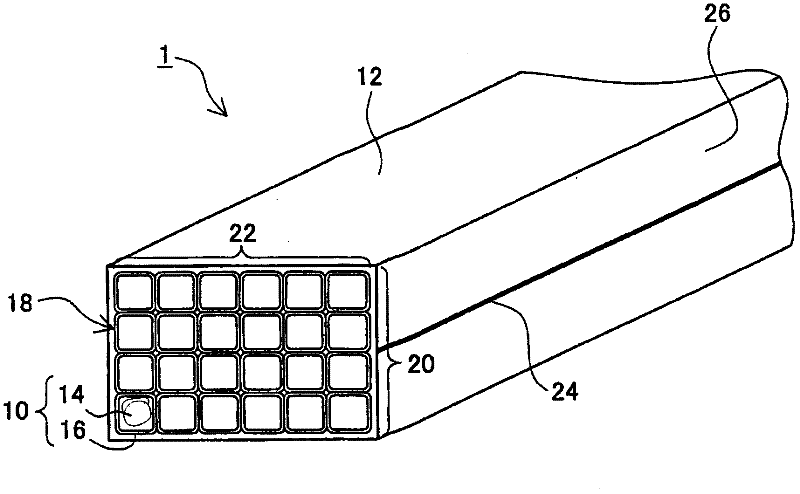
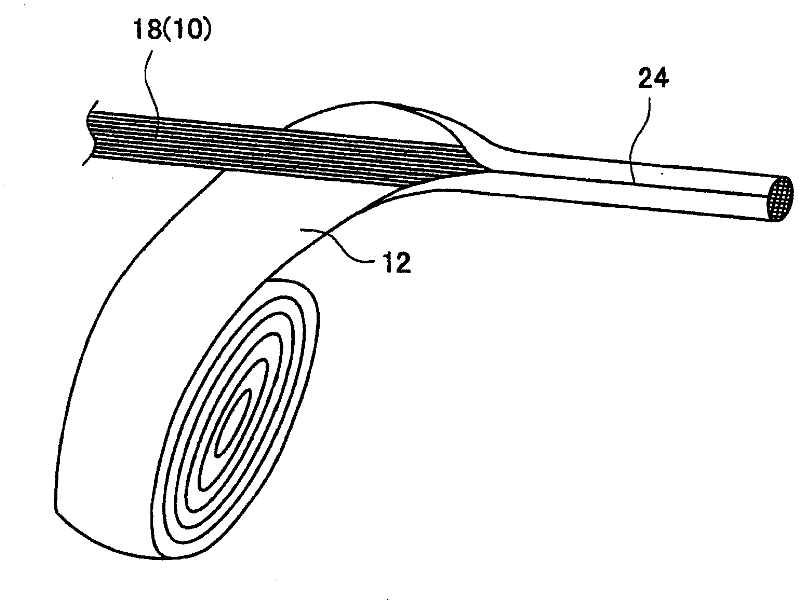
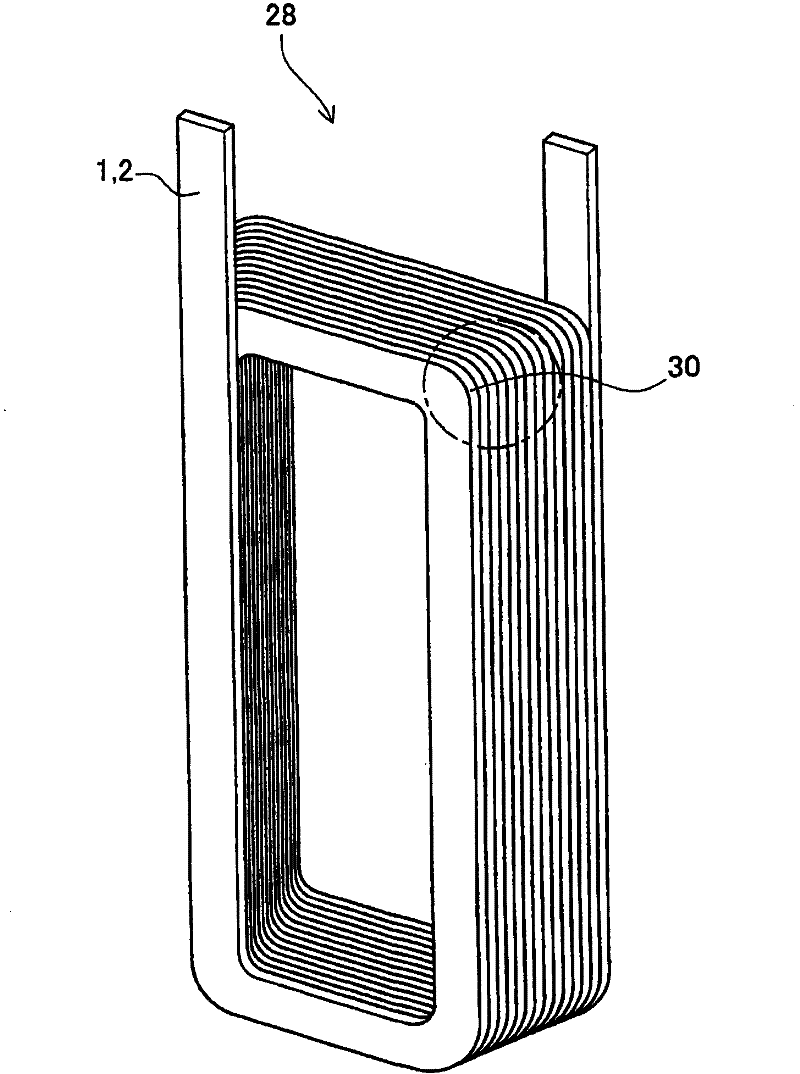
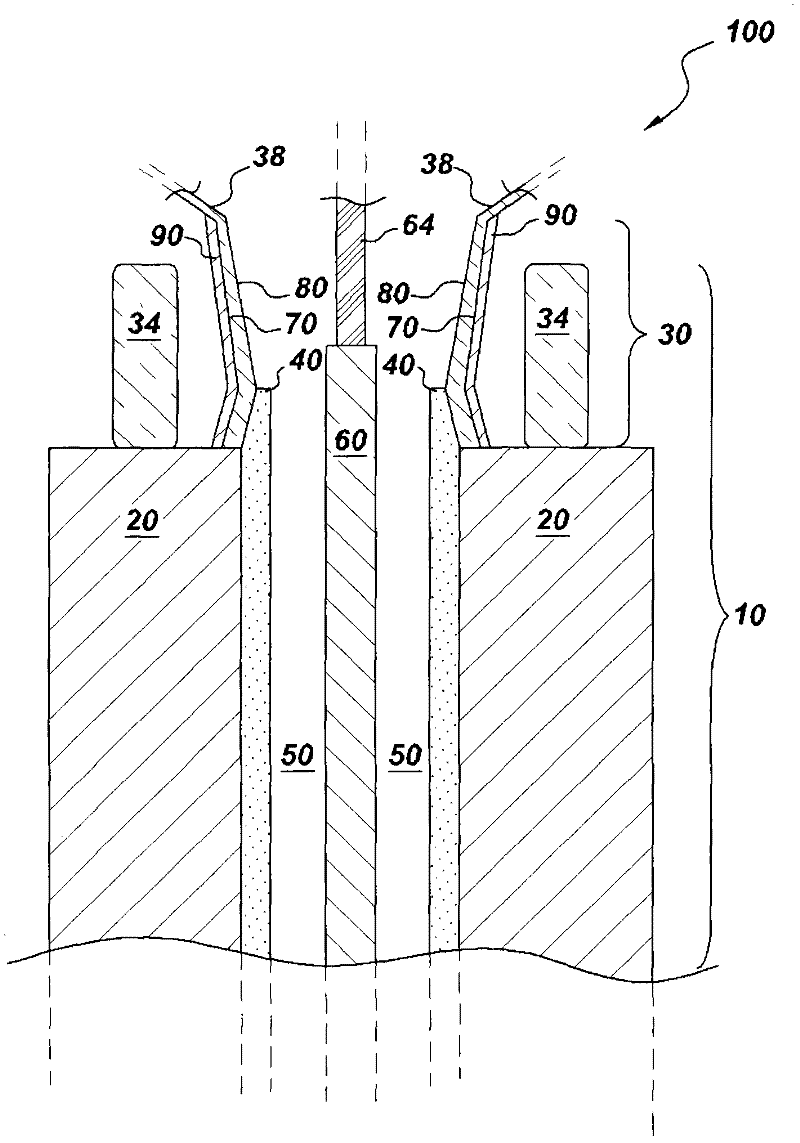
Patents
Literature
160results about "Prevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding heads" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
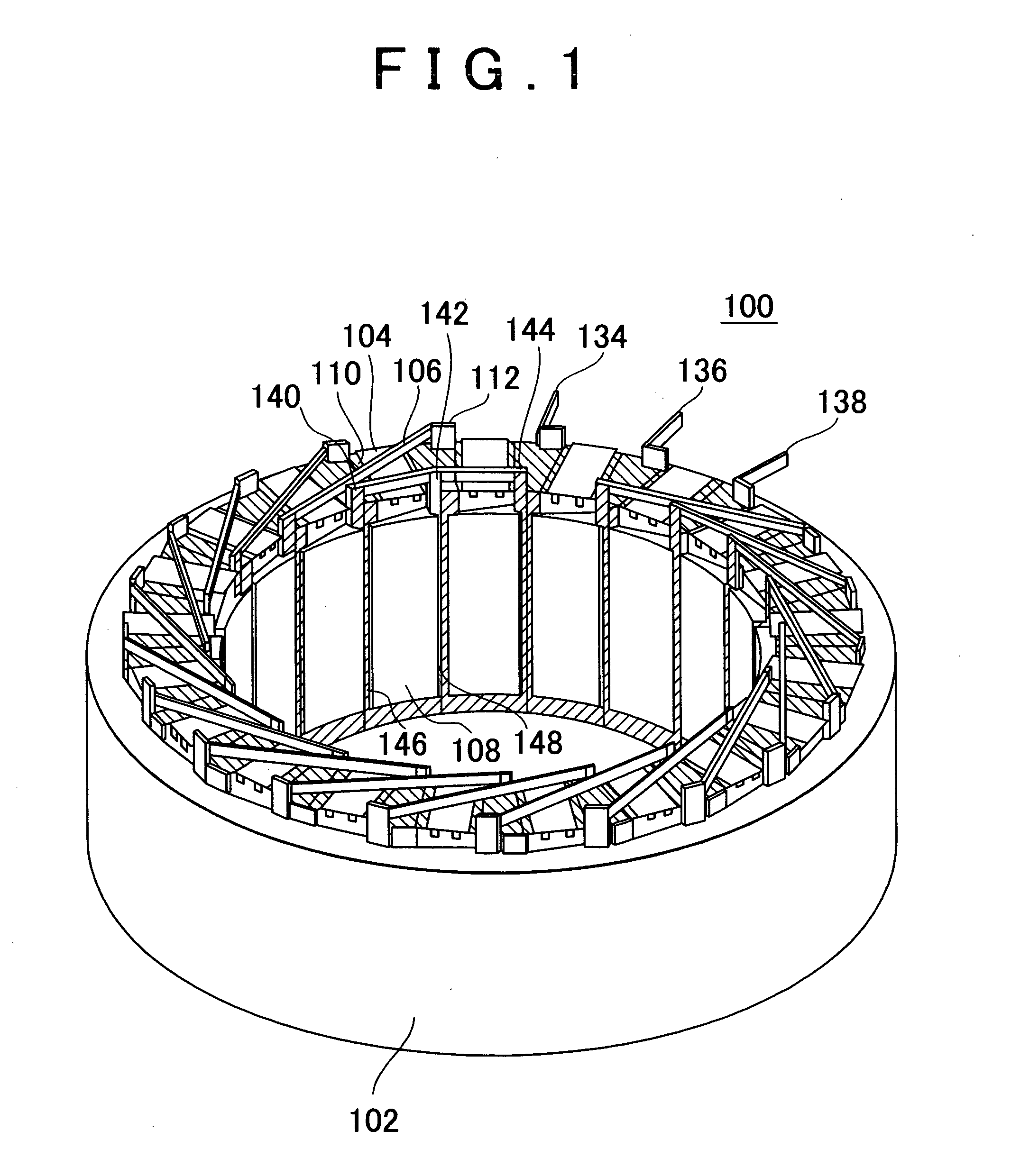
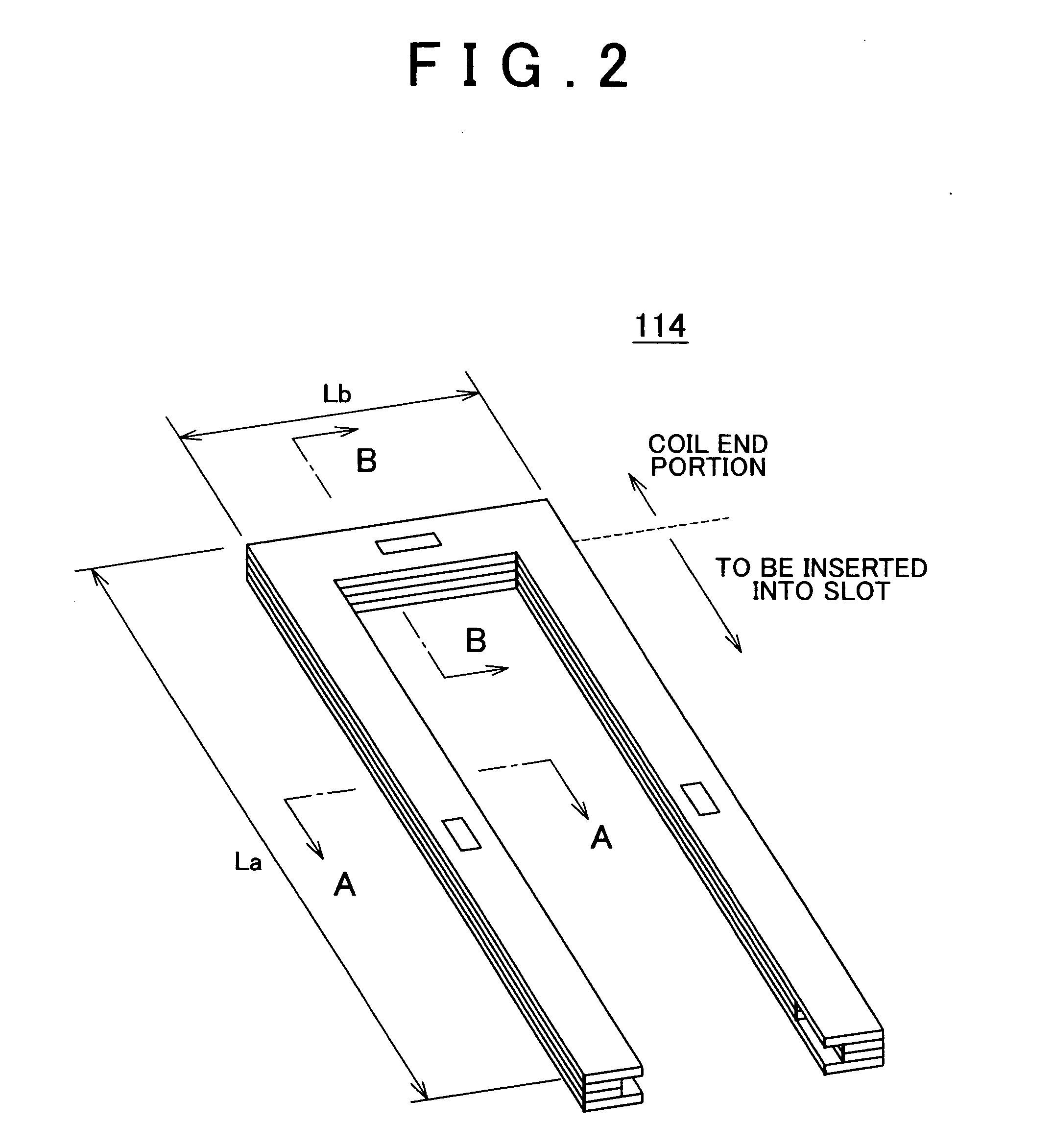
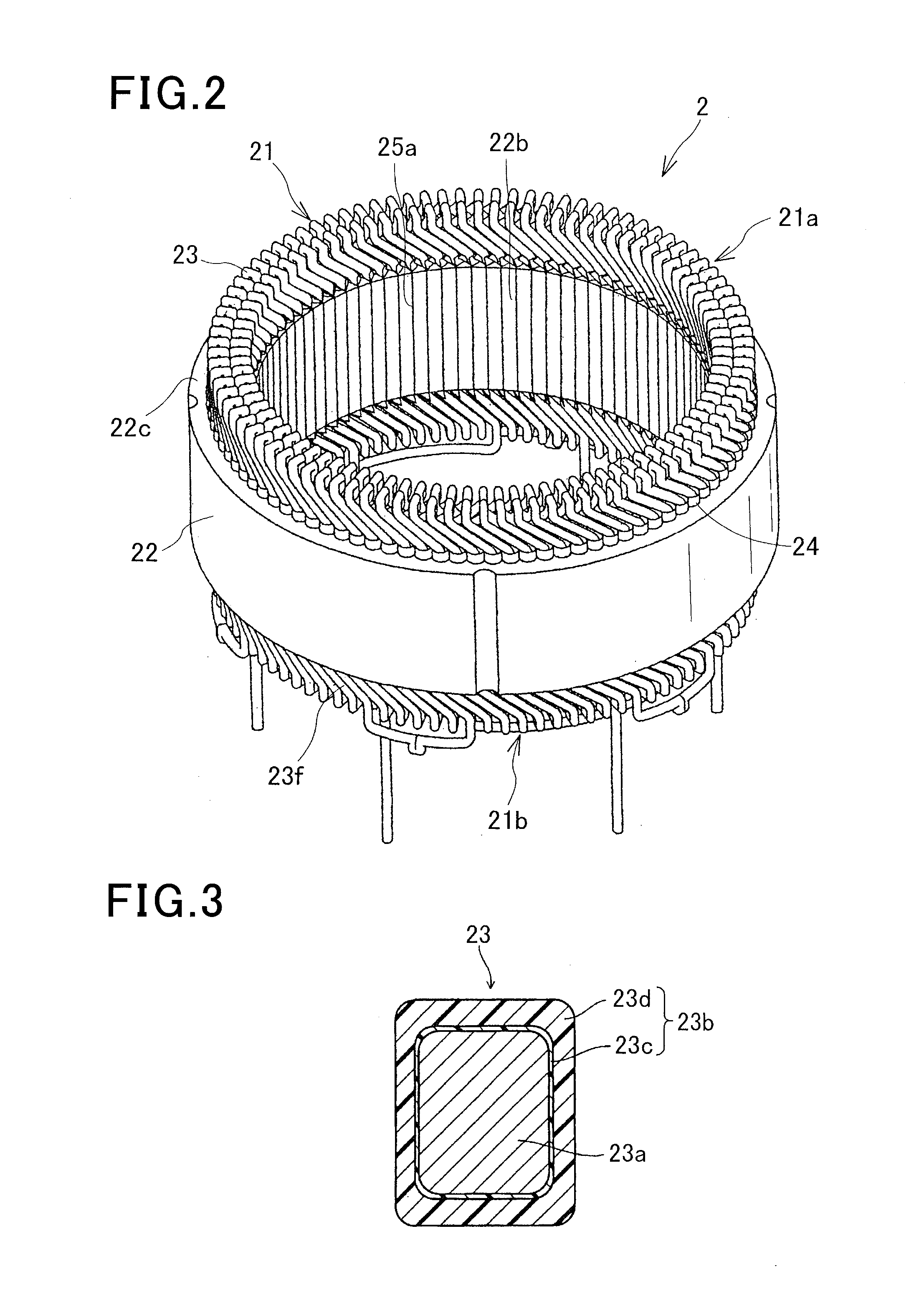
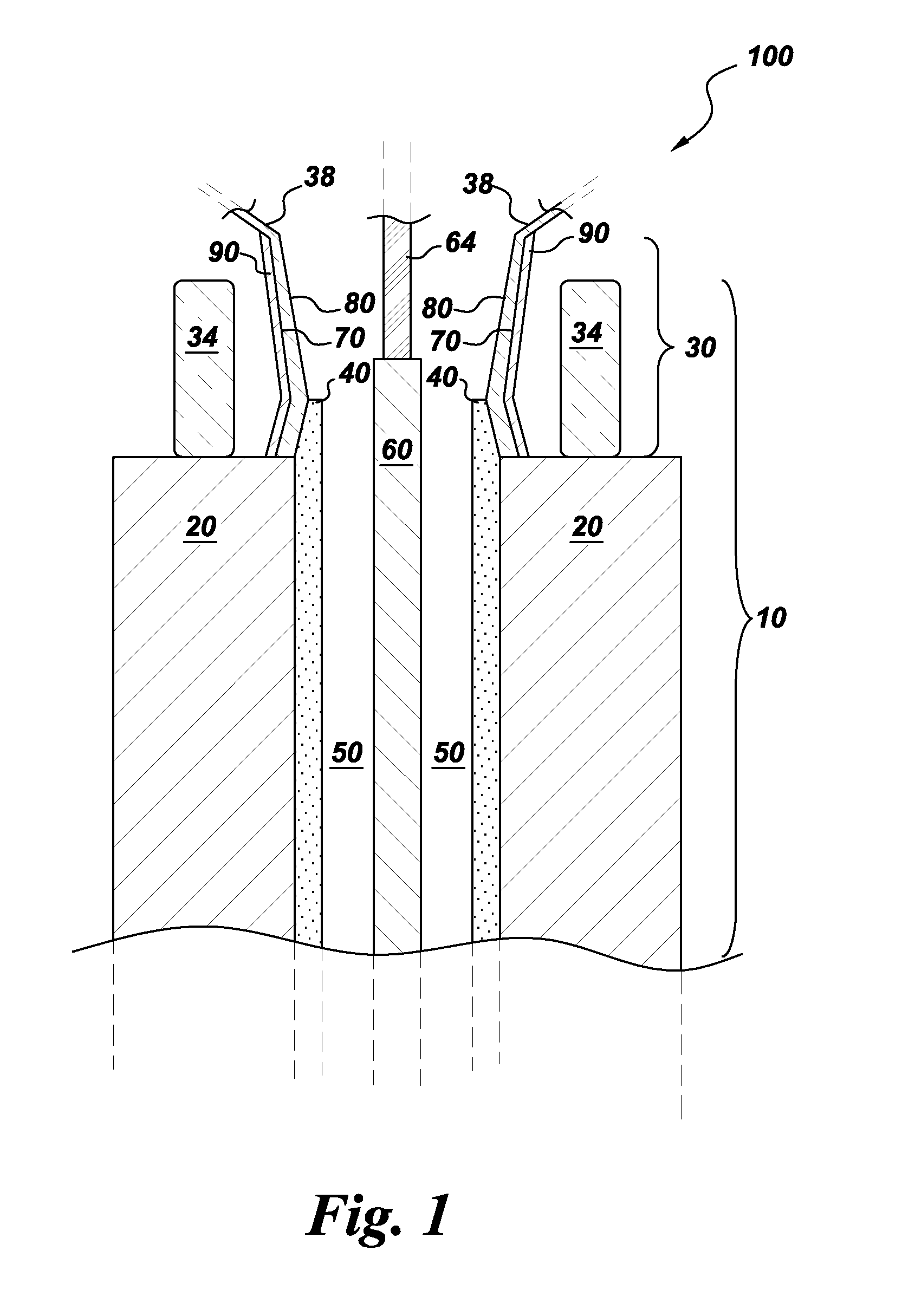
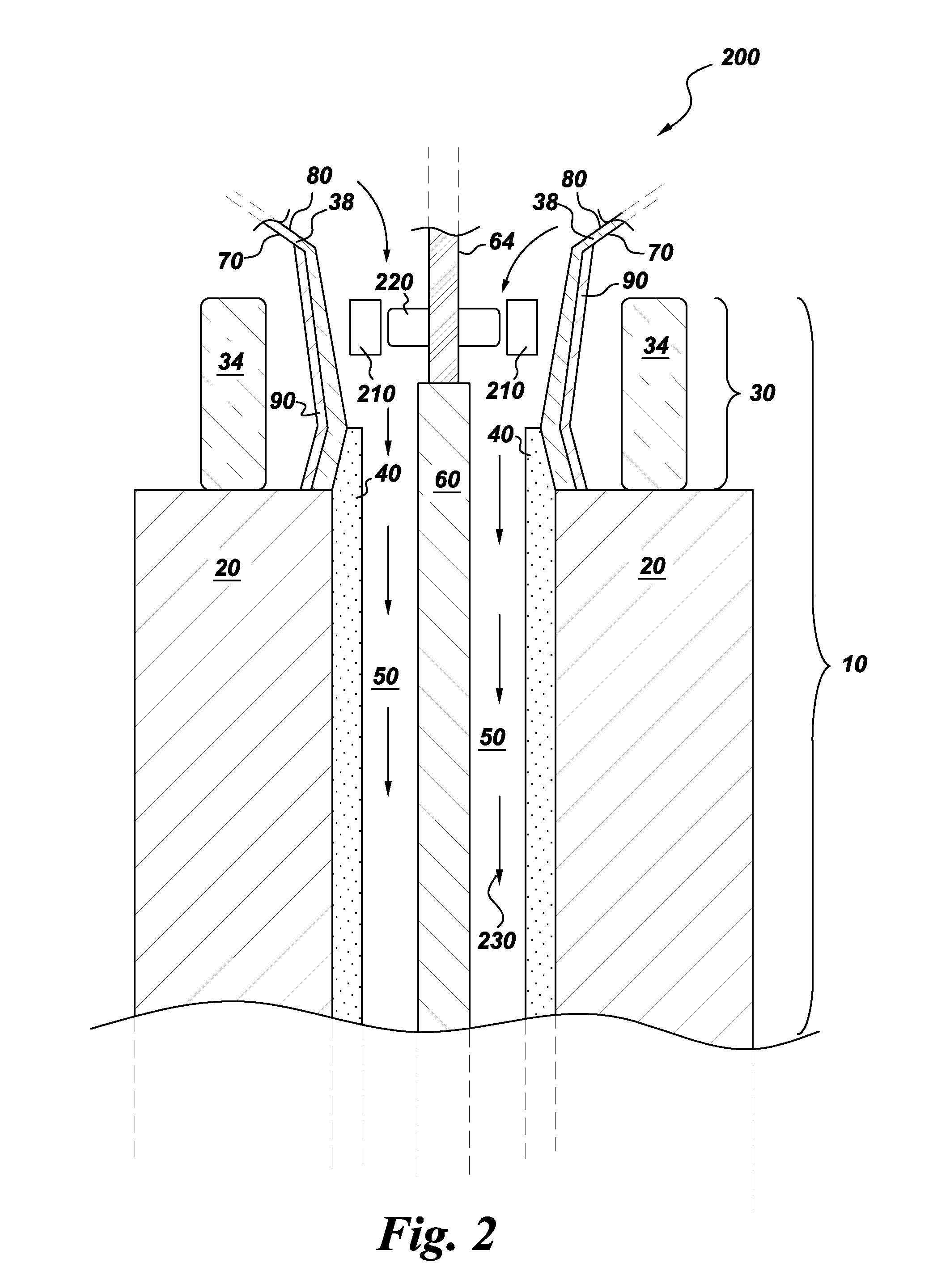
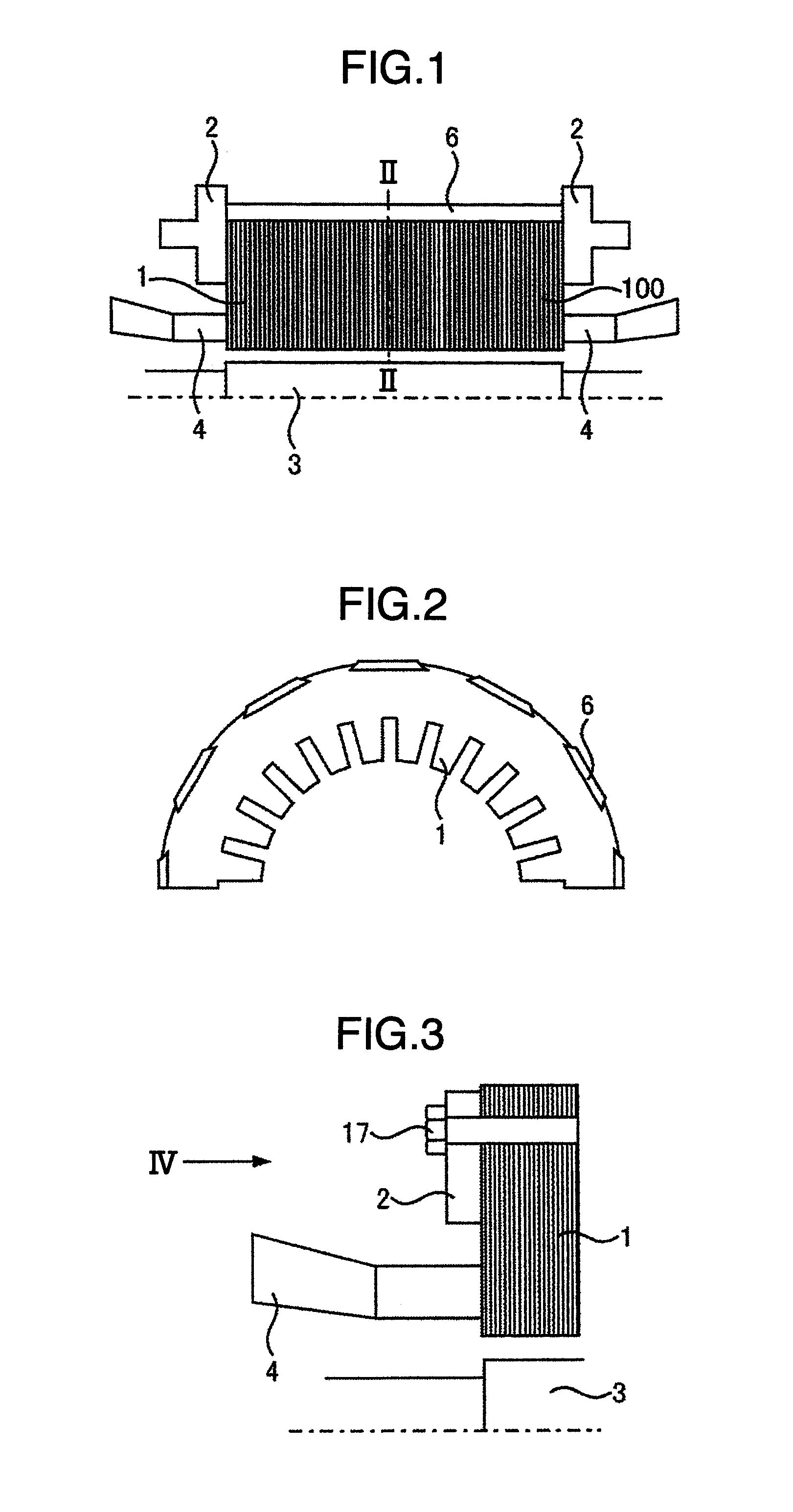
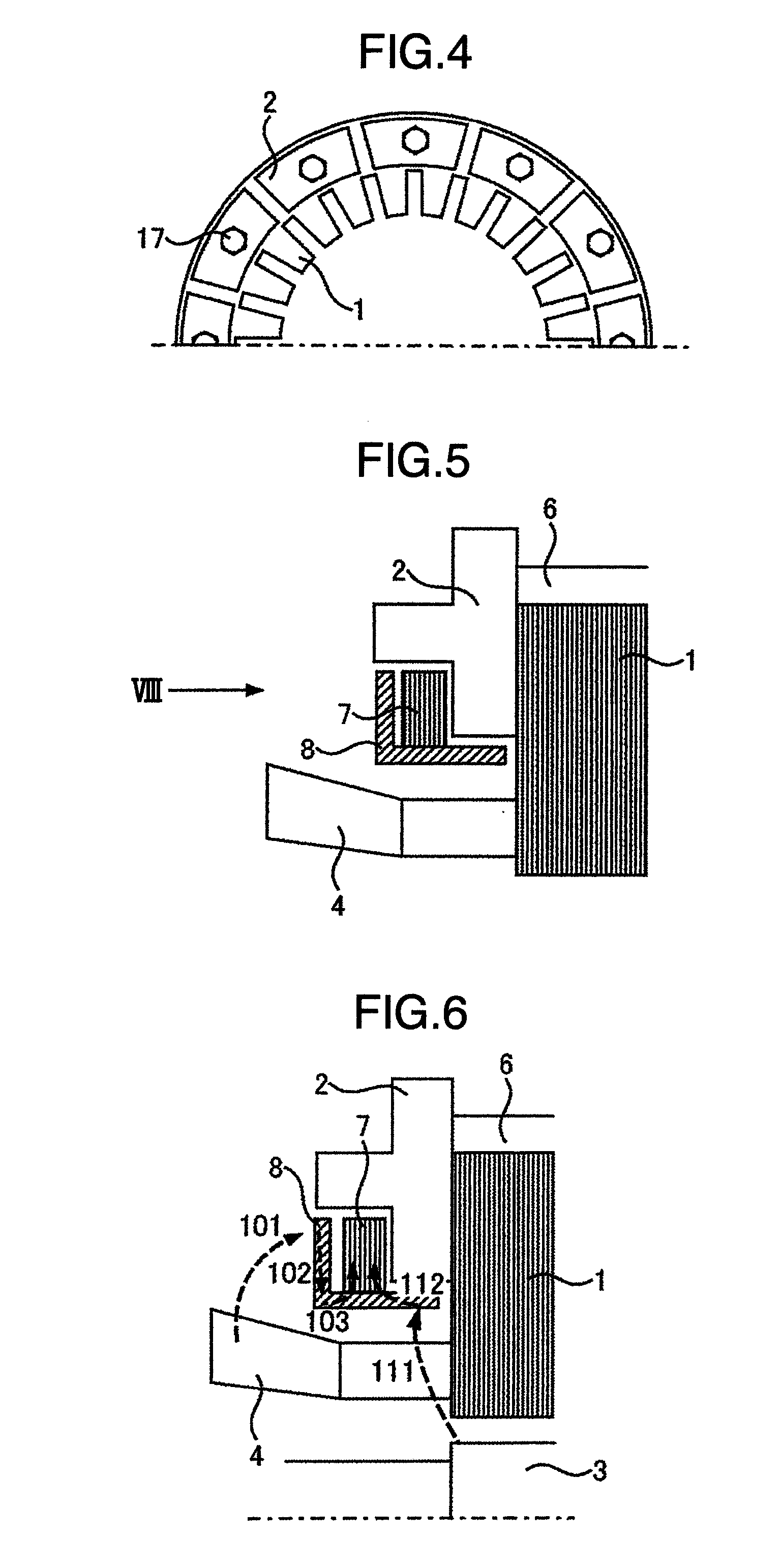
Stator of rotary electric machine
InactiveUS7268456B2Copper loss can be reducedImprove efficiencyWindings insulation shape/form/constructionPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsRotational axisElectrical conductor
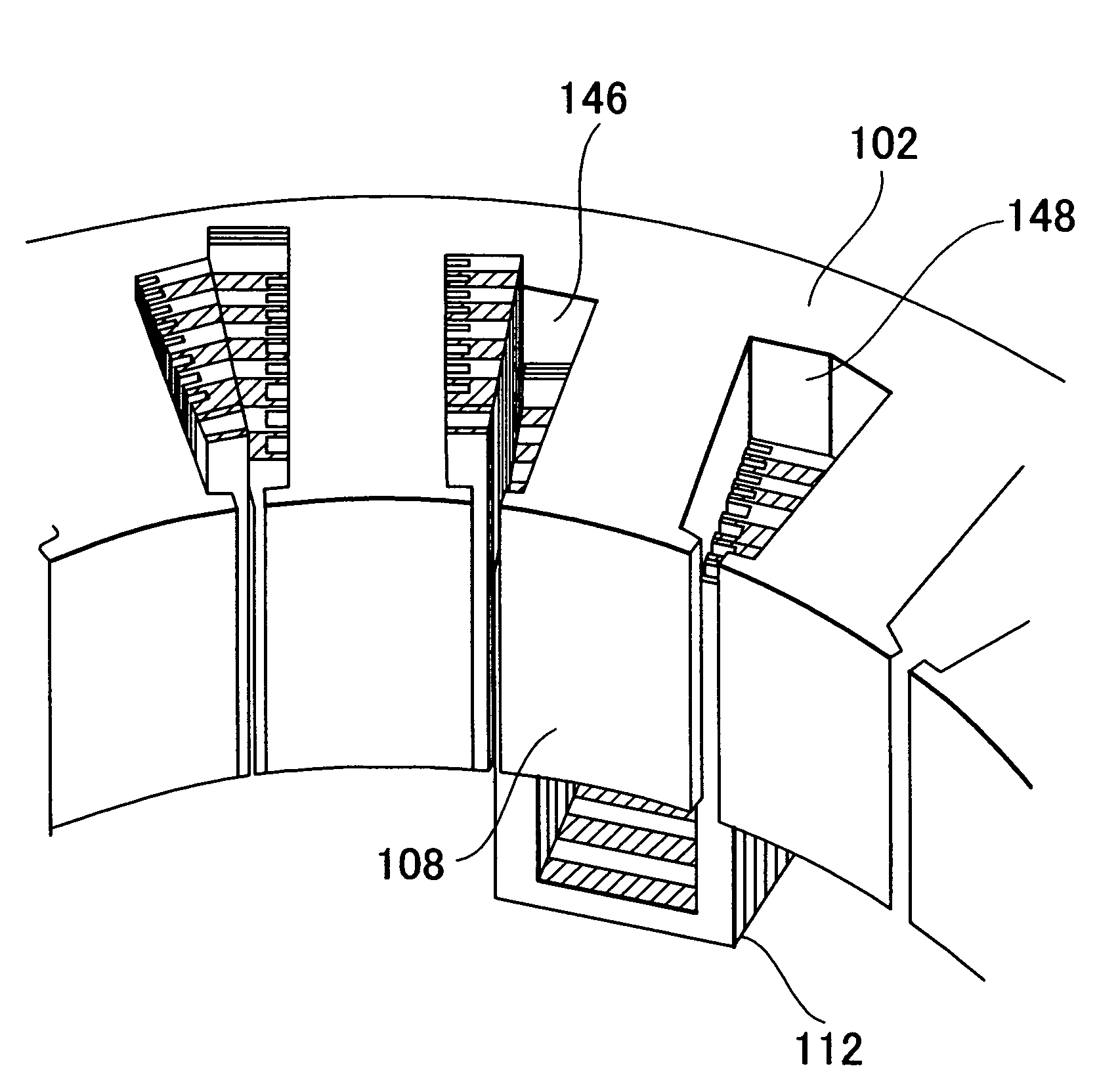
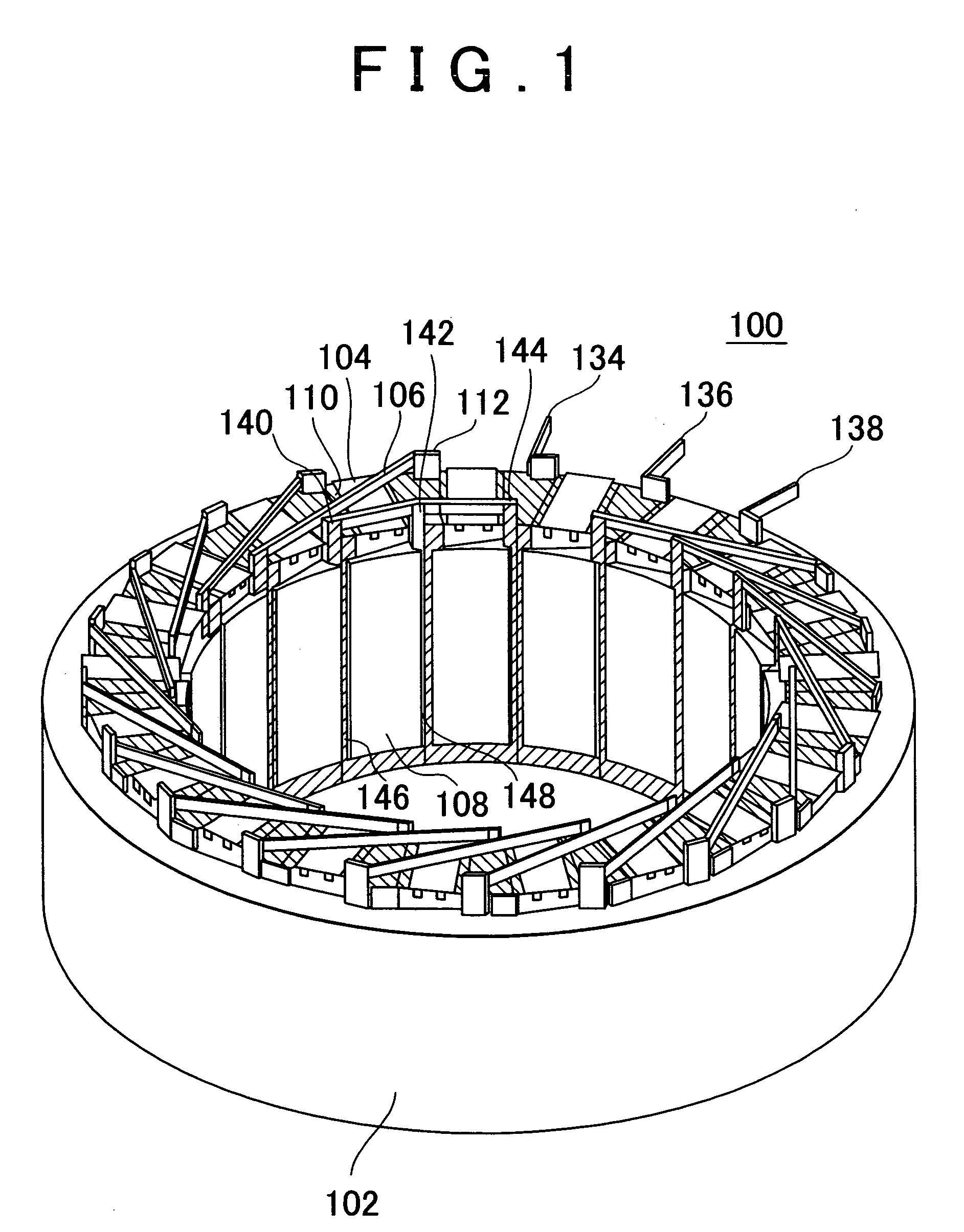
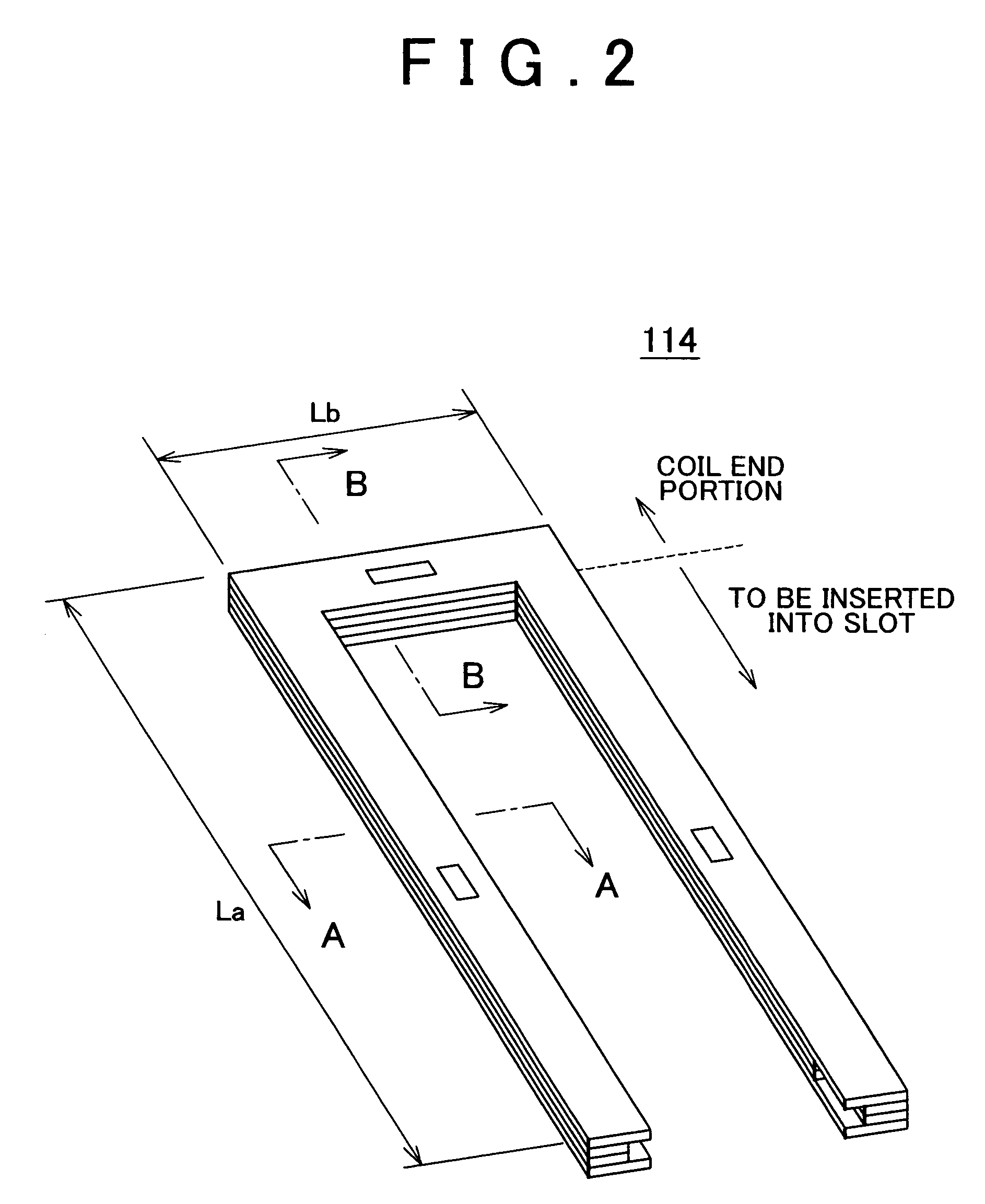
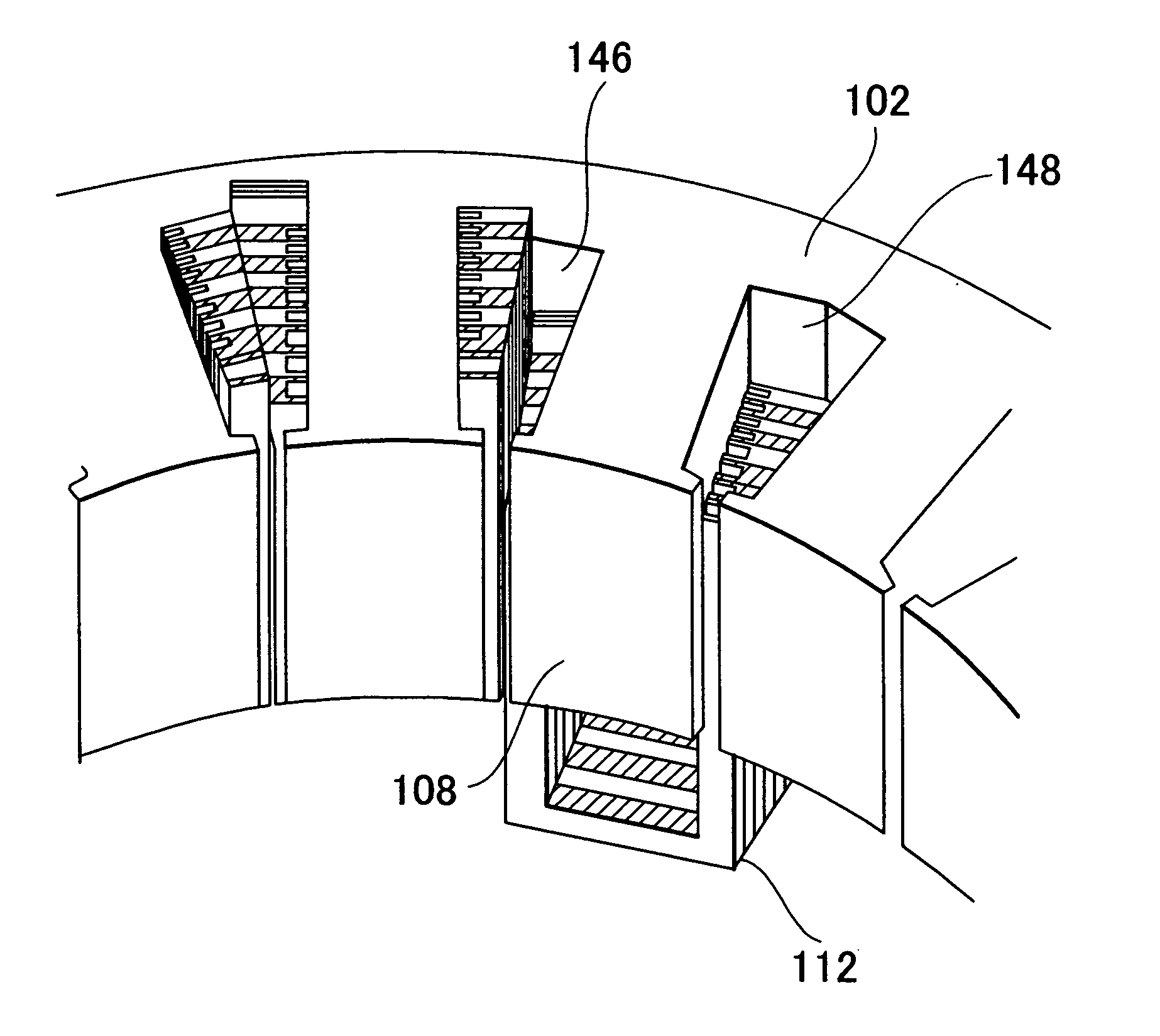
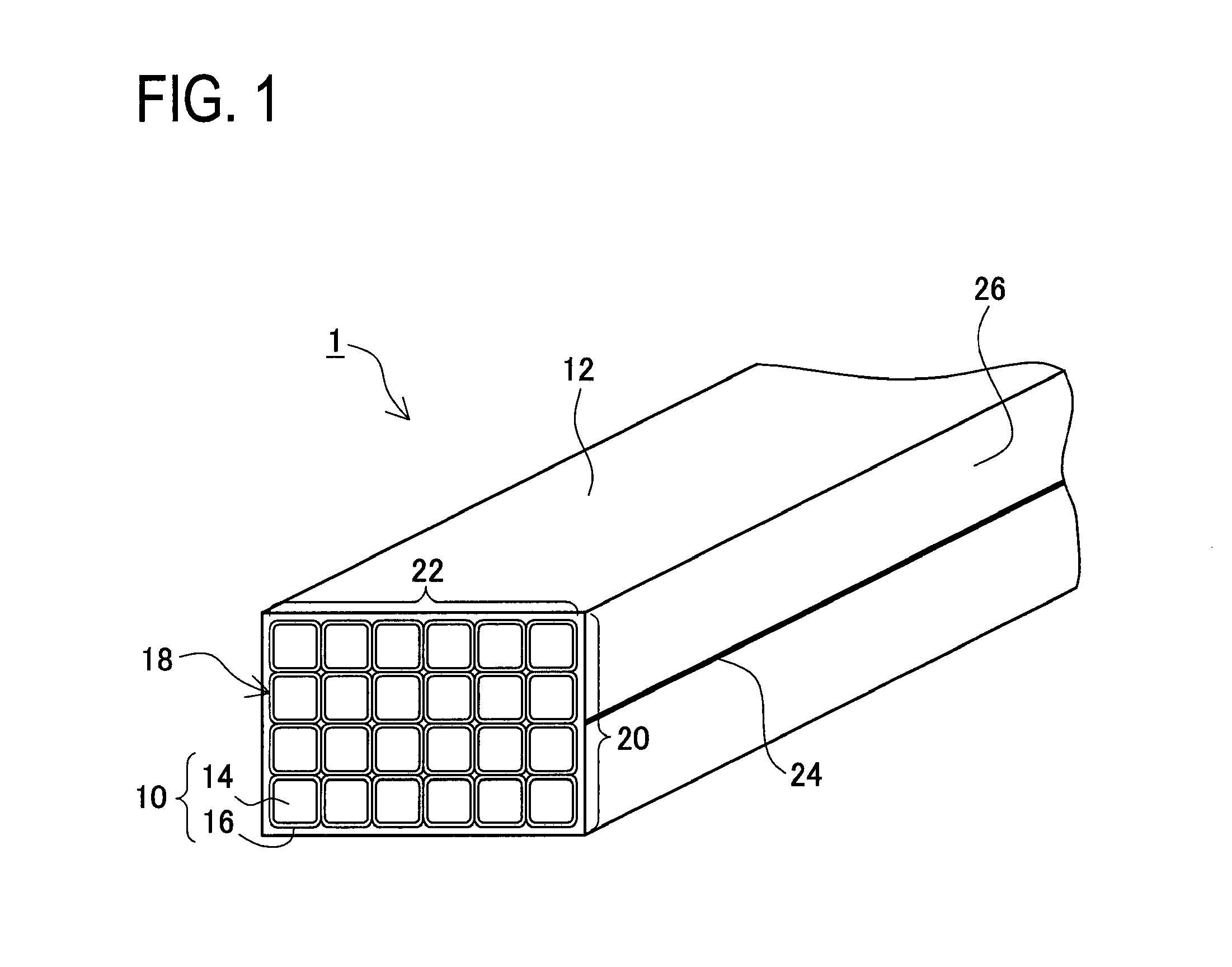
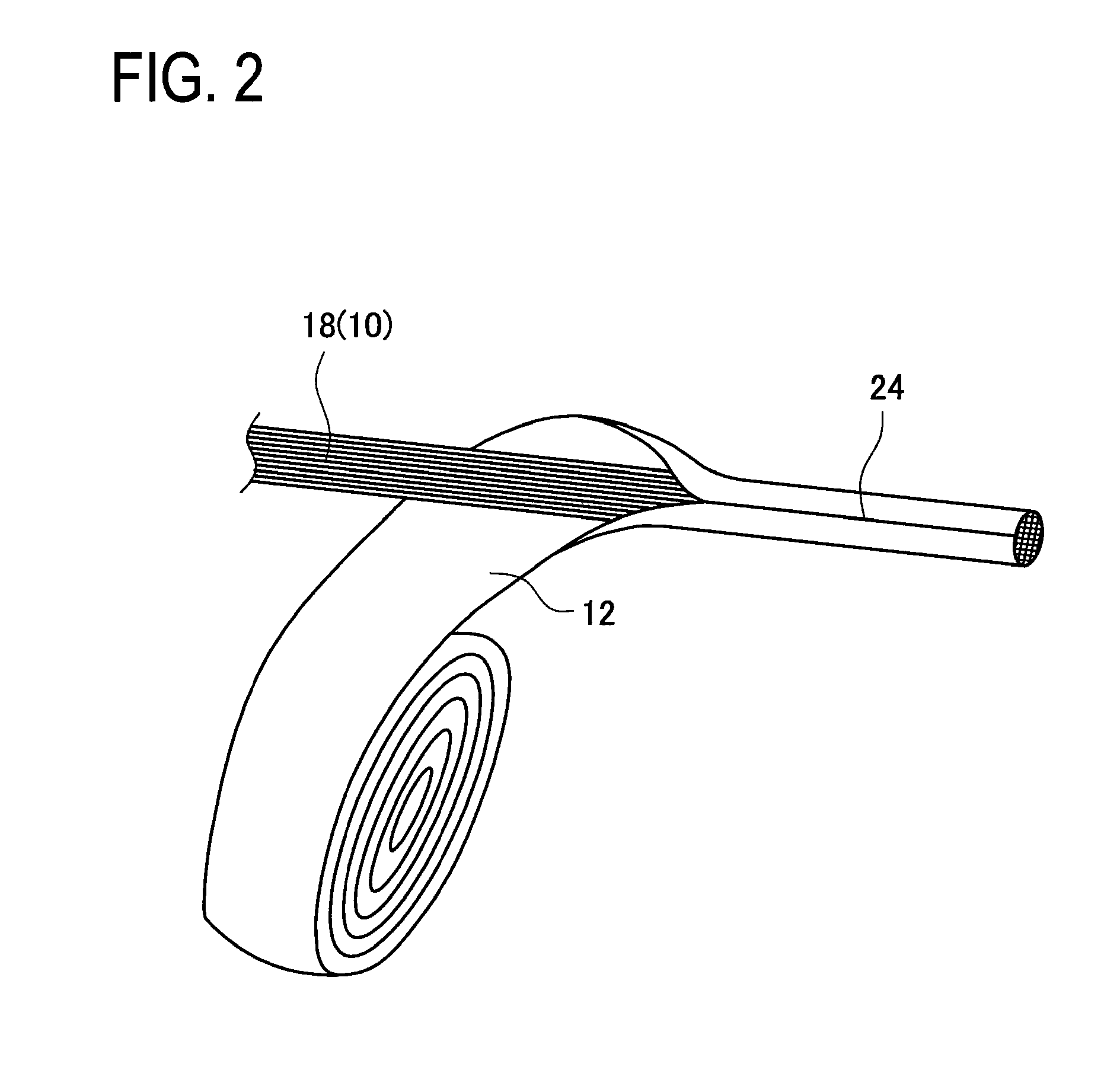
There is provided a stator of a rotary electric machine in which the proportion of the cross sectional area of a coil in the cross sectional area of the slot is high, and an electric power loss due to leakage flux can be reduced. The stator is a stator of a rotary electric machine including a stator and a rotor. The stator includes a stator core having multiple slots in a direction parallel to a rotational axis of the rotary electric machine, and a laminated flat-body conductor which is formed, in a press process, by laminating a predetermined number of flat-body conductors each of which has a predetermined shape. According to the predetermined shape, the flat-plate conductor has an open end portion such that the flat-plate conductor can be fitted in the stator core. The laminated flat-body conductor is inserted in the slots of the stator core, and the open end portion of the laminated flat-plate conductor is closed, whereby a coil is formed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Stator of rotary electric machine
InactiveUS20050108870A1Copper loss can be reducedImprove efficiencyWindings insulation shape/form/constructionPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsRotational axisElectrical conductor
There is provided a stator of a rotary electric machine in which the proportion of the cross sectional area of a coil in the cross sectional area of the slot is high, and an electric power loss due to leakage flux can be reduced. The stator is a stator of a rotary electric machine including a stator and a rotor. The stator includes a stator core having multiple slots in a direction parallel to a rotational axis of the rotary electric machine, and a laminated flat-body conductor which is formed, in a press process, by laminating a predetermined number of flat-body conductors each of which has a predetermined shape. According to the predetermined shape, the flat-plate conductor has an open end portion such that the flat-plate conductor can be fitted in the stator core. The laminated flat-body conductor is inserted in the slots of the stator core, and the open end portion of the laminated flat-plate conductor is closed, whereby a coil is formed.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Dynamoelectric machine having reduced magnetic noise and method
InactiveUS20070182267A1Reduce magnetic noiseSynchronous generatorsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsAlternatorTangential force
An automotive alternator including a rotor having a plurality of poles; a plurality of phases in operable communication with the plurality of poles; and a stator core in operable communication with the rotor, the stator having a number of slots defined by:S=(P×PH)+((M×PH)+N)where S=number of slots P=number of poles PH=number of phases M=a whole integer greater than or equal to 0 N=a whole integer selected from a group of integers ranging from, and including, 1 through the number of phases minus 1. A method for reducing magnetic noise in an automotive alternator includes selecting a number of poles, selecting a number of phases, selecting a number of stator core slots, the foregoing selections interacting in the automotive alternator to produce an order of frequency of a tangential force different than any multiple of the number of phases and different than an order of frequency of a radial force of the alternator.
Owner:REMY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Electromechanical apparatus, robot, and moving body
InactiveUS20130020900A1Reduce amountImprove electromechanical efficiencyPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsRailway vehiclesFiber bundleCarbon fibers
An electromechanical apparatus includes: a rotor including a central shaft and permanent magnets disposed around a cylindrical surface along an outer circumference of the central shaft, and a stator including hollow electromagnetic coils disposed around a cylindrical surface along an outer circumference of the permanent magnets and a pipe member having a hollow cylindrical shape and disposed between the permanent magnets and the electromagnetic coils, wherein the pipe member is made of a carbon fiber reinforced plastic, and the carbon fiber reinforced plastic is formed by weaving carbon fiber bundles formed of bundled carbon fibers.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Structural enclosed rotor configuration for electric machine
InactiveUS6885120B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsElectric machineEngineering
A rotor configuration for an electric machine includes a rotor shaft and a multi-pole rotor core secured to the rotor shaft. A plurality of field winding modules are respectively disposed over each pole of the multi-pole rotor core. An enclosure is disposed over the field winding modules for containing the field winding modules over the rotor core. A magnetic shield is disposed over the field winding modules between the field winding modules and the enclosure. The simplified construction reduces manufacturing time and costs.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Conductor wire for motor and coil for motor
ActiveUS20120092117A1Increased durabilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsElectrical conductorThin wire
The present application has a purpose to provide a conductor wire for motor capable of improving durability against bending, and a coil for motor using the conductor wire for motor. One aspect of the invention, therefore, provides a conductor wire for motor comprising a fine wire assembly and a coating member covering an outer peripheral surface of the fine wire assembly, the fine wire assembly consisting of a plurality of fine wires assembled in a bundle, and each of the fine wires including a conductor and an insulating part provided on an outer peripheral surface of the conductor, wherein the coating member is made of metal, and the coating member has an electrical resistance value larger than an electrical resistance value of the conductor.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Rotating electrical machine
ActiveUS7872392B2Total current dropCurrent lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsEddy currentMechanical engineering
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Rotating machine
InactiveCN102208837AReduce lossesPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsMagnetic circuit stationary partsMagnetic shieldConductor Coil
The invention provides an electric rotating machine which is capable of reducing losses that occur in clamping plates and their shield. The electric rotating machine includes a rotor formed with field winding wound around a rotor core, a stator placed opposite to the rotor at a predetermined space and formed with stator winding wound around a stator core formed by stacking multiple magnetic steelsheets in the axial direction, clamping plates clamping and retaining the stator core from both axial end parts thereof in the stacking direction of the magnetic steel sheets, and a magnetic shield placed around the clamping plates to shield flux leakage flowing into the clamping plates, and the magnetic shield is formed of a cylinder of stacked steel sheets stacked in a form of a cylinder about the rotor shaft and powder magnetic core segments and powder magnetic core segments having portions which are stuck to the cylinder of stacked steel sheets on the stacking cross section, and arranged to cover side surfaces and an inner surface of radial direction of the clamping plates.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Motor convenient for fluid flowing
ActiveCN105680602ASpeed up the flowExpand the range of mobilityPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionEddy currentHeat losses
The invention provides a motor convenient for fluid flowing. The motor comprises stator windings and ventilation channel steel. According to the technical points, two pieces of rectangular ventilation channel steel are arranged between two adjacent stator windings of one group, one piece of trapezoid ventilation channel steel is arranged between one group of two adjacent stator windings and another adjacent group of two stator windings, and the width radio of the upper half part to the lower half part of the trapezoid ventilation channel steel is 2:1. The ventilation channel steel after changing changes a lot both in shape and distribution, and the lower part of each piece of trapezoid ventilation channel steel is narrowed, so that the flowing range of a fluid is increased, and the flowing speed of the fluid is increased; the eddy current loss is reduced due to the change of the direction of the fluid, and the concave-shaped design of the upper part of the trapezoid ventilation channel steel further increases the flowing speed of the fluid; in addition, the distribution mode of the trapezoid ventilation channel steel and the rectangular ventilation channel steel facilitates the heat exchange between the inner part and the outer part of the motor, the temperature rise of the motor is reduced, and heat loss through convection is facilitated.
Owner:无锡市明通动力工业有限公司
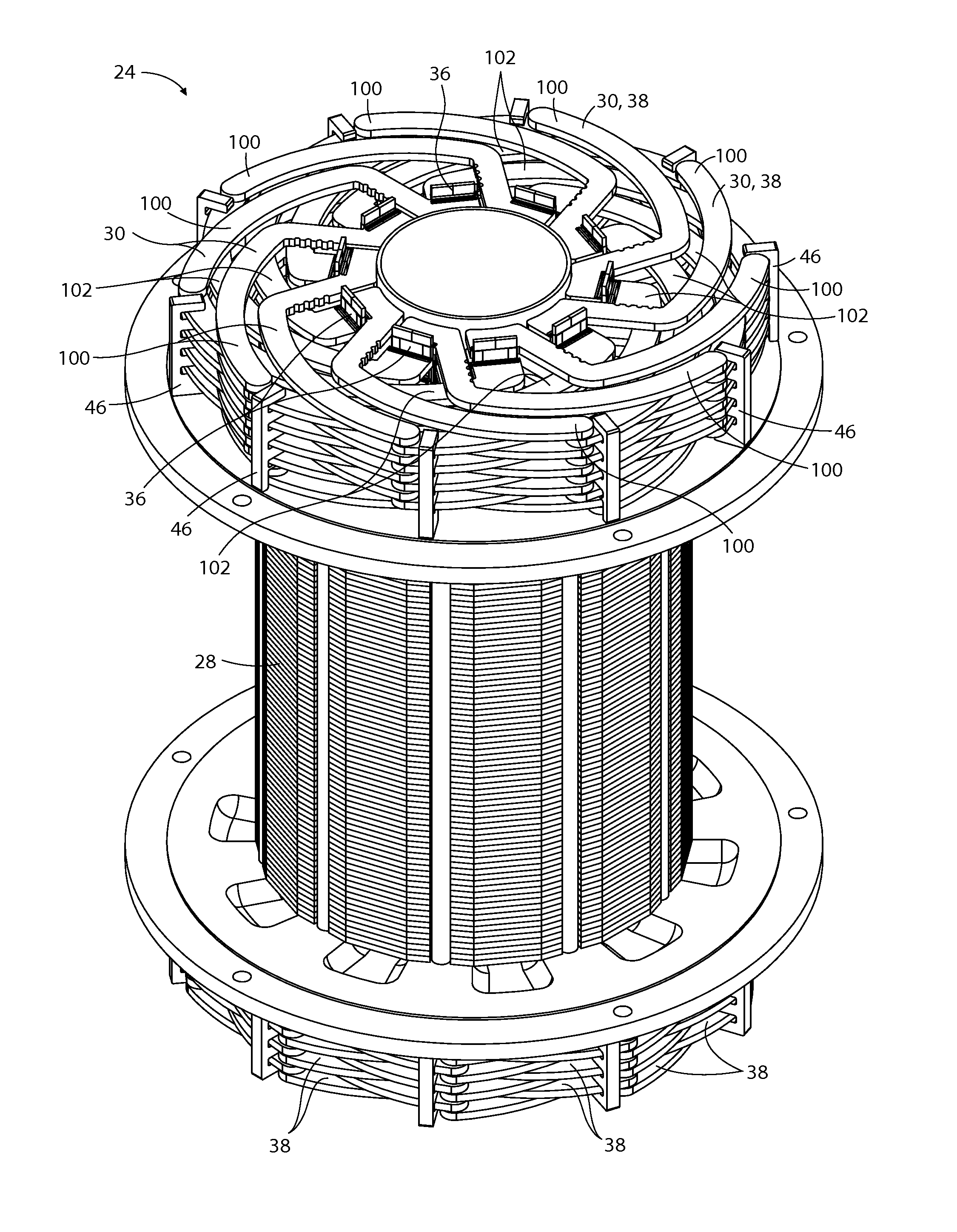
Counteracting magnetic field generator for undesired axial magnetic field component of a power generator stator and associated methods
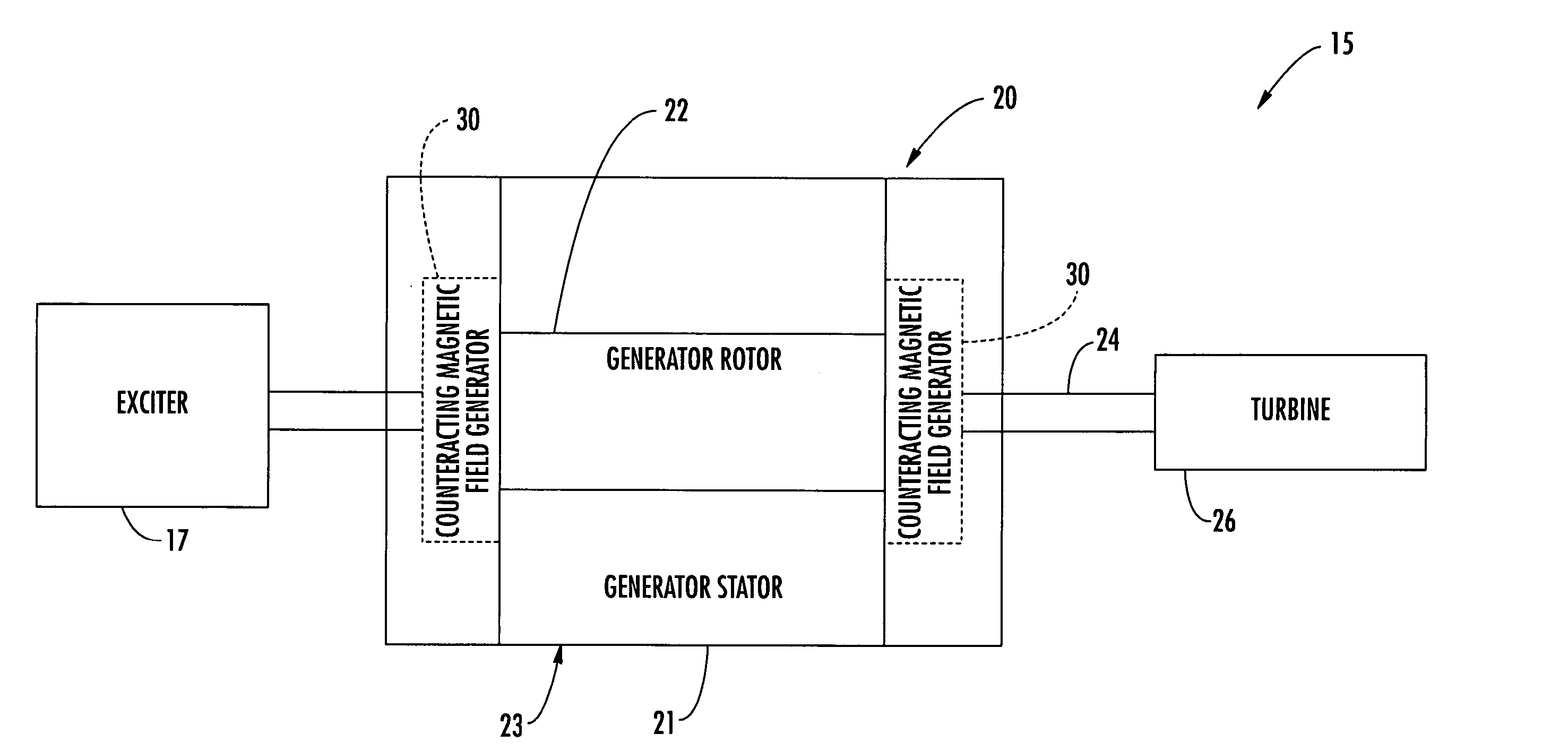
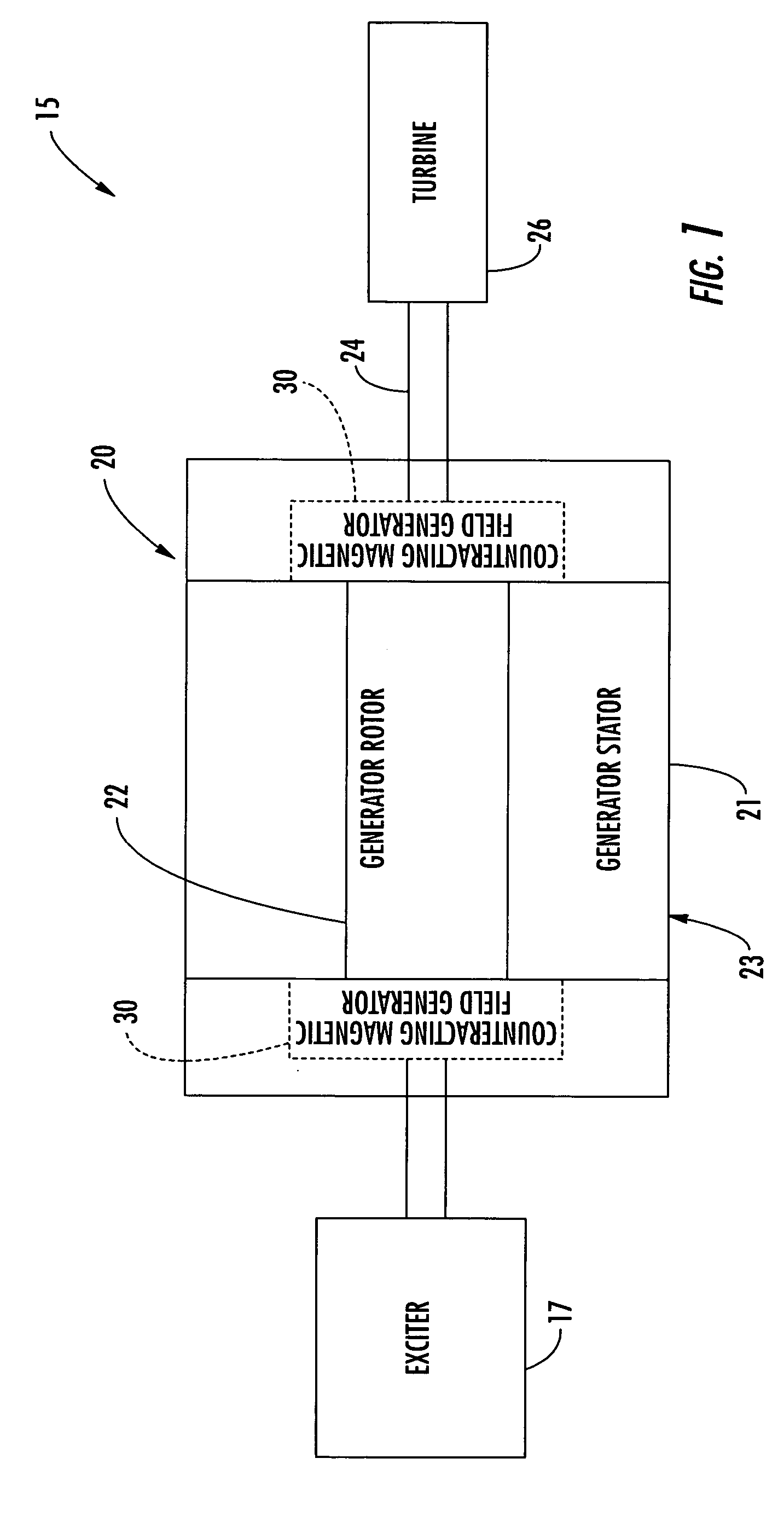
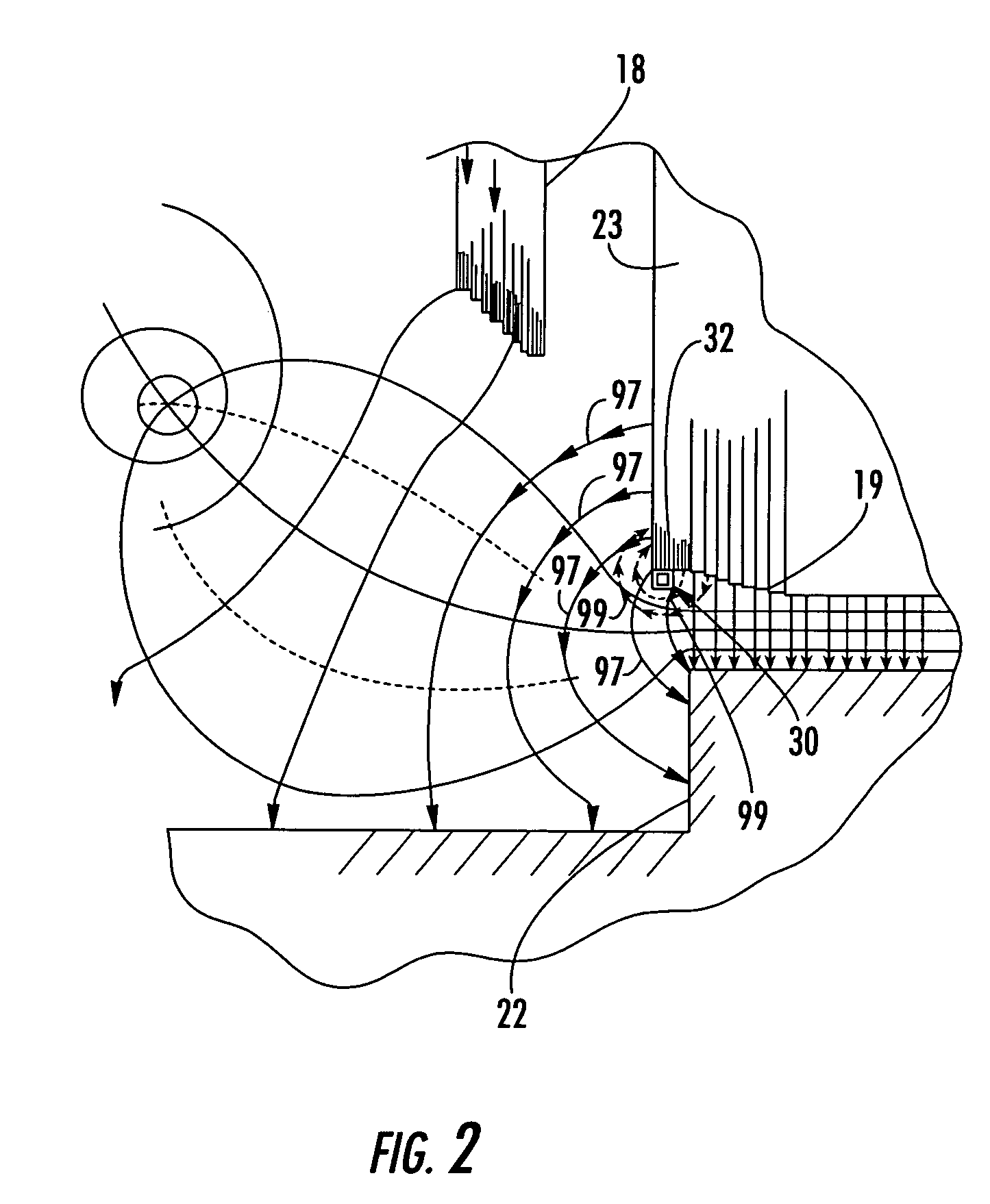
InactiveUS20050121992A1Reduce decreaseReduce componentsSynchronous generatorsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsConductor CoilElectric generator
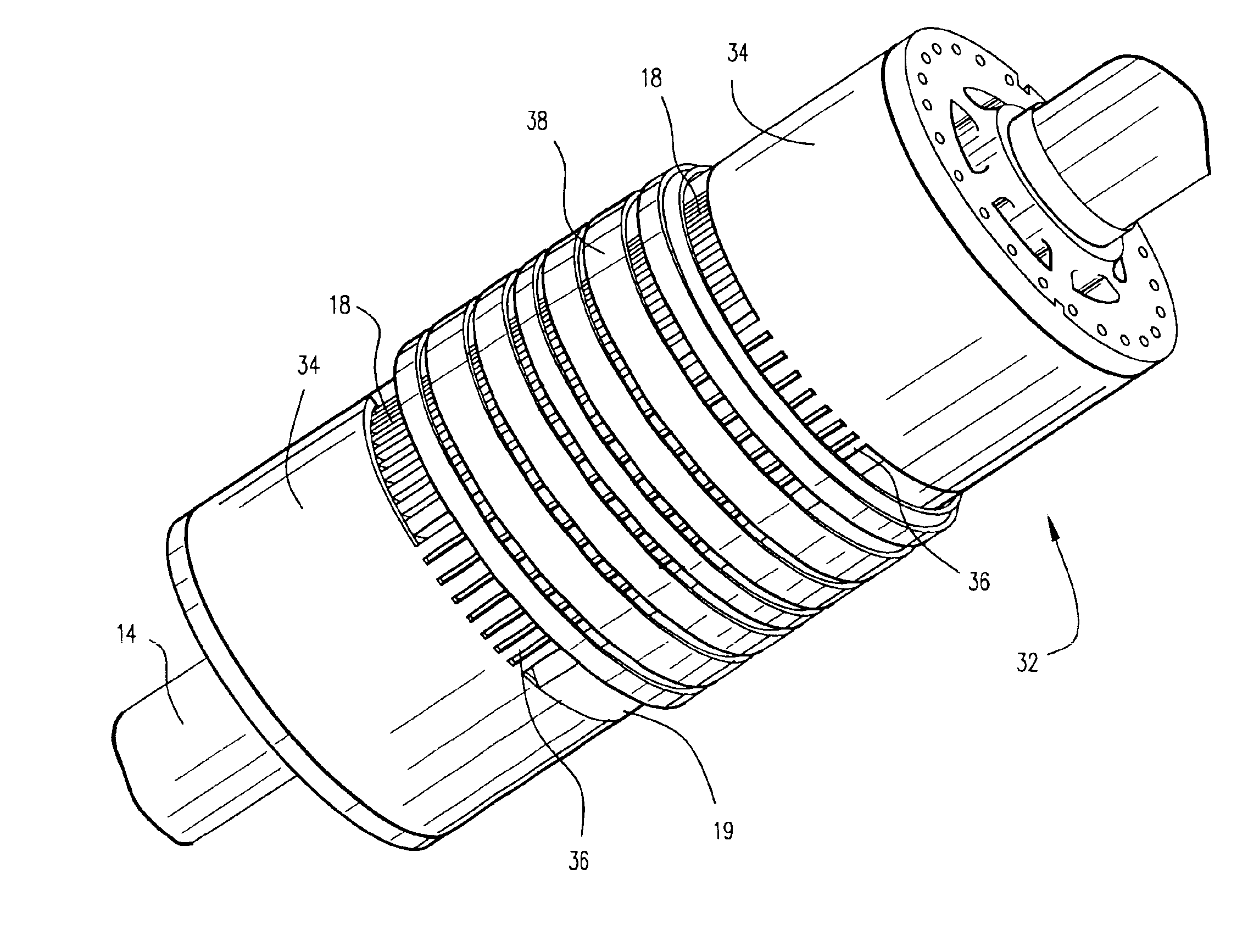
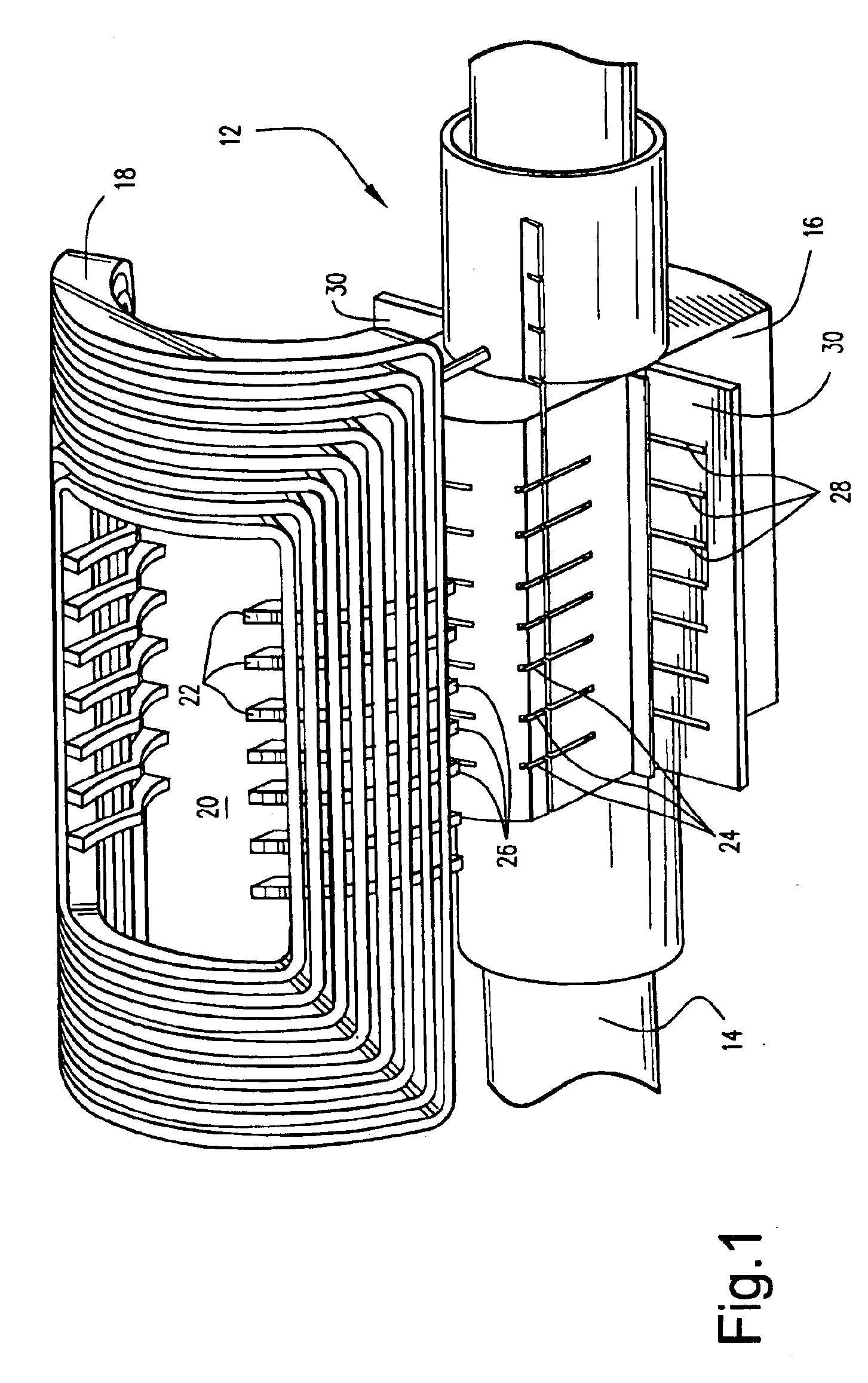
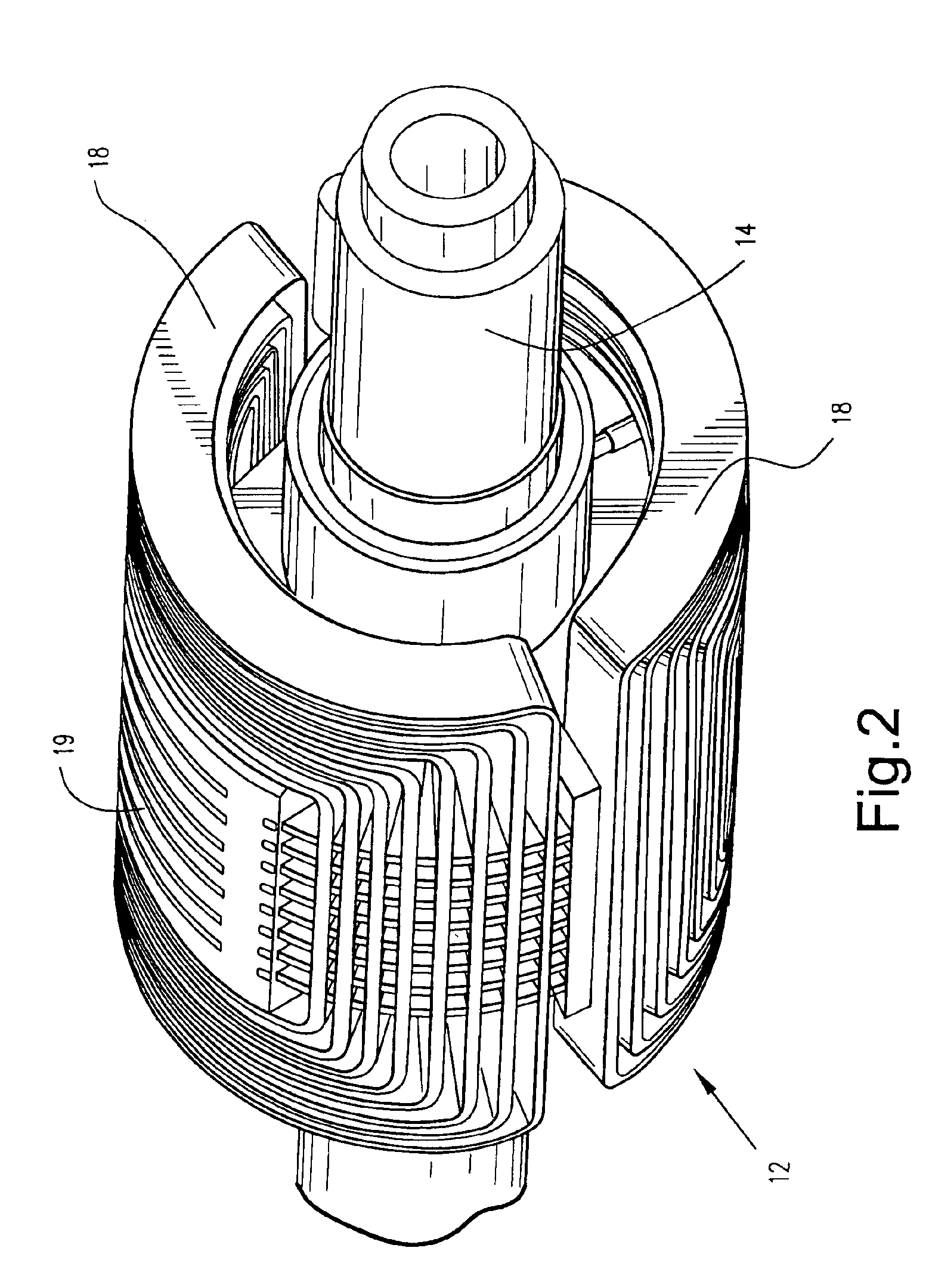
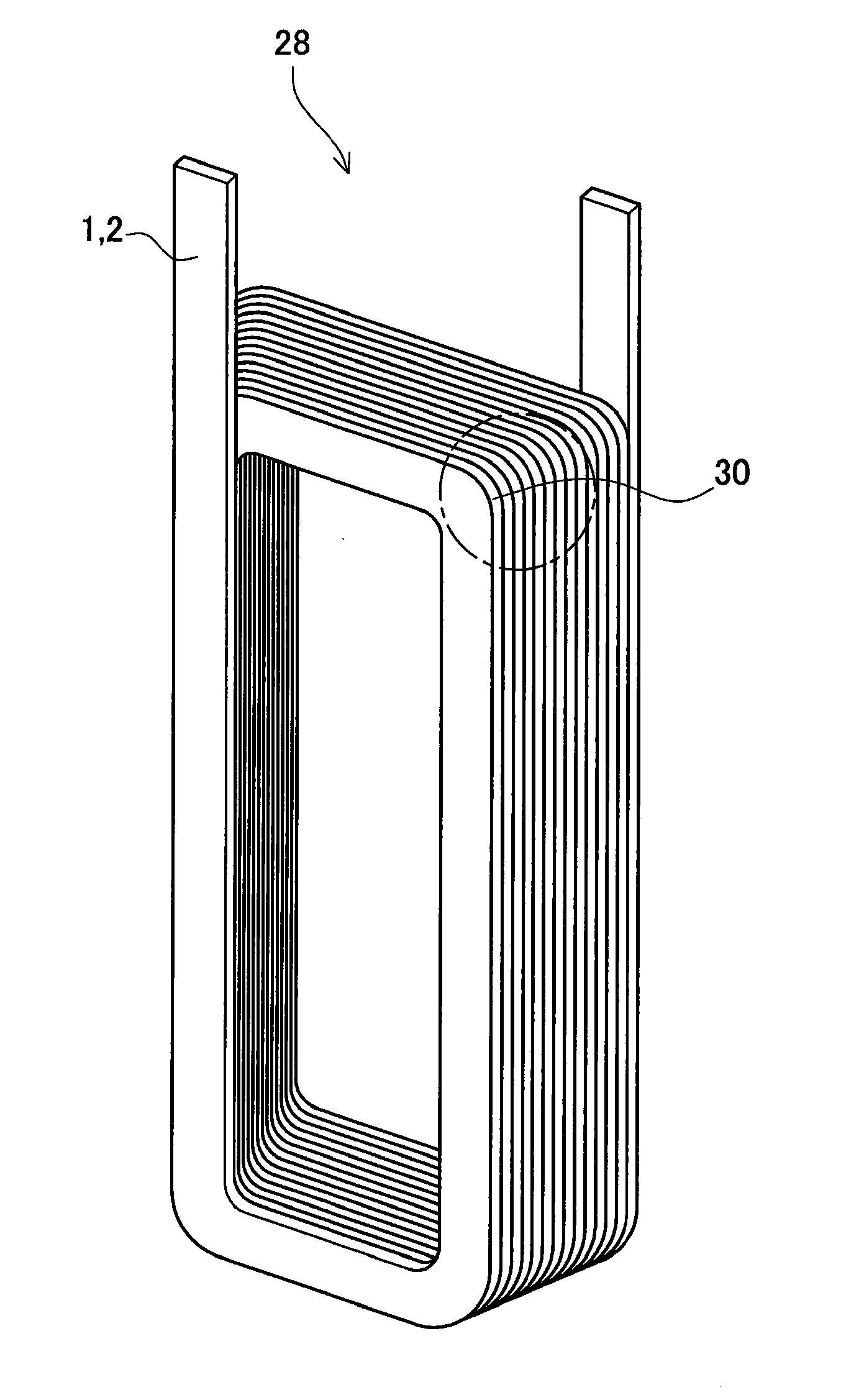
A power generator (20) includes a rotor (22), and a stator (23) surrounding the rotor and having opposing ends. The stator (23) includes a stator core (21) and a plurality of windings (28) carried by the stator core creating an undesired axial magnetic field component adjacent the opposing ends of the stator. The power generator (20) may also include at least one counteracting magnetic field generator (30) associated with at least one end of the stator (23) for generating a counteracting magnetic field for counteracting the undesired axial magnetic field component.
Owner:SIEMENS POWER GENERATION
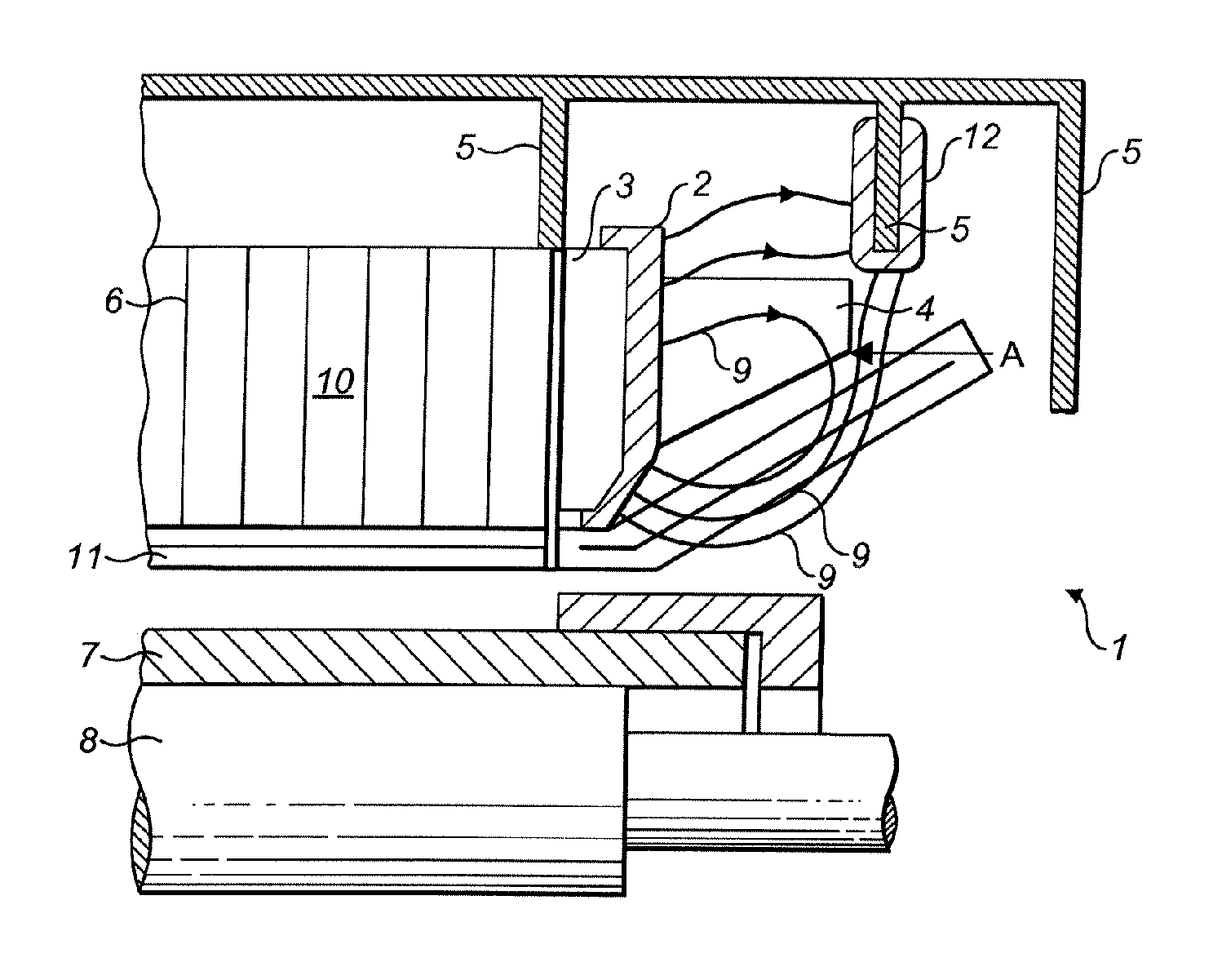
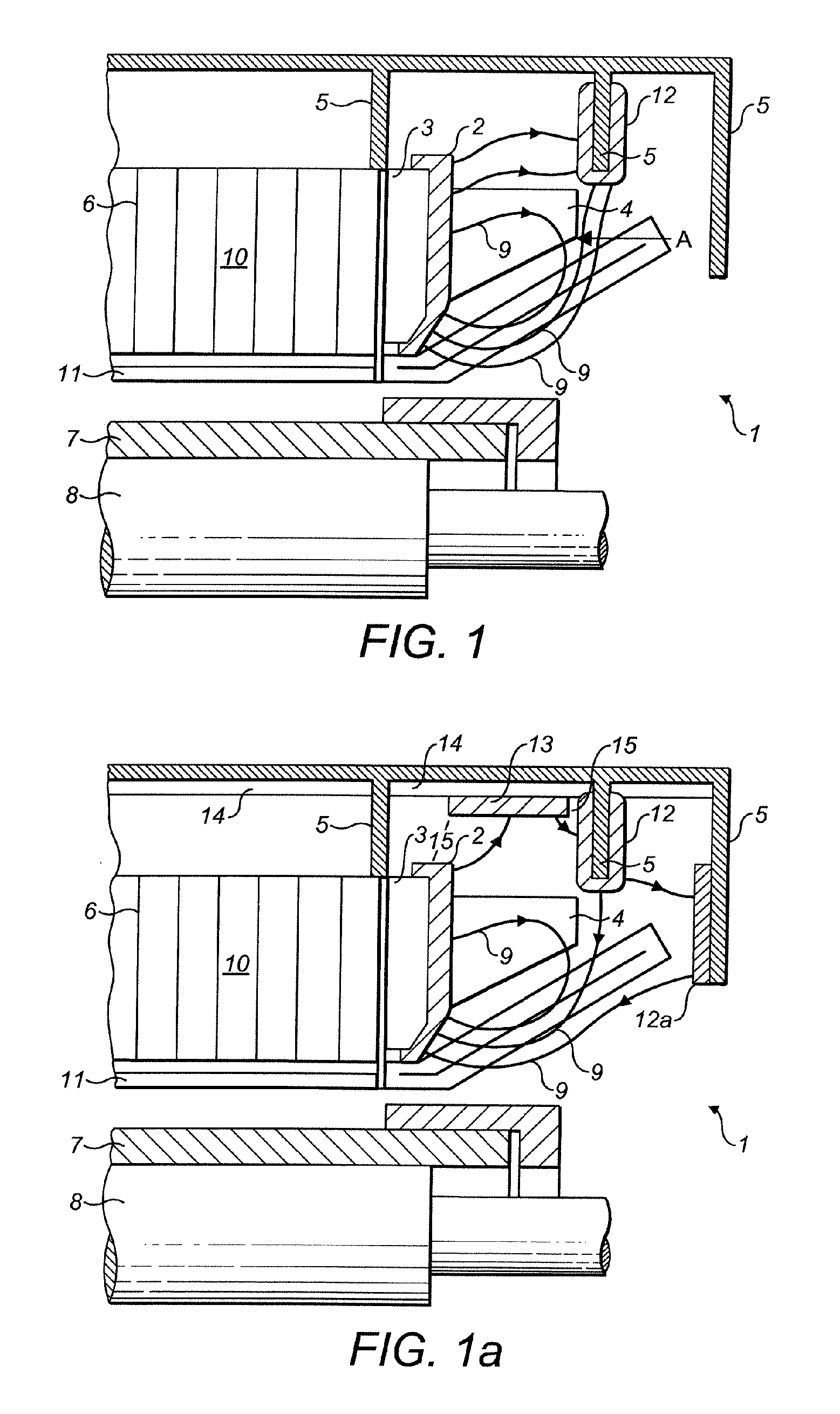
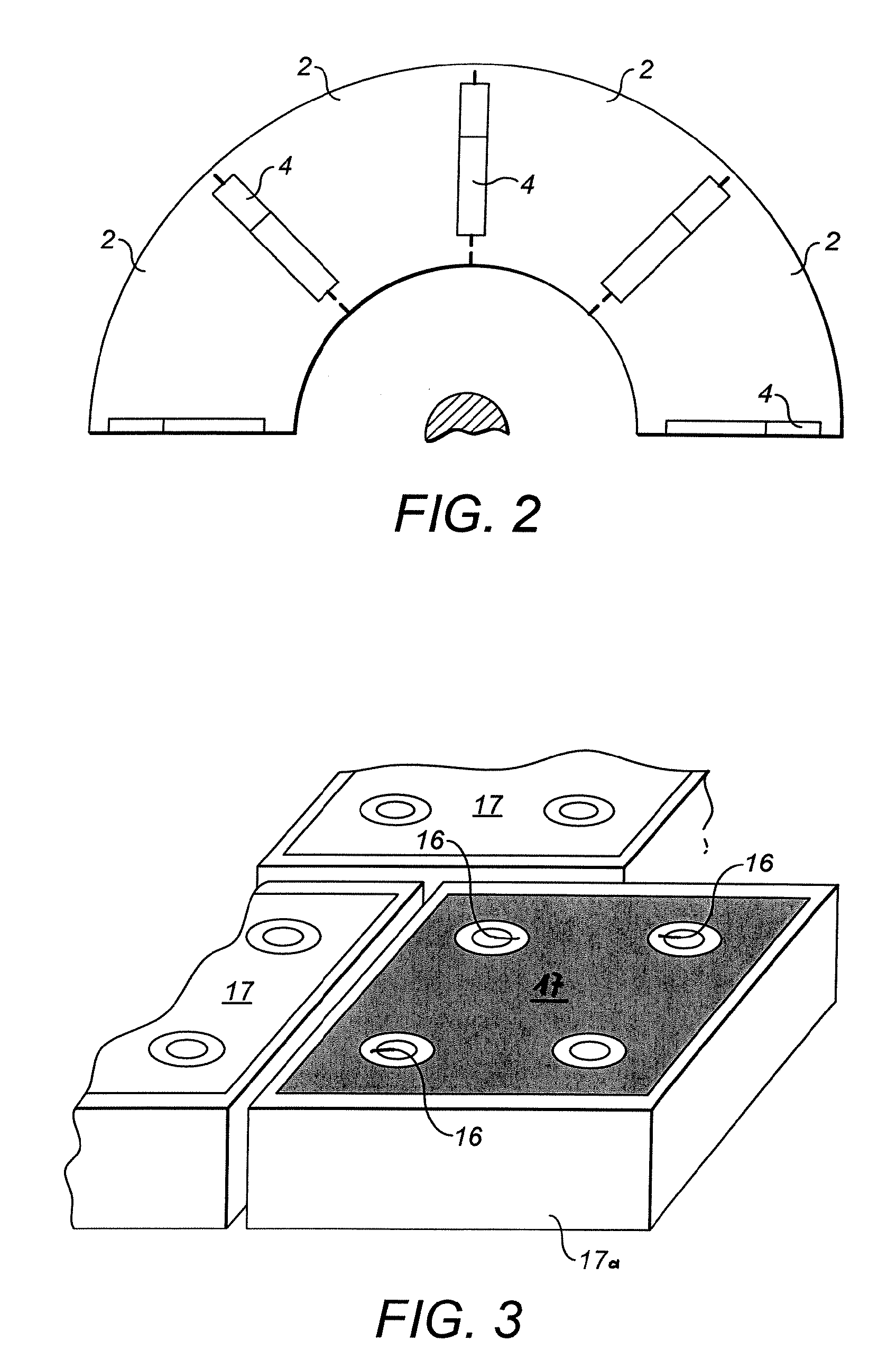
Magnetic Shield in the End Area of the Stator of a Three-Phase Generator
InactiveUS20070262658A1Reduce lossesPrevent buildupPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesEngineeringThree-phase
A shield (2) for components on the stator (10) of a three-phase generator (1), with at least one pressure plate (3) or the like being arranged at the end on the stator core (6), is distinguished in that the shield (2) is composed essentially of a magnetically permeable composite material of low electrical conductivity. A method for production of a shield such as this includes the pressing and heat-treatment of appropriate composite particles. This overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art and provides a shield for components on the stator of a three-phase generator, which reduces the additional losses and prevents a build up of heat. Furthermore, this results in a solution which can be produced and installed easily and at low cost, and which can also easily be retrofitted to existing installations. Furthermore, three-dimensional finite element design methods can be used for optimized guidance of the magnetic field.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
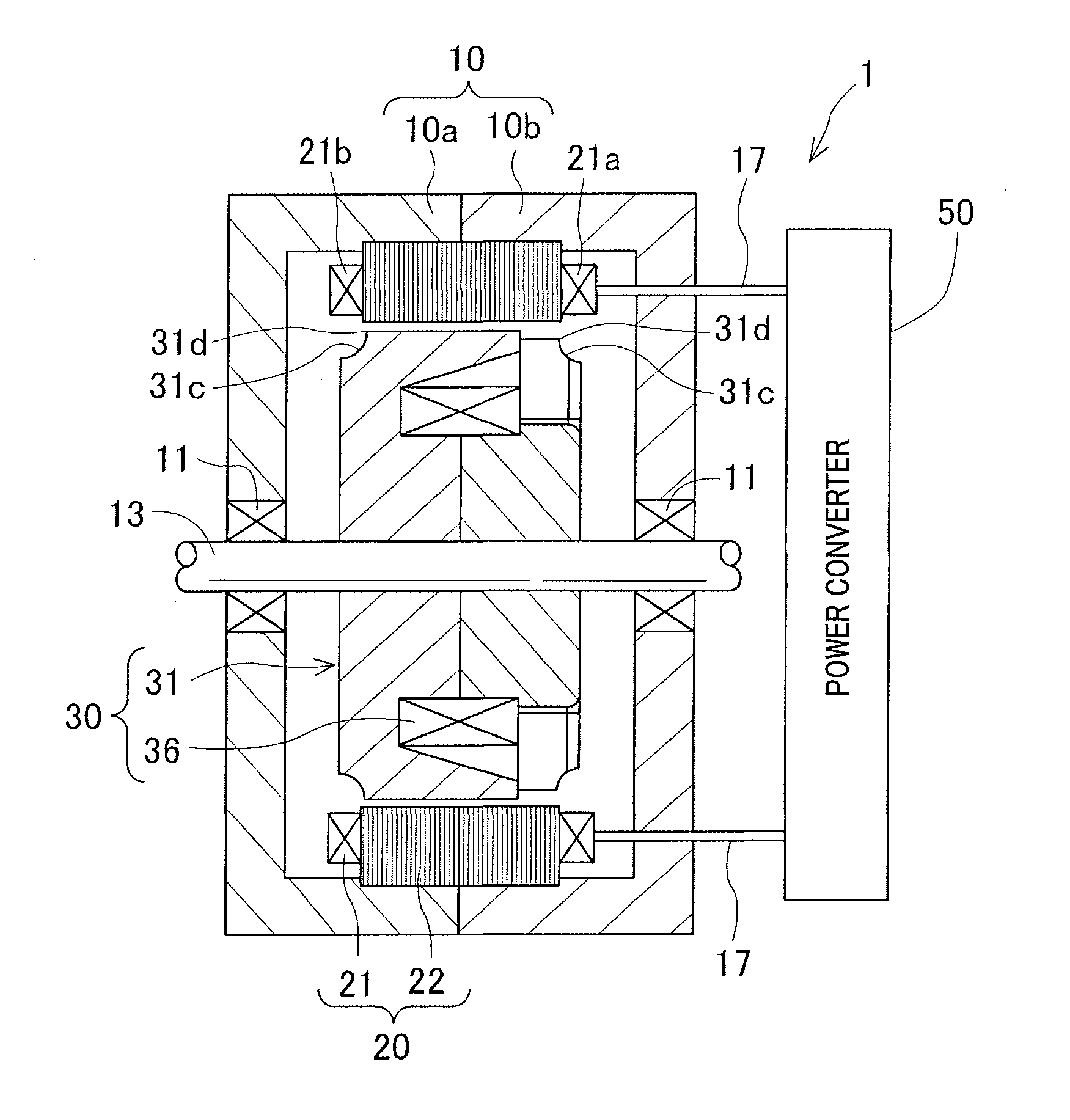
Rotating electric machine for vehicle
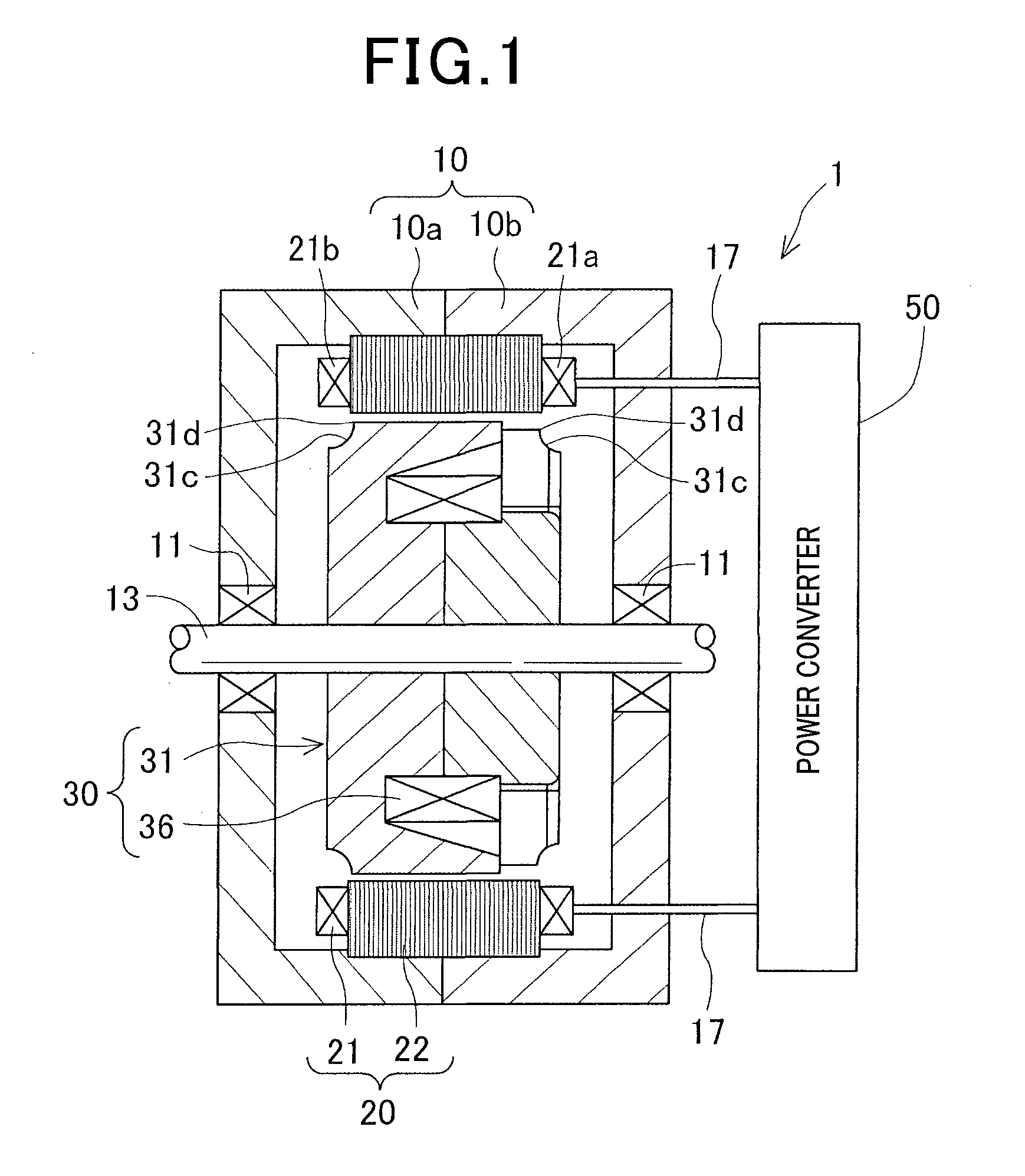
ActiveUS20160105065A1Reduce Flux LeakageReliably curtail eddy-current lossesWindings insulation shape/form/constructionPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A rotating electric machine including a stator including a stator core and a stator coil wound around the stator core, and a rotor including a rotor core arranged coaxially and radially in a face-to-face relationship with the stator core and a field coil wound around the rotor core. Both axial end portions of the rotor core project more axially outward than respective axial end faces of the stator core. The rotor core has a cutout surface between one of the axial end faces of the rotor core and an outer peripheral surface of the rotor core. A corner at which the cutout surface and the outer peripheral surface intersect is not more axially outward than either of the axial end faces of the stator core.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electrical insulation system
ActiveUS20140353000A1Windings insulation shape/form/constructionPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsVacuum pressureNanoparticle
A system and a method are presented. The system includes an electrically conducting material and an electrical insulation system. The electrical insulation system includes a layered insulation tape that has a first layer and a second layer. The first layer includes a mica paper and a binder resin in a range from about 5 wt % to about 12 wt % of the insulation tape. The second layer includes a composite of layered nanoparticles dispersed in a polyetheretherketone (PEEK) matrix. The second layer laminates the first layer. The method includes attaching the first layer and the second layer with or without the addition of further resin; using the layered insulation tape as a turn insulation and ground wall insulation for an electrically conducting material; and impregnating the system with a nanofiller-incorporated resin by a vacuum pressure impregnation method, to form an insulation system within the system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Rotating Electrical Machine
ActiveUS20070170806A1Total current dropCurrent lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsEddy currentMechanical engineering
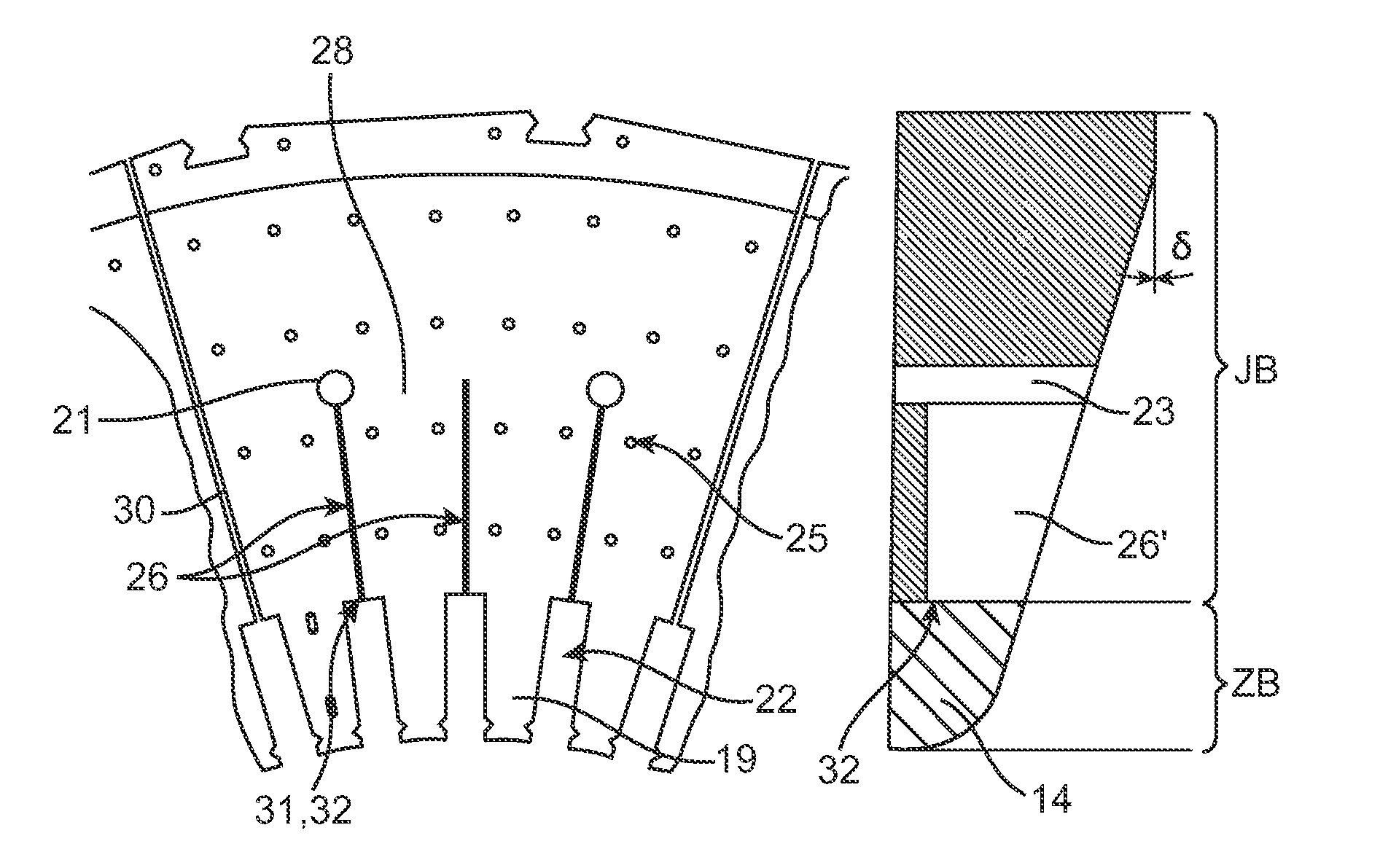
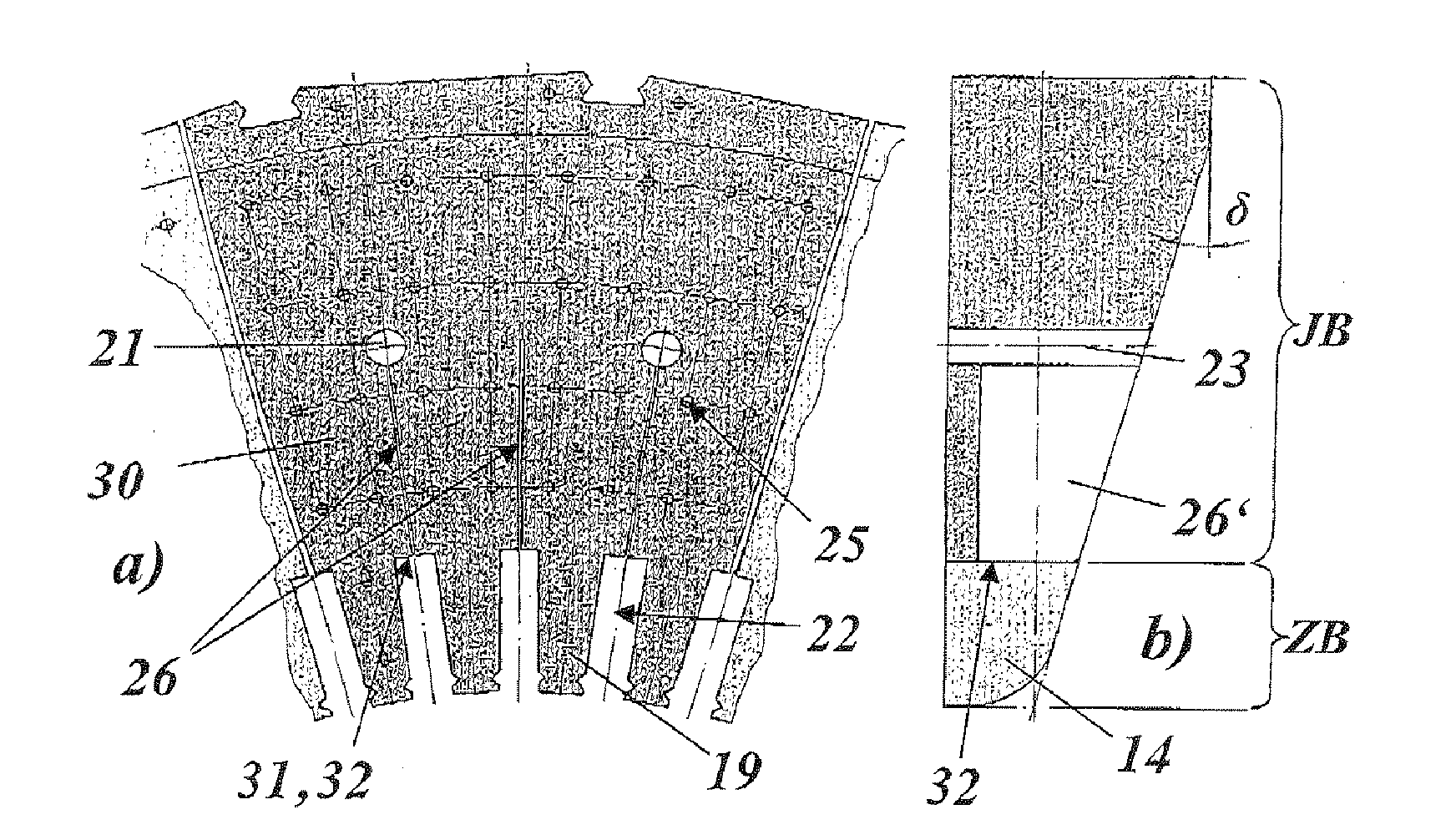
A rotating electrical machine, especially a turbogenerator, includes a rotor and a stator, which concentrically surrounds the rotor and is terminated at each of the two axial ends by a laminated press plate (14), which is constructed from a stack of individual press plate laminates (30). The electrical properties are improved by providing the press plate laminates (30) at least partially with slits (26) for reducing the eddy current losses.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Electric machine with low eddy current losses
InactiveUS6836047B1Synchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorElectric machine
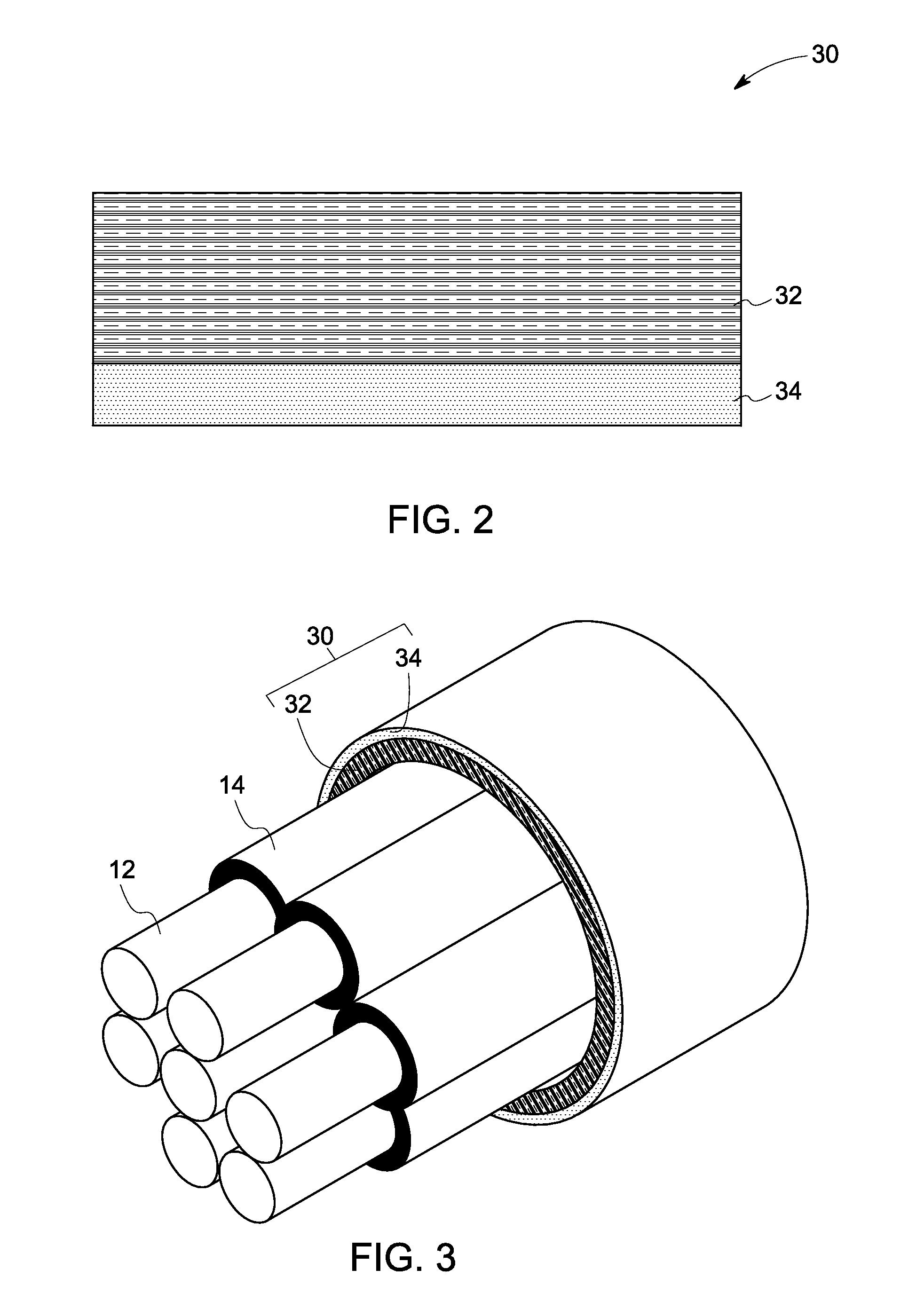
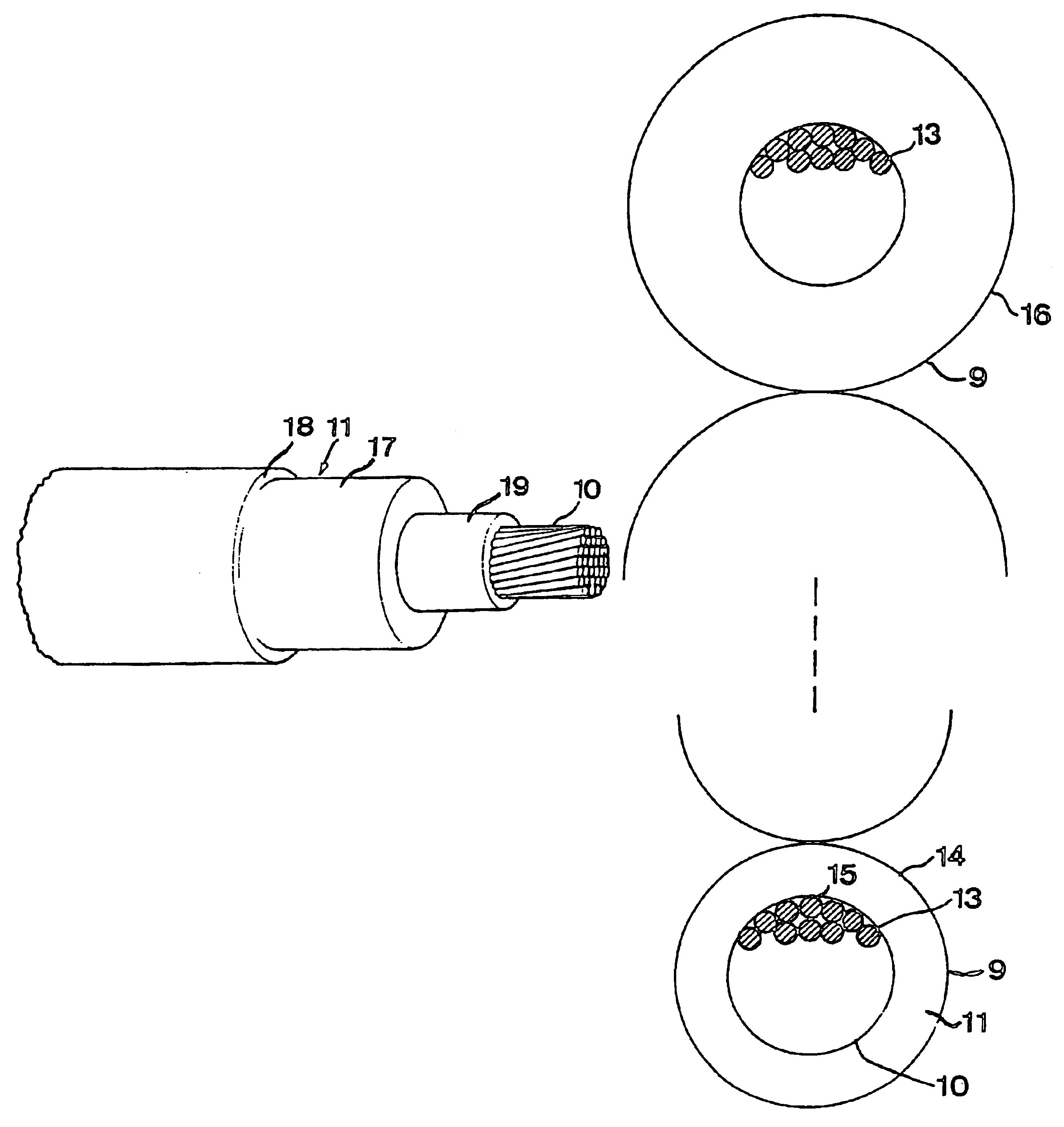
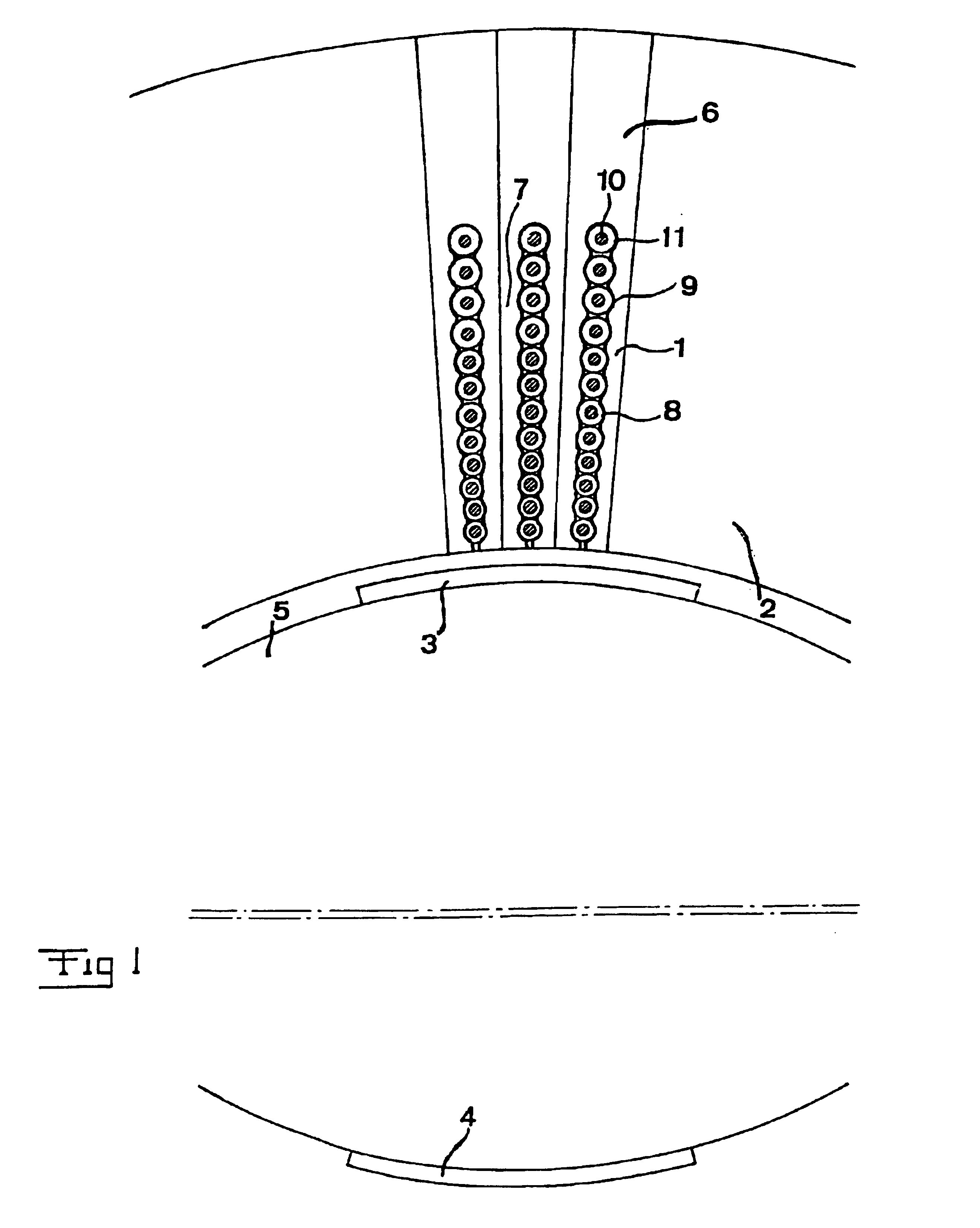
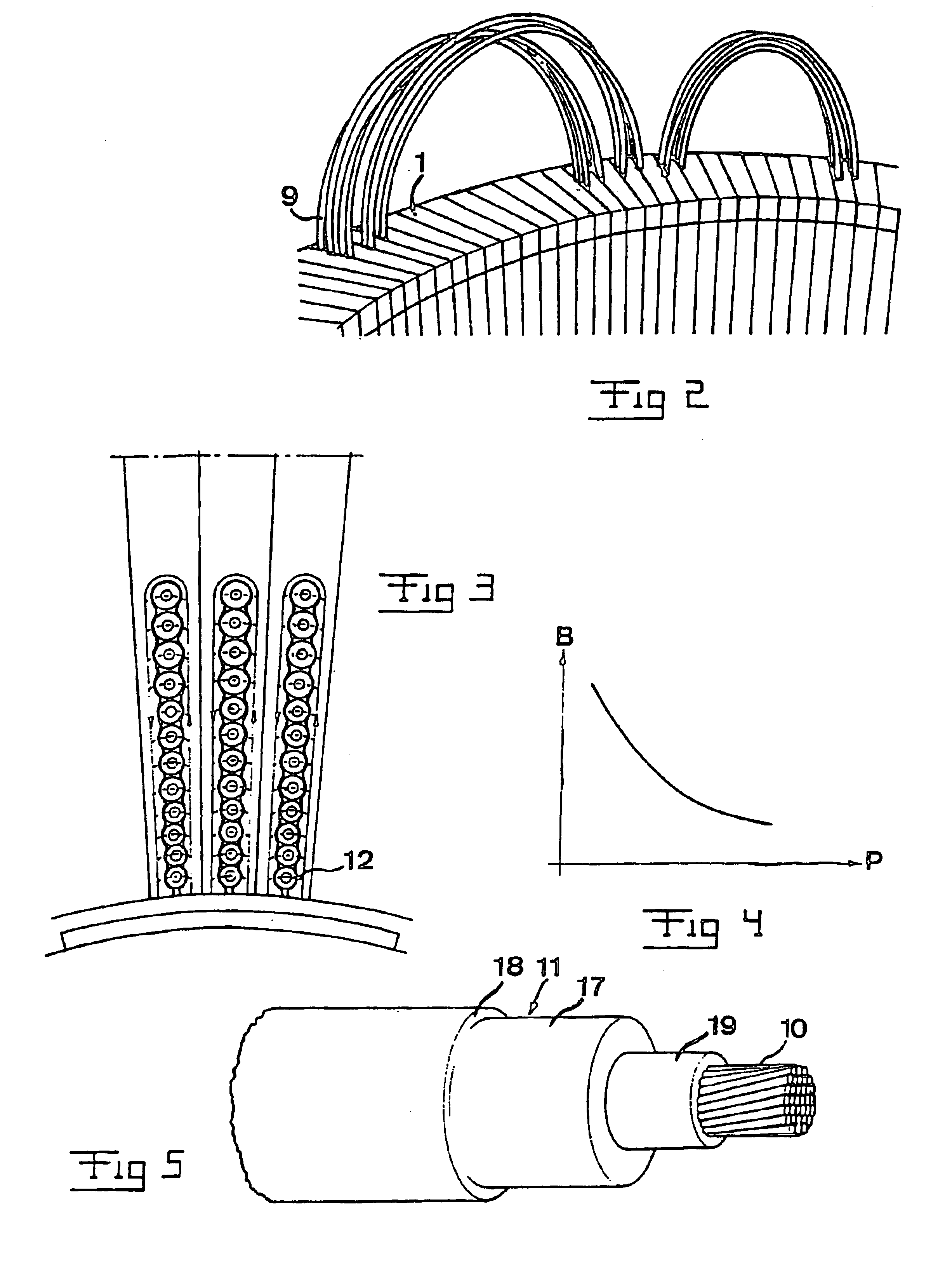
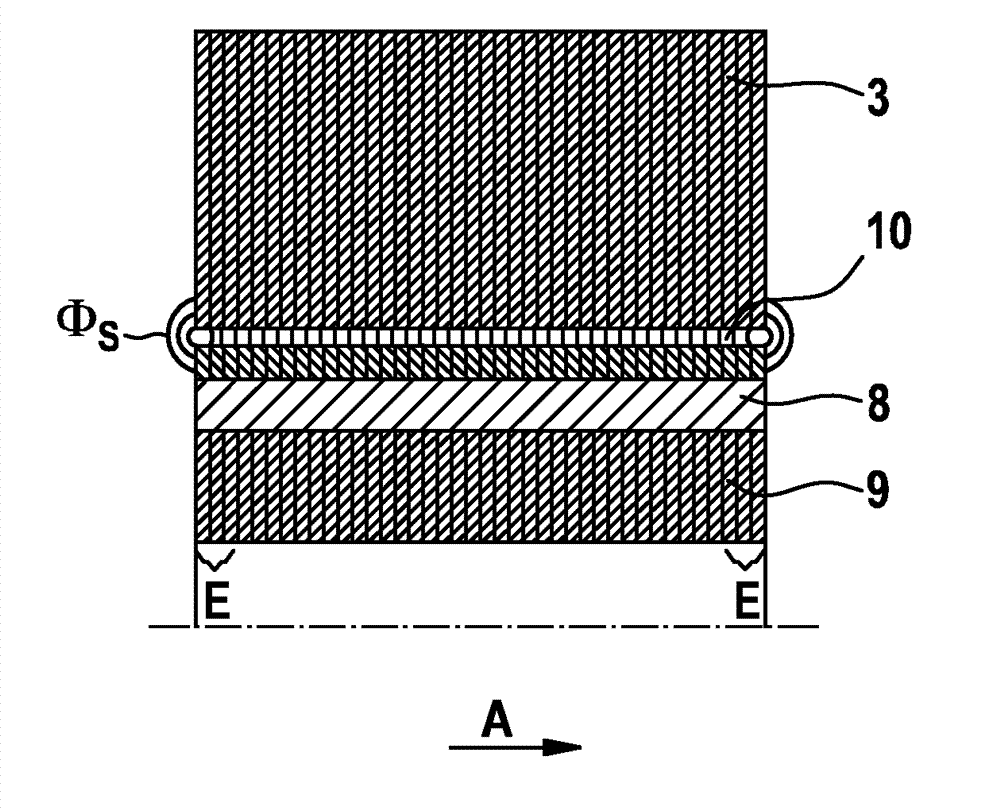
A rotating electric machine having a magnetic circuit which in one of the parts of a rotor and a stator of the machine comprises an element (1) having a slot for a winding of layers (14, 16) of cables (9) extending substantially axially and arranged substantially radially outside each other, said cables comprising an inner conductor (10) comprising a plurality of strands (13) and an insulation (11) arranged outside thereof, has a larger share of strands of the cables closest to the other part of the rotor and the stator electrically insulated (15) with respect to each other than in the cables in the cable layer (16) most far away from said other part.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
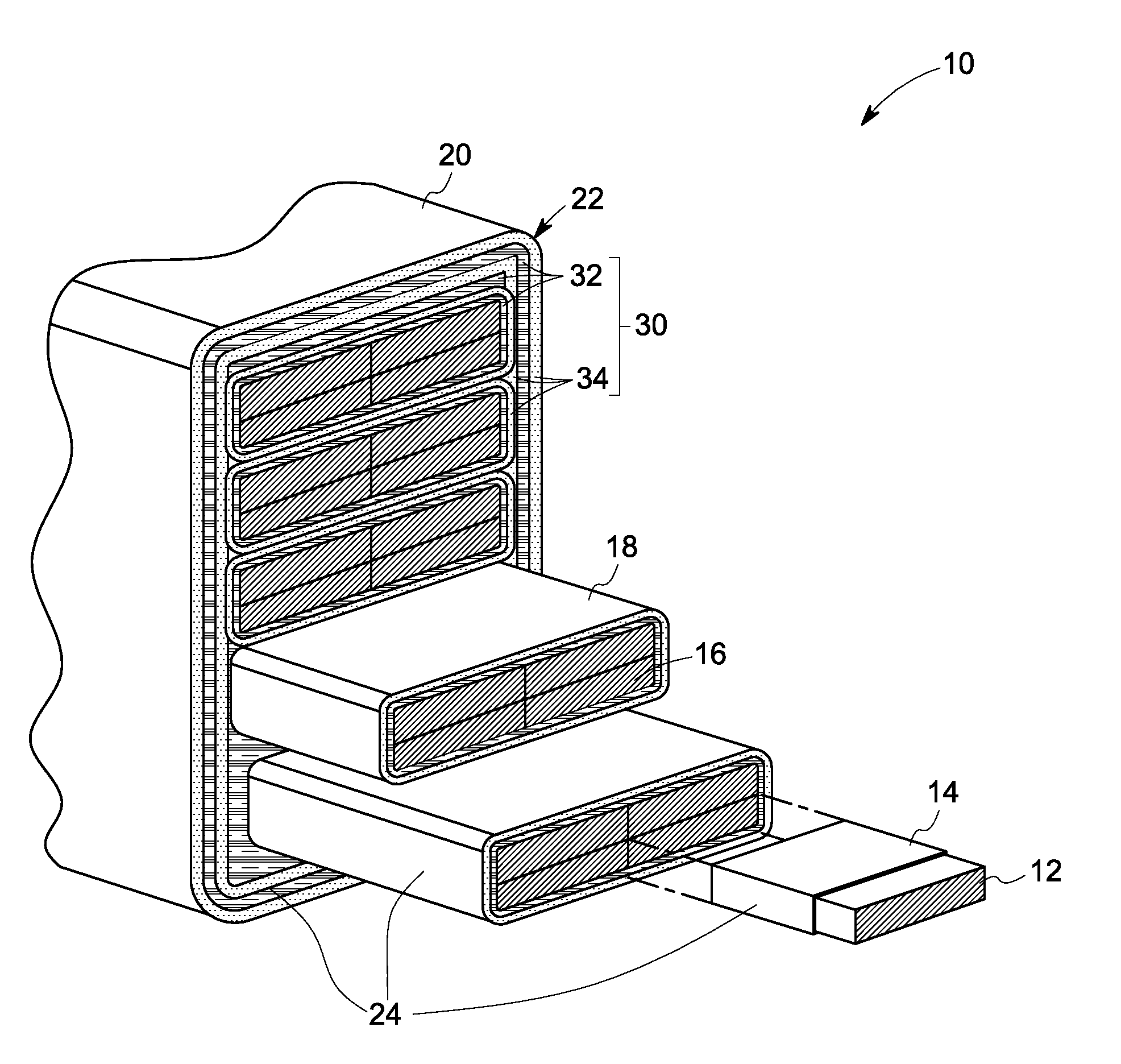
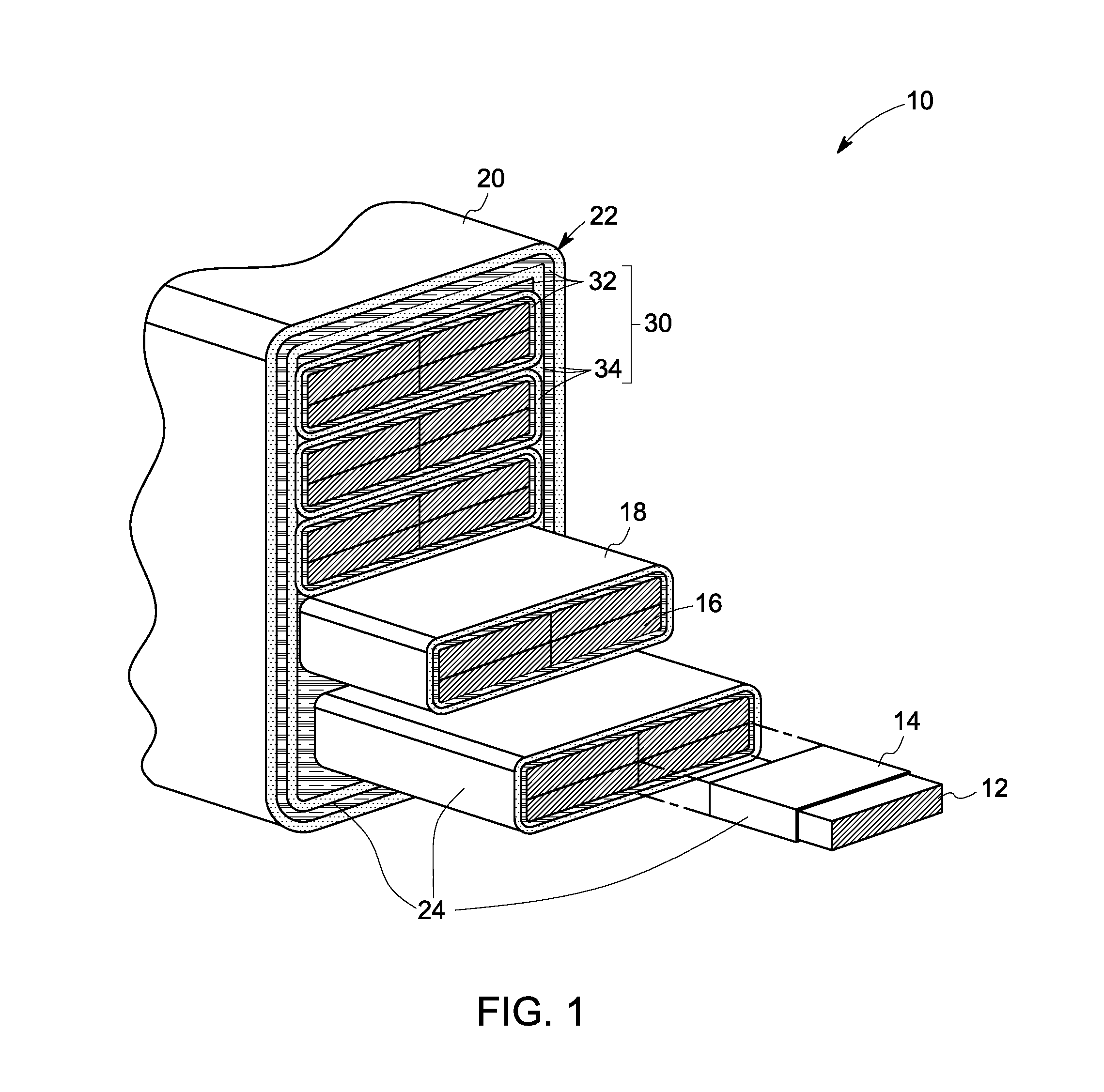
Encapsulated stator assembly
InactiveUS20120112571A1Prevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsStructural associationCopperConductor Coil
The present invention provides an encapsulated stator assembly comprising: (a) a stator having a stator core and a stator end region; and (b) a ceramic bore tube defining a surface of the stator core; wherein the stator end region is disposed adjacent to the stator core, and wherein the stator end region comprises a plurality of stator armature end-windings, and wherein the stator end region comprises an inwardly-facing stator wall, and wherein the ceramic bore tube and the inwardly-facing stator wall define an interior volume configured to accommodate a rotor, said inwardly-facing stator wall having an inner surface and an outer surface, at least a portion of said inner surface comprising a barrier layer of a conductive metal selected from the group consisting of copper, silver and aluminum, said inwardly-facing stator wall comprising a corrosion resistant metal. Also provided are motors comprising the novel encapsulated stator assemblies.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
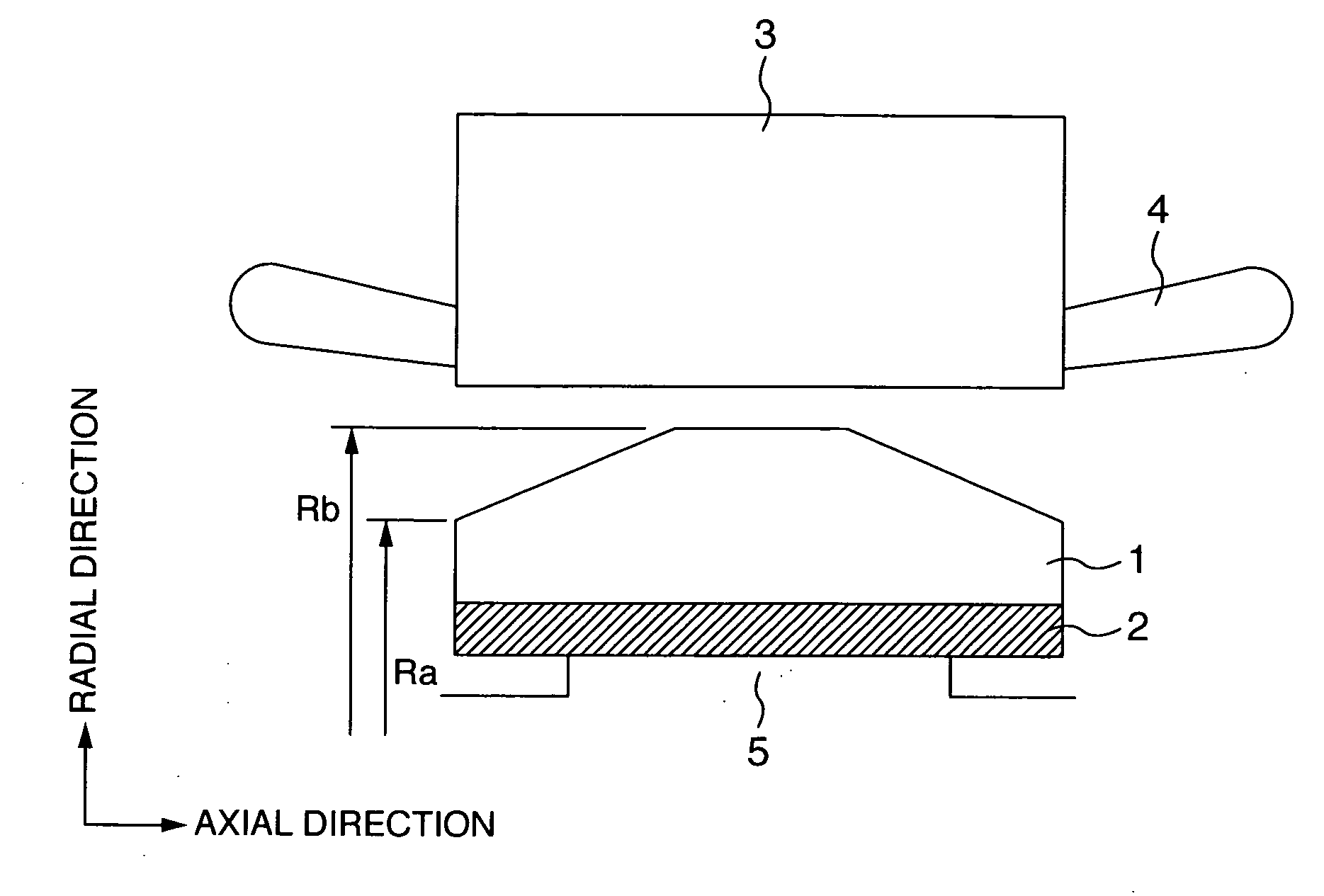
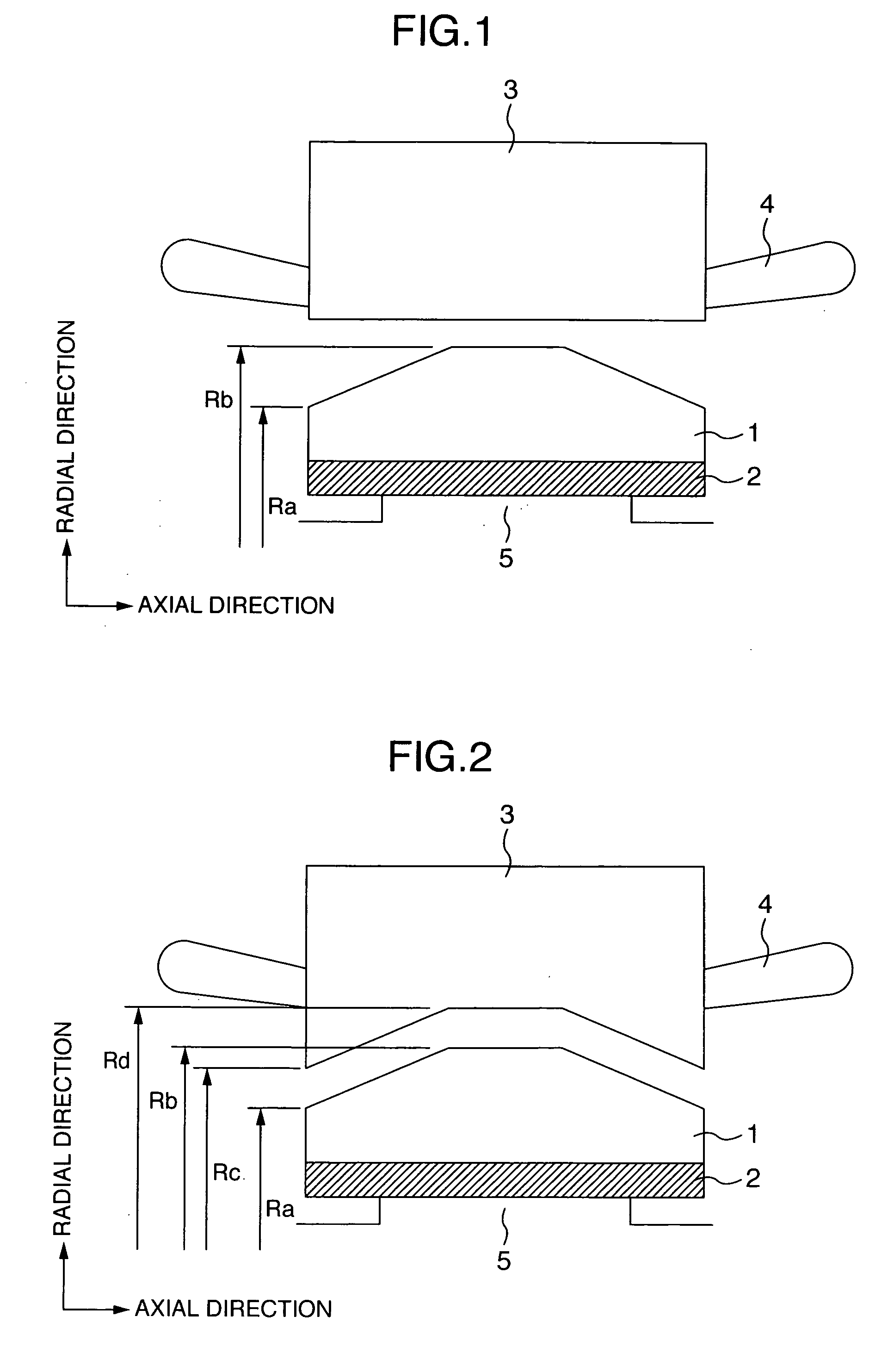
Rotating machine
ActiveUS20070145848A1Avoid displacementPrevent peelingPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringMagnet
A rotation machine is configured such that permanent magnets and pole shoes holding the permanent magnets at the outer diameter side of the permanent magnets are provided for a rotor, and an outer diameter size (Ra) in the axial end portion of the pole shoe is made smaller than an outer diameter size (Rb) in the axial center portion.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Motor core
InactiveUS20200153321A1Prevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
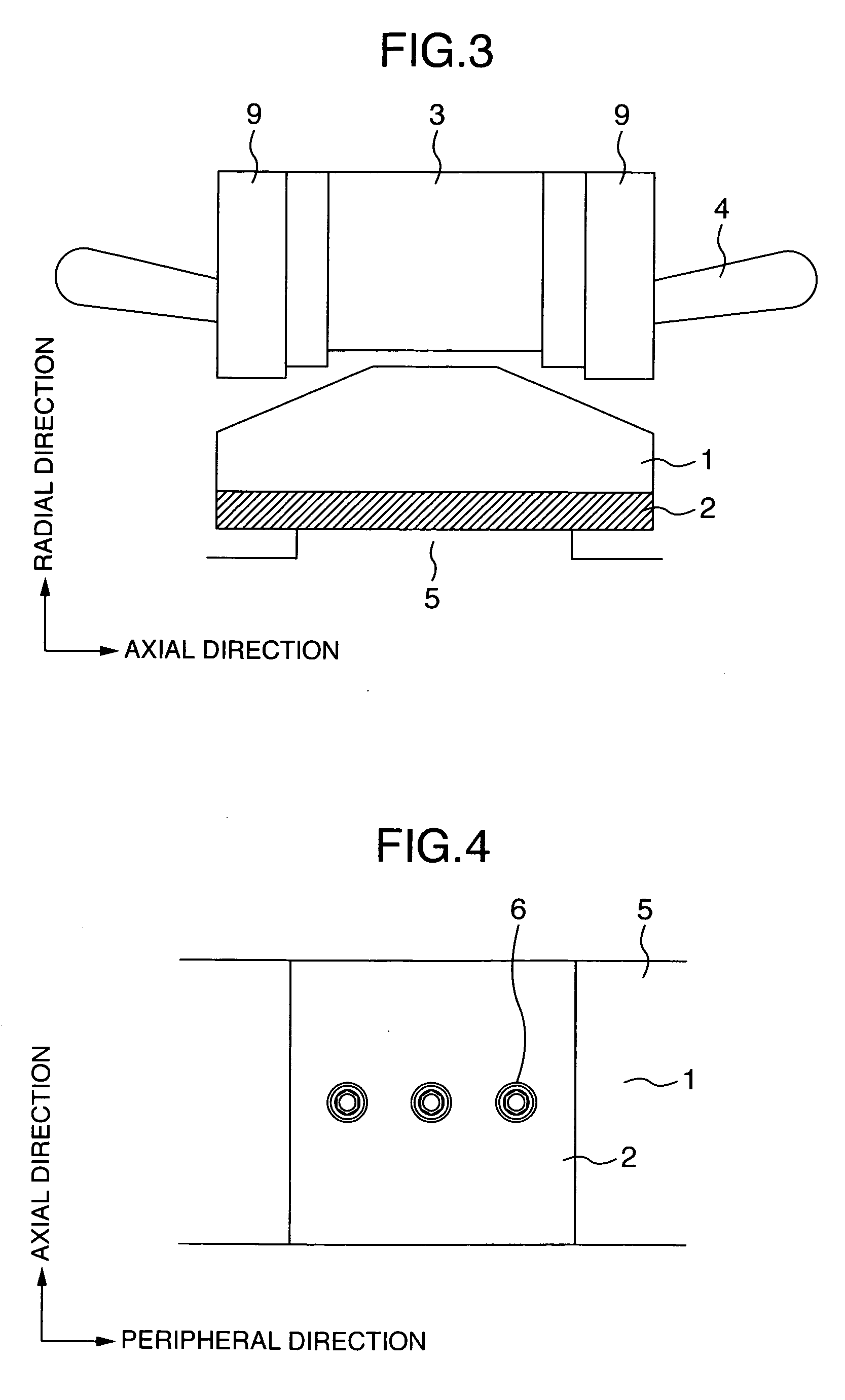
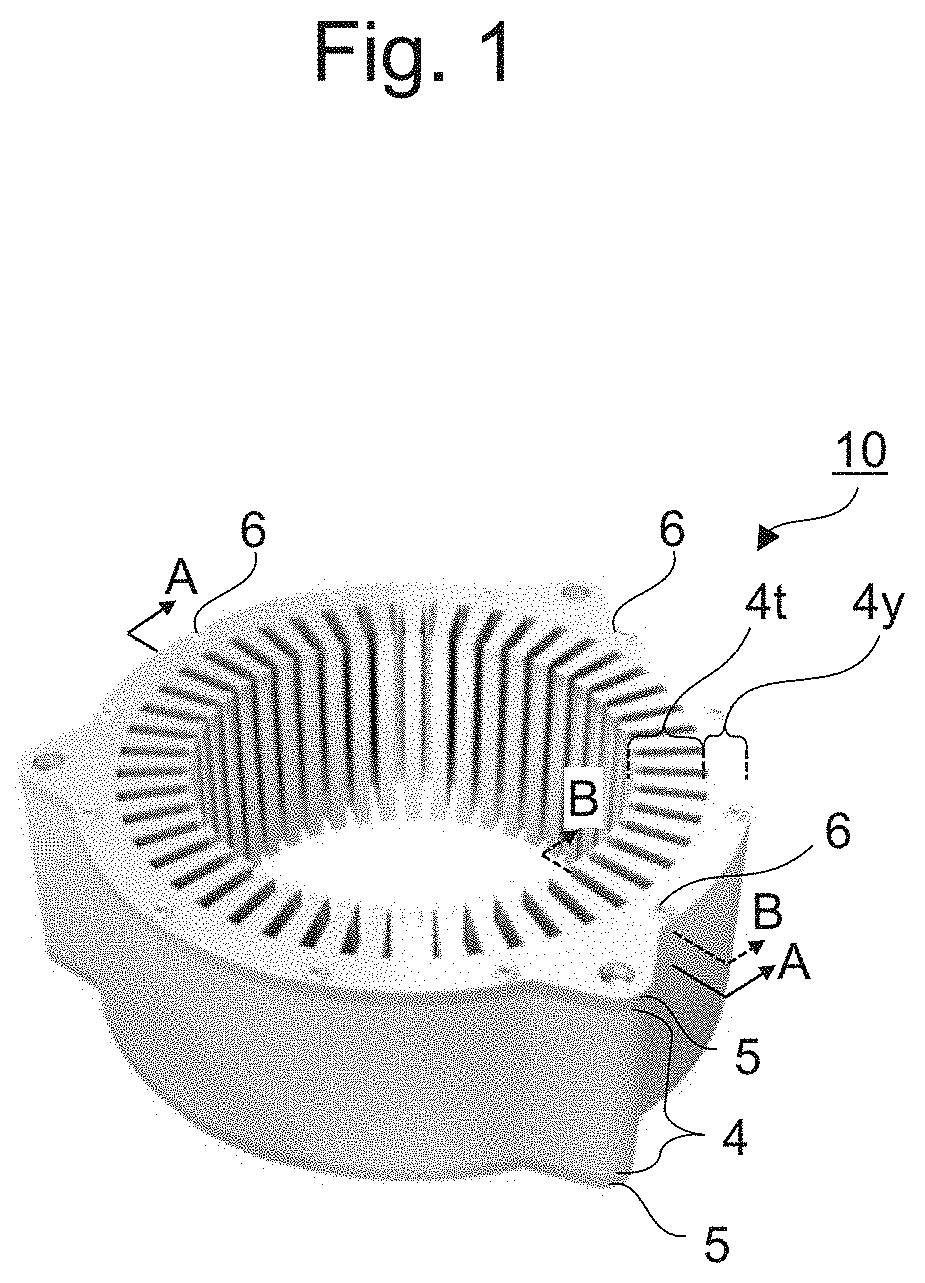
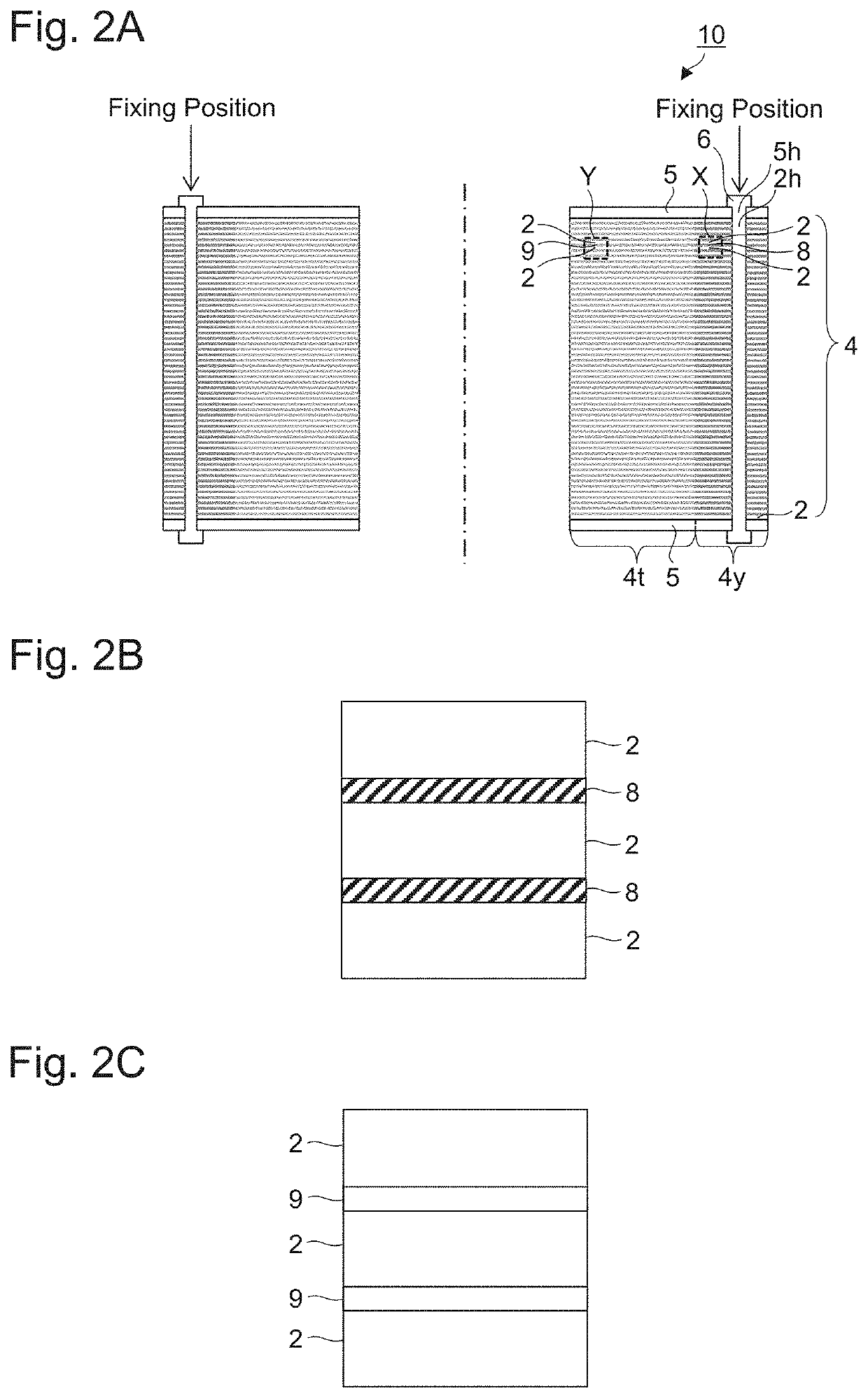
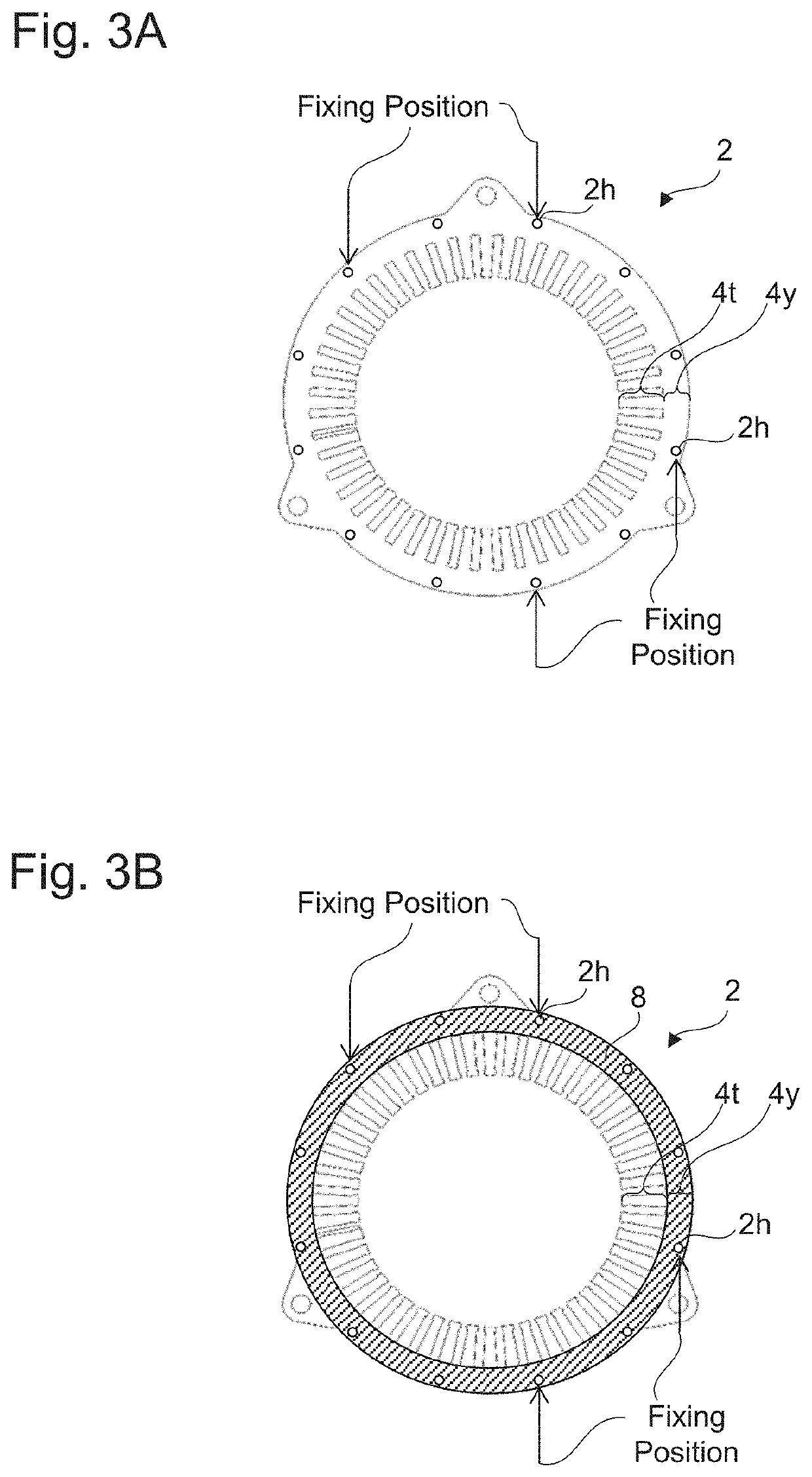
A motor core that ensures reduction of eddy-current loss and improvement of a space factor at the same time is provided. The motor core according to the present disclosure includes a laminated body where a plurality of metal plates are laminated; a fixing member that fixes the plurality of metal plates to each other at a fixing position in a peripheral edge side of the laminated body; and an insulation film disposed between the metal plates in a peripheral edge portion of the laminated body including the fixing position. In a center portion of the laminated body, no insulation film is disposed between the metal plates, or an insulation film thinner than the insulation film in the peripheral edge portion is disposed between the metal plates.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Dynamoelectric device and method of forming the same
InactiveUS8736127B2Synchronous generatorsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsLitz wireConductor Coil
A dynamoelectric device comprises a plurality of armatures arranged circumferentially about an axis, sets of electrically conductive winding members that extend axially through the stack of laminates and are positioned circumferentially between each adjacent pair of the armatures, and first and second layers of end-turn members. Each of the end-turn members of the first axial layer is connected to one of the winding members. Each of the end-turn members of the first axial layer extends clockwise circumferentially from its respective one of the winding members. Each of the end-turn members of the second axial layer is connected to one of the winding members and to each of the end-turn members of the first axial layer of end-turn members. Each of the end-turn members of the second axial layer extends counter-clockwise circumferentially from its respective one of the winding members. The winding members are each formed of Litz wire.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF THE ALICE ANHEUSER BEIMS MOORE IRREVOCABLE TRUST 1 & THE ALICE ANHEUSER BEIMS MOORE IRREVOCALBE TRUST 2 FBO GRANDCHILDREN
Magnetic Shield for Stator Core End Structures of Electric Rotating Machine
InactiveUS20110241455A1Reduce lossesLosses that occur in the clamping plates and their shield can be reducedPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEngineeringMagnetic shield
In an electric rotating machine, for reducing losses that occur in clamping plates and their shield, the electric rotating machine includes a rotor formed with field winding wound around a rotor core, a stator placed opposite to the rotor at a predetermined space and formed with stator winding wound around a stator core formed by stacking multiple magnetic steel sheets in the axial direction, clamping plates clamping and retaining the stator core from both axial end parts thereof in the stacking direction of the magnetic steel sheets, and a magnetic shield placed around the clamping plates to shield flux leakage flowing into the clamping plates, and the magnetic shield is formed of a cylinder of stacked steel sheets stacked in a form of a cylinder about the rotor shaft and powder magnetic core segments and powder magnetic core segments having portions which are stuck to the cylinder of stacked steel sheets on the stacking cross section, and arranged to cover side surfaces and an inner surface of radial direction of the clamping plates.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
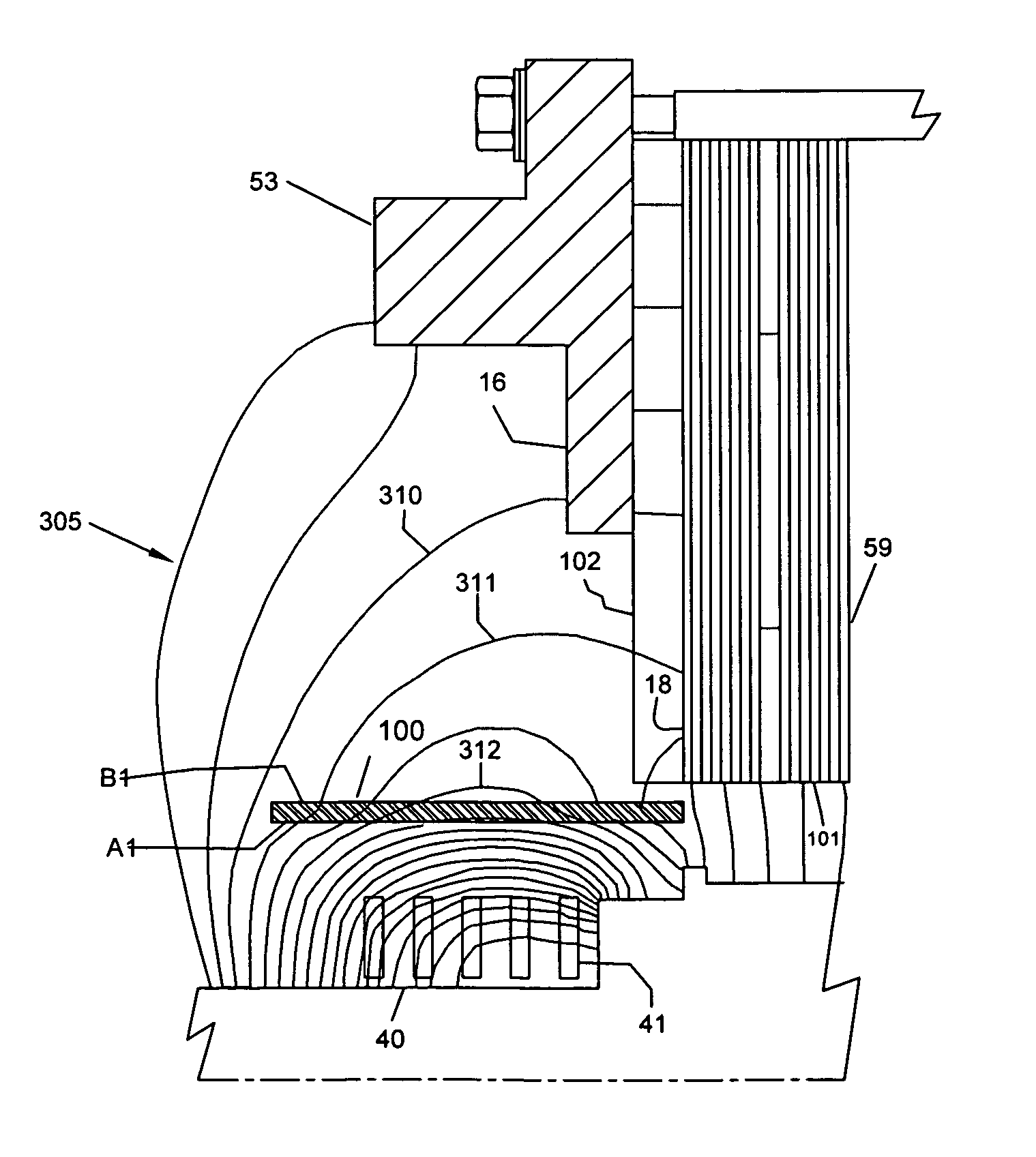
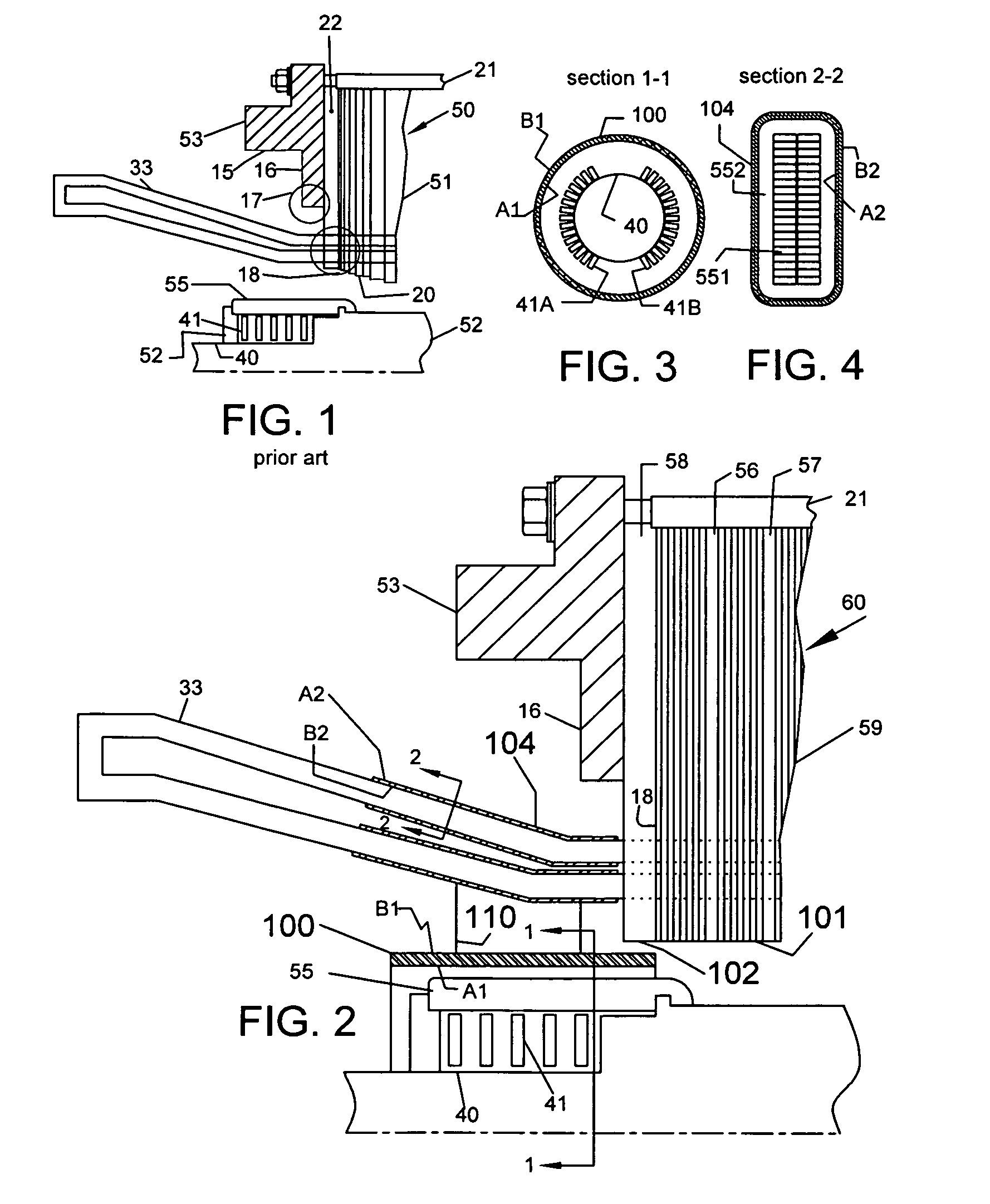
Reducing the core-end heating in large power generators
InactiveUS8203249B1Relieve overheatingLow costPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsMagnetic circuit stationary partsEddy currentConductor Coil
The invention provides for flux-shields wrapped around the flux-sources at the core-end of large power generators. They prevent overheating of all core-end parts under all abnormal conditions of operation. A first flux-shield is an electrically conductive cylindrical shell concentric with rotating end-windings, held outside the retaining ring. The rotating flux source induces eddy currents in the first flux-shield whose flux repels the source flux. Only a small part of the rotating source flux is hence received by all the core-end parts, thereby greatly reducing their temperatures. A second flux-shield comprises an electrically conductive tape wrapped over the ground-insulation of stator bars protruding from the core. Alternating flux generated by the stator bars induces eddy currents in the second flux-shield whose flux repels the source flux. Only a small fraction of the source flux is hence received by all core-end parts, thereby greatly reducing their temperatures. The present invention replaces multiple devices such as step-iron, flux-shields, flux shunts, short-rotors etc, used in the prior-art with only two devices. As a result, the design of the core-end is simplified and the cost of the generator is reduced.
Owner:RAO DANTAM K
Synchronous reluctance motor and underwater pump
InactiveCN104285360AEliminate air gapsEliminate power lossMagnetic circuit rotating partsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsSynchronous reluctance motorUnderwater
The present invention relates to a synchronous reluctance motor for an underwater pump having a stator and a rotor which comprises a fluid barrier section for forming one or more magnetic pole pairs, wherein the airgap between the rotor (12) and the stator (11) is at least partially filled with a ferrofluid (20). A further partial aspect of the invention relates to an underwater pump with such a synchronous reluctance motor for driving the pump.
Owner:KSB AG
Conductive wire for motor, and coil for motor
InactiveCN102668335AIncreased durabilityConductive layers on insulating-supportsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Encapsulated stator assembly
InactiveCN102570639APrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsMagnetic circuit stationary partsCopperConductor Coil
The present invention provides an encapsulated stator assembly comprising: (a) a stator having a stator core and a stator end region; and (b) a ceramic bore tube defining a surface of the stator core; wherein the stator end region is disposed adjacent to the stator core, and wherein the stator end region comprises a plurality of stator armature end-windings, and wherein the stator end region comprises an inwardly-facing stator wall, and wherein the ceramic bore tube and the inwardly-facing stator wall define an interior volume configured to accommodate a rotor, said inwardly-facing stator wall having an inner surface and an outer surface, at least a portion of said inner surface comprising a barrier layer of a conductive metal selected from the group consisting of copper, silver and aluminum, said inwardly-facing stator wall comprising a corrosion resistant metal. Also provided are motors comprising the novel encapsulated stator assemblies.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Stator end electric shielding structure of synchronous generator
InactiveCN103545963AImprove reliabilityReduce Flux LeakagePrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsElectricityStator coil
The invention discloses a stator end electric shielding structure of a synchronous generator. The stator end electric shielding structure of the synchronous generator comprises an outer shielding ring, a cushion block, a stator coil, an inner shielding ring, a stator pressing ring and a stator tooth support. The stator pressing ring compresses the stator tooth support and is fixed on the end portion of a stator core through bolts, the inner shielding ring is fixed on the stator pressing ring through bolts, and the outer shielding ring is fixed with the inner shielding ring through bolts and the cushion block. The end portion of the stator coil is placed among the inner shielding ring, the outer shielding ring and the stator tooth support. The inner shielding ring, the outer shielding ring and the stator tooth support are made of nonmagnetic material copper. The stator end electric shielding structure of the synchronous generator is simple in structure and high in reliability, magnetic leakage on the end portion of the stator coil is reduced, heating of the stator pressing ring and heating of a rotor retaining ring are reduced, and the operation reliability of the synchronous generator is improved.
Owner:SEC ELECTRIC MACHINERY
AC asynchronous motor with circumferential windings
PendingCN106411082AEliminate magnetic flux leakageIncrease powerPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsAsynchronous induction motorsBusbarMagnetic poles
An AC asynchronous motor with circumferential windings includes three phases of stator magnetic cores (145, 146 and 147), three phases of circumferential windings (167, 168 and 169), an a asynchronous motor rotor and accessories including a casing and a bearing. the three phases of stator magnetic cores are arranged axially phase by phase, and each phase of stator magnetic core comprises a cylindrical magnetic core, stator magnetic poles arranged in parallel with the axial direction of the cylindrical wall and magnetic circuit connectors; the magnetic poles form a circumferential range, a gap exists between the adjacent magnetic poles, one end of the magnetic pole and one end of the adjacent magnetic pole are connected to the two ends of the cylinder via the magnetic circuit connectors respectively, and the circumferential winding is embedded into an annular space between the magnetic poles and the inner cylindrical wall; and three phases of rotor magnetic cores are aligned and connected in series along the axial direction, busbars in the three phases of rotor slotways share short-circuit rings at the two ends, under the three-phase AC of the three-phase circumferential windings, induction currents of the busbars of the rotors bear a force in a mixed manner, self-startup operation is realized, and loss and end-portion loss of traditional windings are avoided. Thus, the AC asynchronous motor has the advantages including little magnetic flux leakage, simple structure, reduced copper material, less heating, high efficiency and reliability and energy-saving performance.
Owner:杨明
Stator
ActiveCN102857004AWindings insulation shape/form/constructionPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsElectric machineEngineering
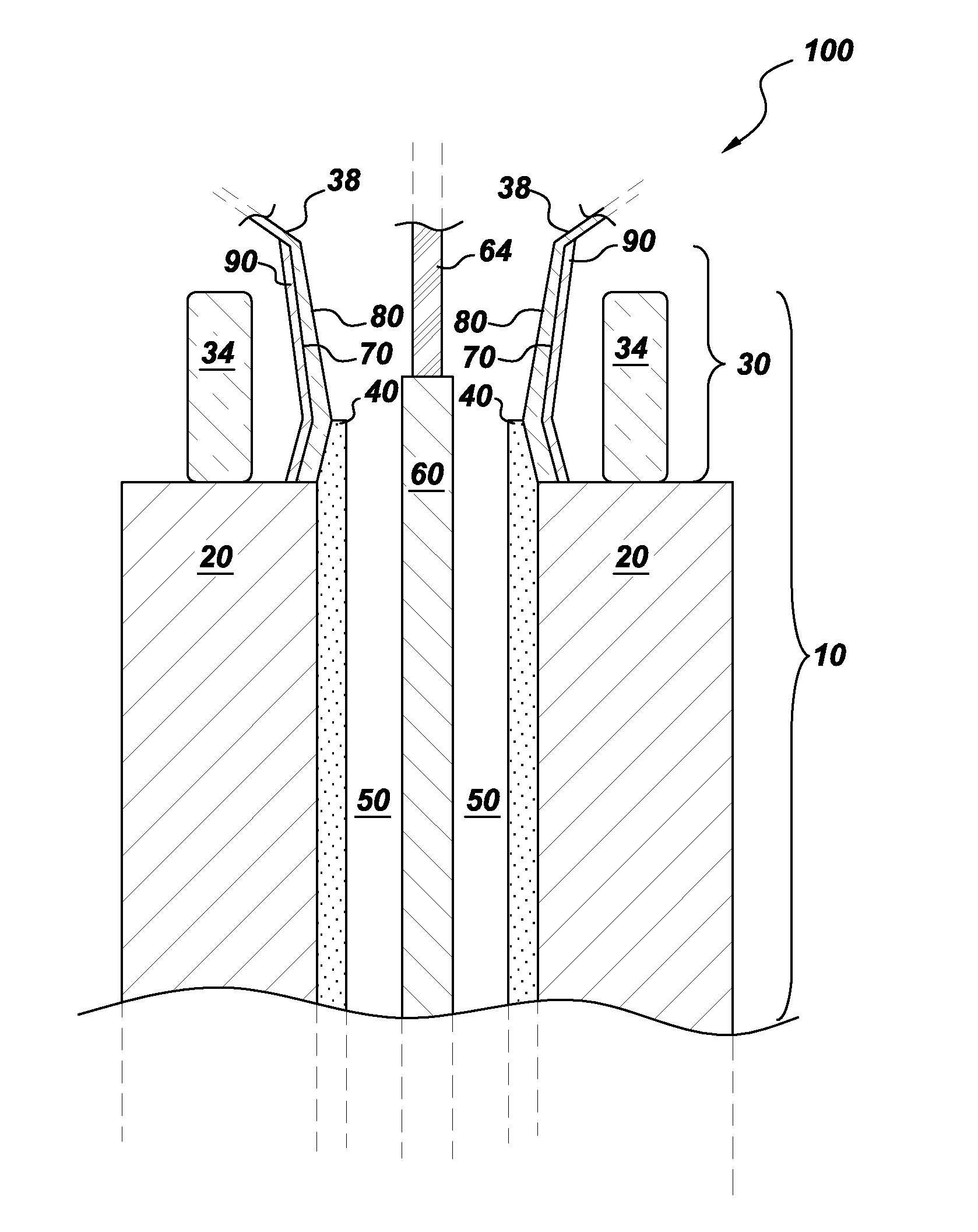
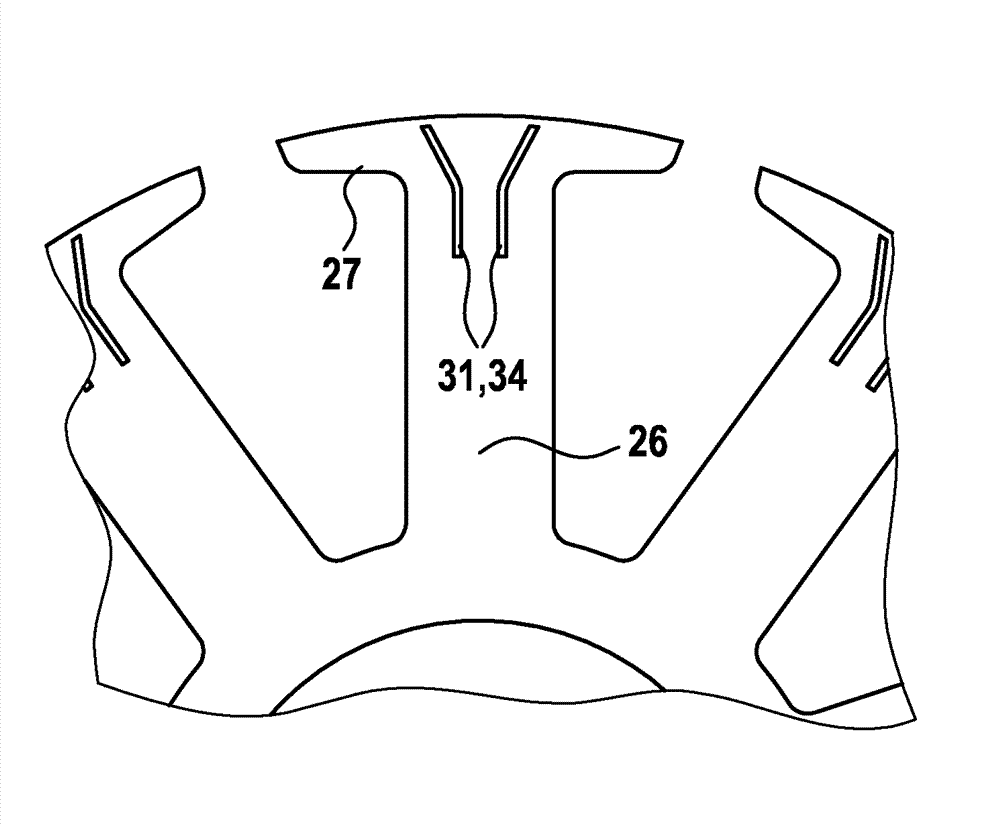
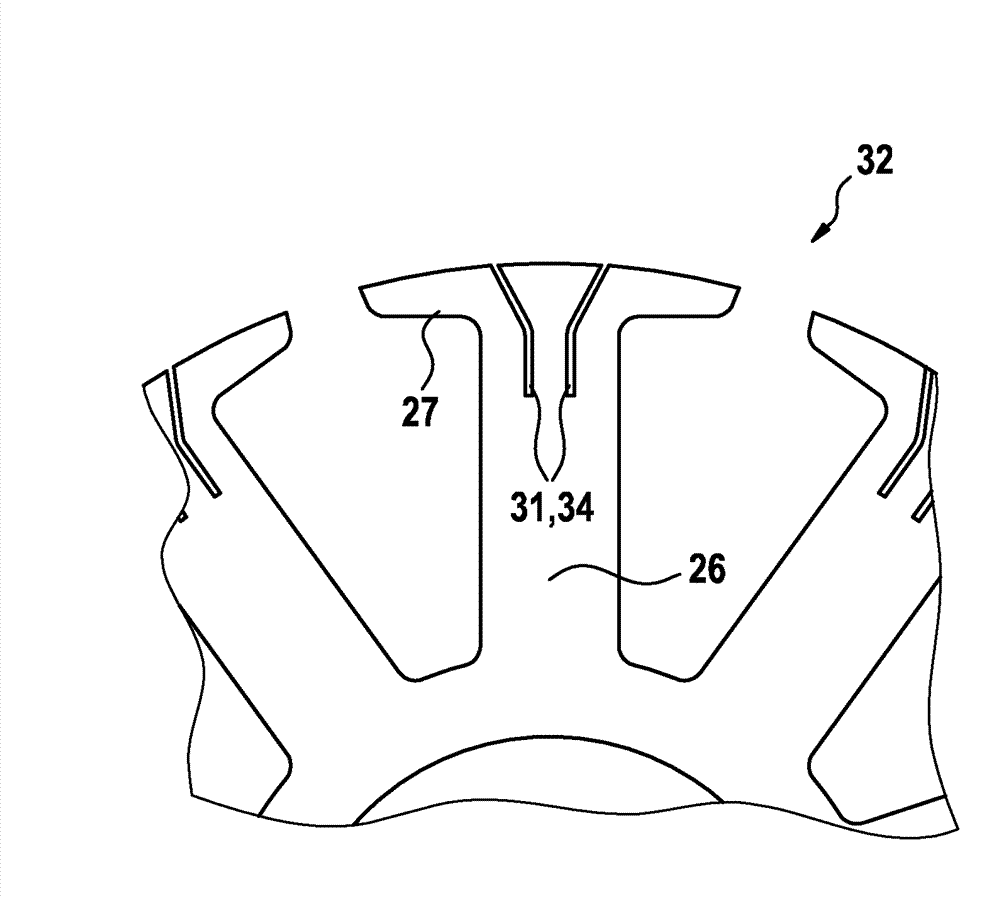
The invention relates to a stator of an electric motor, including a stator lamination bundle (2) which is provided with windings (3) which pass through this and which in the regions projecting beyond the stator lamination bundle (2) form end-windings. An end-winding shielding which is electrically conductively connected to the stator lamination bundle (2) is provided. This shielding is formed by segmented and distanced shielding sections (6) which in each case shield at least one end-winding (4) completely or partly.
Owner:GRUNDFOS HLDG
Rotor winding shield for a superconducting electric generator
InactiveUS20080143208A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsEngineeringConductor Coil
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Winding tooth and component for an electrical machine for reducing eddy currents
ActiveCN103026584AReduce eddy currentMagnetic circuit rotating partsPrevention/reducing eddy-current losses in winding headsElectric machineEngineering
The invention relates to a winding tooth (3) for a component (2) of an electrical machine (1), in particular for a stator and / or a rotor, comprising: a tooth shaft for being wound with a winding coil (4); and a tooth head (5) which is arranged at one end of the tooth shaft with respect to a winding axis; wherein one or more slots (14) are provided at at least one end section of the winding tooth (3), said slots extending along the winding axis through the tooth head (5), wherein the end section corresponds to a region at one or both ends of the winding tooth (3) along a transverse direction which runs substantially perpendicular to the winding axis.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Motor driving device and motor driving method
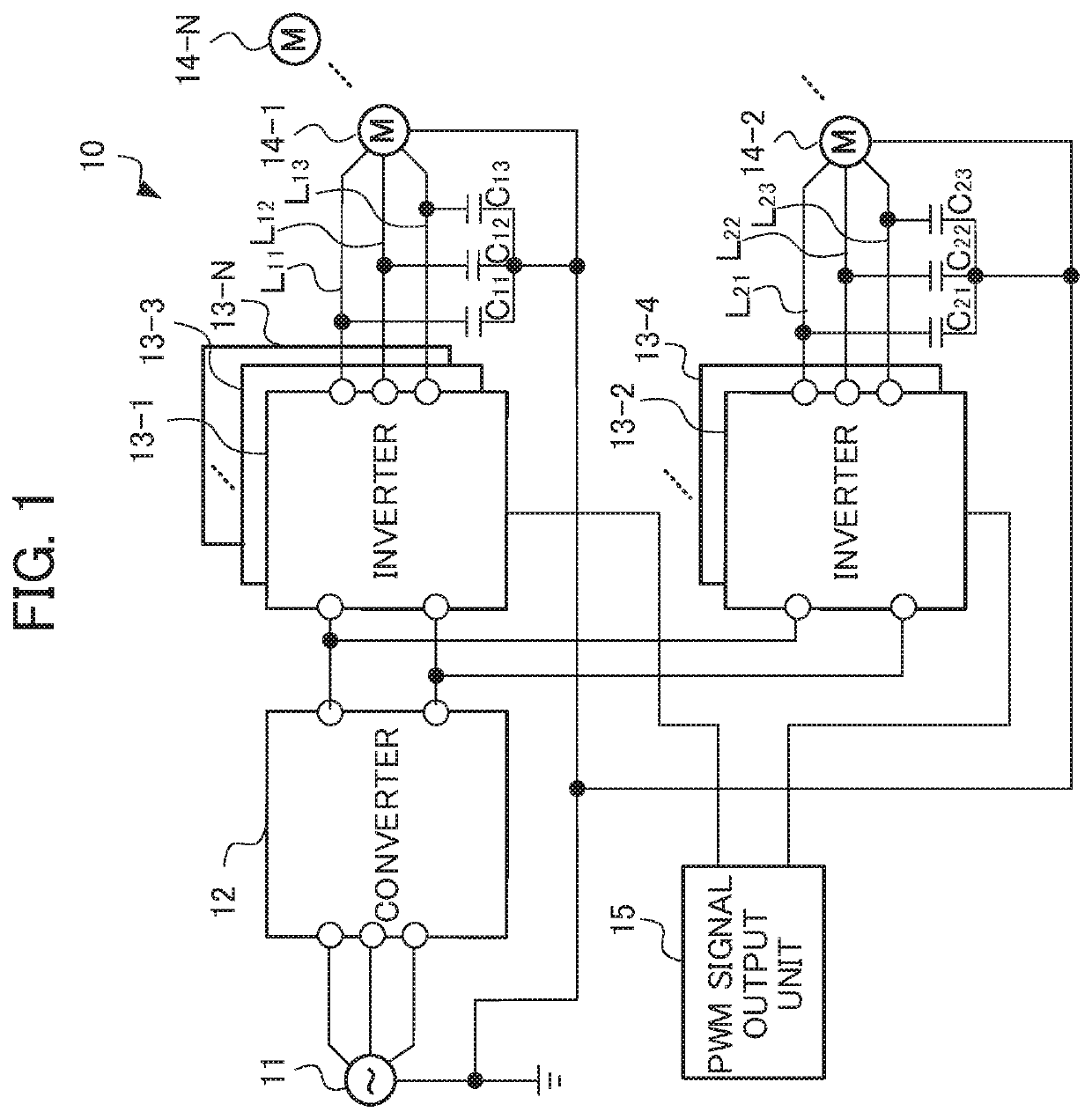
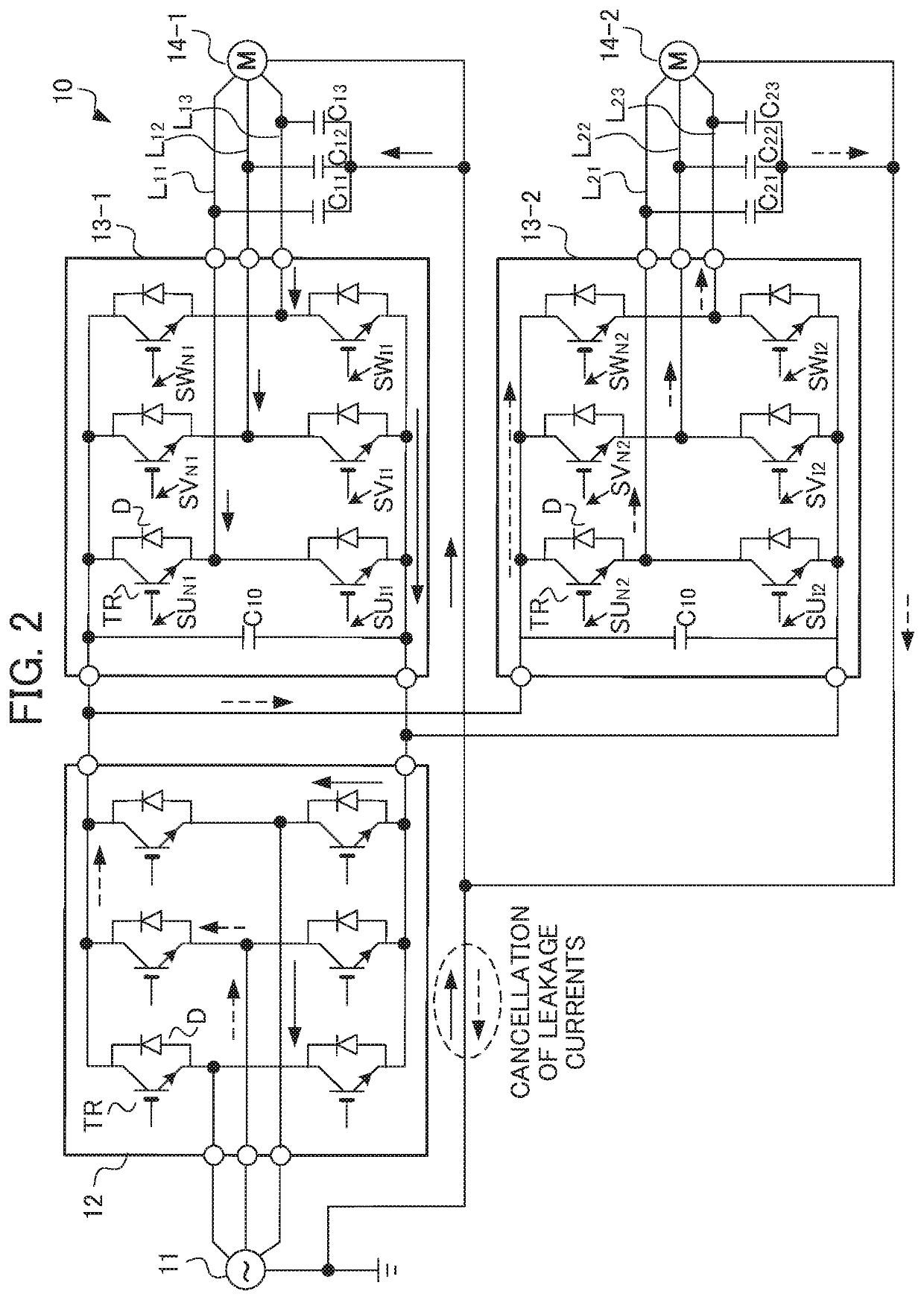
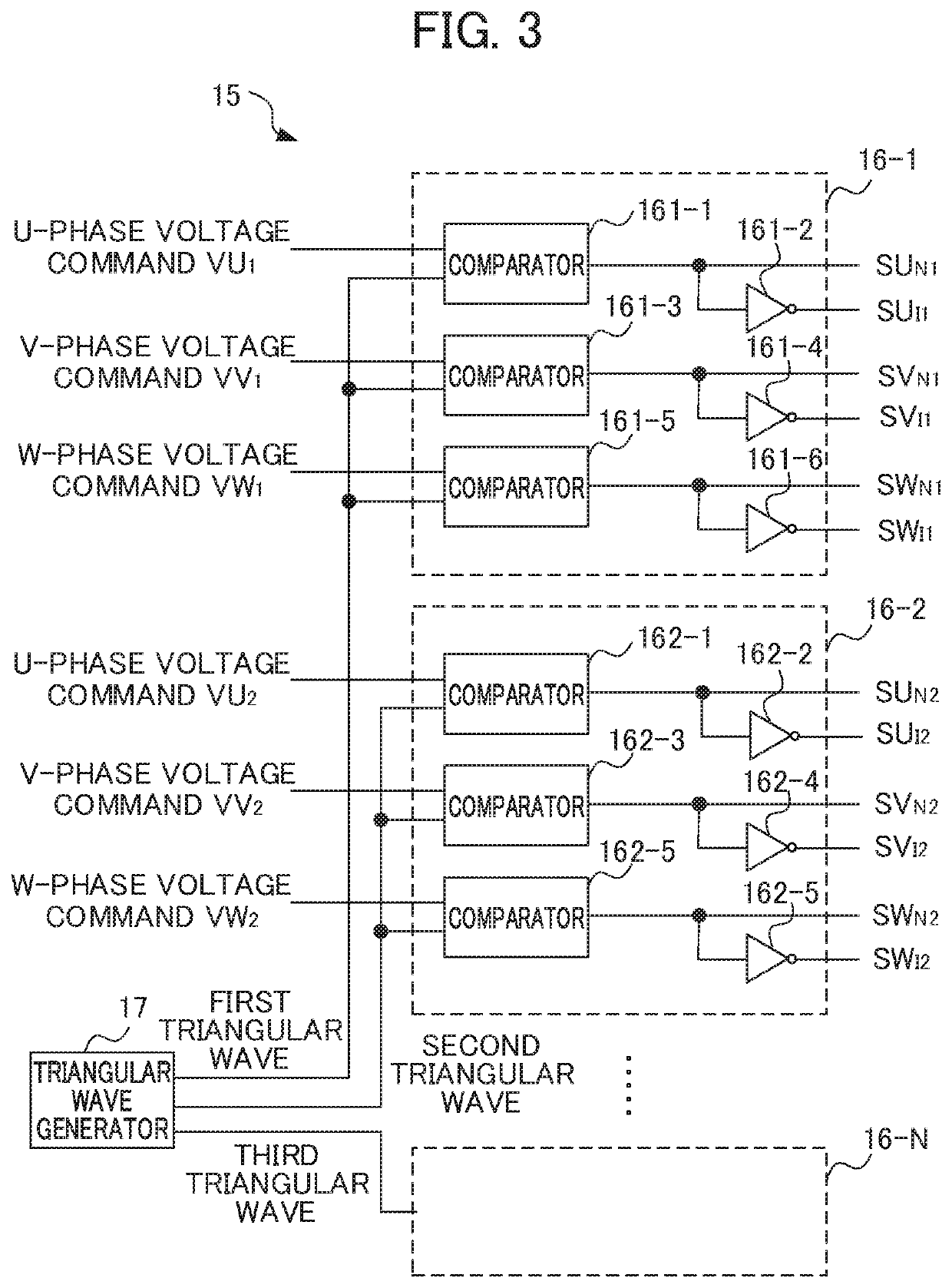
ActiveUS20190363600A1Suppress high-frequency leakage currentSuppress leakage currentAC motor controlElectric motor controlPower inverterMotor drive
A motor driving device includes N units (N is a natural number equal to or greater than 2) of inverters configured to control N units of motors, respectively, a×N units (a is a natural number) of cables configured to allow connection between the N units of inverters and the N units of motors, respectively, and a PWM signal output unit configured to transmit a PWM signal to the N units of inverters. The N units of inverters and the a×N units of cables are divided into M groups (M≤N). The PWM signal output unit outputs the PWM signal for driving at least one inverter belonging to each group of the M groups so that the PWM signals have phase differences shifted by 360 degrees / M among the groups.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com