Methods for treating lysosomal acid lipase deficiency
a technology of lysosomal acid lipase and treatment method, which is applied in the direction of drug composition, peptide/protein ingredient, metabolic disorder, etc., can solve the problems of massive build-up of fatty material in various tissues, lal deficiency, etc., to reduce or eliminate tissue weakness or waste, promote weight gain, and reduce or prevent weight loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of Recombinant Human Lysosomal Acid Lipase (rhLAL)
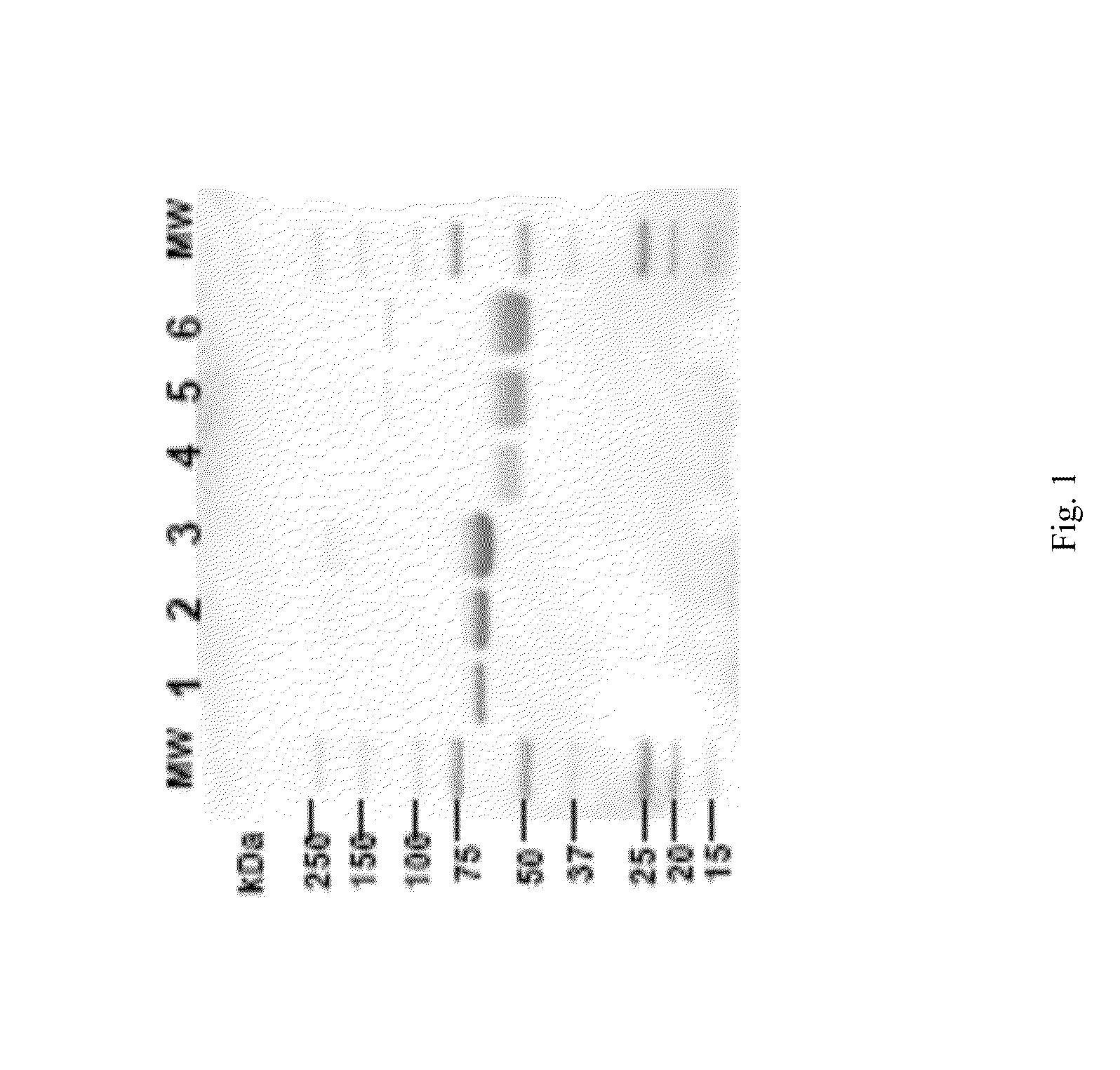
[0137]Experiments described in this example show that recombinant LAL can be expressed and purified from mammalian cells.
[0138]Specifically, cultured human cells were transfected with a plasmid containing human Lysosomal Acid Lipase open reading frame by electroporation and cloned by limiting dilution. Stable clones were selected using cloning media containing 0.4 mg / mL G418. Clones were expanded and rhLAL expression and activity was analyzed using ELISA and LAL activity assays.
[0139]In total, 384 clones were analyzed for rhLAL expression and activity. Clone 35 was determined to have the highest and most stable rhLAL expression. Expression in shake flasks was 3-4 pcd on average and expression in wave reactor was 4-6 pcd on average. Clone 35 was expanded and a cell bank was prepared.
[0140]Clone 35 was seeded into 5 mL Wave cultures in 10 L wave bags. Wave bags were perfused at 5 L per day and conditioned media (CM) were har...
example 2
Treatment of LAL Deficient Yoshida Rats Using rhLAL
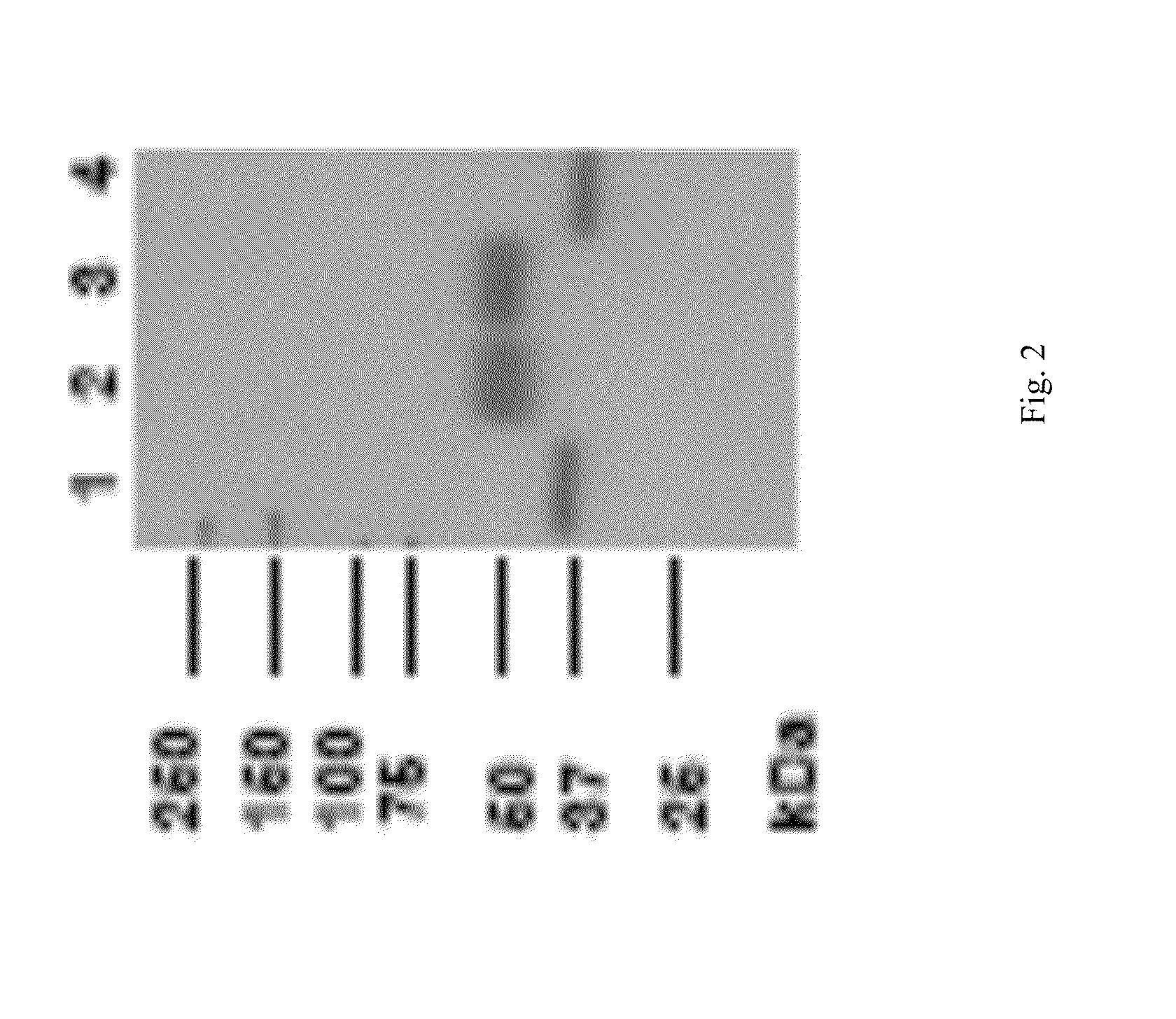
[0143]Experiments described in this example are designed to show that rhLAL can effectively treat LALD diseases, such as Wolman's disease and Cholesteryl Ester Storage Disease (CESD). The Yoshida (LAL deficient) rat was used as animal model.
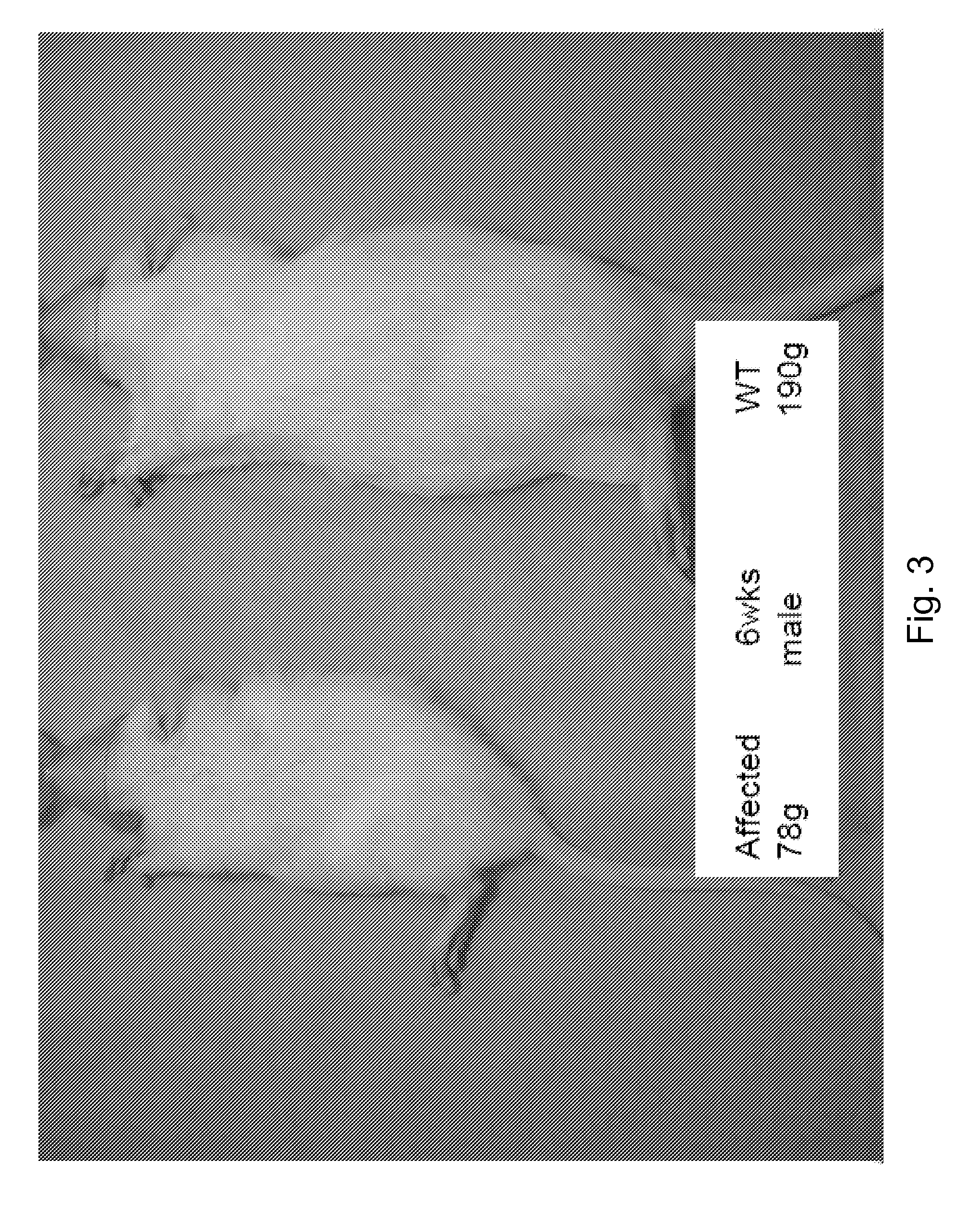
[0144]As described above, the Yoshida (LAL deficient) rat is a naturally occurring animal model of LALD disease (Yoshida and Kuriyama, Laboratory Animal Science 40(5) 1990). Affected rats inherit the disease in an autosomal recessive manner and the disease is characterized by developmental impairment and / or failure, hepatosplenomegaly, lymph node enlargement, and thickened dilated intestine. Many characteristic foam cells are observed in livers and spleens of affected mice. Typically, Kupffer cell, which is macrophage, becomes “foam cell” with lipid accumulation. Massive intracellular storage of both cholesteryl esters and triglycerides are observed in the liver, adrenal gland and intestine. Affe...
example 3
Survival / Maintenance Dose Study Design and Dose Selection
[0163]It is contemplated that a two-dose (i.e., survival / maintenance) treatment regimen is desirable for treating LALD disease (e.g., Wolman's disease). This example is designed to select appropriate survival / maintenance doses. As observed from clinical signs, body weights, gross and microscopic pathology, doses such as 0.1, 0.5, and 1 mg / kg were selected for the survival study. In order to select an appropriate dose for the “loading” dose phase of the survival study, reductions in lipid accumulation in liver, spleen and small intestine of animals treated at 1 or 2 mg / kg (5 weekly doses starting on day 35) were compared. Exemplary results are shown in FIG. 35. As can be seen, greater reductions in lipid accumulation were observed at 2 mg / kg compared to 1 mg / kg following 5 doses. This data indicates that 2 mg / kg more effectively resolves lipid accumulation in tissues following 5 doses; therefore, this dose is selected for the “...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dimensionless property | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com