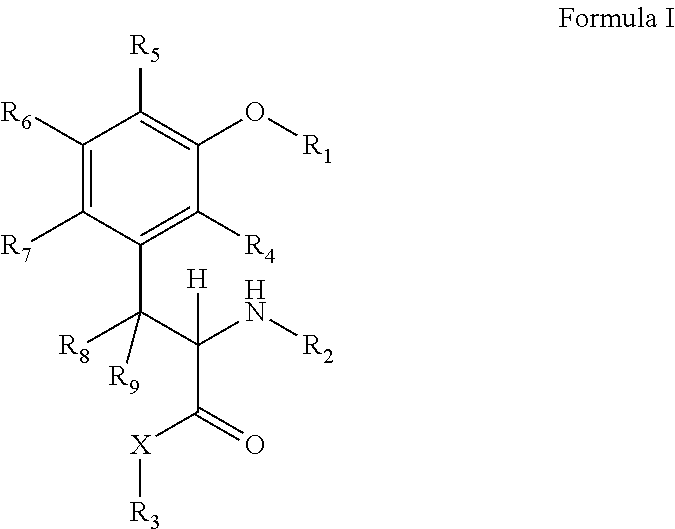
Transgenic Plants Resistant To Non-Protein Amino Acids
a technology plants, applied in the field of transgenic plants, can solve the problems of inability to differentiate between phe and tyr, and inability to bind non-protein amino acids in proteins, etc., to prevent the incorporation of non-protein amino acids into proteins, and the plant is resistant to meta-tyrosine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
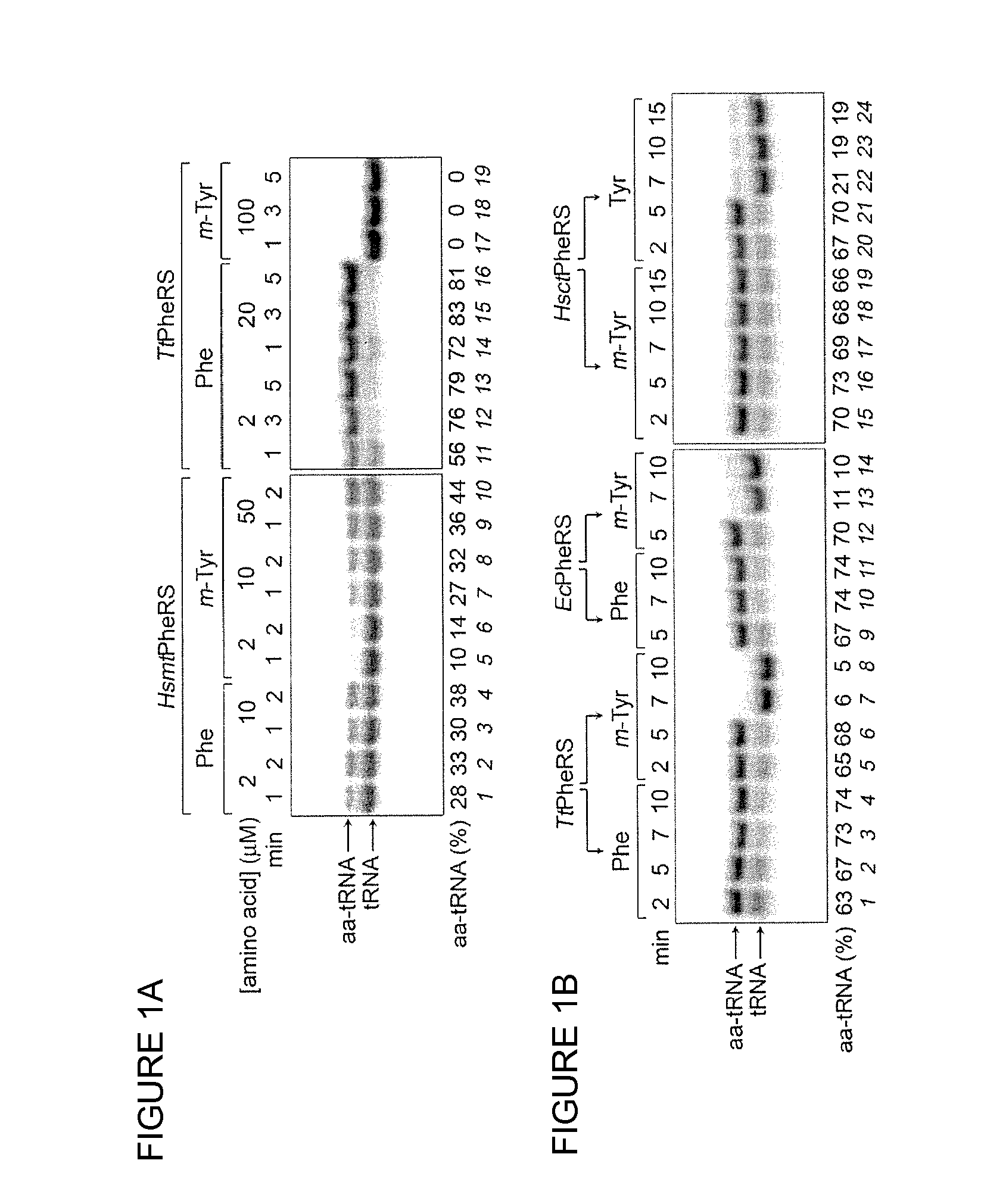
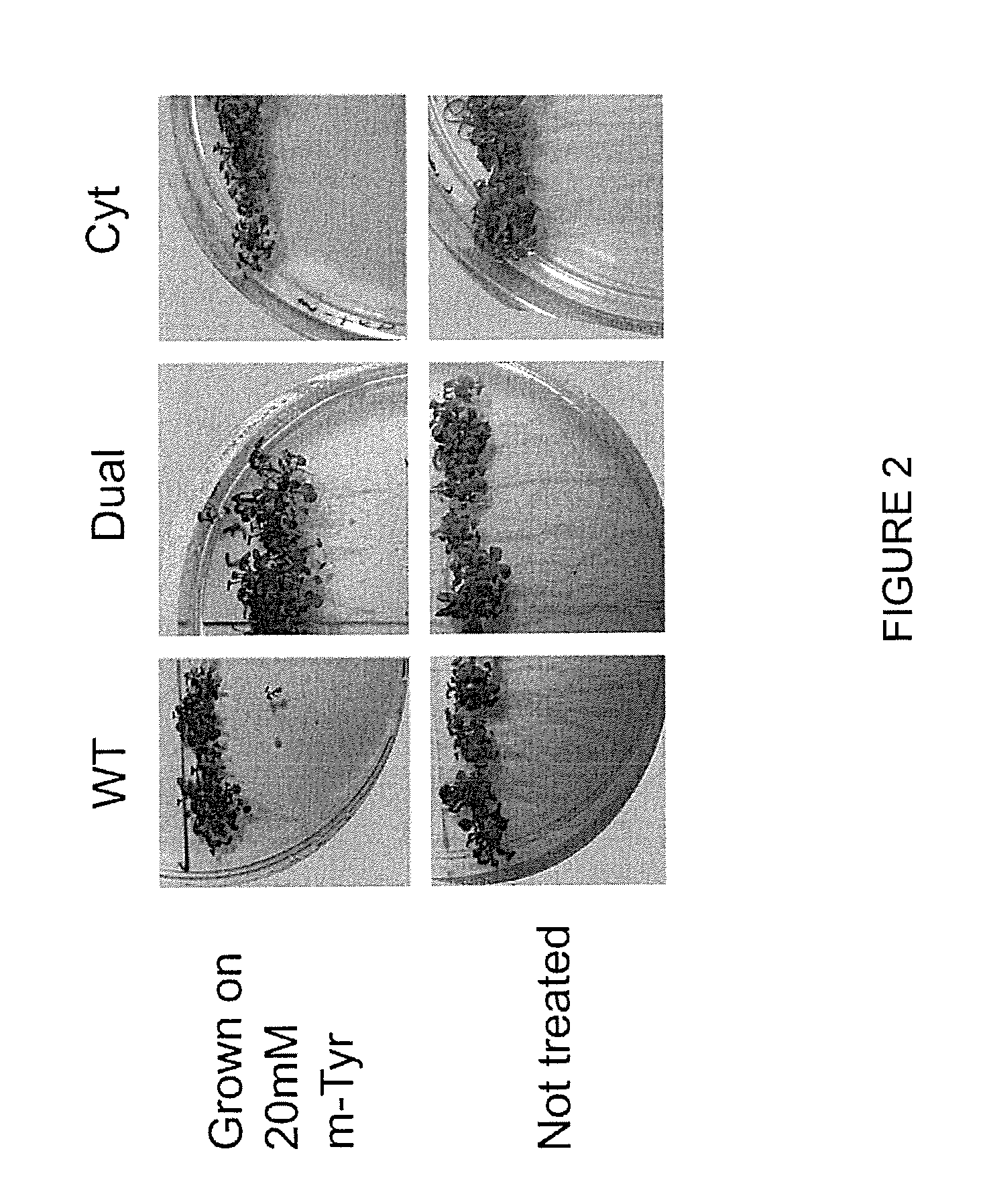
The Effect of Bacterial PheRS Expression on Arabidopsis Resistance to m-Tyr
[0091]The bacterial PheRS genes described in the “Material and Methods” section hereinabove were expressed under the control of the constitutive 35S CaMV promoter. A transit peptide was appended to N-terminus of EcPheRS-α and EcPheRS-β subunits of the bacterial enzyme in order to direct them into the mitochondria and chloroplast of Arabidopsis thaliana. The second constructs pair including PheRS-α and PheRS-β lacked the transit peptides. Thus, four different constructs were transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana, and homozygote self-pollinated plants were generated as described hereinabove. Each line was further crossed to create plants containing heterodimeric EcPheRS possessing editing activity localized in cytoplasm (cyt-PheRS) and heterodimeric EcPheRS localized in plant mitochondria and chloroplast (mtp-PheRS). Several independent transgenic lines were obtained, and their resistance to m-Tyr was analyzed....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com