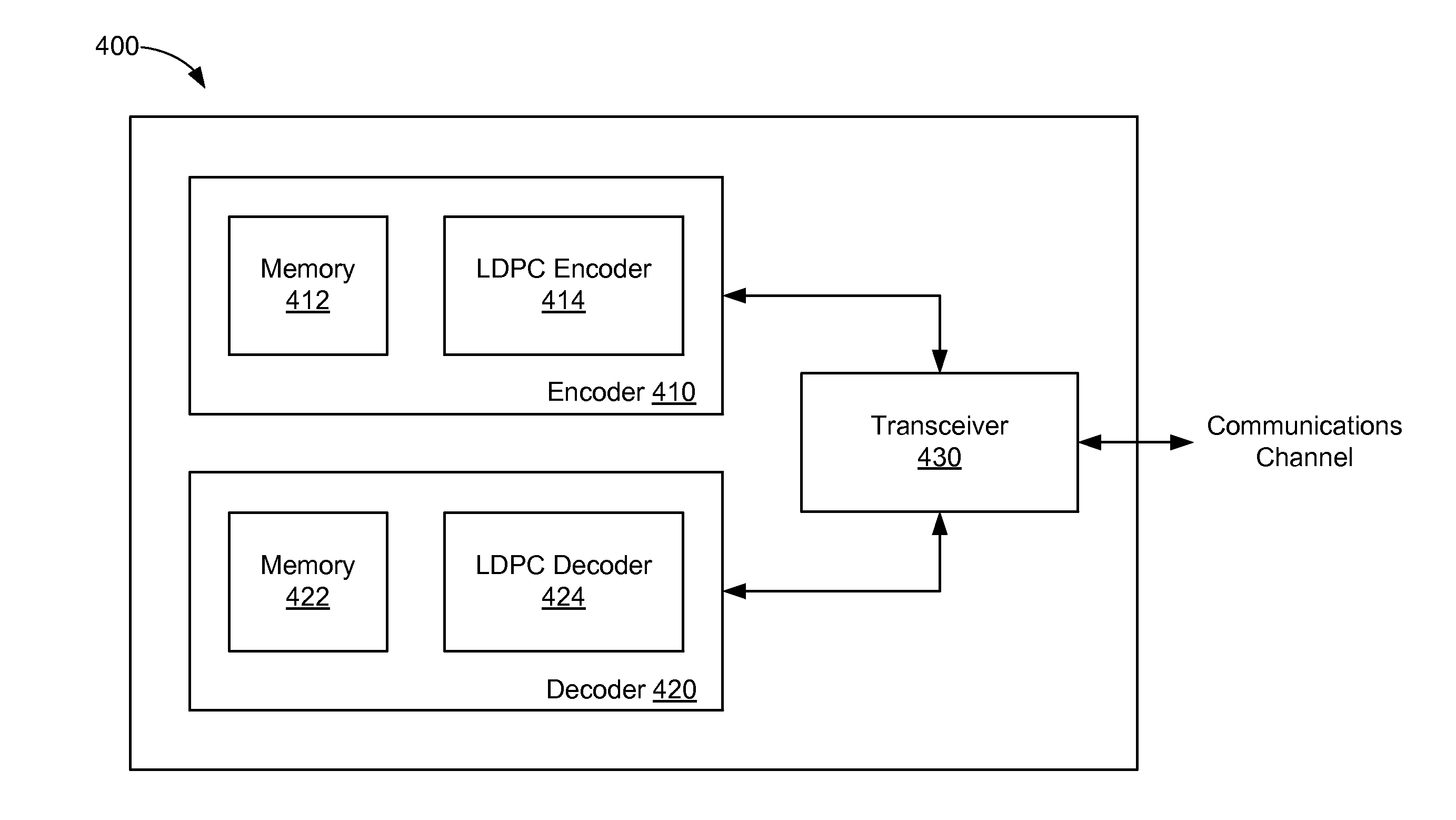
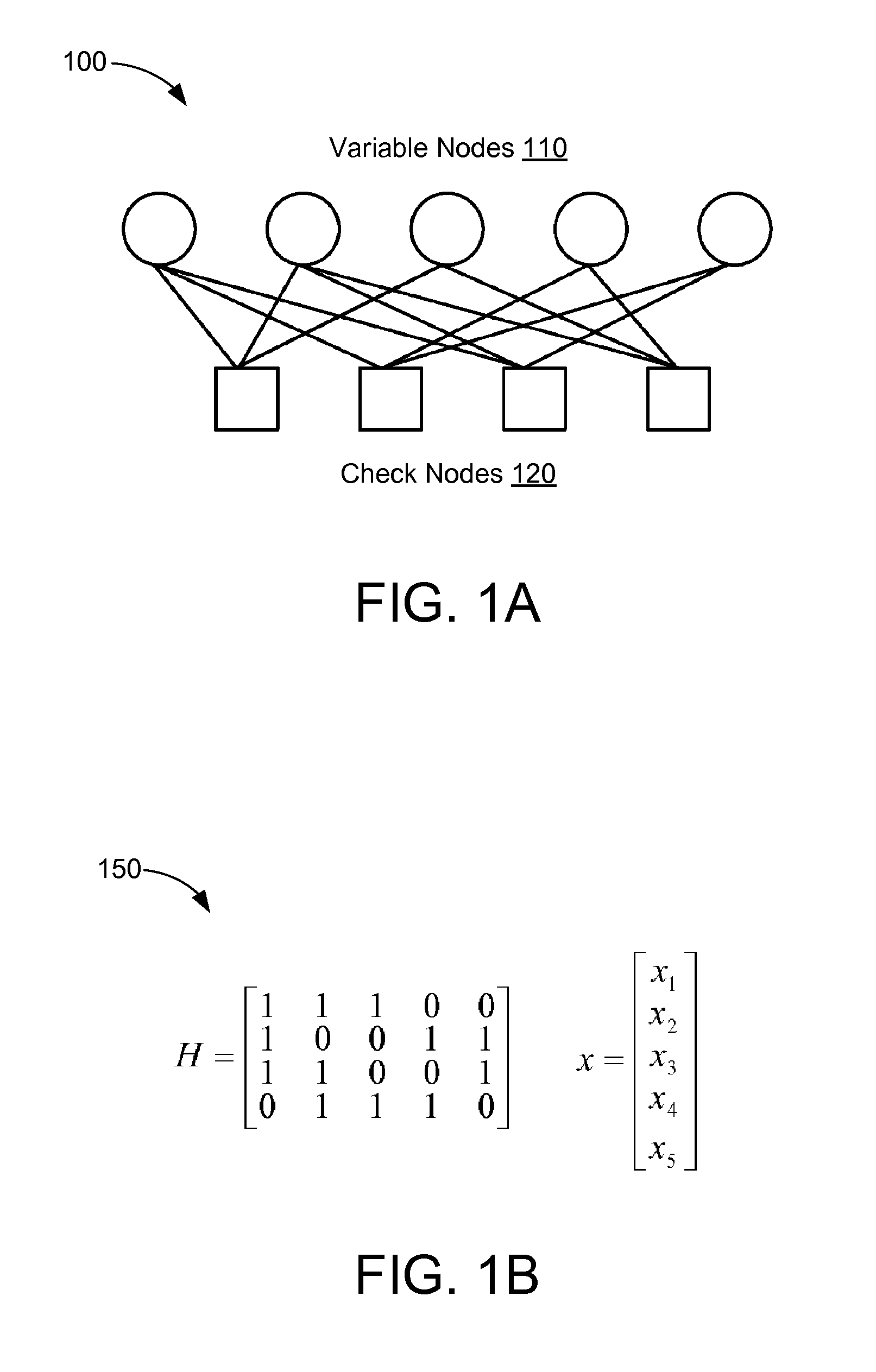
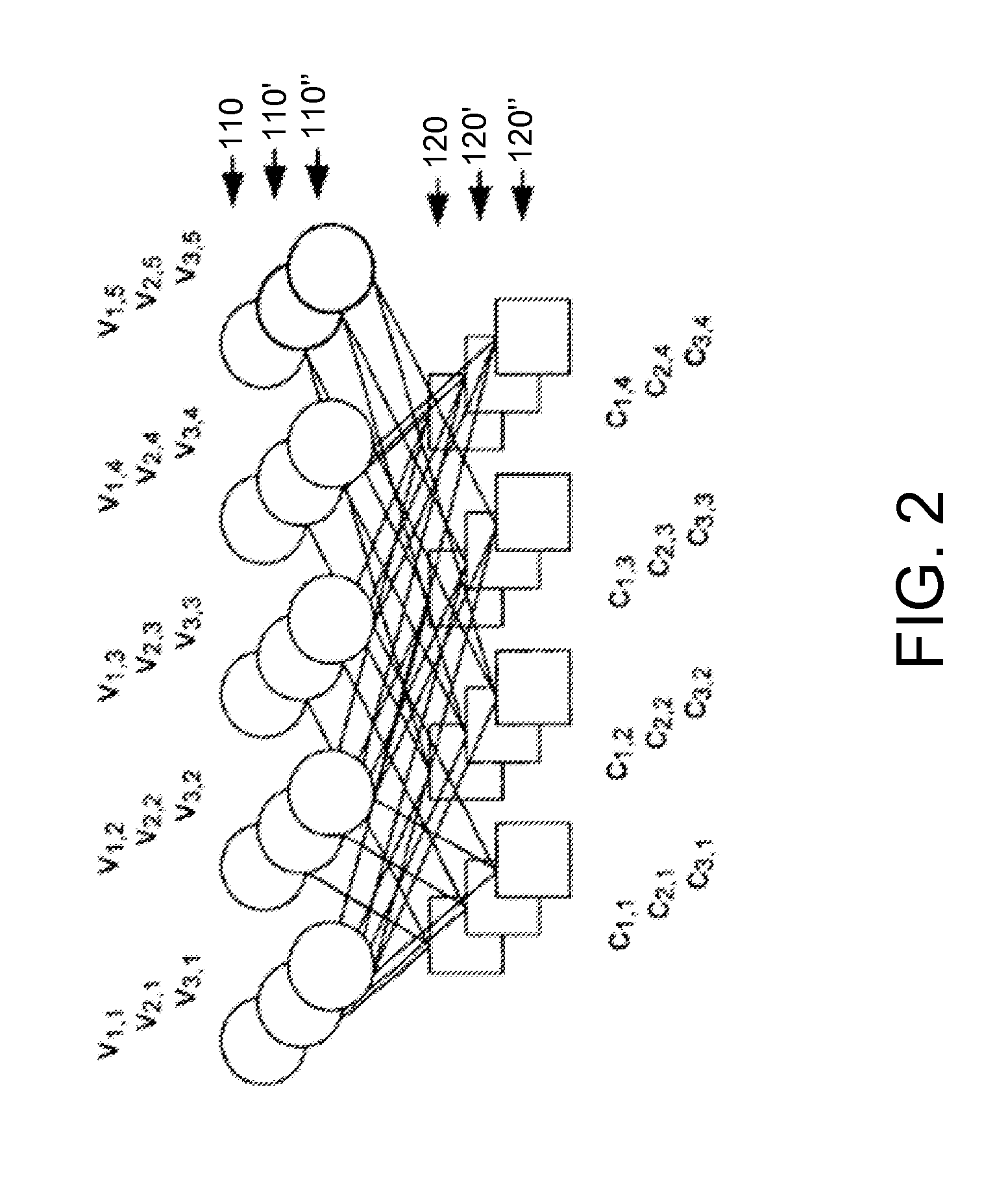
LDPC design for high rate, high parallelism, and low error floor
a high-efficiency, parallelism-based technology, applied in the field of communication and data storage systems, can solve the problems of data coherency problems, affecting the pipelining of parallel message updates, and generally undesirable parallel hardware implementation of nodes connected by two or more edges, so as to increase the number of checks in the graph, enhance the code performance, and improve the degree of nodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022]In the following description, numerous specific details are set forth such as examples of specific components, circuits, and processes to provide a thorough understanding of the present disclosure. The term “coupled” as used herein means connected directly to or connected through one or more intervening components or circuits. Also, in the following description and for purposes of explanation, specific nomenclature is set forth to provide a thorough understanding of the present embodiments. However, it will be apparent to one skilled in the art that these specific details may not be required to practice the present embodiments. In other instances, well-known circuits and devices are shown in block diagram form to avoid obscuring the present disclosure. Any of the signals provided over various buses described herein may be time-multiplexed with other signals and provided over one or more common buses. Additionally, the interconnection between circuit elements or software blocks...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com