Polyphenylene sulfide fiber and nonwoven fabric
a polyphenylene sulfide fiber and nonwoven fabric technology, applied in textiles, papermaking, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of significant thermal shrinkage of fibers or nonwoven fabrics, poor thermal bonding properties, poor thermal dimensional stability, etc., and achieve excellent thermal bonding properties and excellent mechanical strength.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
PPS Resin
[0085]A 100 mol % linear polyphenylene sulfide resin that was intentionally not copolymerized with trichlorobenzene (made by Toray Industries, Inc., Product No. E2280, MFR: 160 g / 10 min) was dried in a nitrogen atmosphere at 160° C. for 10 hours, and used in the following procedure.
Spinning and Forming into Nonwoven Web
[0086]The PPS resin was molten in an extruder, and spun from a rectangular spinneret having a hole diameter of 0.50 mm at a spinning temperature of 320° C. and at a discharge rate per hole of 1.38 g / min. The spun filamentary streams were allowed to cool down and solidify between the rectangular spinneret and a rectangular ejector at a distance of 55 cm in an atmosphere at room temperature (20° C.). The filamentary streams that had cooled down and solidified were passed through the rectangular ejector and were pulled and drawn by compressed air that was heated to 230° C. with an air heater and blown out from the ejector at an ejector pressure of 0.15 MPa. The ...
example 2
[0090]PPS Resin, Spinning, and Forming into Nonwoven Web
[0091]The same PPS resin as in Example 1 was spun and formed into a nonwoven web in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the temperature of the compressed air was 200° C.
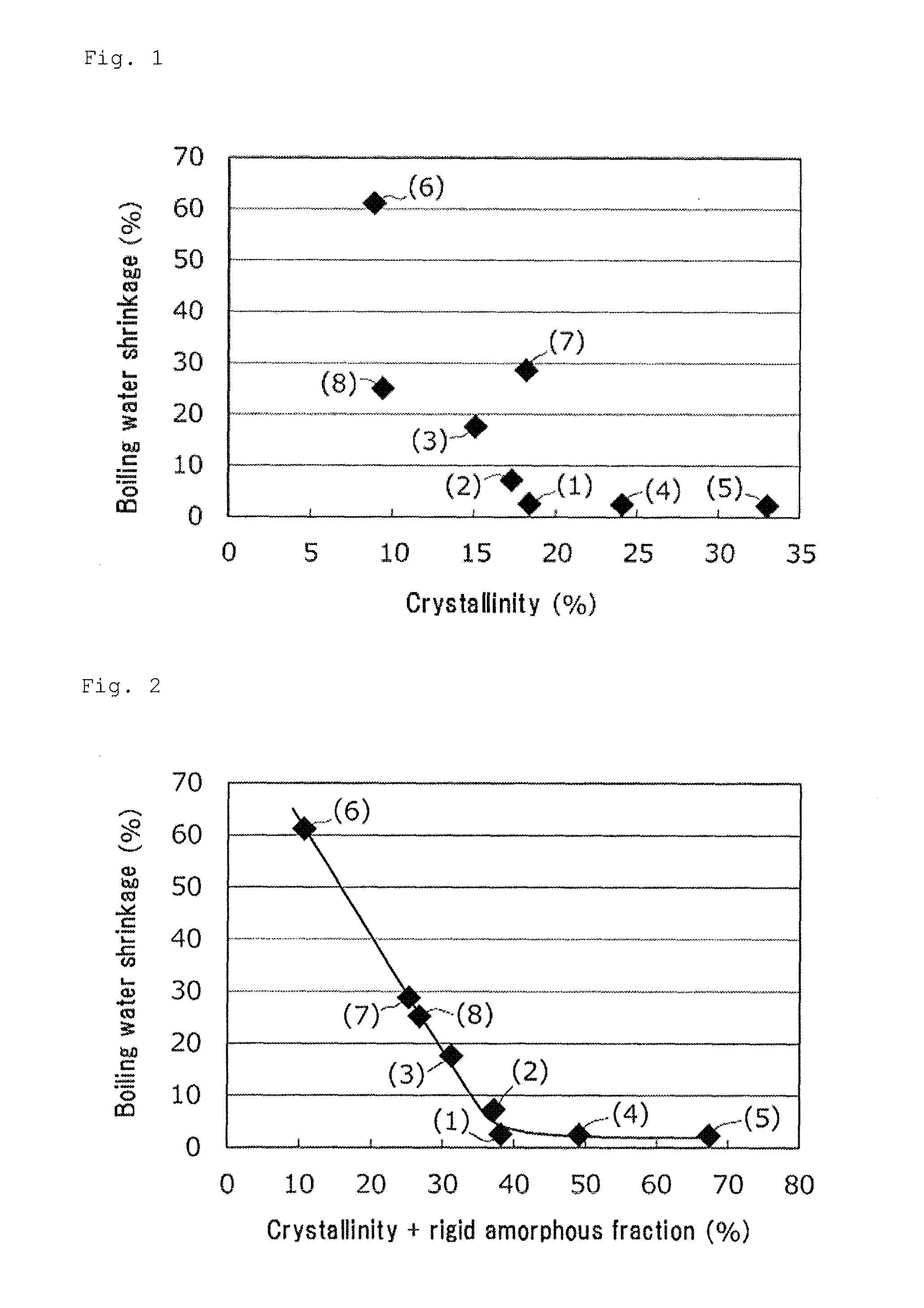
[0092]The obtained filaments had an average single fiber fineness of 2.8 dtex, a crystallinity of 17.3%, the sum of the rigid amorphous fraction and the crystallinity of 37.3%, and a boiling water shrinkage of 7.0%. The spinning speed was 4,991 m / min. During the one-hour spinning, the occurrence of the breakage of the filaments was zero and thus good spinnability was observed.
Temporary Bonding and Thermal Bonding
[0093]Next, the nonwoven web was temporarily bonded and then thermally bonded in the same manner as in Example 1 to produce a filament nonwoven fabric of Example 2.
[0094]The obtained nonwoven fabric had no significant shrinkage in width due to thermal shrinkage by thermal bonding with the embossing roll pair and showed good quality without wrinkl...
example 3
[0095]PPS Resin, Spinning, and Forming into Nonwoven Web
[0096]The same PPS resin as in Example 1 was spun and formed into a nonwoven web in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the temperature of the compressed air was 140° C.
[0097]The obtained filaments had an average single fiber fineness of 2.9 dtex, a crystallinity of 15.1%, the sum of the rigid amorphous fraction and the crystallinity of 31.3%, and a boiling water shrinkage of 17.5%. The spinning speed was 4,824 m / min. During the one-hour spinning, the occurrence of the breakage of the filaments was zero and thus good spinnability was observed.
Temporary Bonding and Thermal Bonding
[0098]Next, the nonwoven web was temporarily bonded and then thermally bonded in the same manner as in Example 1 to produce a filament nonwoven fabric of Example 3.
[0099]The obtained nonwoven fabric had no significant shrinkage in width due to thermal shrinkage by thermal press-bonding with the embossing roll pair and showed good quality without...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com