Composition and method for treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders
a neuropsychiatric disorder and composition technology, applied in the field of combination therapy compositions, can solve the problems of limited human utility of neuropsychiatric disorders, ineffectiveness of drug currently used for pud patients, and inability to strictly test the effectiveness of drug treatments, so as to reduce symptoms and/or signs of neuropsychiatric disorders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
nd-PR2]: Proof-of-Concept Phase IIA Safety / Efficacy Study
[0109]Ond-PR2 is a bead formulation prepared from ondansetron as the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). MPh-IR is an immediate-release generic formulation of methylphenidate. [MPh-IR+Ond-PR2] is a single encapsulated dosage form consisting of MPh-IR and Ond-PR2 as Components 1 and 2, respectively. Following in vitro dissolution testing and PK and safety determinations in normal healthy volunteers (Phase 1 trial), we conducted a proof-of-concept, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 2A safety / efficacy clinical trial. A total of 48 patients residing in a residential program and meeting the DSM-4 criteria for primary psychostimulant abuse were screened, and 30 qualifying subjects were randomized into either [MPh-IR+Ond-PR2] or placebo treatment group.
[0110]Single capsules containing either [MPh-IR+Ond-PR2] or dextrose (placebo) were administered once a day for 14 days. Subjects also underwent single fMRI-based ...
example 2
of Levodopa-Induced Abnormal Involuntary Movement (LIAIM) by Treatment with Pergolide and Ketanserin
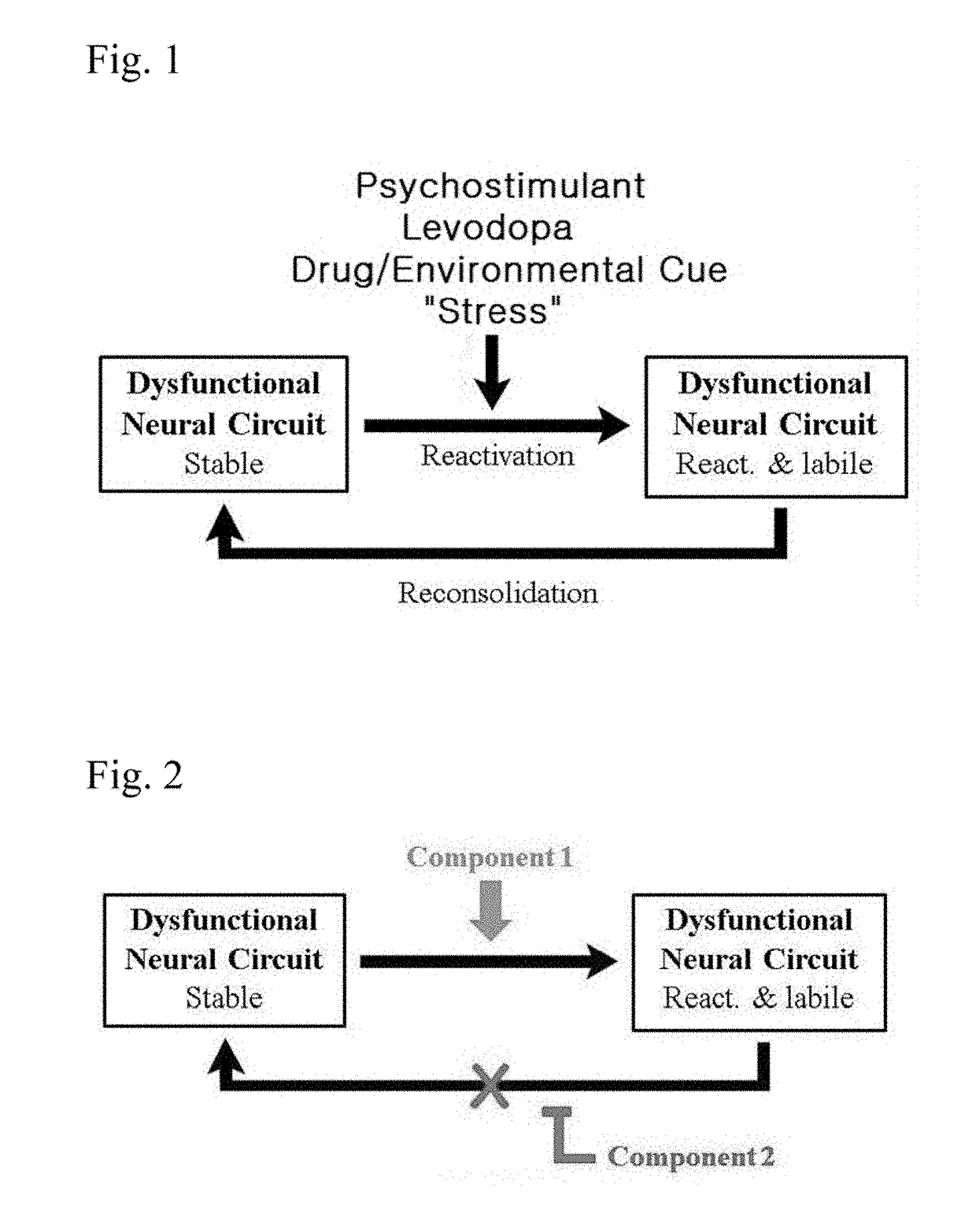
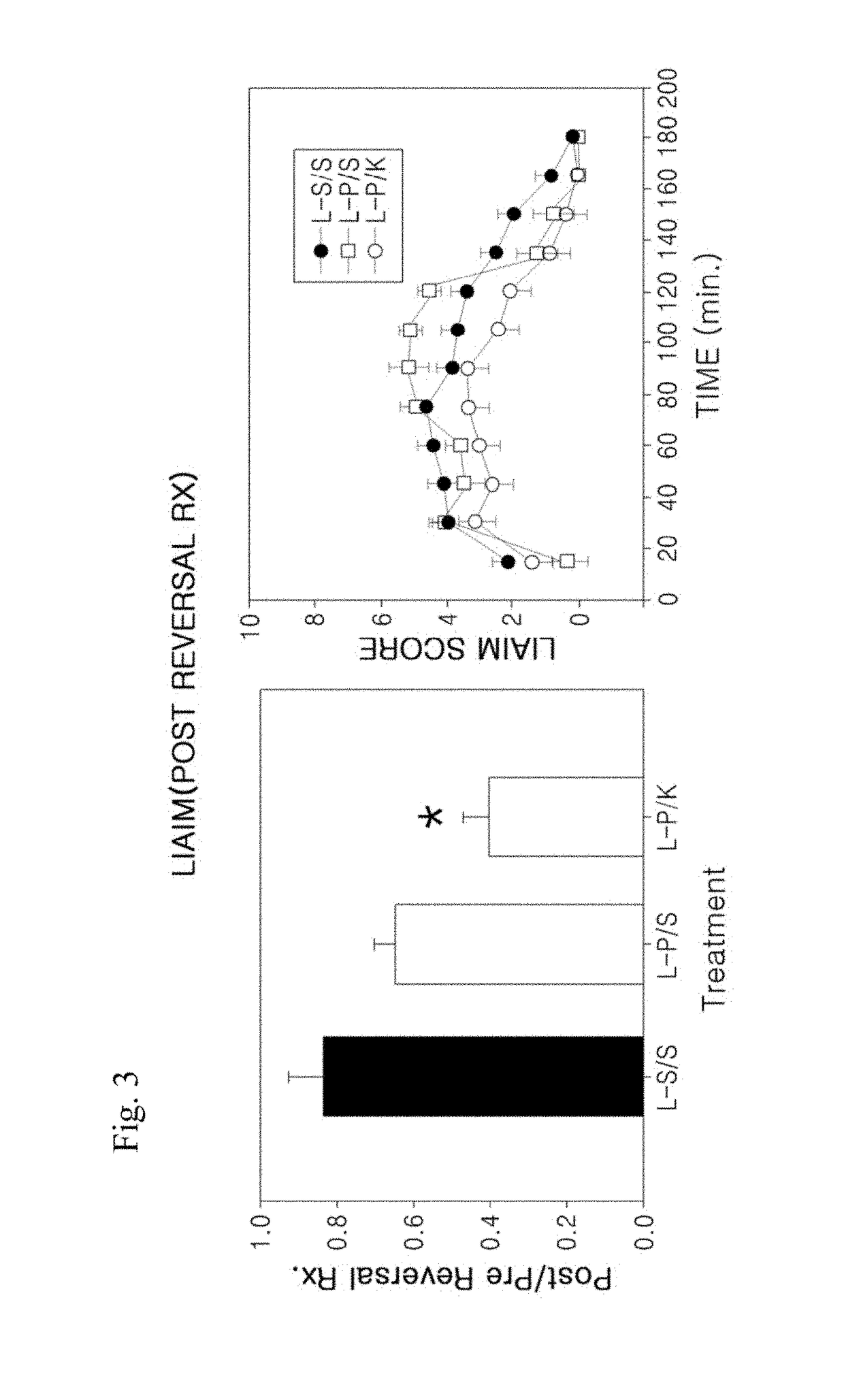
[0122]In order to demonstrate that the agonist / antagonist combination therapy according to the present invention can effectively reverse LID and restore levodopa efficacy, an animal model study of LID was carried out using a combination of the DA agonist pergolide and the 5-HT2A / 2C antagonist ketanserin. In this study, it was found that the combination therapy significantly reduced levodopa-induced abnormal involuntary movement (LIAIM) in the rat animal models of LID (FIG. 3).
[0123]Preparation of the animal models used in this experiment was performed as follows.
[0124]First, the dopaminergic neurotoxin 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) was injected into the right medial forebrain bundle of rats to induce unilateral lesions of the nigrostriatal DA pathway. Starting 3 weeks after 6-OHDA lesion, animals were treated twice daily with levodopa methyl ester (25 mg / kg, i.p., bid immediately precede...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elimination half life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| terminal elimination half life | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com