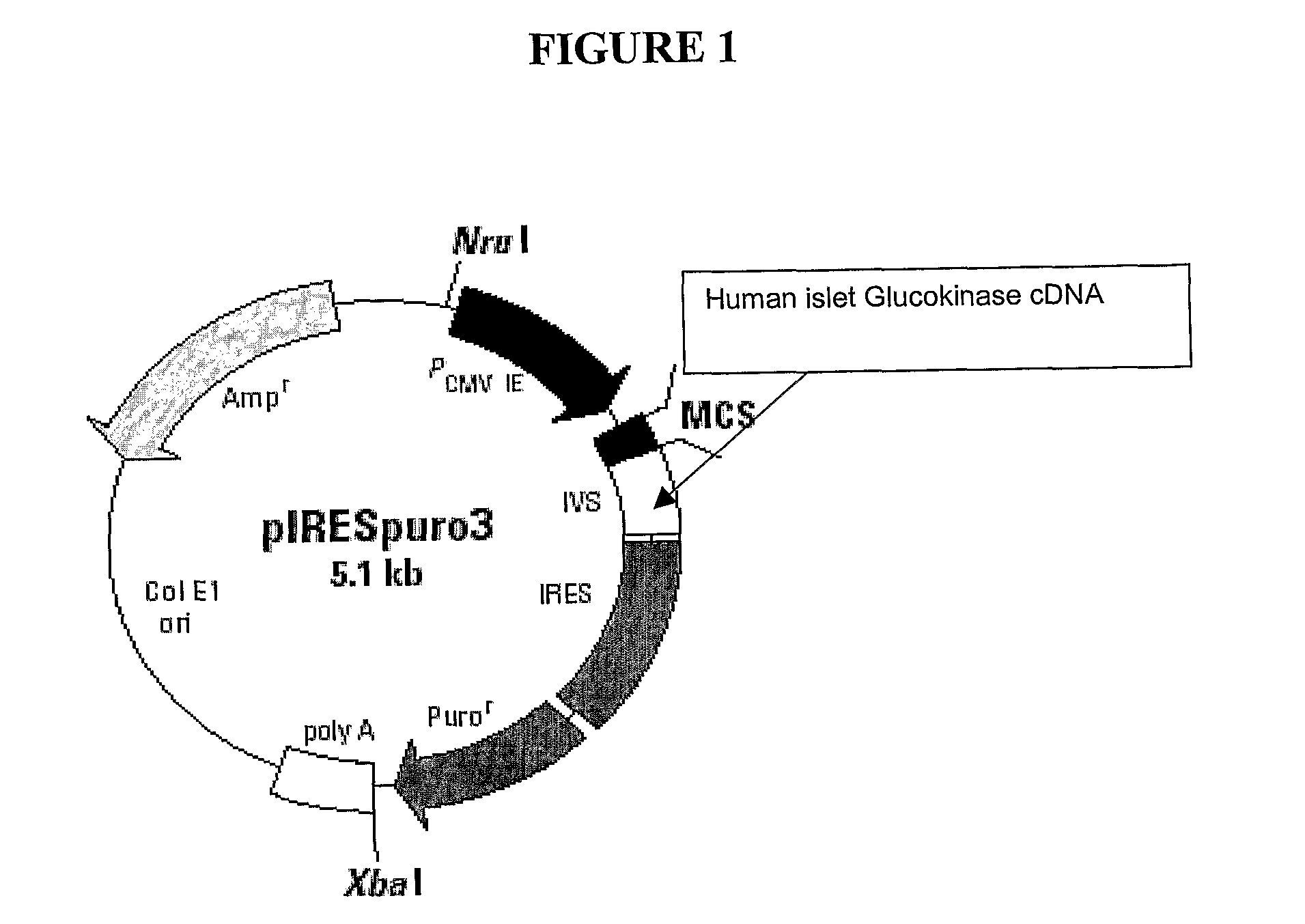
[0157]Plasmid construct
[0158]Human islet glucokinase cDNA contained in the pBluescript commercial vector, was a gift from Dr M. Alan Permutt, the University of Washington (St Louis, USA). The human islet glucokinase cDNA was cut out of the pBrescript SK+ by restriction enzyme ECOR I. The 2733 base pair fragment containing the human islet glucokinase cDNA was inserted into the pIERSpuro3 expression vector (Clontech, USA) at the ECOR I site in the multi cloning site (971-972 bp) (FIG. 1).
Cell Culture
[0159]Huh7ins cells were cultured as monolayers in Dulbecco's Modification of Eagles's Medium containing 10% fetal calf serum (FCS) in 5% CO2 in air plus 0.55 mg / ml G418 as described (Tuch et al., 2003, Gene Therapy 10:490-503).
Transfection of Plasmid with Human Islet Glucokinase cDNA
[0160]Huh7ins cells were transfected with the pIRESpuro3-glucokinase construct or the pIRESpuro3 vector alone using Effectenen transfection reagent ...
example 2
Melligen Cells can Correct Diabetes by Retaining Insulin Secretory Responsiveness to Glucose Stimulation In Vivo
[0175]In vivo glucose responsiveness in the millimolar concentration range is the hallmark of an artificial β cell for insulin replacement therapy in Type 1 diabetes. Where this can be achieved, such artificial β cells offer a potential strategy to overcome the limited availability of human pancreatic donor tissue. The survival of unencapsulated Huh7ins cells in a diabetic immunodeficient mouse model has been demonstrated.
[0176]To test the feasibility of Melligen cells to correct the diabetic state without inducing hypoglycaemia, Melligen cells (107 cells) are transplanted subscapularly into non-autoimmune non-obese diabetic severe combined immunodeficiency (NOD.scid) mice. Groups of eight animals are required for these experiments. Diabetes (blood glucose levels exceeding 14 mM on two separate occasions and serum insulin concentration below 0.15 ng / mL) is induced by a sin...
example 3
Microencapsulation Melligen Cells to Provide a Means of Ectopic Insulin Production and Secretion Both (A) In Vitro and (B) In Vivo with the Avoidance of Autoimmune Destruction
(a) In Vitro Experiments Using Encapsulated Melligen Cells
[0177]Melligen cells are microencapsulated and then cultured in vitro for up to 6 weeks. Viability and glucose responsiveness of encapsulated Melligen cells are determined after 1, 2, 4 and 6 weeks in culture prior to commencing any in vivo studies using microencapsulated cells. A dose response curve for insulin secretion in response to glucose from basal to high glucose levels of the encapsulated cells is established. Chronic and acute insulin release by the encapsulated cells is determined. To measure acute insulin release, static incubations are carried out with traditional stimuli (glucose, theophylline, and 8-Br-cAMP [which increases intracellular cAMP]). Insulin storage is also examined after sonication and extraction overnight in acid ethanol. Ins...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com