Extrusion coated textile laminate with improved peel strength
a non-breathable, extrusion coating technology, applied in the direction of synthetic resin layered products, chemistry apparatus and processes, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of poor elasticity and softness of hpp fabrics, poor fit, poor elasticity, etc., to improve abrasion resistance, improve elasticity, and improve abrasion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0077]The following resins are used in the following Examples:
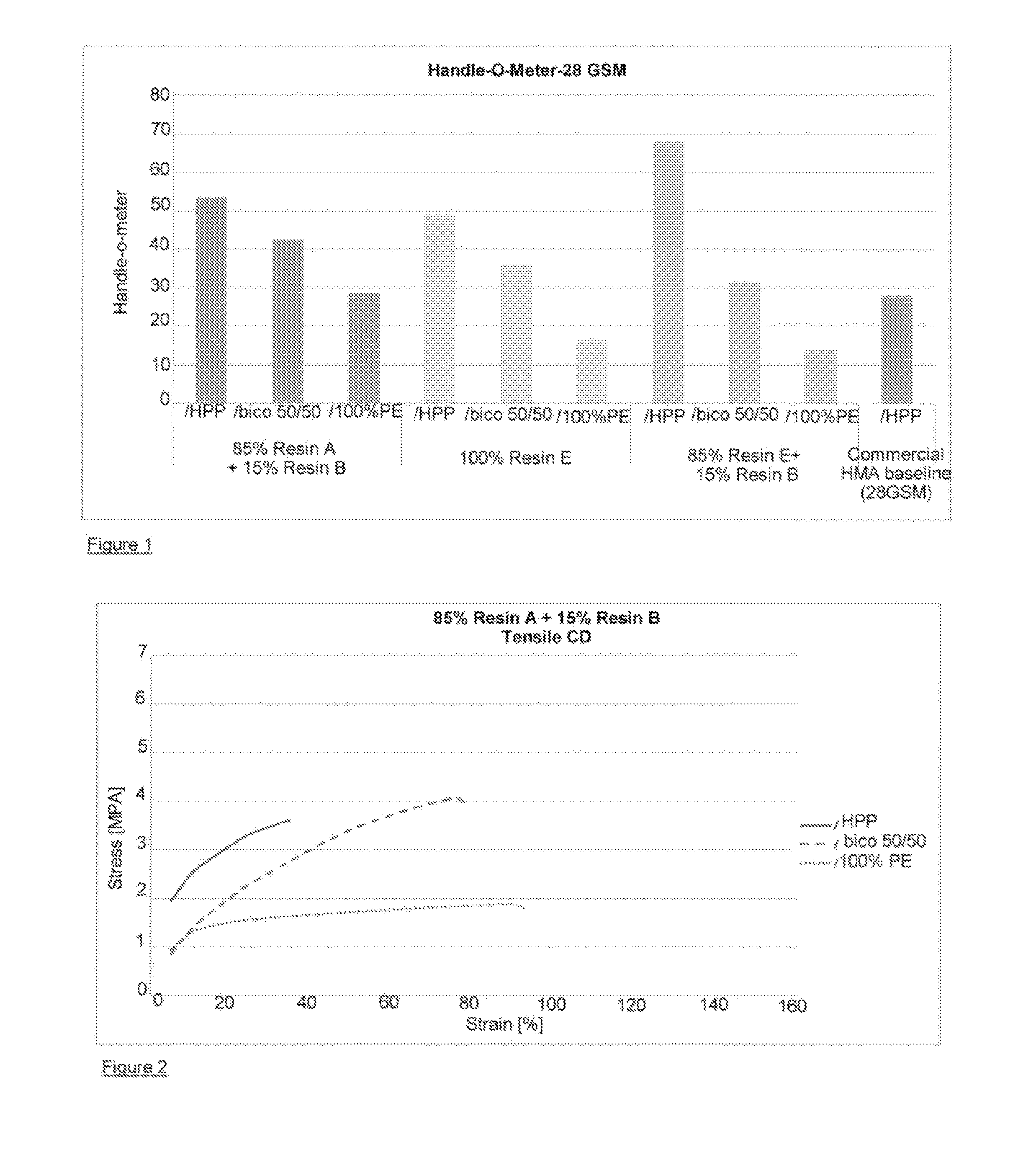
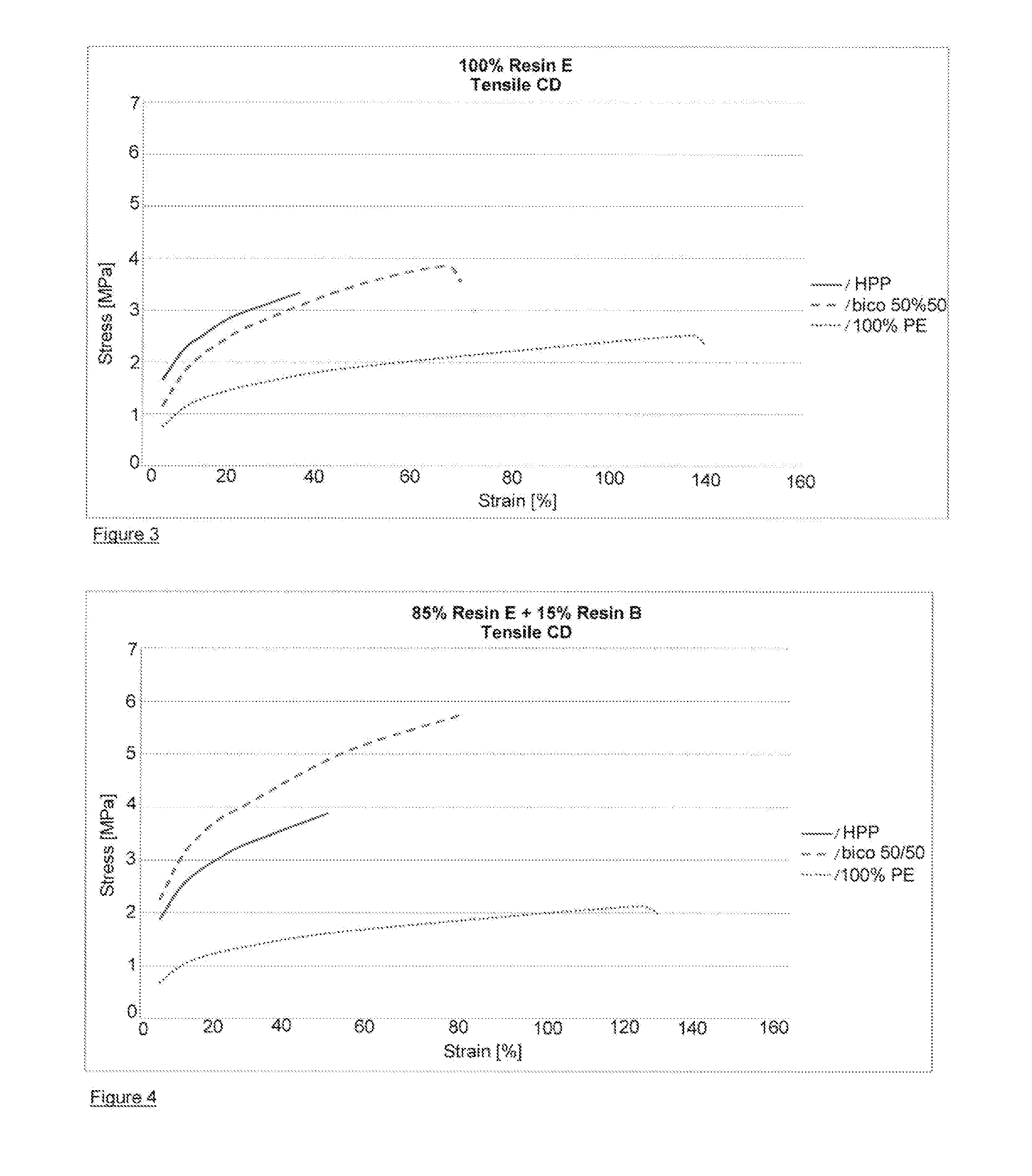
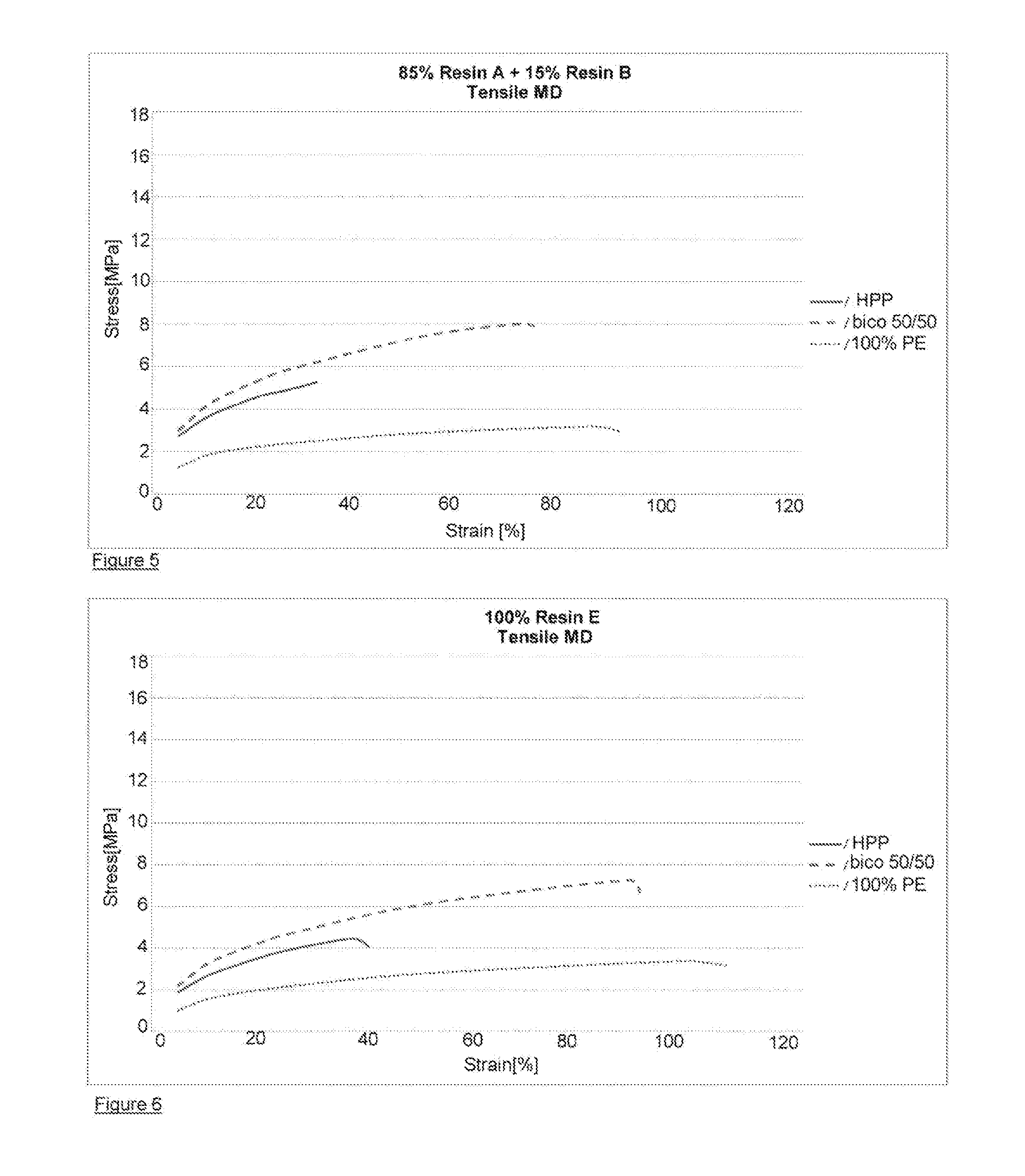
[0078]Resin A is an LDPE prepared in an autoclave reactor having a density of 0.918 g / cc and a melt index (190° C. / 2.16 kg) of 7.5 g / 10 min;
[0079]Resin B is a PBPE produced in solution process via metallocene catalysis having an ethylene content of 9% and an MFR (230° C. / 2.16 kg) of 25 g / 10 min and a density of 0.876 g / cc
[0080]Resin C is a linear polyethylene resin having a melt index (190° C. / 2.16 kg) of 21.5 g / 10 min and a density of 0.907 g / cc.
[0081]Resin D is an LDPE prepared in an autoclave reactor having a density of 0.918 g / cc and a melt index (190° C. / 2.16 kg) of 2.3 g / 10 min
[0082]Resin E is a blend of 70% Resin C and 30% Resin D. The blend has a density of 0.911 g / cc and a MI (190° C. / 2.16 kg) of 12 g / 10 min.
[0083]The nonwovens used for the examples are all spunbond nonwovens having a basis weight of 20 g / m2. The fibers used to make the nonwoven are 1.8 denier fibers which were either polypropylene, polyethylene ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| speed | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com