Optimised heat pump system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
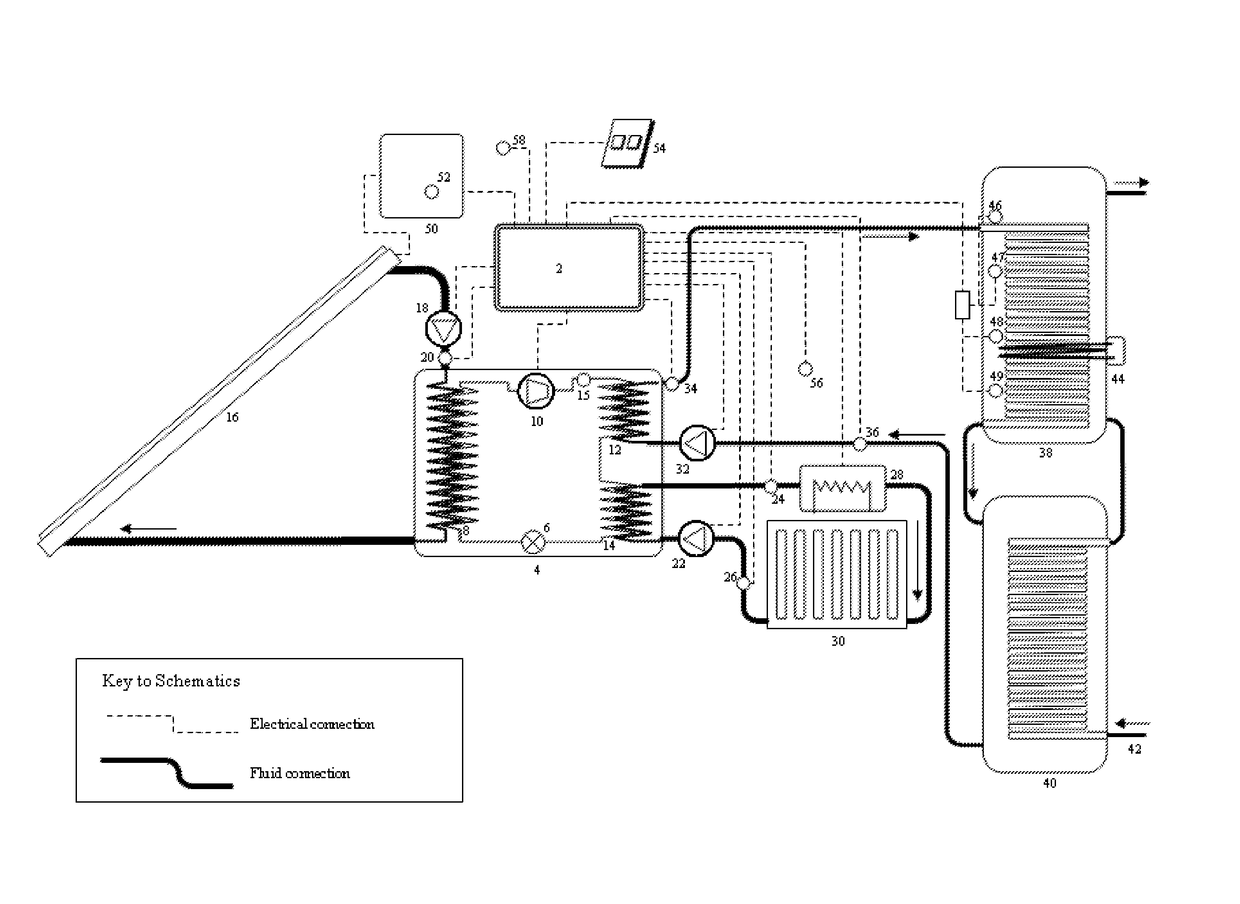
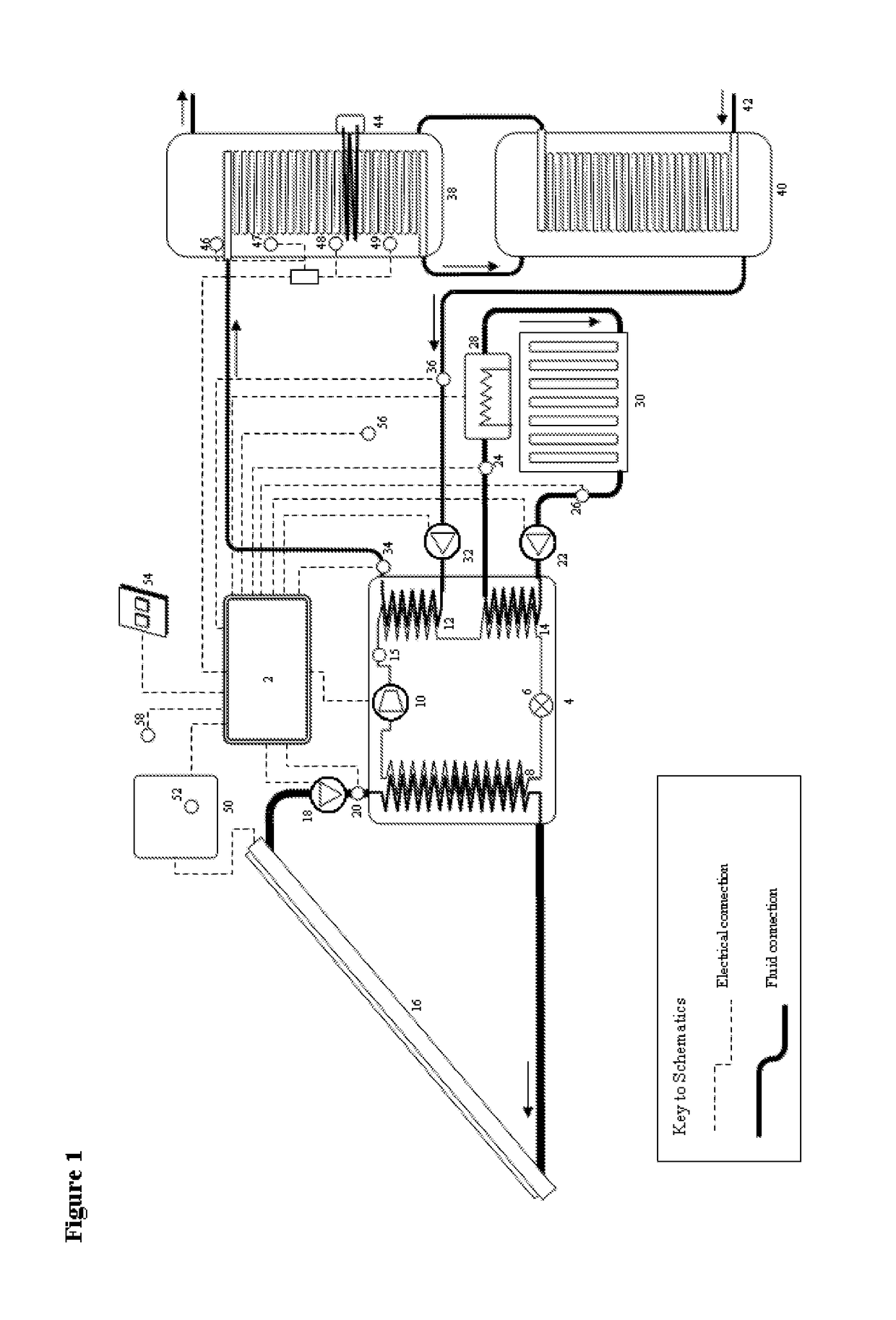
[0079]In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, FIG. 1, a system controller 2 (herein termed “the controller”) regulates a heat pump 4 which comprises a vapour-compression cycle for transferring heat from a heat source to a heat load.
[0080]The refrigeration circuit shown in FIG. 1 follows a ‘dual temperature’ heat pump design. At the start of the cycle, a refrigerant is expanded by an electronically-controlled expansion valve 6 to drop its evaporating temperature to below the source fluid return temperature such that it can absorb heat from a source fluid by evaporating said refrigerant in an evaporator 8. The refrigerant vapour is subsequently compressed by a compressor 10 with an inverter-driven electric motor, and through a desuperheater 12 that is cooled in contraflow heat exchange by a minor fluid circuit, and then subsequently passed through a condenser 14 that is cooled by a major circuit before re-entering the expansion valve 6. The evaporator, desuperheater and con...
second embodiment
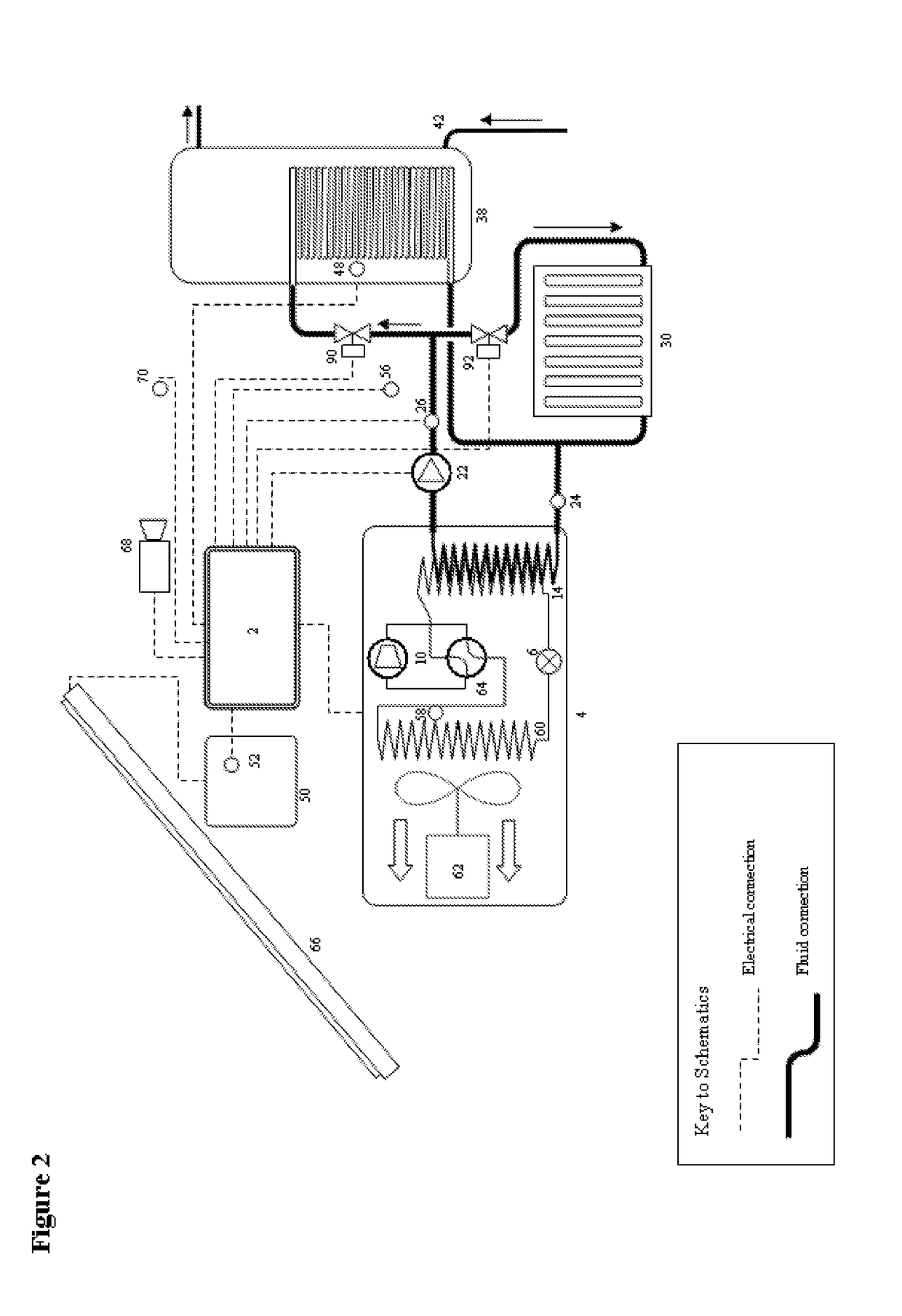
[0144]In a second embodiment of the invention, FIG. 2, the heat pump 4 includes a motorized electric fan 62 which is arranged to propel air through a finned-coil evaporator 60 in the manner of an “air-source heat pump”. In this embodiment the outdoor air temperature sensor is preferably mounted at the intake vent to the evaporator. The refrigeration circuit comprises only one condenser 14 which may supply heat to either a space heating circuit or a hot water tank 38 as regulated by the switching of two motorized valves including a hot water zone valve 90 and a space heating output zone valve 92. The refrigeration circuit also contains a 4-way reversing valve 64, which is arranged in the configuration illustrated in EP0134015B1 (1984) and permits the source and load circuits to be reversed such that heat can be extracted from the ‘load’ and rejected to the ‘source’. This design of heat pump enables the load circuit to perform either heating or cooling functions, thus expanding the ab...
third embodiment
[0153]In a third embodiment of the invention, FIG. 3, heat collectors, which may be plastic pipes that form a ground source heat exchange loop 72, are mounted in the ground in the manner of a “ground-source heat pump” system, and a circulating pump 18 transports heated coolant from the heat collectors to the heat pump evaporator 8. Ground source collectors provide a more stable temperature over daily and seasonal periods compared to air and solar-source collectors, which assist the ability of the controller to predict the net cost of heat and devise more optimised heating plans. The disadvantages of ground source collectors are the high installation and maintenance costs compared to other heat sources, and the relatively low source temperatures which are available during the summer.
[0154]The controller monitors the AC power output of a wind turbine generator 74 with a current transformer used as the electric generator power output sensor 52. The measured AC power is connected to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com