Methods of cardiac repair
a cardiac and ventricular technology, applied in the field of cardiac repair, can solve the problems of ventricular function, ventricular remodeling, deterioration of ventricular function, heart failure, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing cardiomyocyte cell cycle activation, increasing cardiomyocyte proliferation, and increasing cardiomyocyte formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Fetal Cells Home to and Engraft in Injured Maternal Myocardium
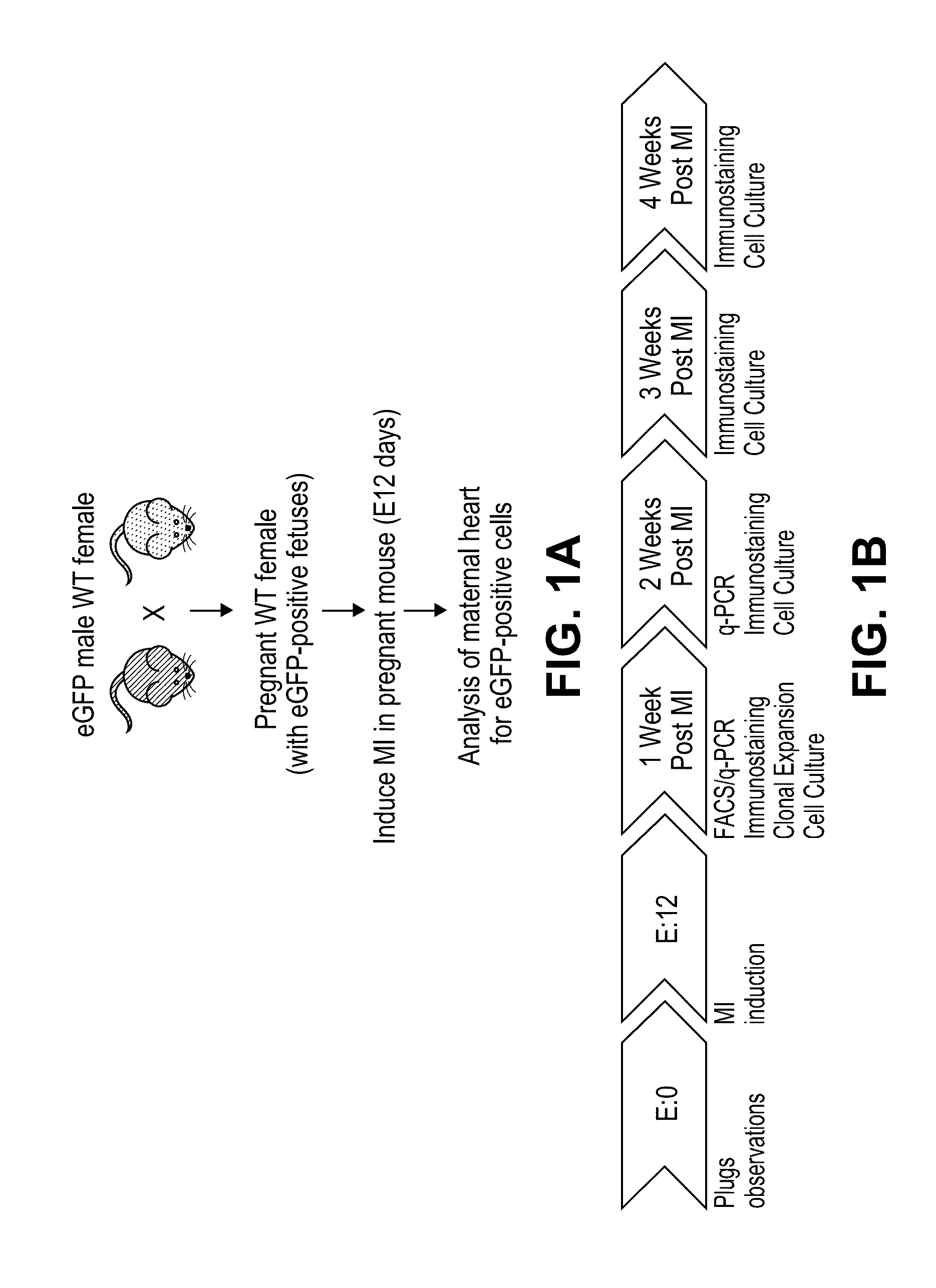
[0191]Wild-type (WT) virgin female mice, age 3-6 months, were crossed with heterozygous eGFP transgenic male mice. The female mice underwent ligation of the left anterior descending (LAD) artery in order to induce an anterolateral myocardial infarction (MI) at gestation day 12 (FIG. 1A). This results in approximately 50% left ventricular infarction. In accordance with Mendelian autosomal inheritance, approximately 50% of embryos were eGFP+.
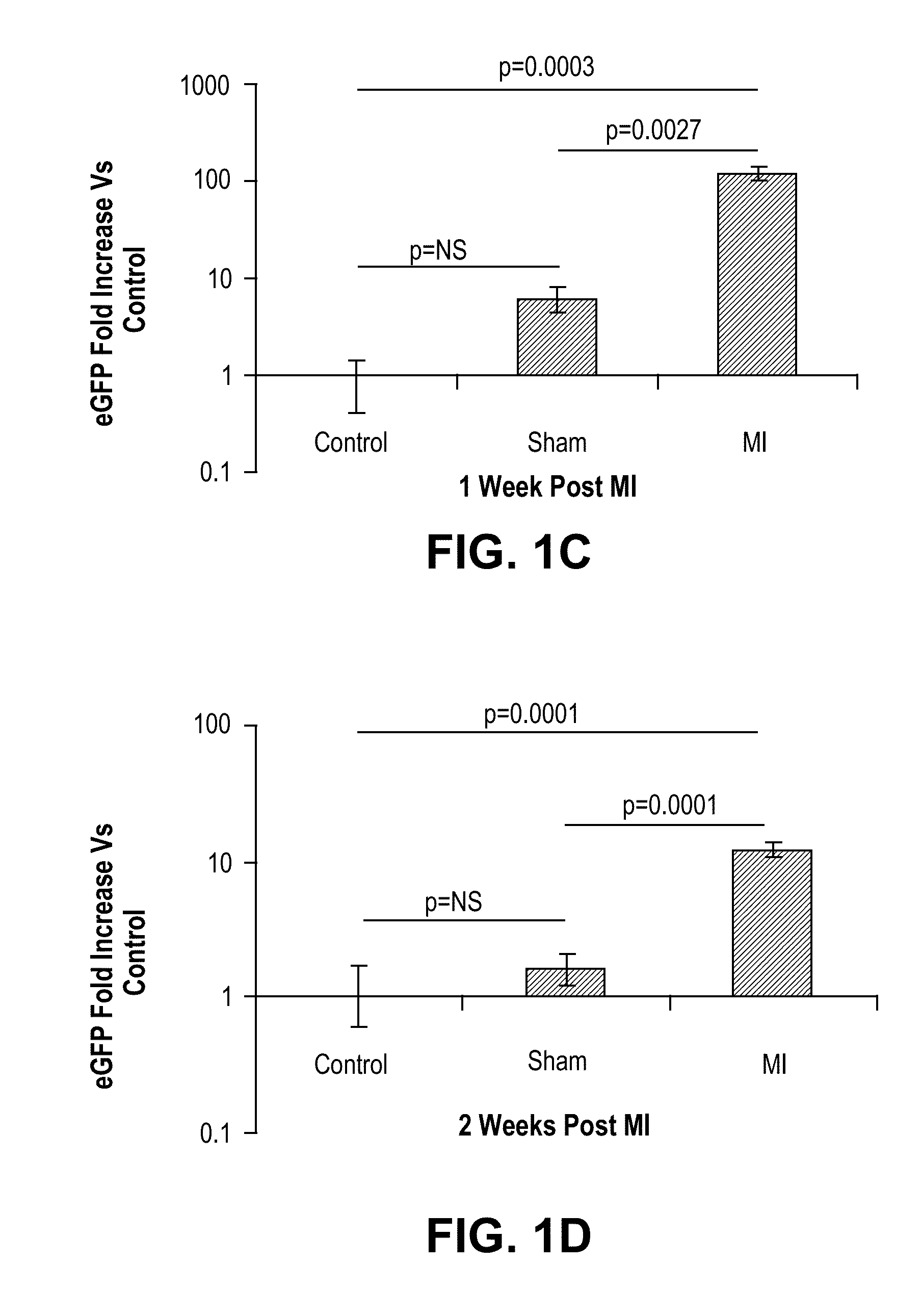
[0192]Initially, we quantified eGFP expression in injured maternal hearts relative to sham-operated pregnant mice and controls in which no injury was induced. Post-partum females were sacrificed at 1 or 2 weeks post-MI. Total DNA was extracted from each total heart and eGFP expression analyzed according to the methods described by Pfaffl, 2001 (FIG. 1B). Experimental infarcted hearts harvested at 1 week post-MI contained 120 times more eGFP than controls (p=0.0003) and 20 times more eGF...
example 2
Fetal Cells Adopt Diverse Cardiac Lineages In Vivo
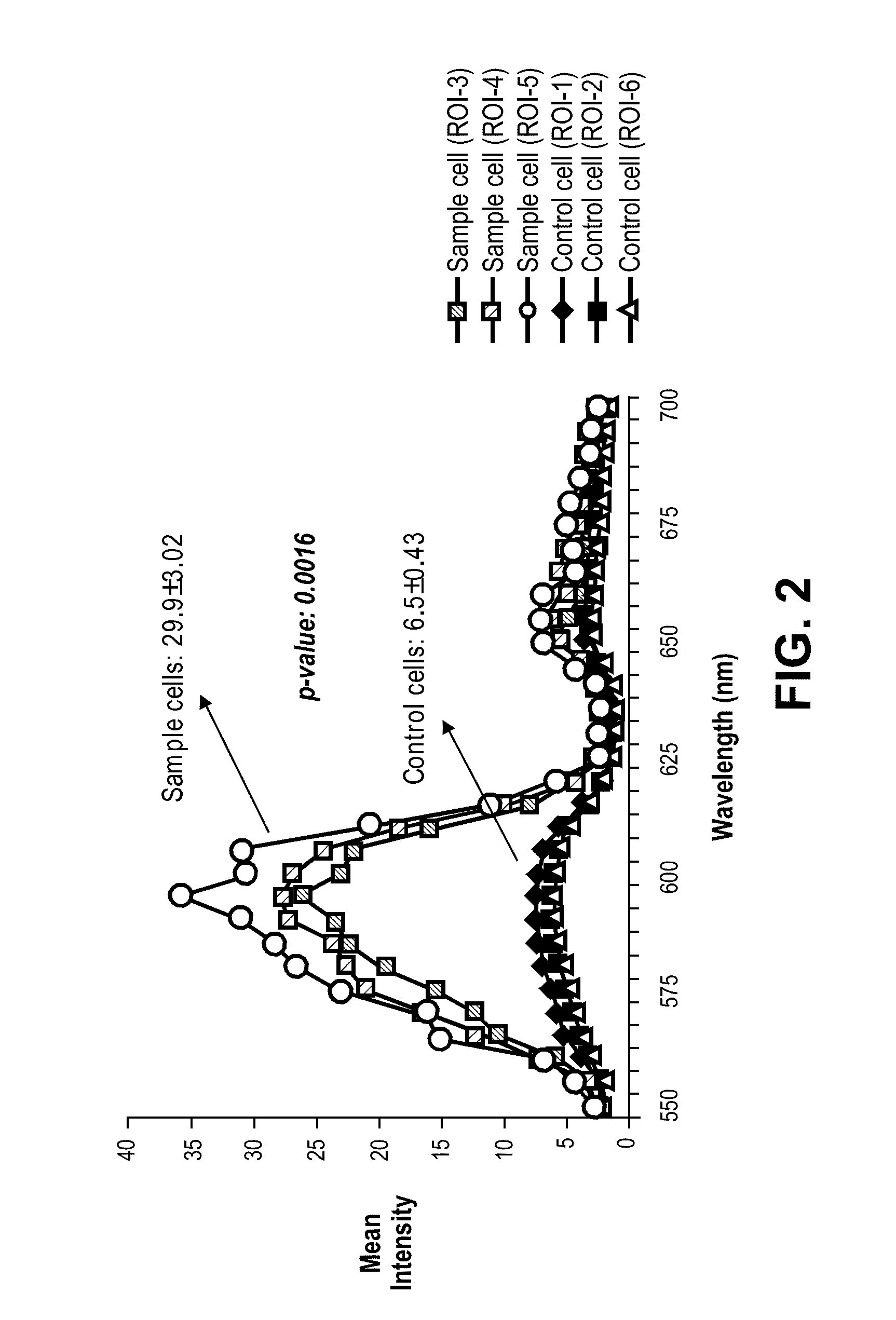
[0193]In a separate group of infarcted and control mice, immunofluorescence analysis with confocal microscopy was utilized to detect eGFP+ cells in ventricular tissue sections of maternal hearts at various time points subsequent to myocardial injury (FIG. 1B and data not shown). EGFP+ cells were noted in infarct zones and peri-infarct zones of infarcted maternal hearts at 1, 2, 3, or 4 weeks post-MI (data not shown and Table 1A). Negligible numbers of eGFP cells were noted in non-infarct zones of the infarcted maternal hearts (Table 1B).
[0194]We further sought to determine whether the eGFP+ cells were differentiating into more mature cardiac cells as we noted a decrease in nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio with an increase in post-injury time (data not shown). Briefly, ventricular sections from maternal hearts analyzed at 1, 2, 3, and 4 weeks post-injury illustrated eGFP+ cells engrafting within infarct and peri-infarct zones. Fetal cells...
example 3
Fetal Cells Isolated from Injured Maternal Hearts Differentiate to Endothelial Cells, Smooth Muscle Cells, and Spontaneously Beating Cardiomyocytes In Vitro
[0198]We next used fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) to isolate fetal eGFP+ cells that had homed to maternal hearts and analyzed their in vitro behavior. When plated on CMFs, we noted clonal expansion of the fetal cells, their differentiation into smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells, and the formation of vascular structures (data not shown). Other cellular phenotypes, some of which have the appearance of neuronal cells, were also observed in these in vitro experiments with CMFs (data not shown).
[0199]Briefly, in vitro analysis of fetal cells isolated from maternal hearts demonstrated clonal expansion on CMFs. 14 days after plating, vascular tube formation was noted in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix. Fetal cells isolated from maternal hearts and plated on CMFs underwent differentiation into smooth muscle cells (α-S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com