Biomarkers for Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas and Uses Thereof
a non-hodgkin lymphoma and biomarker technology, applied in the field of cancer detection methods, can solve the problems of limited knowledge of the specific genetic events leading to dlbcl and fl, and the difficulty of clearly identifying b-cell nhls, so as to reduce molecular weight, reduce size, and reduce mrna.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of Recurrently Mutated Genes
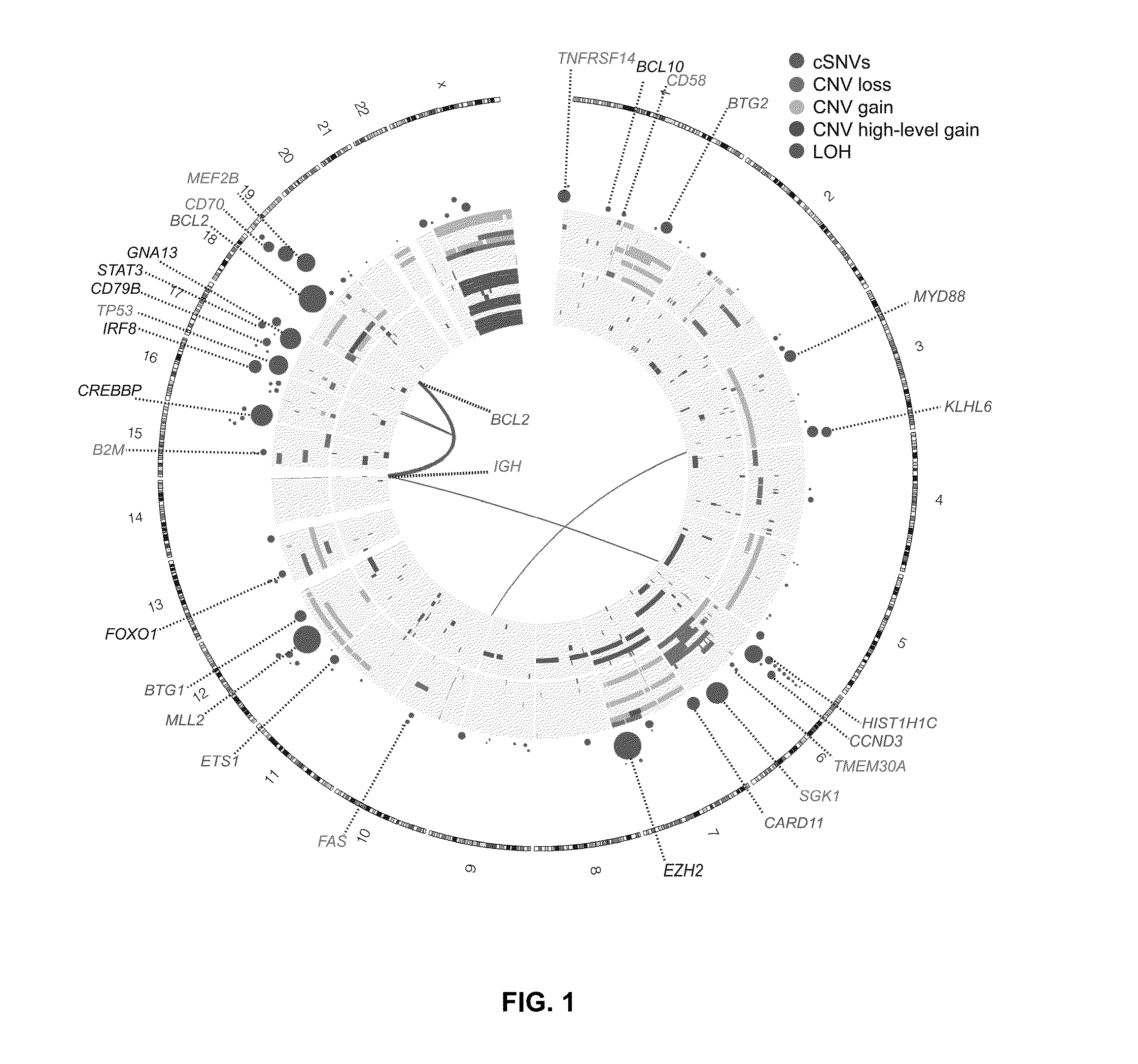
[0082]The genomes or exomes of 14 NHL cases were sequenced, all with matched constitutional DNA sequenced to comparable depths. After screening for single nucleotide variants followed by subtraction of known polymorphisms and visual inspection of the sequence read alignments, 717 nonsynonymous (coding single nucleotide variants; cSNVs) affecting 651 genes were identified. Between 20 and 135 cSNVs in each of these genomes were identified. Only 25 of the 651 genes with cSNVs were represented in the cancer gene census (December, 2010 release) [14].
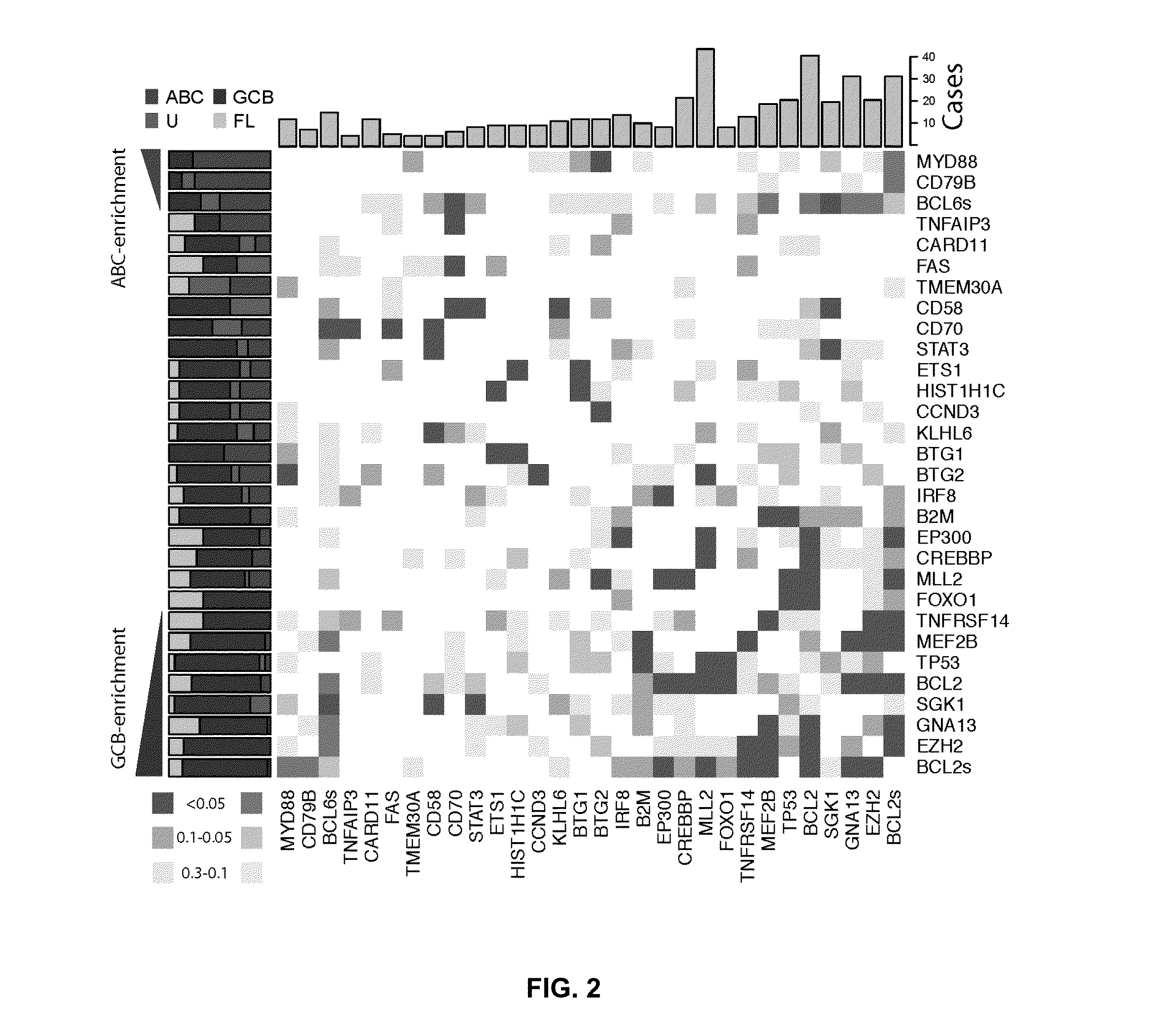
[0083]RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was performed on these 14 NHL cases and an expanded set of 113 samples comprising 83 DLBCL, 12 FL and 8 B-cell NHL cases with other histologies and 10 DLBCL-derived cell lines. These data were analysed to identify novel fusion transcripts and cSNVs (FIG. 1). 240 genes were identified with at least one cSNV in a genome / exome or an RNA-seq “mutation hot spot” (below), and...
example 2
Mutations in EZH2 at Position Y641 are Common in NHL
[0136]This example relates to the identification of novel mutations and biomarkers useful for the diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of response to treatment of Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Additionally, embodiments of the invention relate to the disclosure of novel drug targets in non-Hodgkin lymphoma useful for development of new therapeutic agents.
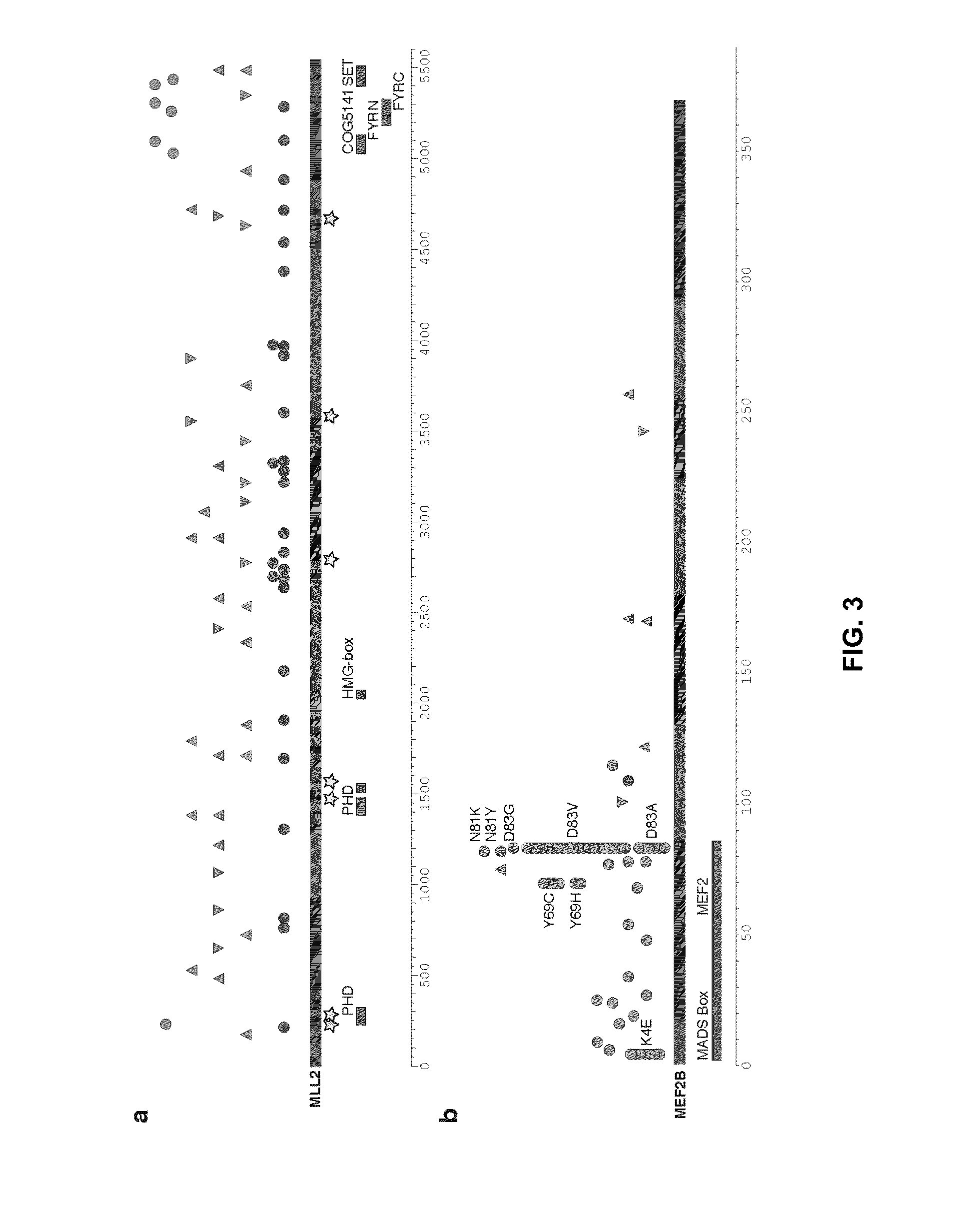
[0137]Protein-altering point mutations were identified by sequencing NHL genomes and exomes and in particular by the sequencing of one Follicular Lymphoma genome (tumor / normal) and two DLBCL exomes (tumor / normal). A total of 160 protein-altering somatic point mutations were identified, including 64 in each DLBCL and 32 in FL. 79 of these mutations were predicted to be damaging to protein function using SIFT. Remarkably, very few genes were found to be mutated in more than one sample, namely EZH2, FAT2, BLR1 and CARD11.
[0138]Matched RNA-seq libraries were then sequenced for each sample....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com