Patents
Literature
61 results about "Illicit drug" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Types of Illicit Drugs. There are several different types of illicit drugs and each has different effects on the body. Illicit drugs examples include stimulants like cocaine, narcotics like heroin, hallucinogens like LSD, and depressants or sedatives.
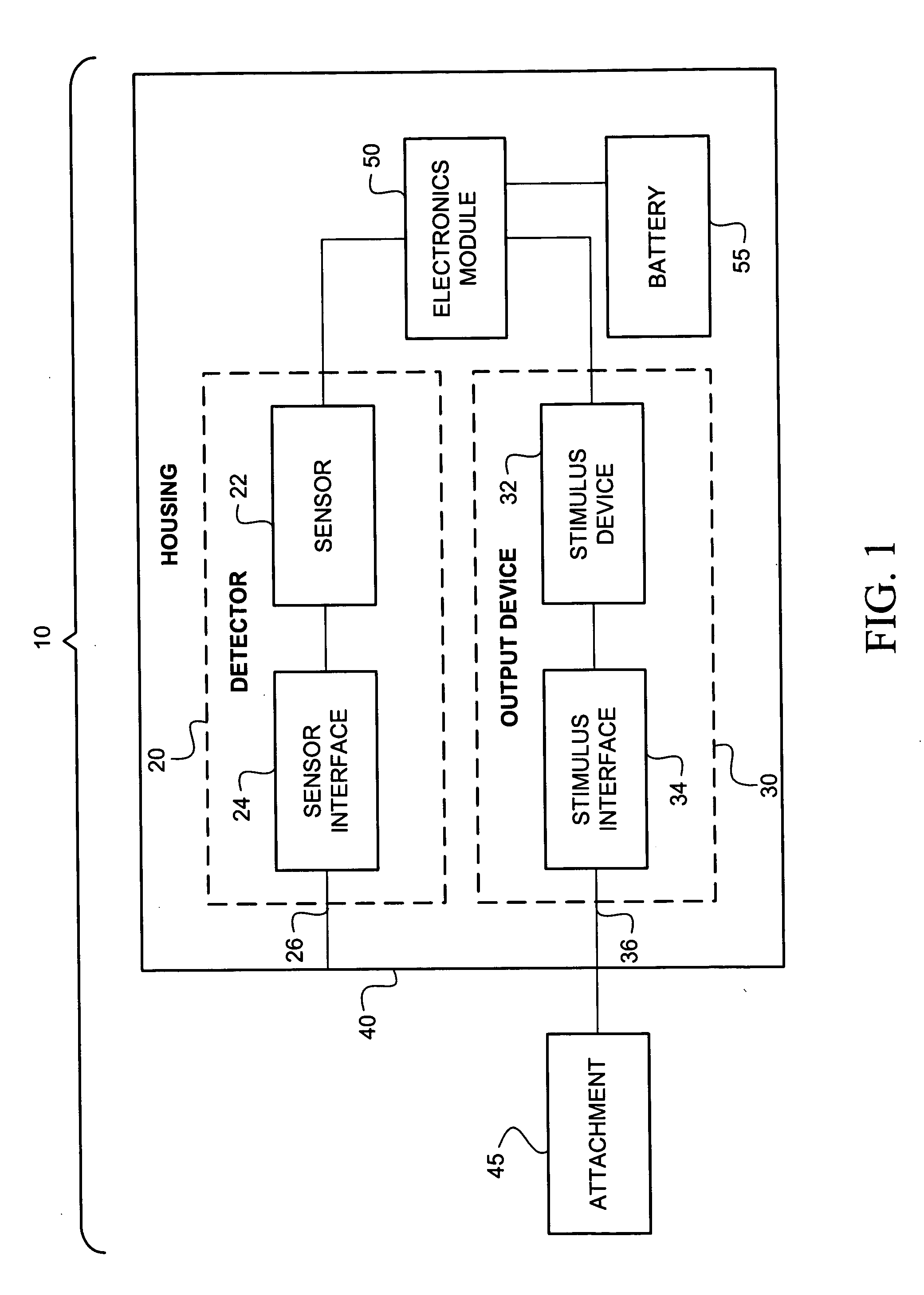
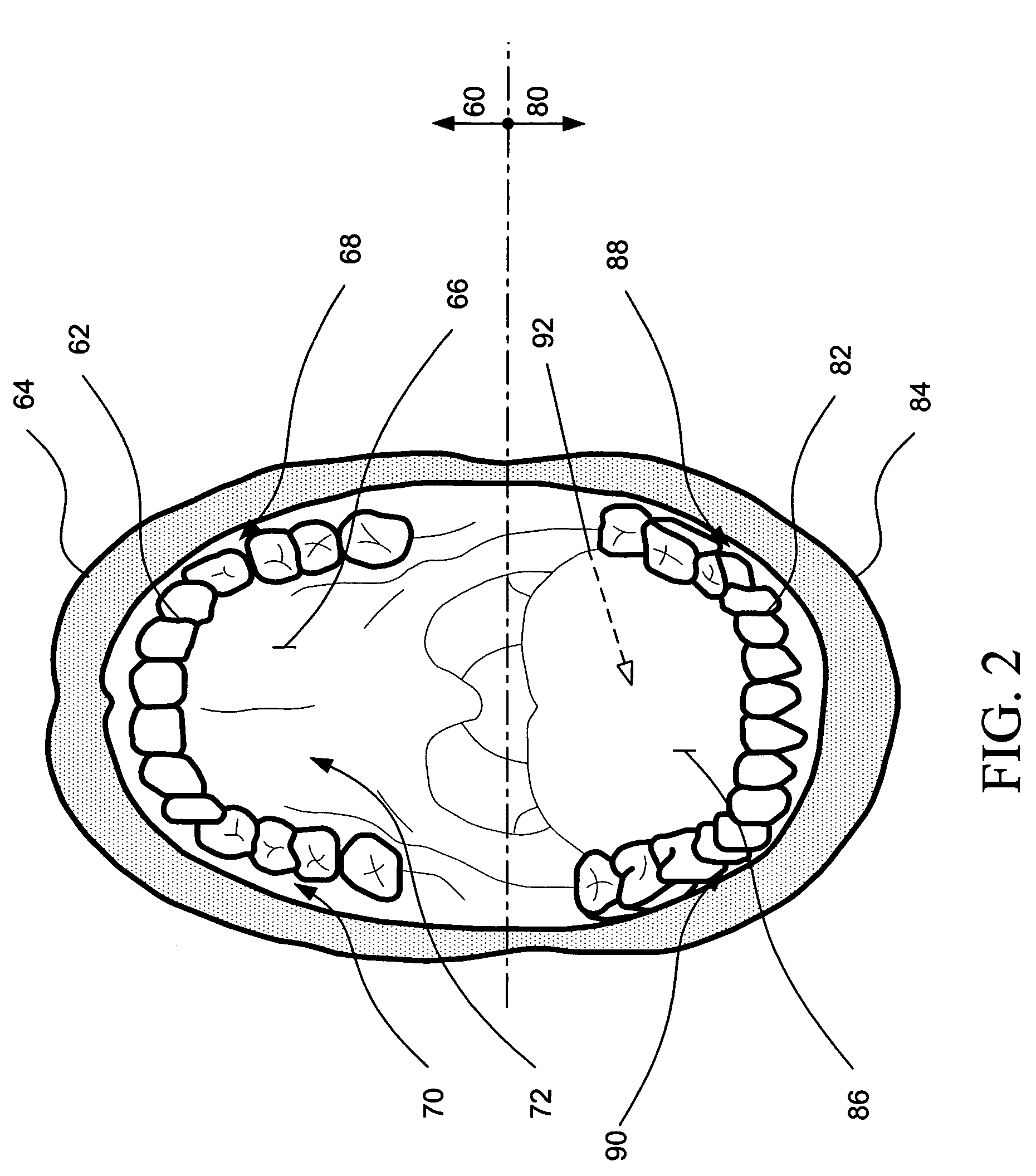
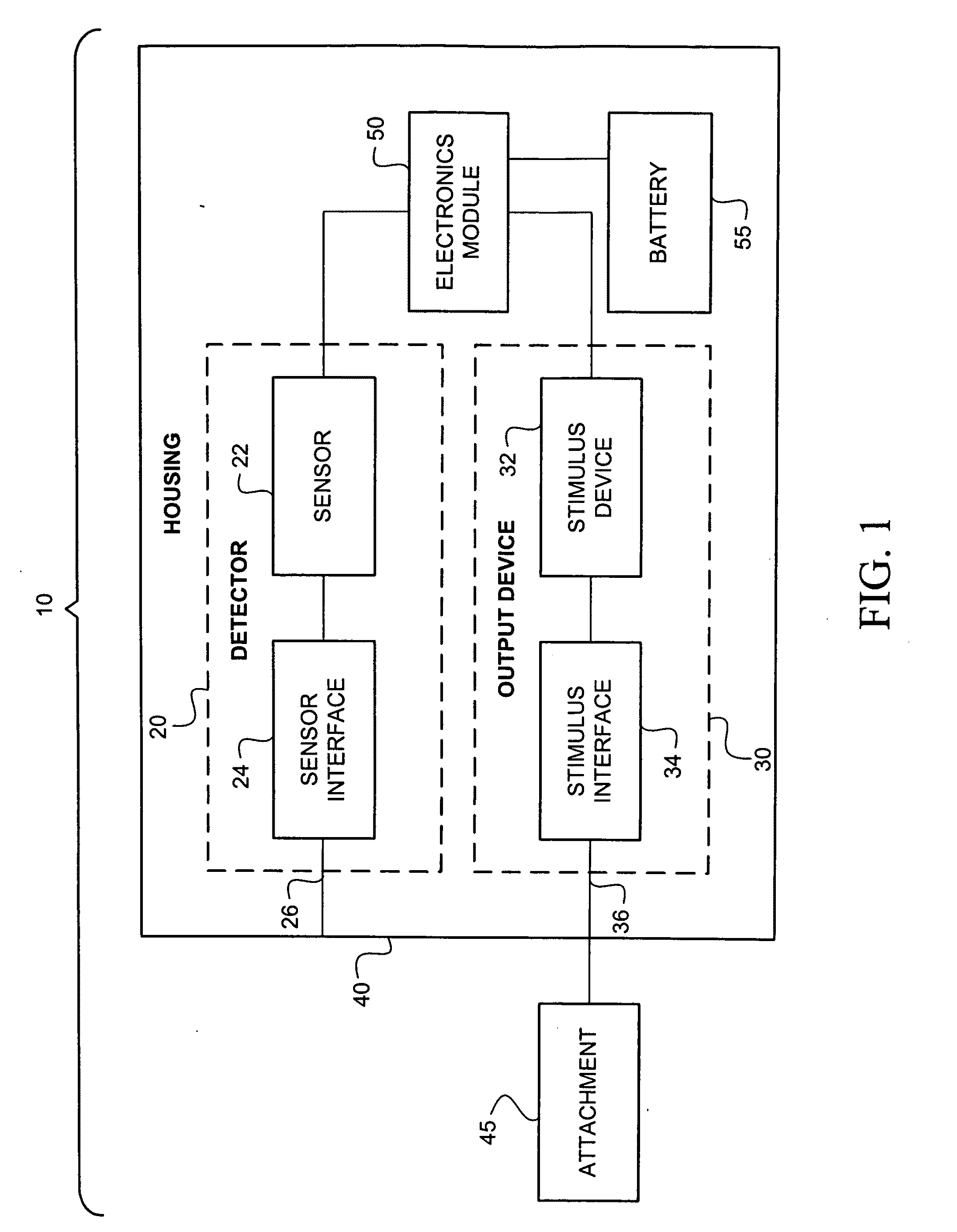
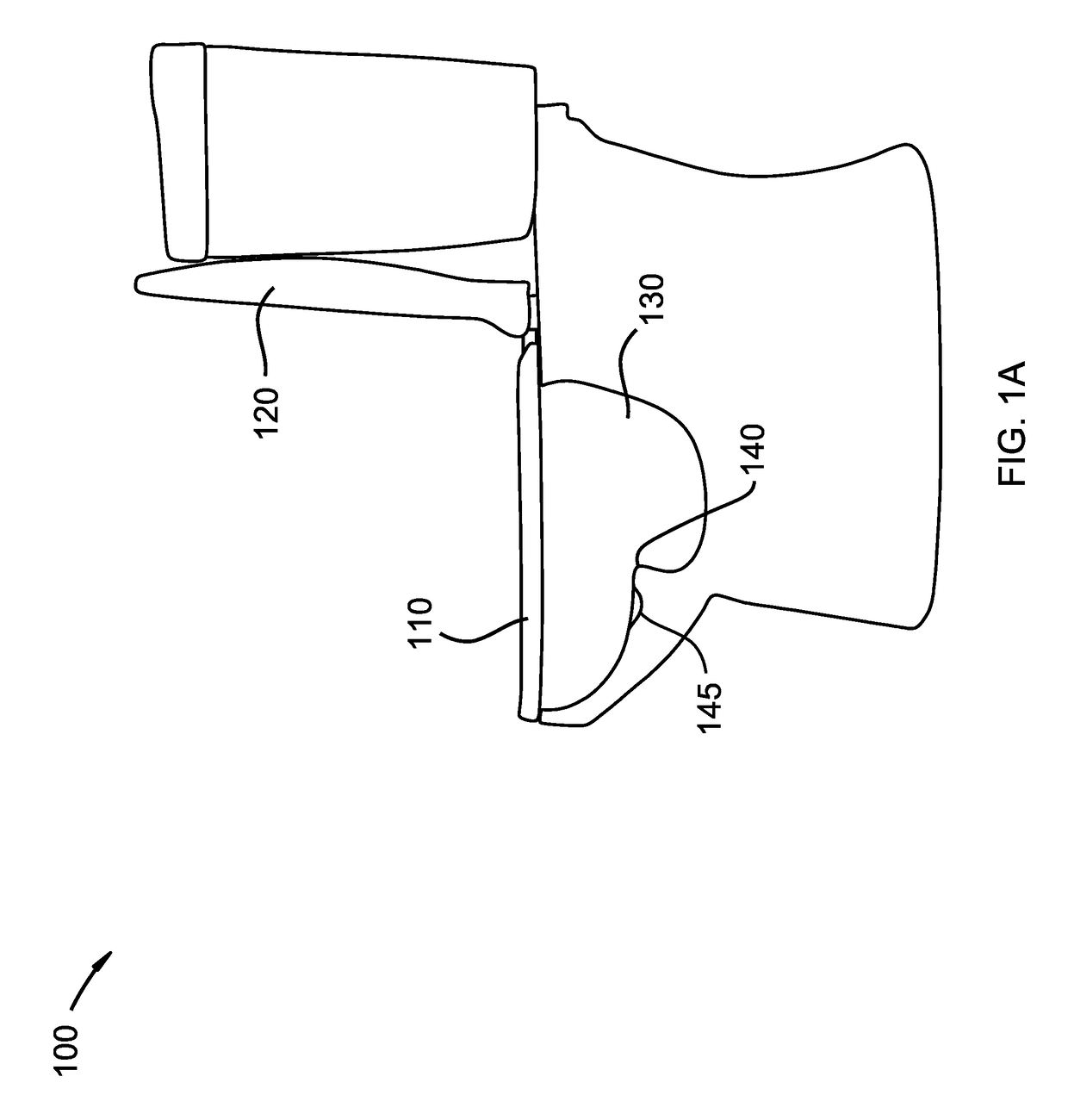
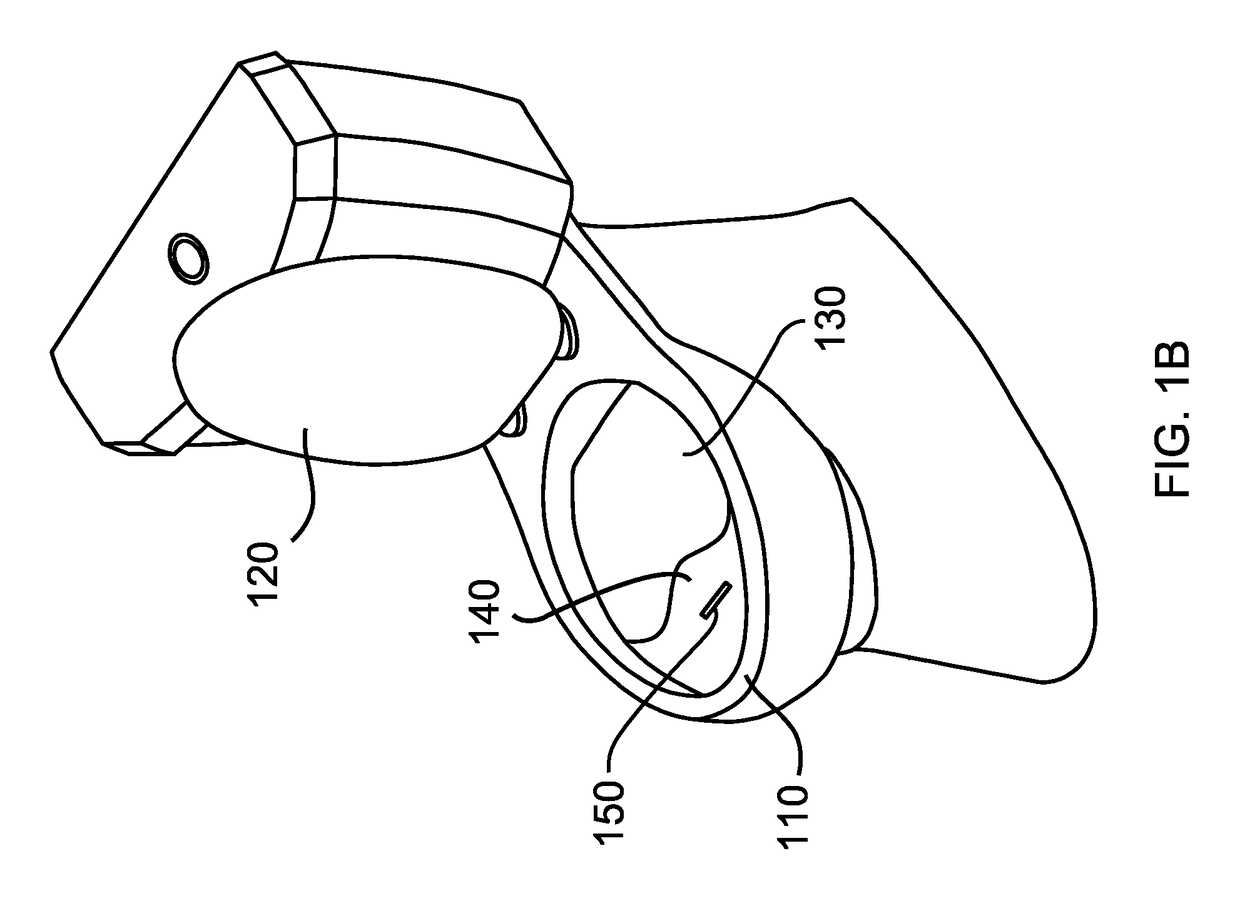
Intraoral aversion devices and methods
InactiveUS20050263160A1Readily detect undesirable activityLimit ability of to remove and defeatTobacco devicesNegative feedbackIllicit drug
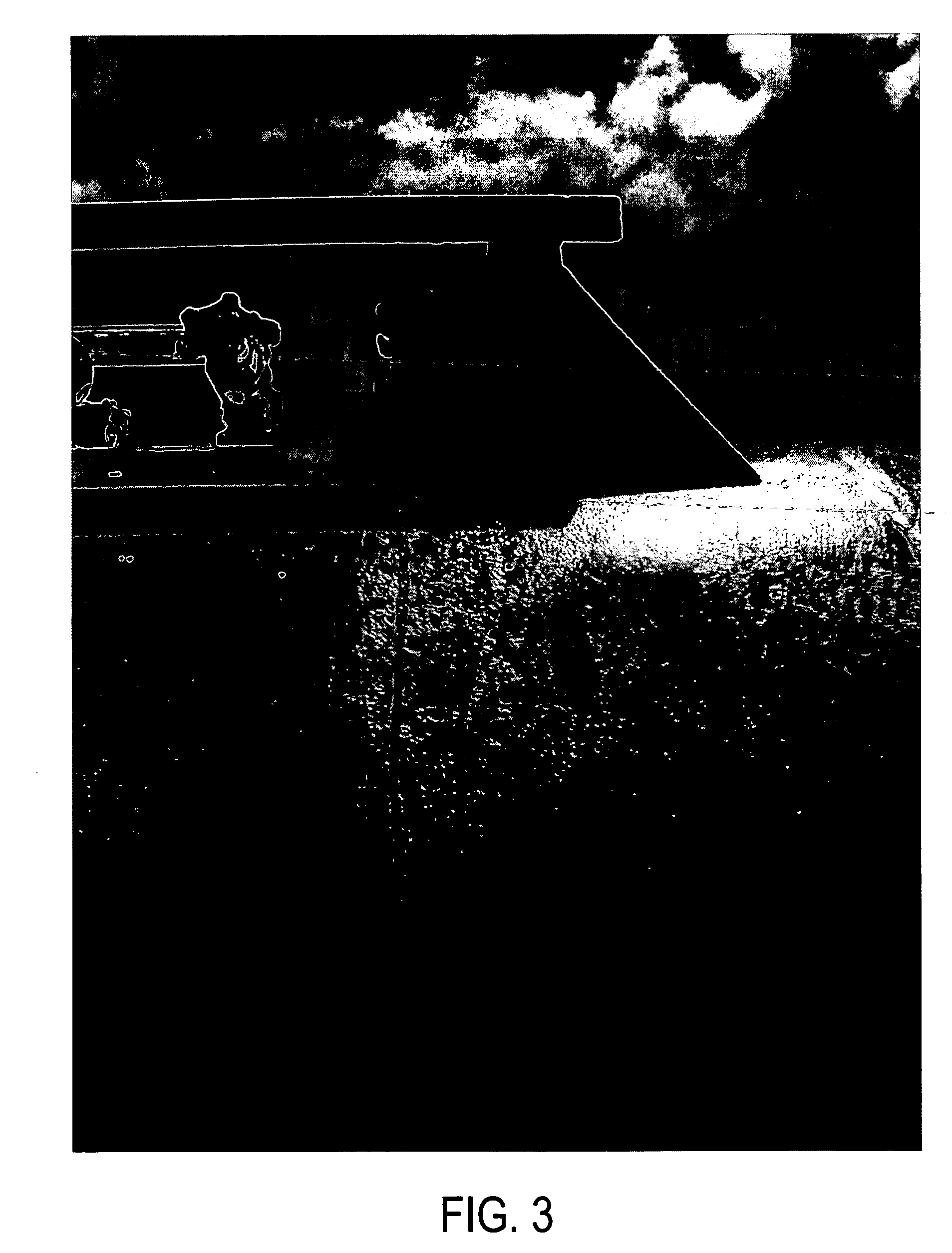
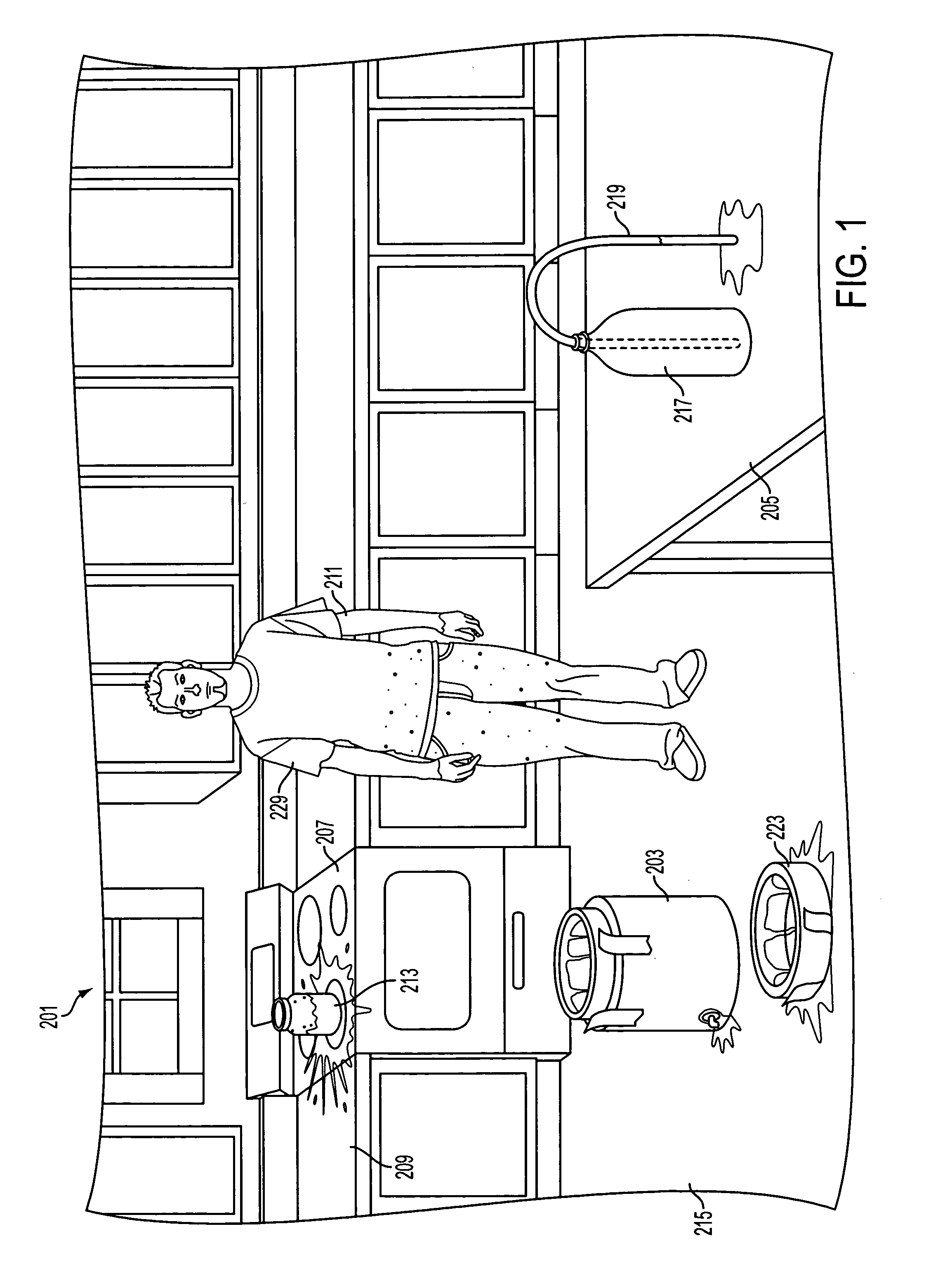
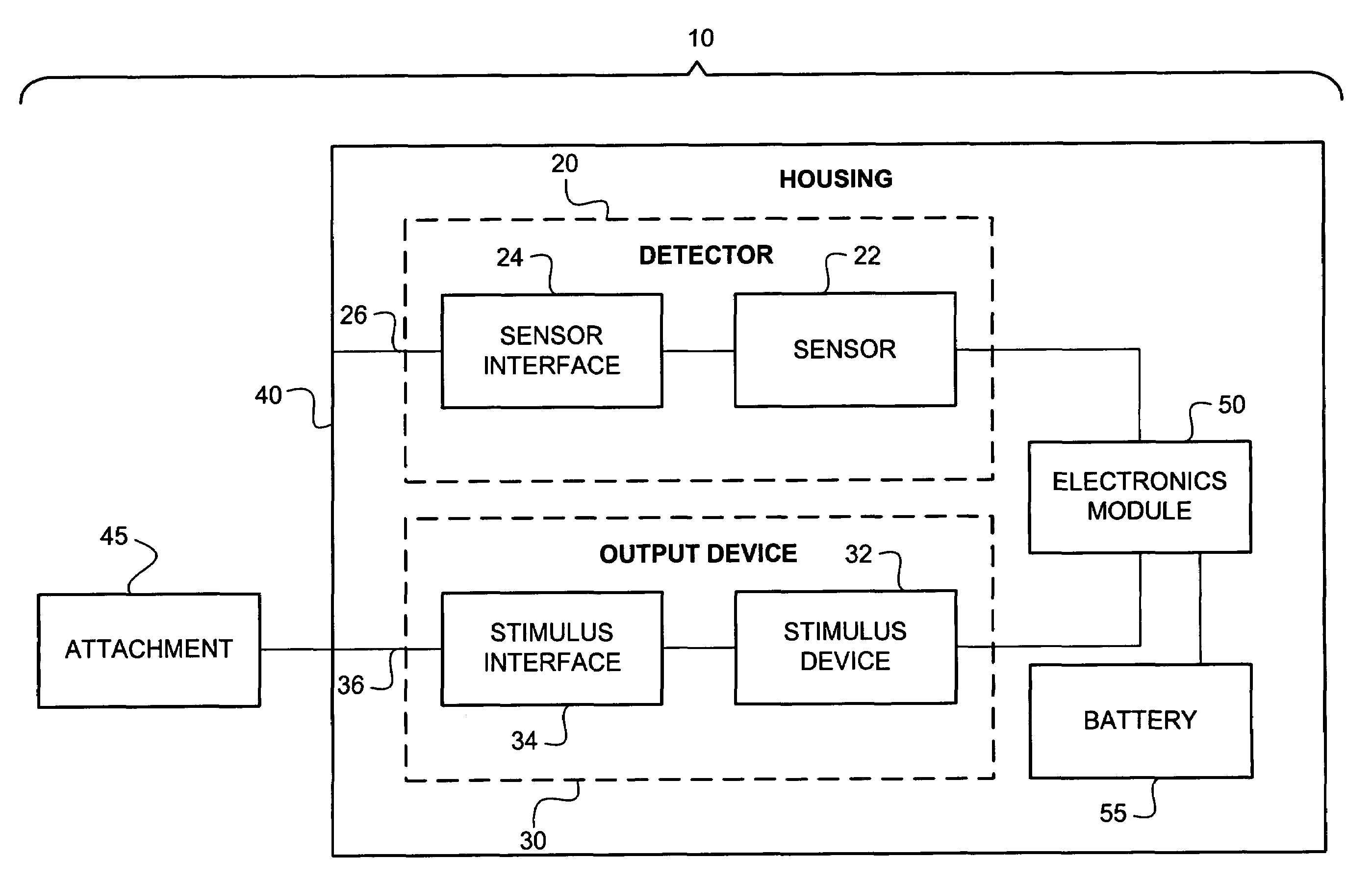
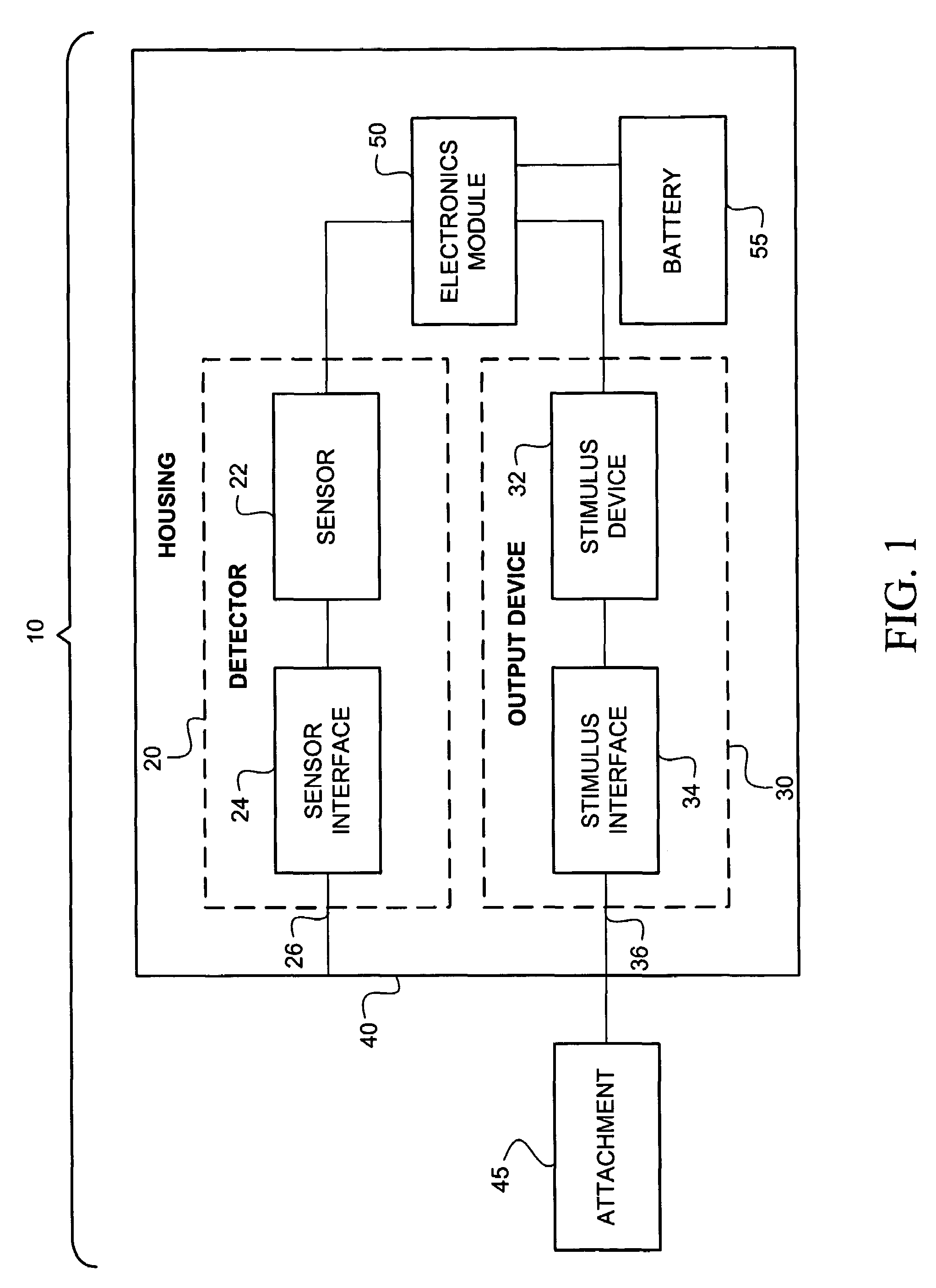
An intraoral aversion device to assist a user in quitting an undesirable behavior such as tobacco smoking, tobacco chewing, use of snuff, illicit drug use, excessive alcohol consumption, excessive food consumption, and / or other undesirable activity facilitated via the mouth. The aversion device may be wholly or partially configured to be disposed in the user's mouth, for example. The aversion device may include a detector and a output device, wherein the detector is configured to detect a parameter indicative of the user engaging in the habit or undesirable activity. If (and only if) the detector detects such a parameter, the output device delivers a negative stimulus to the user, thus providing negative feedback and creating an incentive for the user to limit if not eliminate the undesirable activity.
Owner:PIVOT HEALTH TECH INC
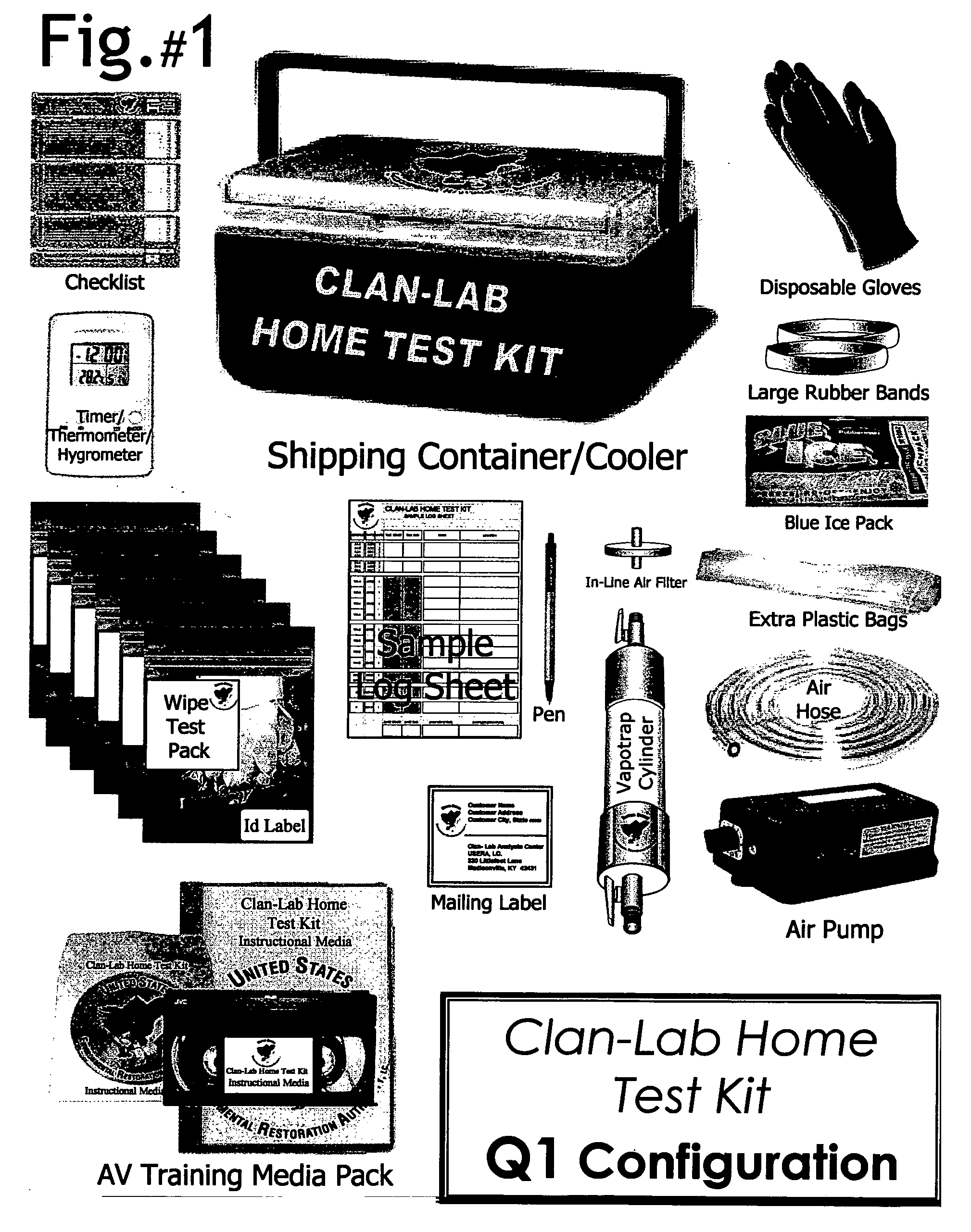
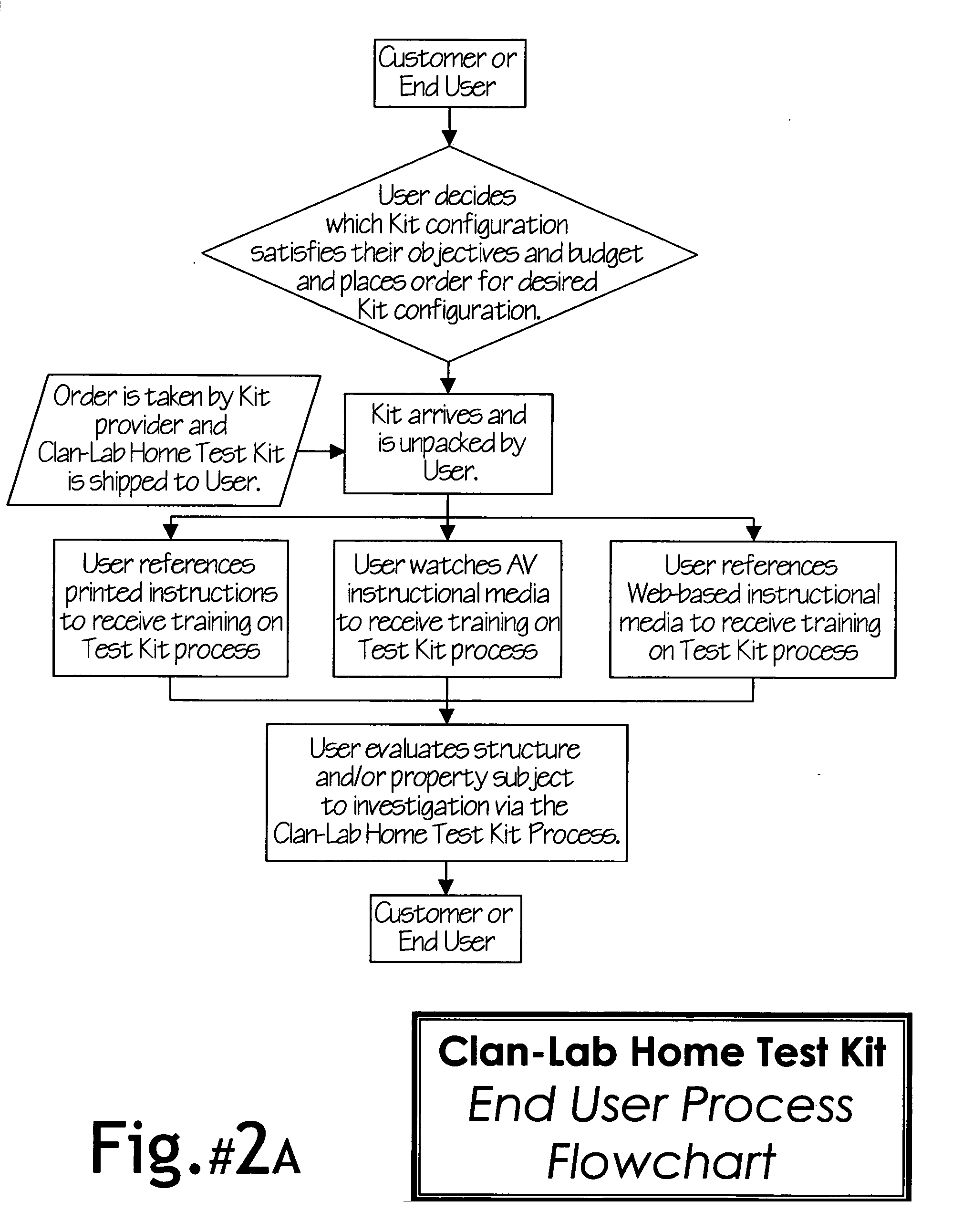
Clandestine Laboratory (Clan-Lab) Home Test Kit system, protocol, method and apparatus
This invention is comprised of a system, protocol, method and apparatus for the assessment of properties that may have been, or are being, subject to clandestine drug manufacturing and / or processing activities. The invention includes a comprehensive home test kit to be used in or upon a suspect premises to detect, identify, and delineate toxic chemical hazards that may have originated from an illegal drug making operation. The test kit is designed to be conveniently equipped with all-inclusive content consisting of an assortment of user-selected sampling equipment, media, containers, materials, documentation, instruction manual, as well as an audio-visual instructional media pack. This Kit is designed to enable a person of average intelligence to conduct the sampling activities and the Kit to a designated analytical laboratory for processing and reporting of results in order to determine the risk presented by a property and damages it may have sustained.
Owner:OLIVER TROY LEE
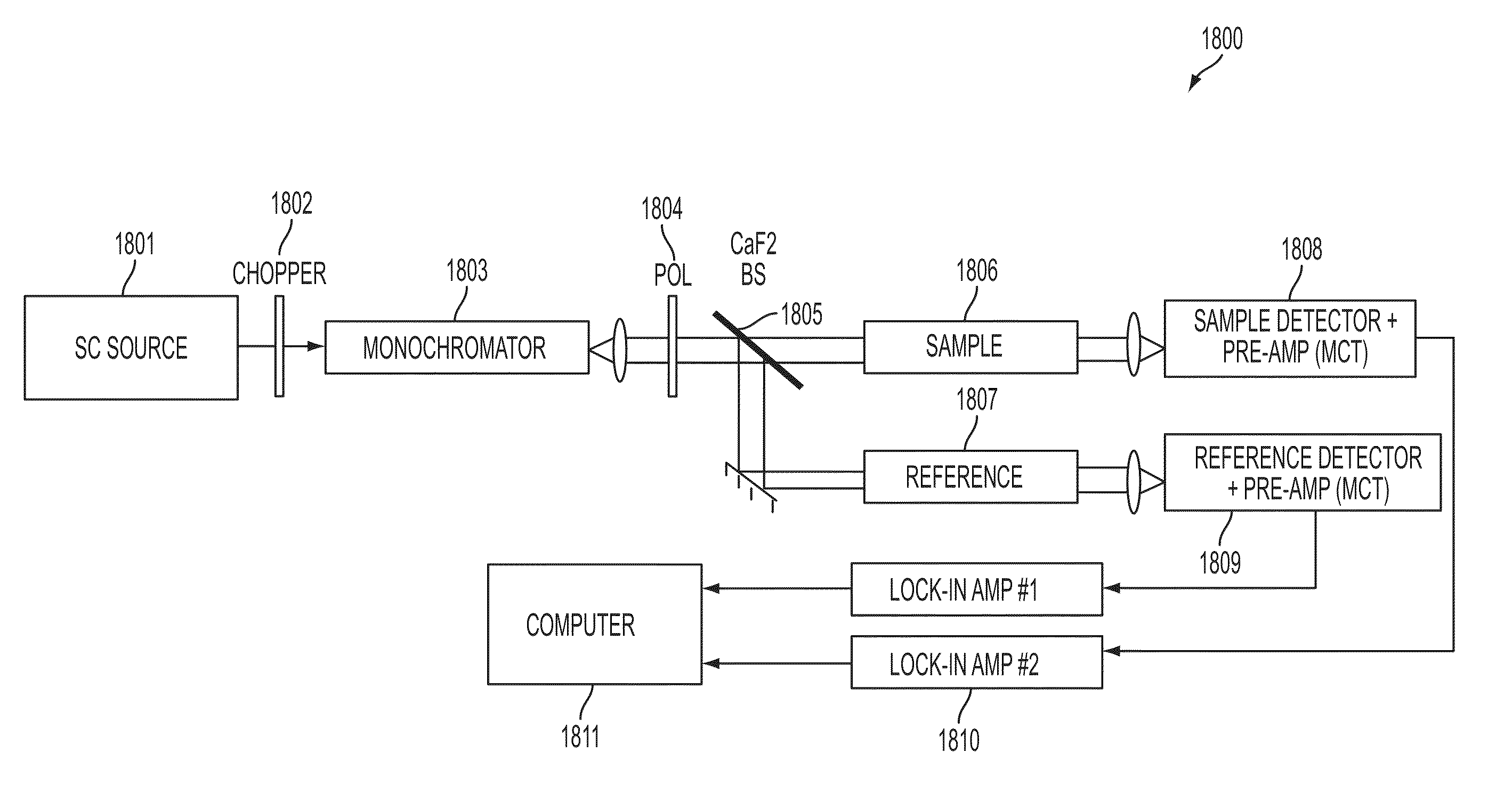
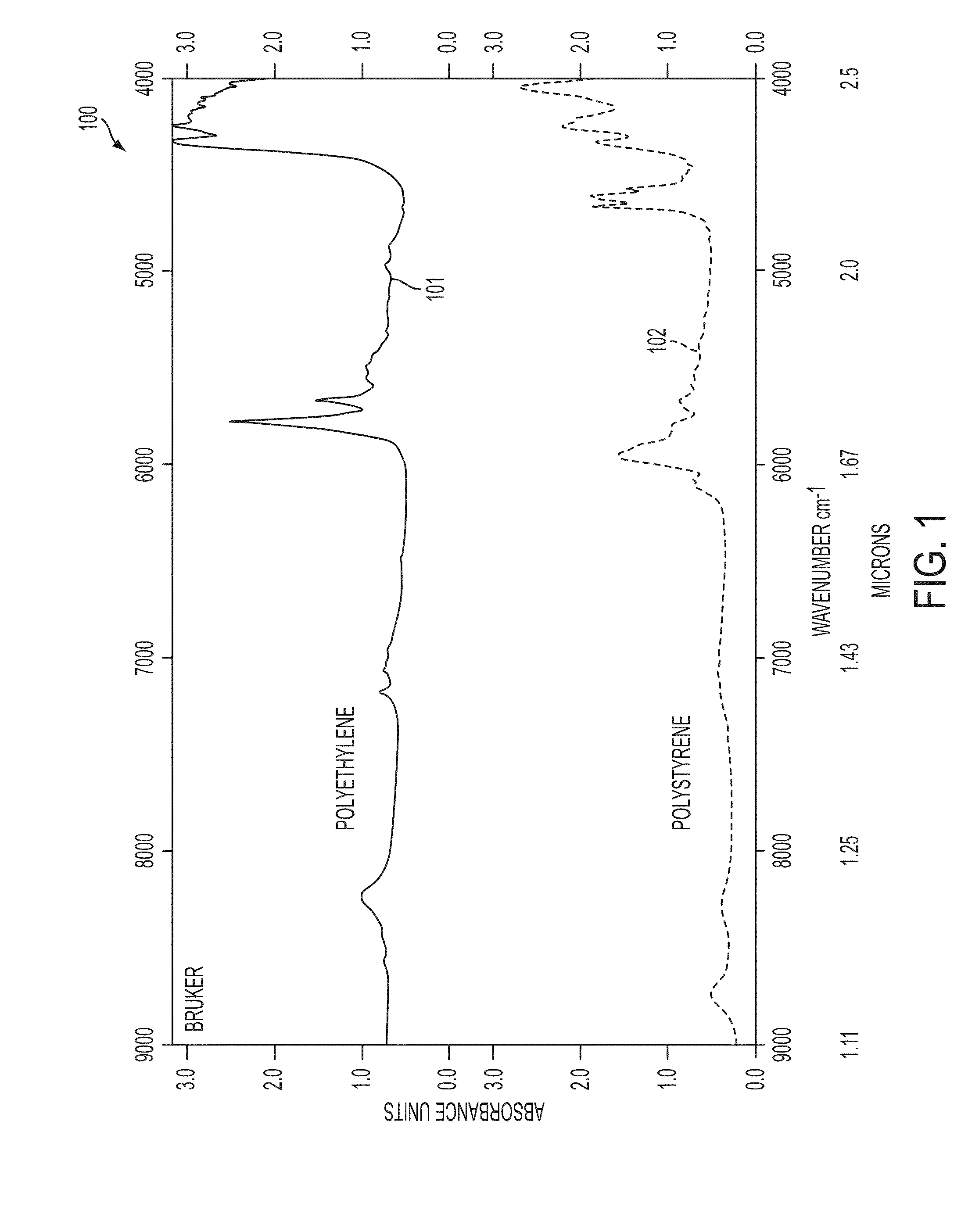
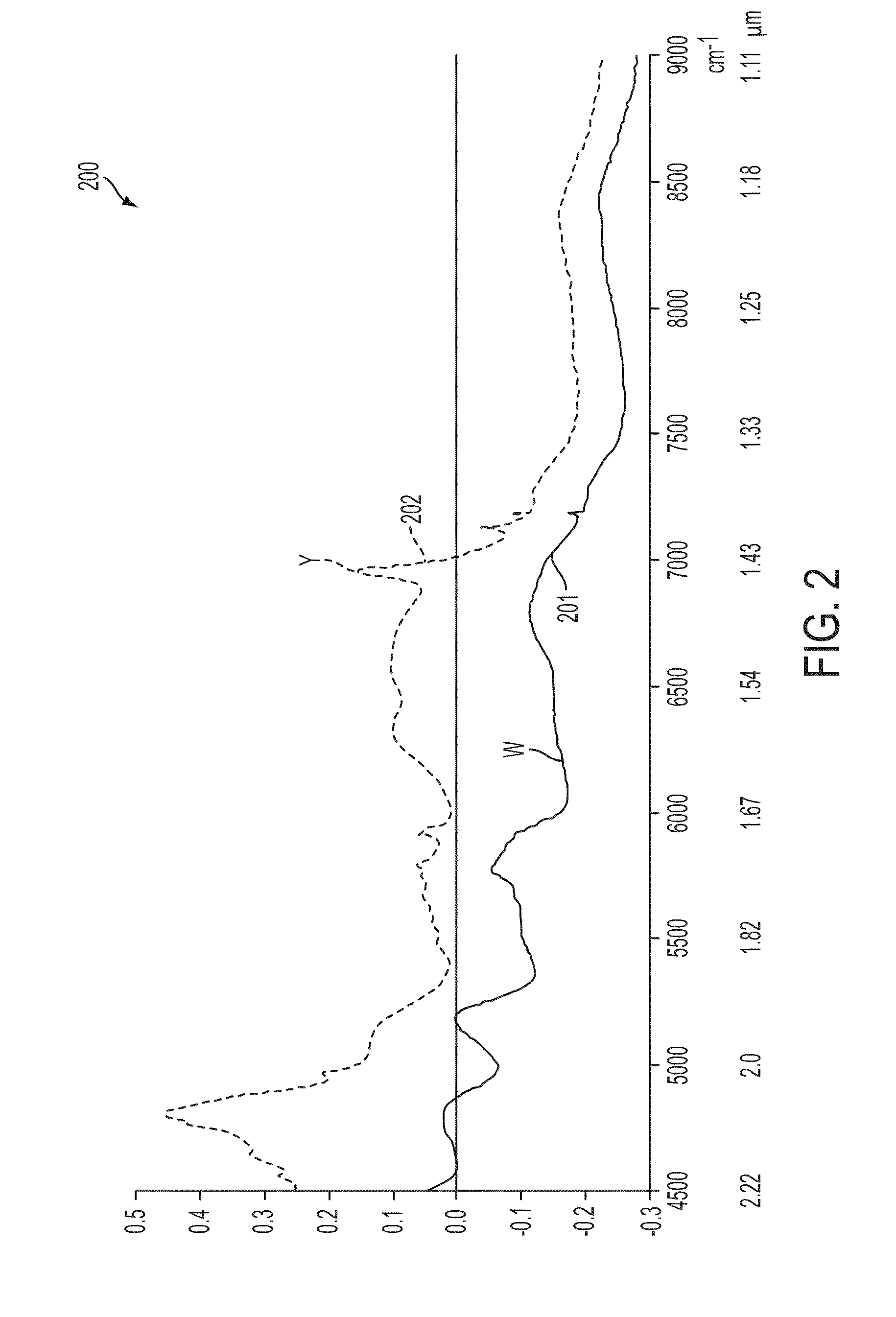
Short-wave infrared super-continuum lasers for detecting counterfeit or illicit drugs and pharmaceutical process control
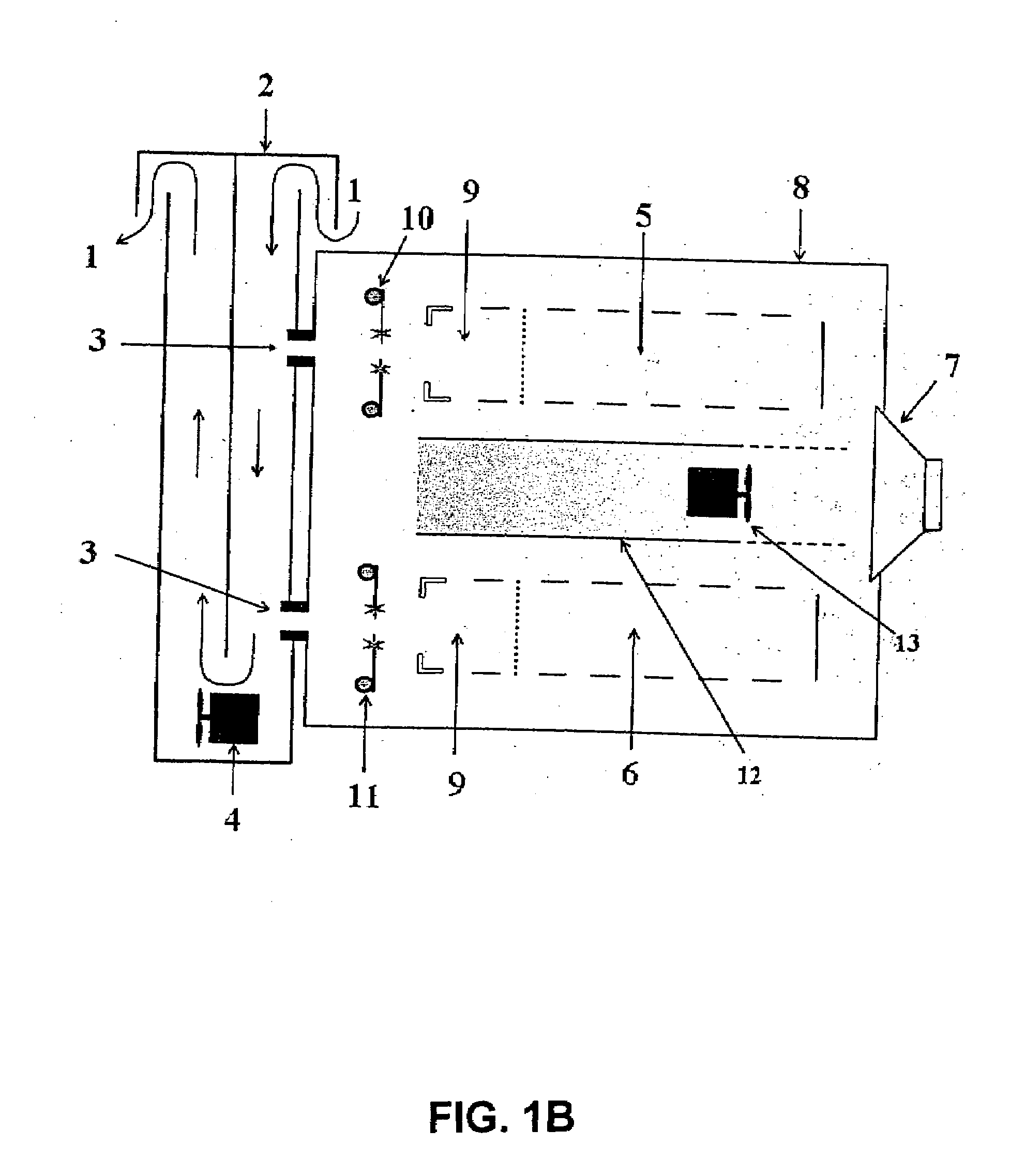
A system and method for using near-infrared or short-wave infrared (SWIR) light sources for identification of counterfeit drugs may perform spectroscopy using a super-continuum laser to provide detection in a non-contact and non-destructive manner at stand-off or remote distances with minimal sample preparation. Also, near-infrared or SWIR light may penetrate through plastic containers and packaging, permitting on-line inspection and rapid scanning. The near-infrared or SWIR spectroscopy may also be used to detect illicit drugs and their chemical composition. Moreover, the spectroscopic techniques may also be applied to quality assessment and control in pharmaceutical manufacturing, thus permitting the implementation of smart manufacturing with feedback control. Fiber super-continuum lasers may emit light in the near-infrared or SWIR between approximately 1.4-1.8 microns, 2-2.5 microns, 1.4-2.4 microns, 1-1.8 microns. In particular embodiments, the detection system may be a dispersive spectrometer, a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, or a hyper-spectral imaging detector or camera.
Owner:OMNI MEDSCI INC
Dye solutions for use in methods to detect the prior evaporation of anhydrous ammonia and the production of illicit drugs
InactiveUS20050026298A1Stop theftAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorStainingEvaporation
Systems and methods providing for the introduction of a dye, particularly a xanthene dye, and more particularly a rhodamine dye, to liquid anhydrous ammonia to discourage theft of the anhydrous ammonia and provide for leak detection in storage vessels. The dye will stain objects which come into contact with the liquid anhydrous ammonia allowing for the detection of such contact. Generally, the staining will be visible to the naked eye, but may also fluoresce when exposed to a particular light source such as ultra violet (UV) light.
Owner:GAS TECH INST +1
Intraoral aversion devices and methods
InactiveUS7610919B2Readily detect undesirable activityLimit ability of to remove and defeatElectrotherapyTeeth fillingNegative feedbackIllicit drug
An intraoral aversion device to assist a user in quitting an undesirable behavior such as tobacco smoking, tobacco chewing, use of snuff, illicit drug use, excessive alcohol consumption, excessive food consumption, and / or other undesirable activity facilitated via the mouth. The aversion device may be wholly or partially configured to be disposed in the user's mouth, for example. The aversion device may include a detector and a output device, wherein the detector is configured to detect a parameter indicative of the user engaging in the habit or undesirable activity. If (and only if) the detector detects such a parameter, the output device delivers a negative stimulus to the user, thus providing negative feedback and creating an incentive for the user to limit if not eliminate the undesirable activity.
Owner:PIVOT HEALTH TECH INC
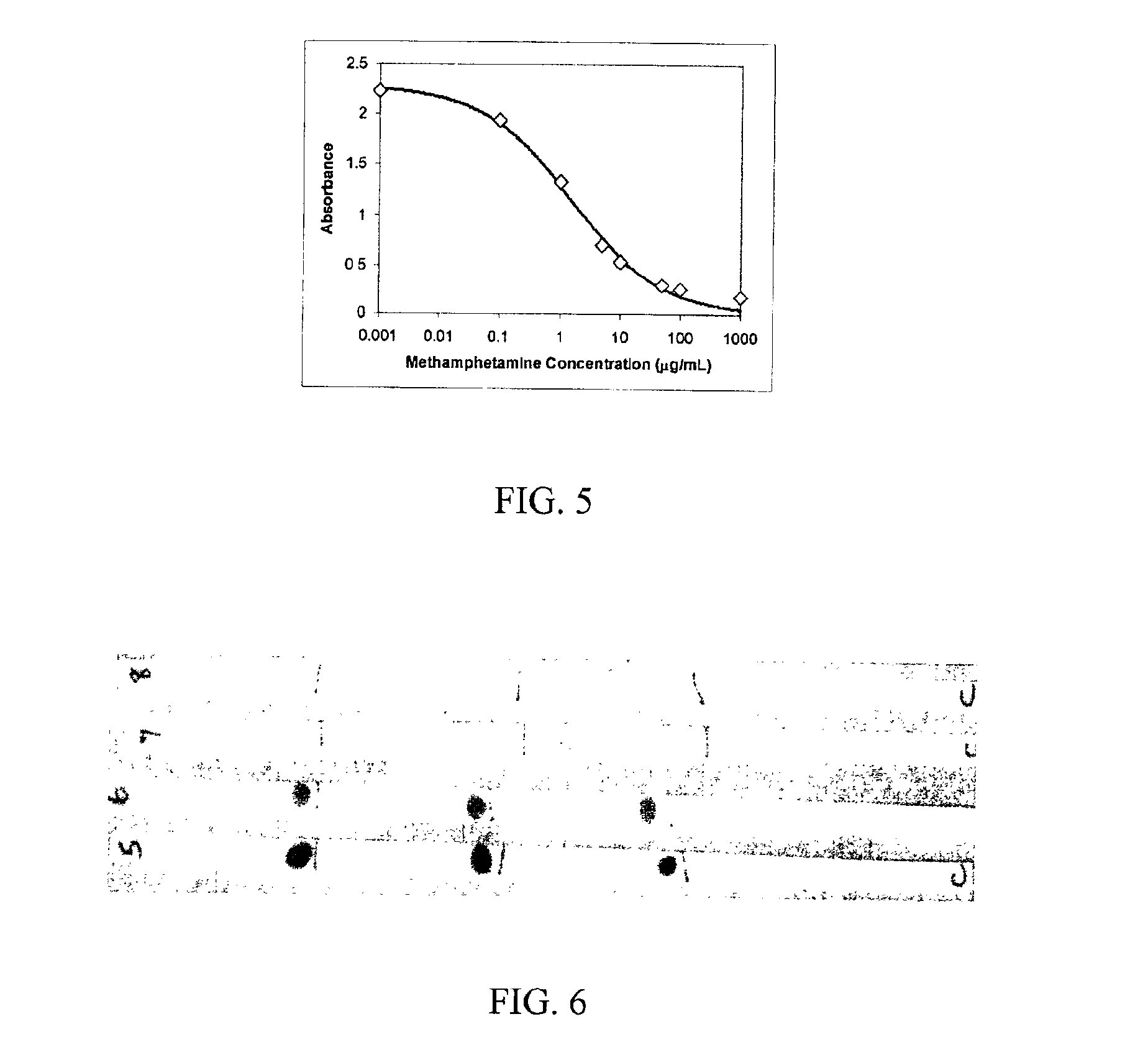
Rapid classification of biological components
InactiveUS6989276B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteImmune complex deposition
A method is disclosed for analyzing a biological sample by antibody profiling for identifying forensic samples or for detecting the presence of an analyte. In an illustrative embodiment of the invention, the analyte is a drug, such as marijuana, cocaine, methamphetamine, methyltestosterone, or mesterolone. The method involves attaching antigens to the surface of a solid support in a preselected pattern to form an array wherein the locations of the antigens are known; contacting the array with the biological sample such that a portion of antibodies in the sample reacts with and binds to antigens in the array, thereby forming immune complexes; washing away antibodies that do form immune complexes; and detecting the immune complexes, thereby forming an antibody profile. Forensic samples are identified by comparing a sample from an unknown source with a sample from a known source. Further, an assay, such as a test for illegal drug use, can be coupled to a test for identity such that the results of the assay can be positively correlated to the subject's identity.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Intraoral behavior monitoring and aversion devices and methods
InactiveUS20100209897A1Readily detect undesirable activityLimit ability of to remove and defeatTobacco devicesTeaching apparatusNegative feedbackIllicit drug
An intraoral behavior monitoring and aversion device to assist a user in quitting an undesirable behavior such as tobacco smoking, tobacco chewing, use of snuff, illicit drug use, excessive alcohol consumption, excessive food consumption, and / or other undesirable activity facilitated via the mouth. The aversion device may be wholly or partially configured to be disposed in the user's mouth, for example. The aversion device may include a detector and a output device, wherein the detector is configured to detect a parameter indicative of the user engaging in the habit or undesirable activity. If (and only if) the detector detects such a parameter, the output device may, optionally, deliver a negative stimulus to the user, thus providing negative feedback and creating an incentive for the user to limit if not eliminate the undesirable activity. The device may be configured to store and / or relay data representing sensed conditions in the mouth.
Owner:PIVOT HEALTH TECH INC
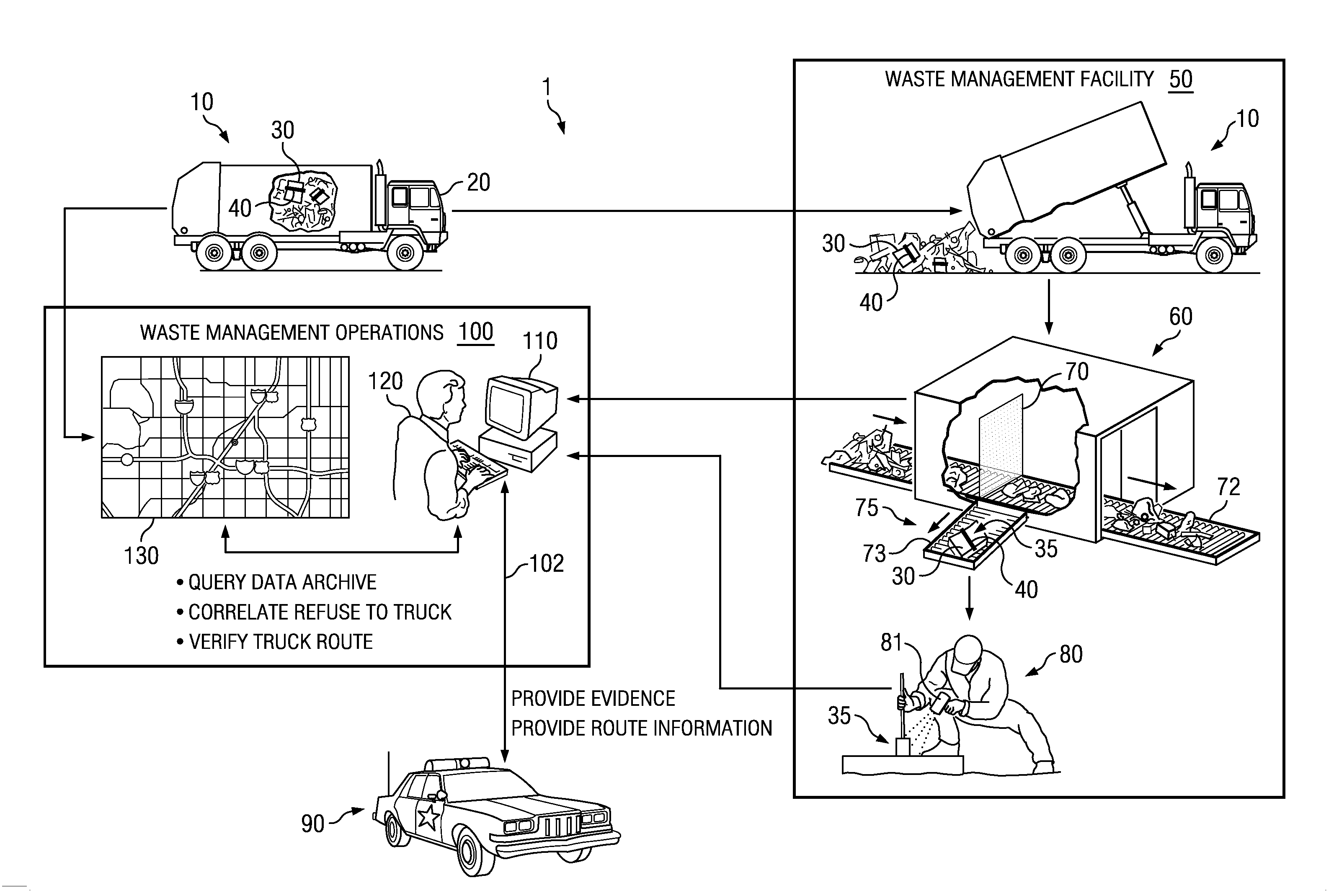
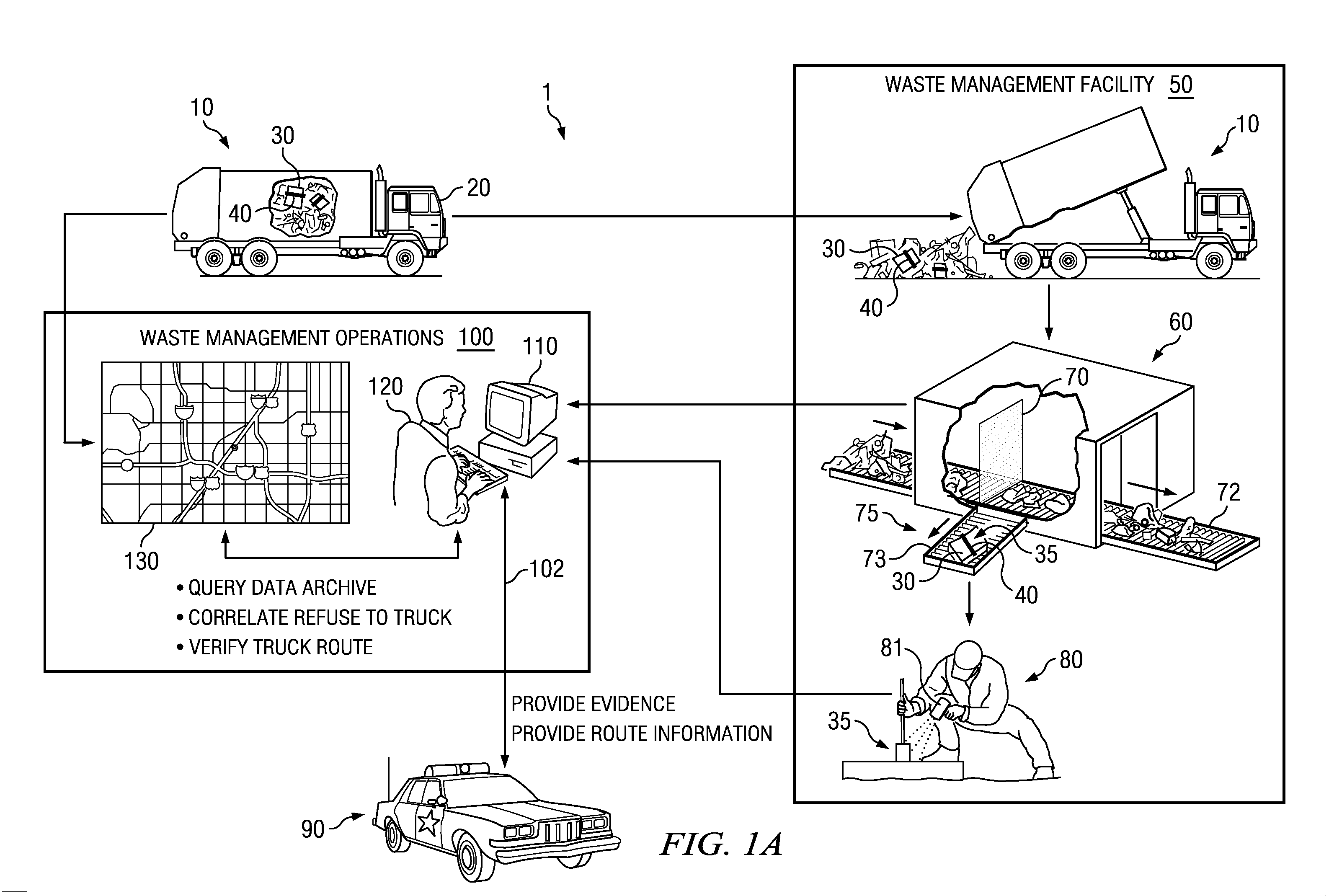
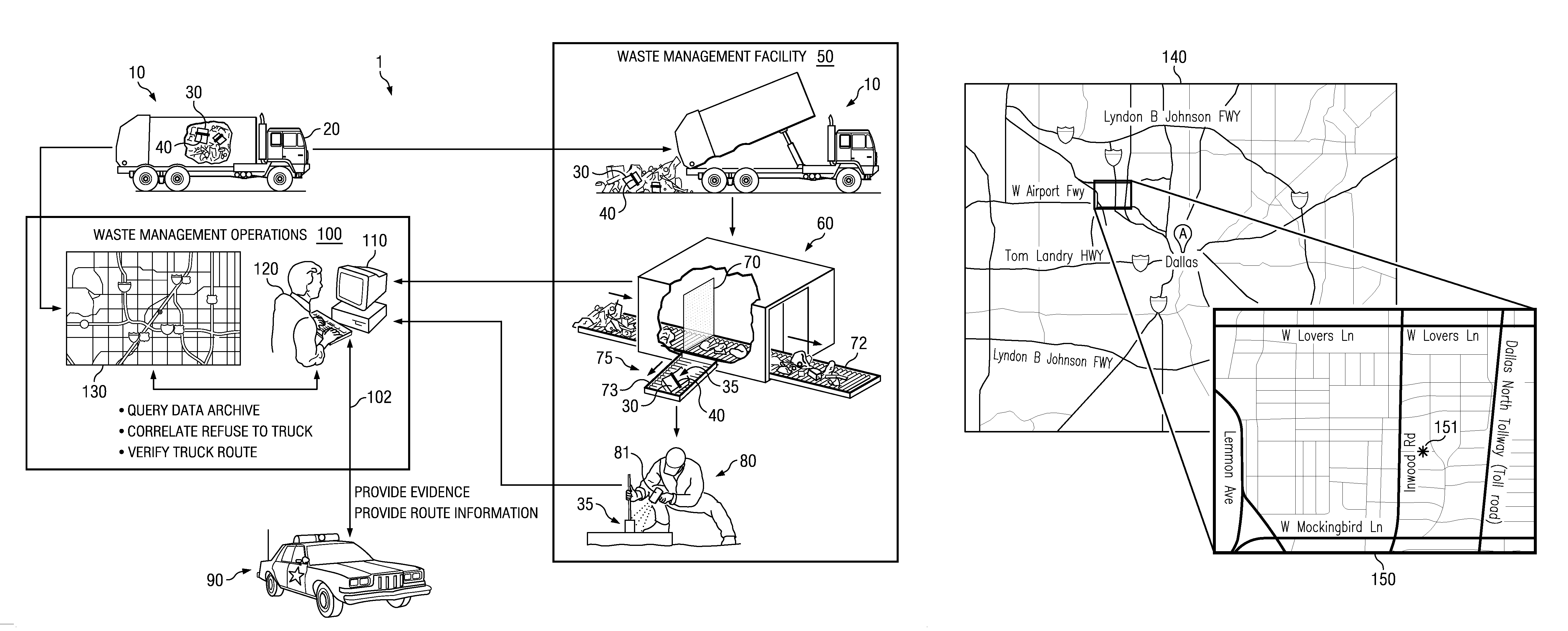
Systems and Methods for Detecting and Geo-Locating Hazardous Refuse
ActiveUS20110316689A1Reducing geographic areaLow costFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexParticulatesHazardous substance
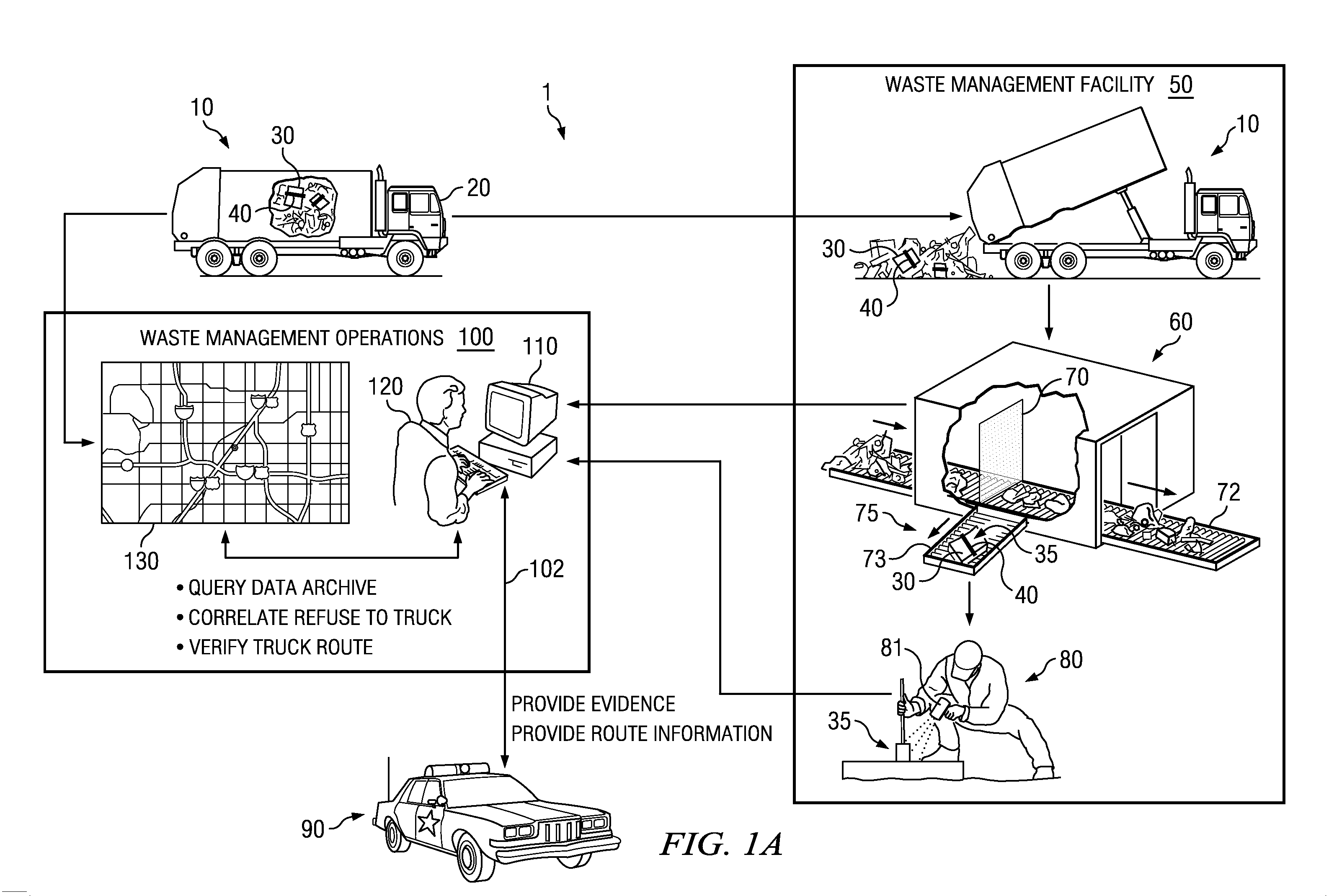
The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for scanning refuse (garbage, trash) from a large geographic area to detect the presence of hazardous materials in the refuse. Hazardous material may comprise CBRNE agents, components of terrorist devices, environmental pollutants and toxins and illegal drugs and may include trace particulates of such agents as well as by-products thereof. Systems and methods, according to some embodiments, may further comprise geo-locating to a small geographic area the origin of hazardous material. Accordingly, in some embodiments the disclosure provides systems and methods to geo-locate facilities or addresses where hazardous materials are generated, thereby geo-locating facilities that make terrorist devices, sources of environmental pollutants and / or sources of illegal drugs. According to some embodiments, systems and methods of the disclosure enable focusing efforts of law enforcement authorities to identify terrorists, drug activities and / or environmental offenders to small geographic areas (e.g. a street address).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
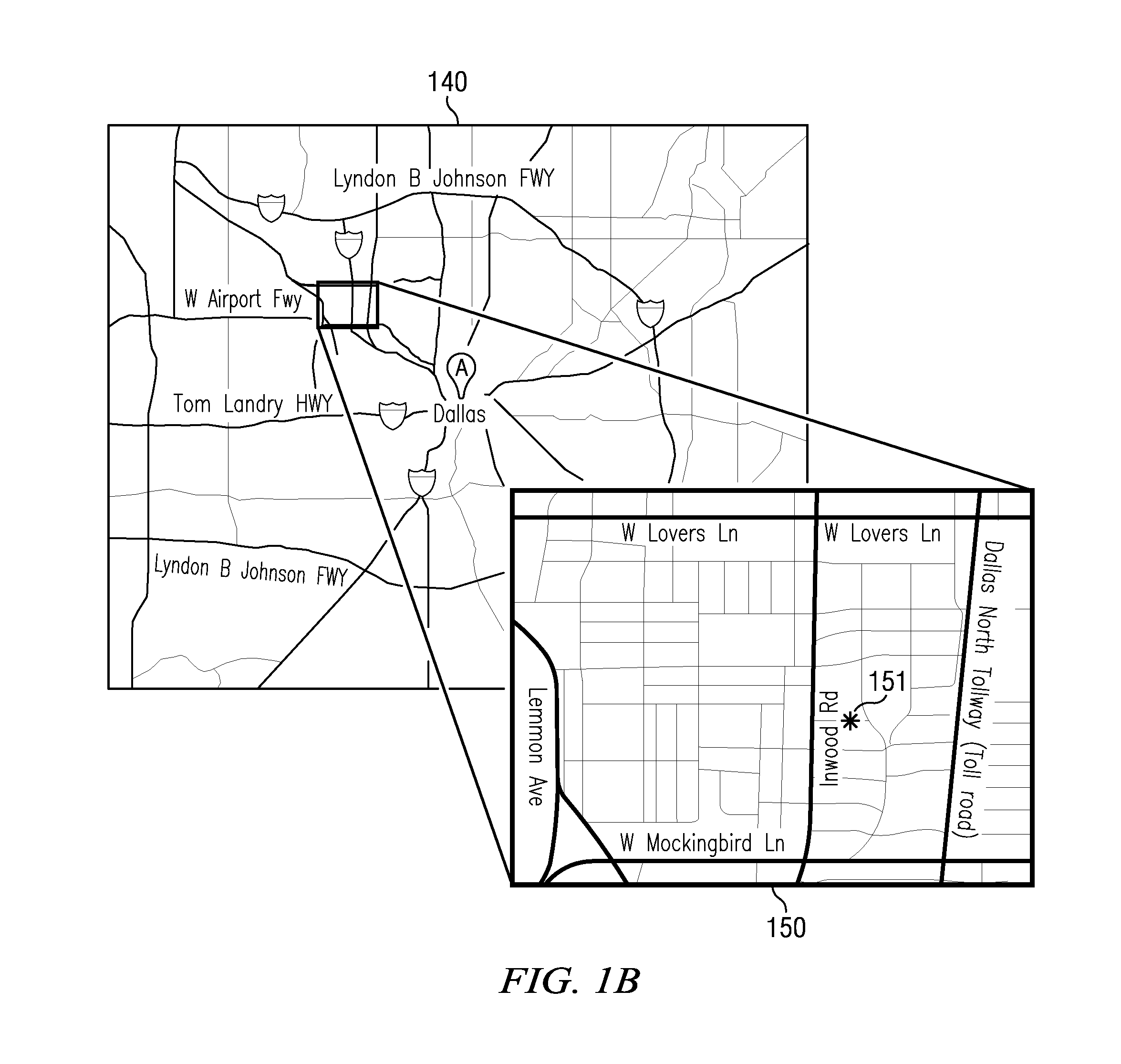
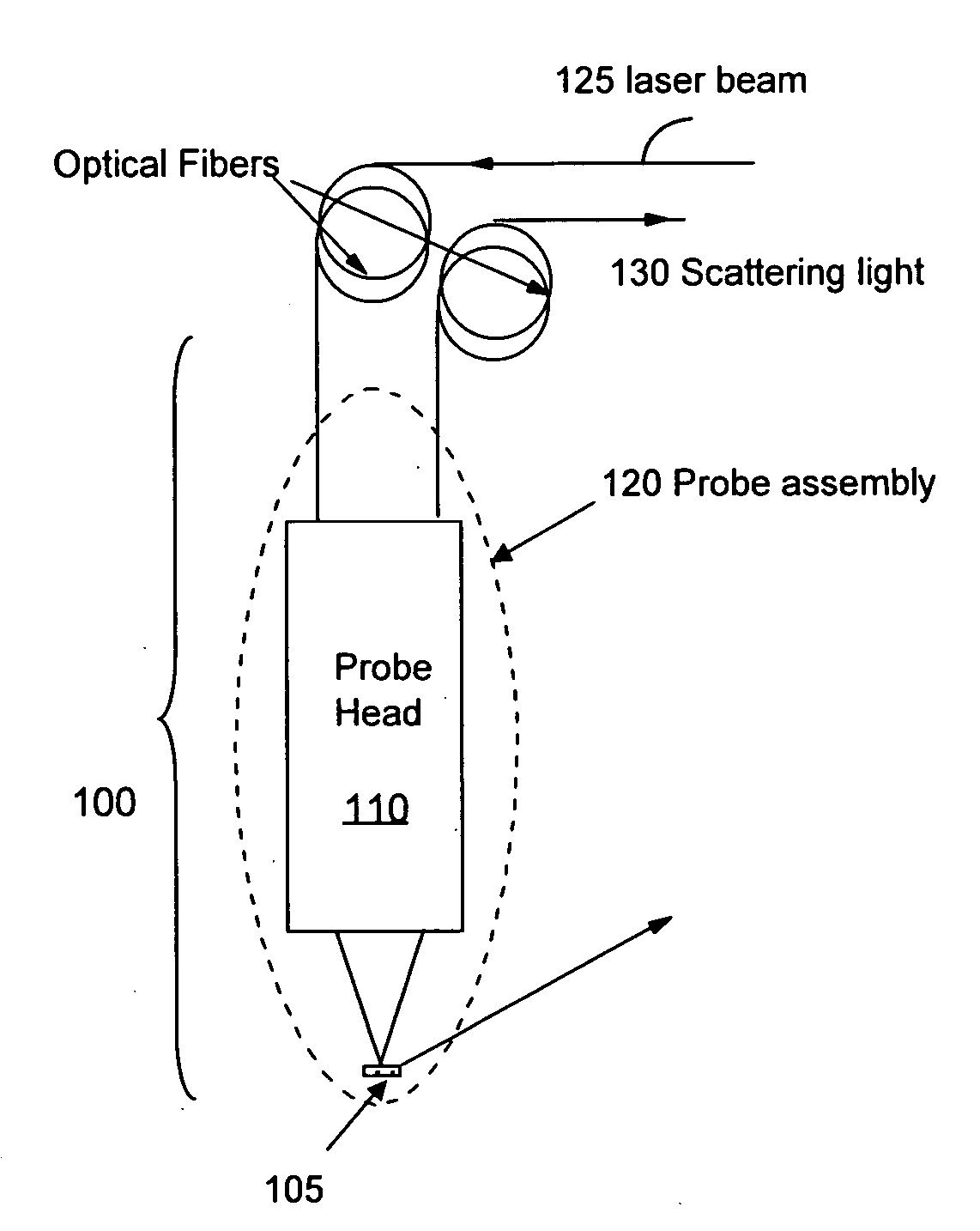
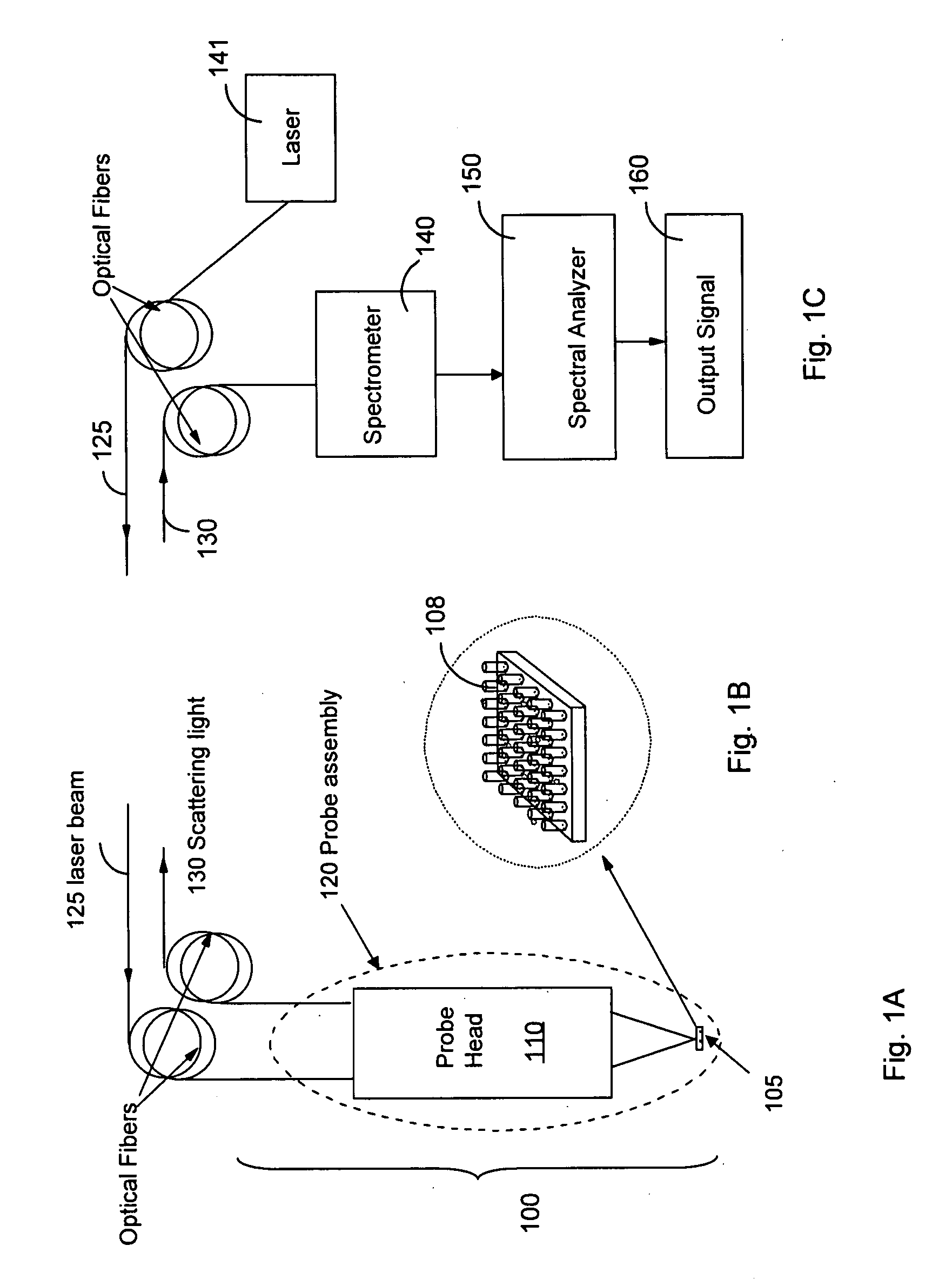
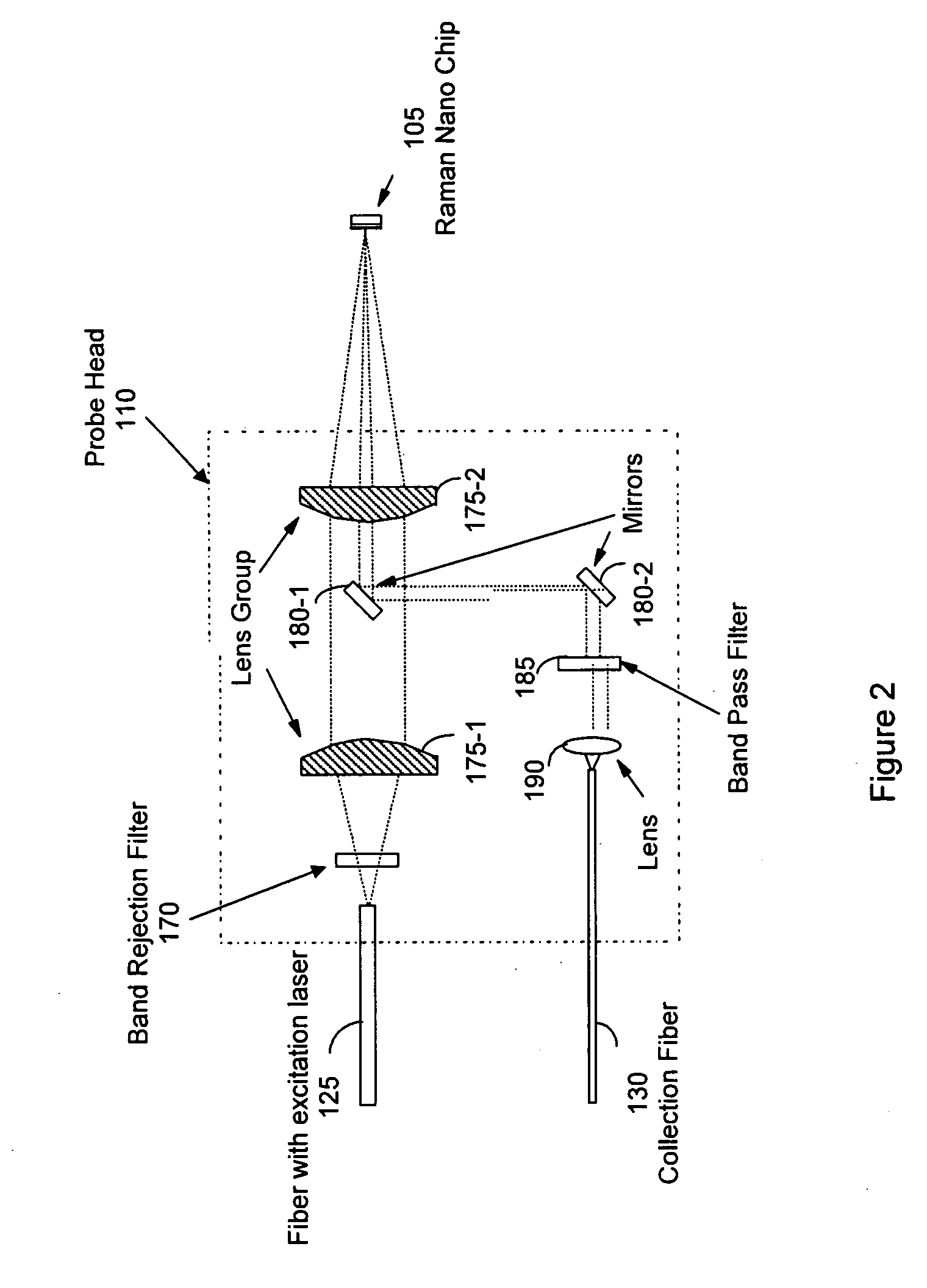
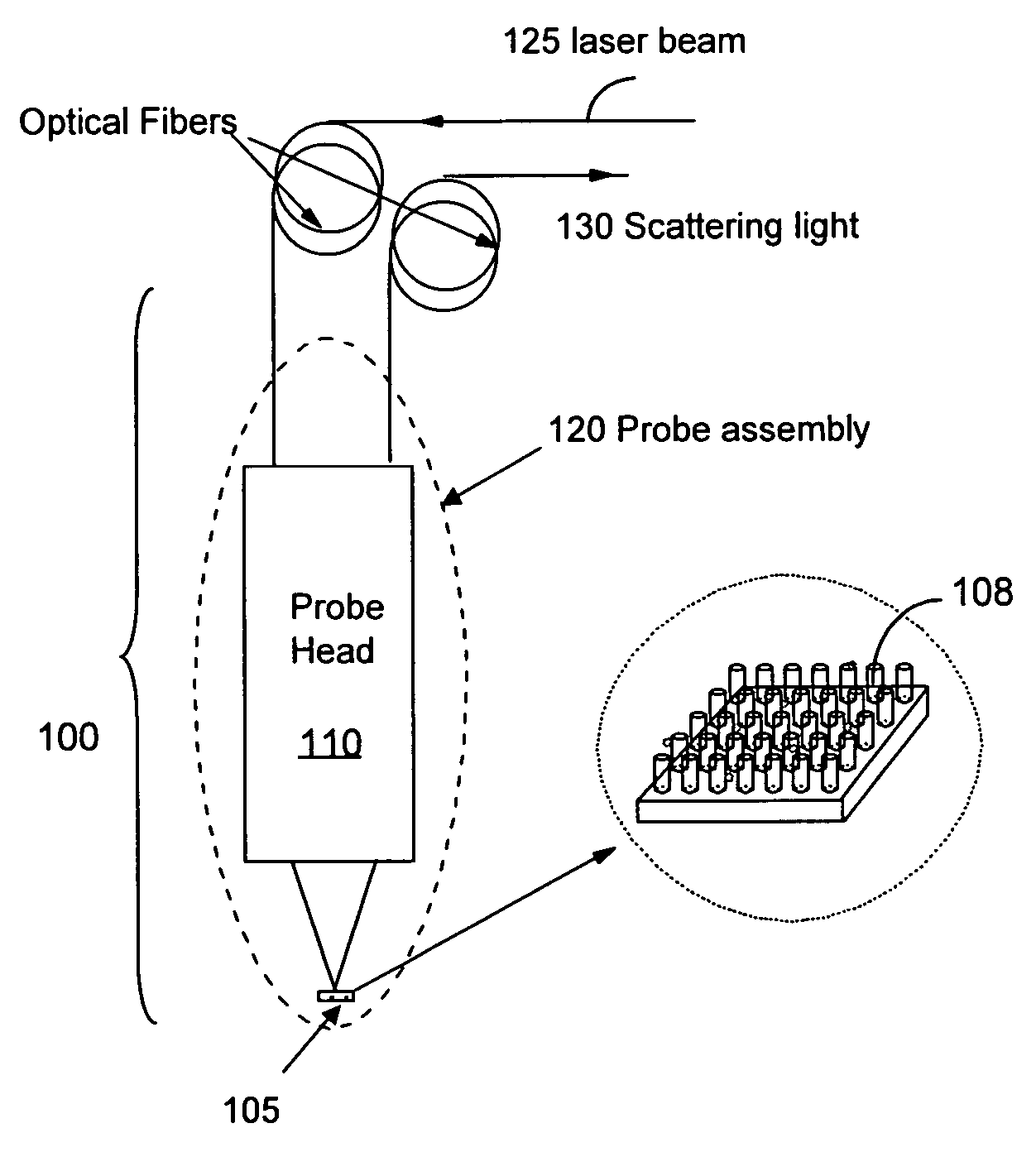
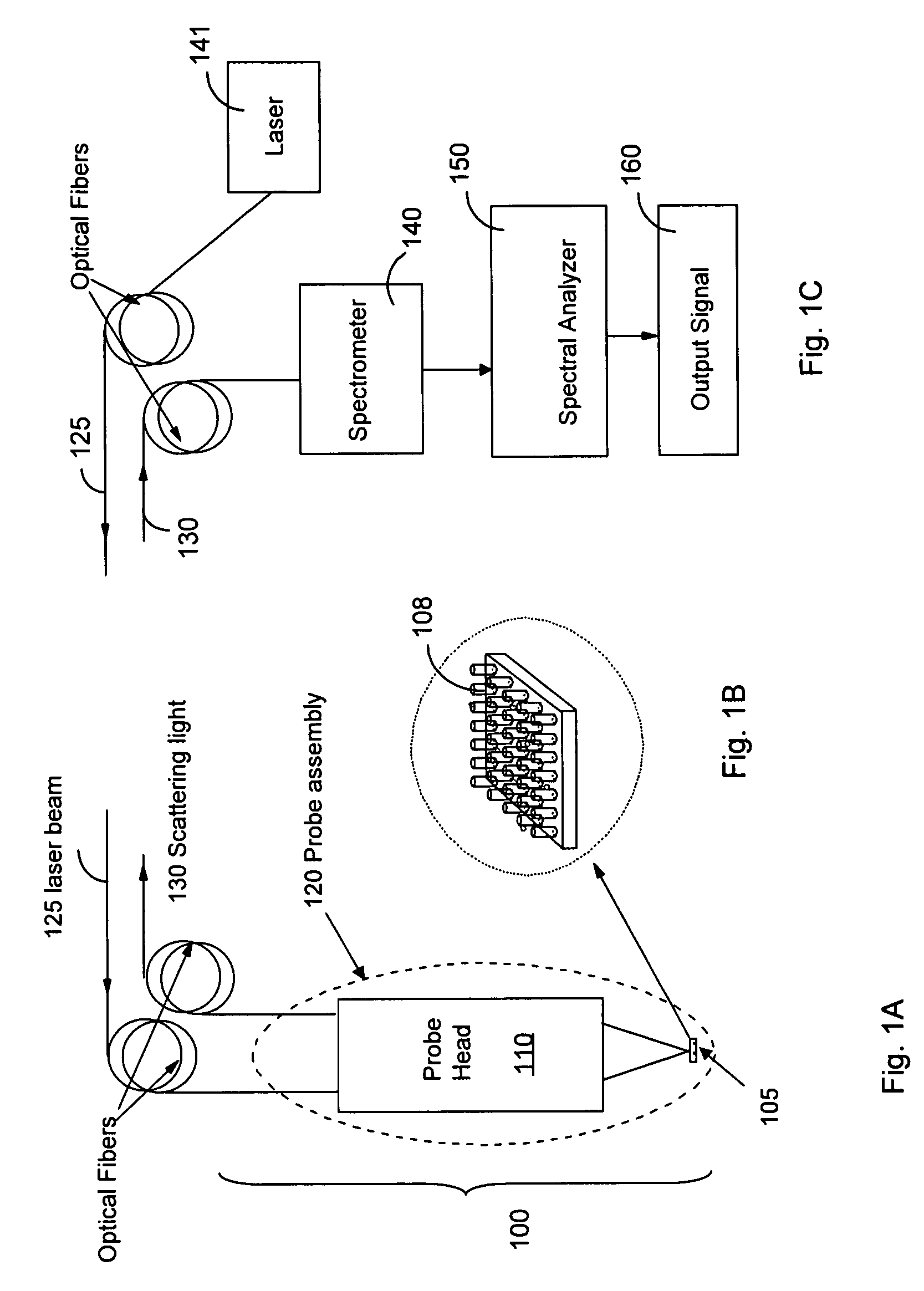
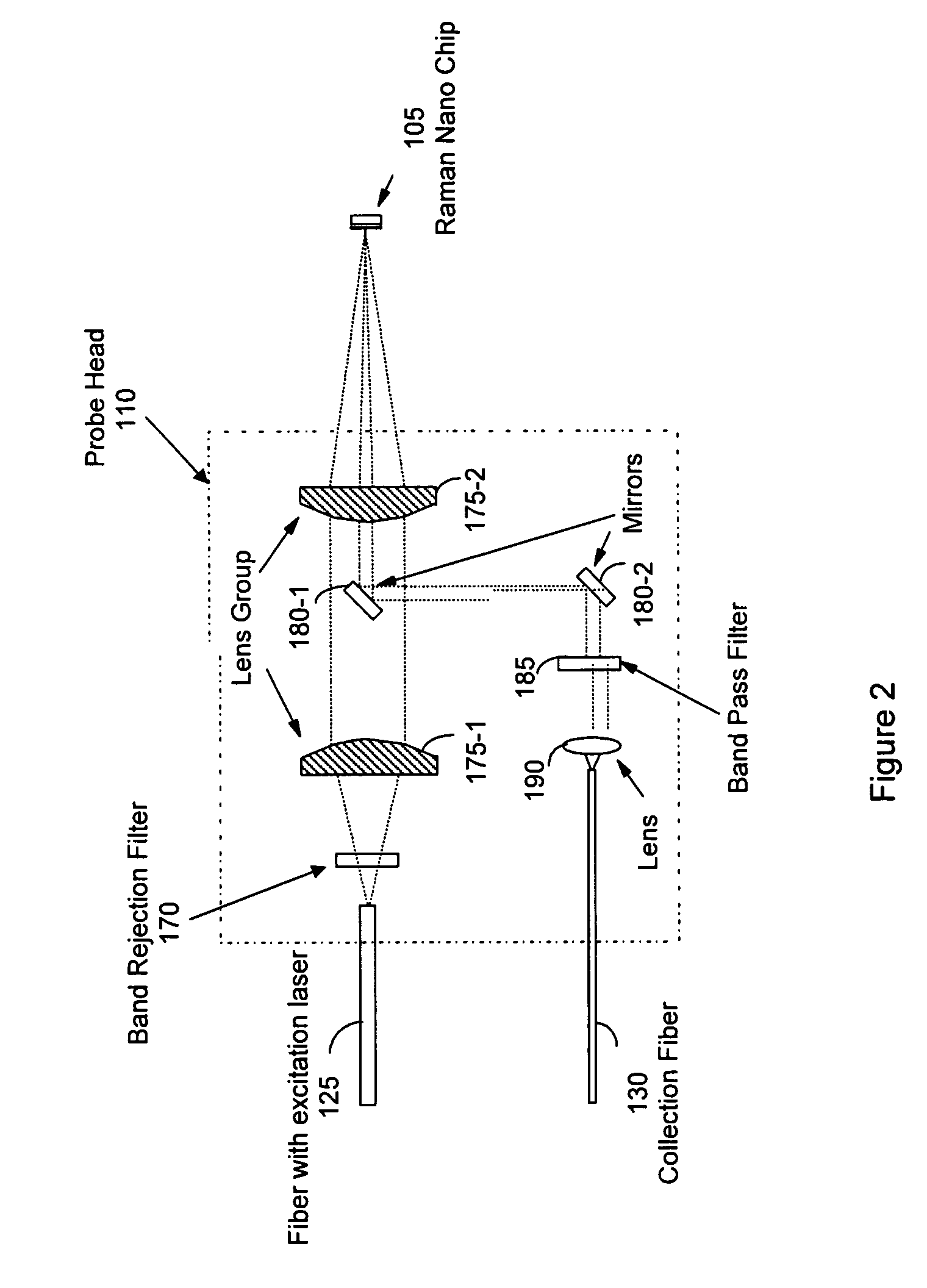
Non-invasive disease diagnosis using light scattering probe
ActiveUS20090086202A1Wide applicationExpected can be lowRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansIllicit drugSmoking status
A method for non-invasive detection of a disease, a status of illicit-drug use, or smoking status includes transferring a body fluid obtained from a patient to a sensor comprising a nano-scale surface structure to allow the body fluid to come in contact with the nano-scale surface structure, illuminating the body fluid and the nano-scale surface structure by a laser beam, scattering the laser beam by the body fluid and the nano-scale surface structure to produce a scattered light, and analyzing the scattered light using a spectral analyzer to diagnose a disease, the status of illicit-drug use, or smoking status in the patient.
Owner:EXCELLENT CAPACITY LTD
Personal illicit drug detection method
Personal illicit drug detecting apparatus is disclosed which includes a substance chemically reactive to a suspected drug. The substance is provided in the form of a layer positioned on at least one finger of a user. The substance can be blended into finger nail polish and positioned on at least one nail by painting or positioned anywhere on a finger in the form of a decal. To test a suspected beverage the user inconspicuously moistens the substance on the finger or finger nail with liquid from a beverage and observes any change (e.g. color, image, etc.) of the layer on the finger nail or finger nail, wherein the change indicates the presence of the suspected drug in the beverage.
Owner:NELSON JOELLEN +2
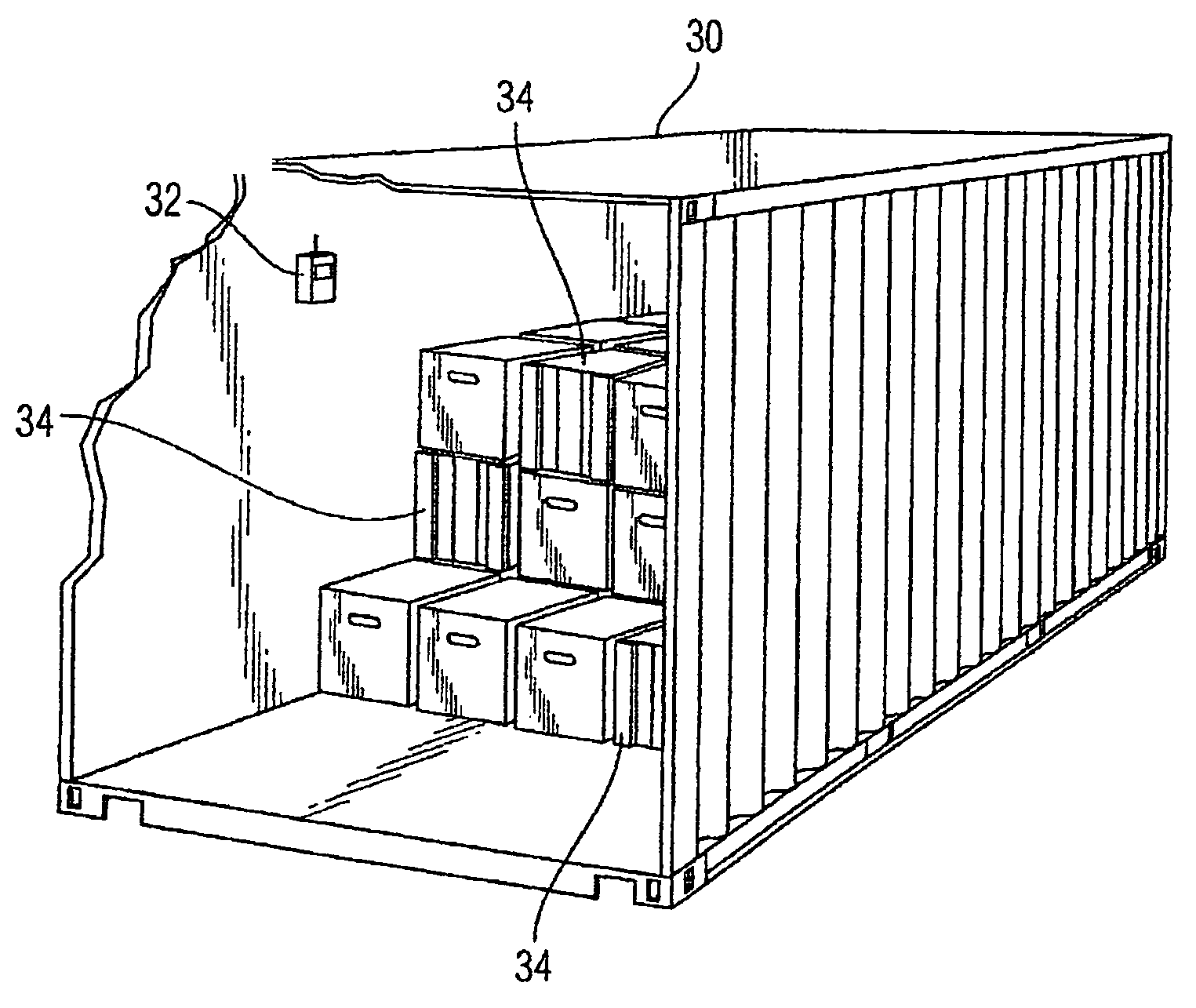
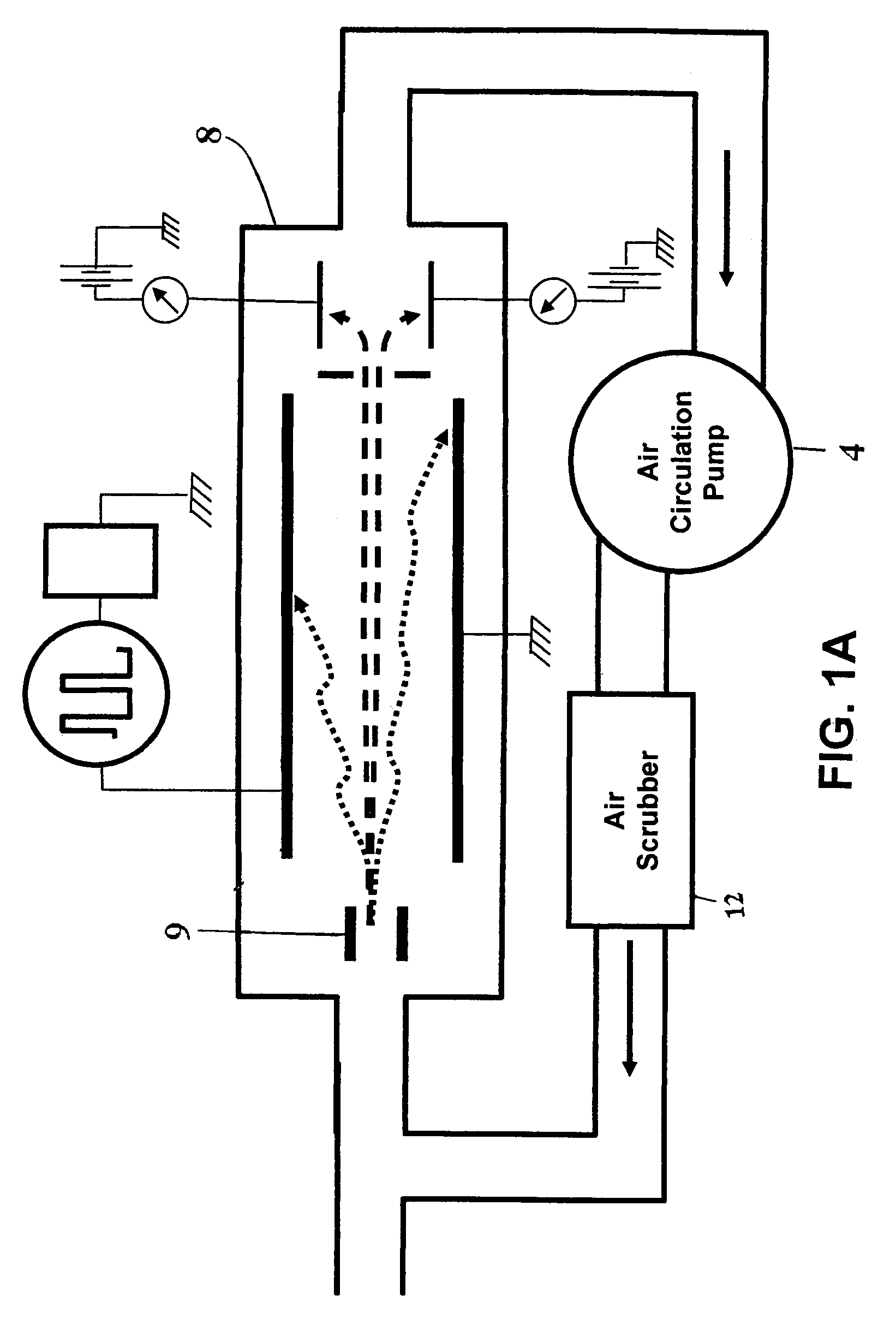
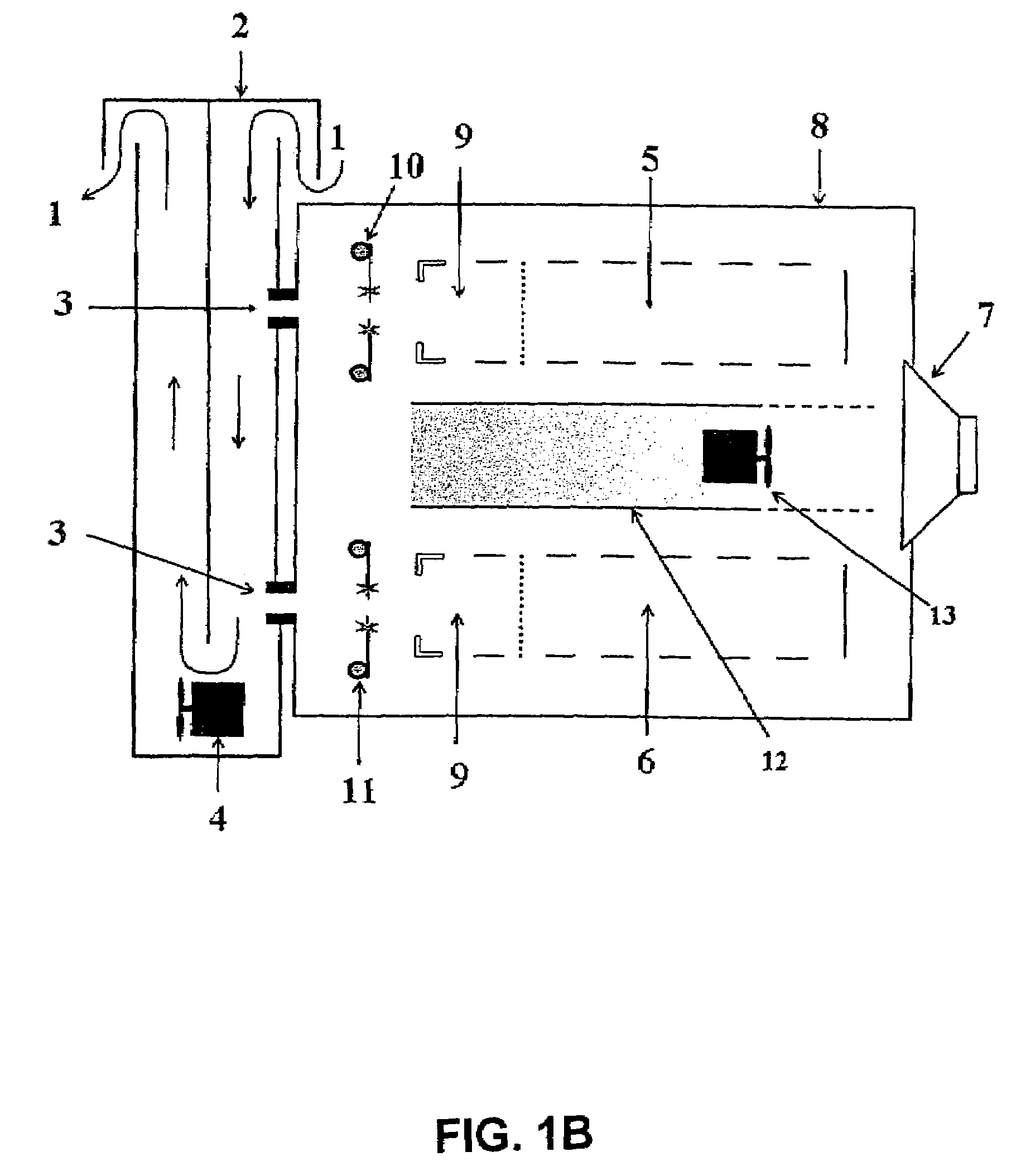
Detection and identification method for in-transit determination of chemical contraband, decaying animal and vegetable matter, and concealed humans in cargo shipping containers and other secure spaces
InactiveUS20070277589A1High sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUsing mechanical meansDeterministic analysisIllicit drug
A chemical analysis method for detecting, identifying and reporting contraband, illegal drugs, explosives, toxic chemicals, decaying animal and vegetable matter, and concealed human beings located in secure spaces such as cargo shipping containers. Chemical analysis results are accumulated and added to effect definitive analyses over extended periods of time while the containers are in transit. Individual containers are equipped with a device employing the method. The analysis method consists of accumulation and addition of analytical chemical instrumentation, measurements of trace quantities of target chemical vapors inside of shipping containers while the containers are in transit. Cumulative and additive spectrometric analyses coupled with increased target chemical concentrations, due to chemical vapor build up over the long periods of time that containers are in transit, result in significantly increased electronic signal-to-noise in spectrometric measurements and increased spectrometric signal strengths that are indicative of the presence of target chemicals.
Owner:HARDEN CHARLES S
Short-wave infrared super-continuum lasers for detecting counterfeit or illicit drugs and pharmaceutical process control
A system and method for using near-infrared or short-wave infrared (SWIR) light sources for identification of counterfeit drugs may perform spectroscopy using a super-continuum laser to provide detection in a non-contact and non-destructive manner at stand-off or remote distances with minimal sample preparation. Also, near-infrared or SWIR light may penetrate through plastic containers and packaging, permitting on-line inspection and rapid scanning. The near-infrared or SWIR spectroscopy may also be used to detect illicit drugs and their chemical composition. Moreover, the spectroscopic techniques may also be applied to quality assessment and control in pharmaceutical manufacturing, thus permitting the implementation of smart manufacturing with feedback control. Fiber super-continuum lasers may emit light in the near-infrared or SWIR between approximately 1.4-1.8 microns, 2-2.5 microns, 1.4-2.4 microns, 1-1.8 microns. In particular embodiments, the detection system may be a dispersive spectrometer, a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, or a hyper-spectral imaging detector or camera.
Owner:OMNI MEDSCI INC
Detection and identification method for in-transit determination of chemical contraband, decaying animal and vegetable matter, and concealed humans in cargo shipping containers and other secure spaces
InactiveUS7468672B2High sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAlarmsDeterministic analysisIllicit drug
A chemical analysis method for detecting, identifying and reporting contraband, illegal drugs, explosives, toxic chemicals, decaying animal and vegetable matter, and concealed human beings located in secure spaces such as cargo shipping containers. Chemical analysis results are accumulated and added to effect definitive analyses over extended periods of time while the containers are in transit. Individual containers are equipped with a device employing the method. The analysis method consists of accumulation and addition of analytical chemical instrumentation, measurements of trace quantities of target chemical vapors inside of shipping containers while the containers are in transit. Cumulative and additive spectrometric analyses coupled with increased target chemical concentrations, due to chemical vapor build up over the long periods of time that containers are in transit, result in significantly increased electronic signal-to-noise in spectrometric measurements and increased spectrometric signal strengths that are indicative of the presence of target chemicals.
Owner:HARDEN CHARLES S
Systems and methods for detecting and geo-locating hazardous refuse
ActiveUS8384540B2Reduce areaLow costFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexParticulatesHazardous substance
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Process for control of restricted product sales in accordance with legal restrictions and expedited creation of a customer log
InactiveUS20070124170A1SpeedProcessing speedOffice automationIndividual entry/exit registersPharmacyCommon cold
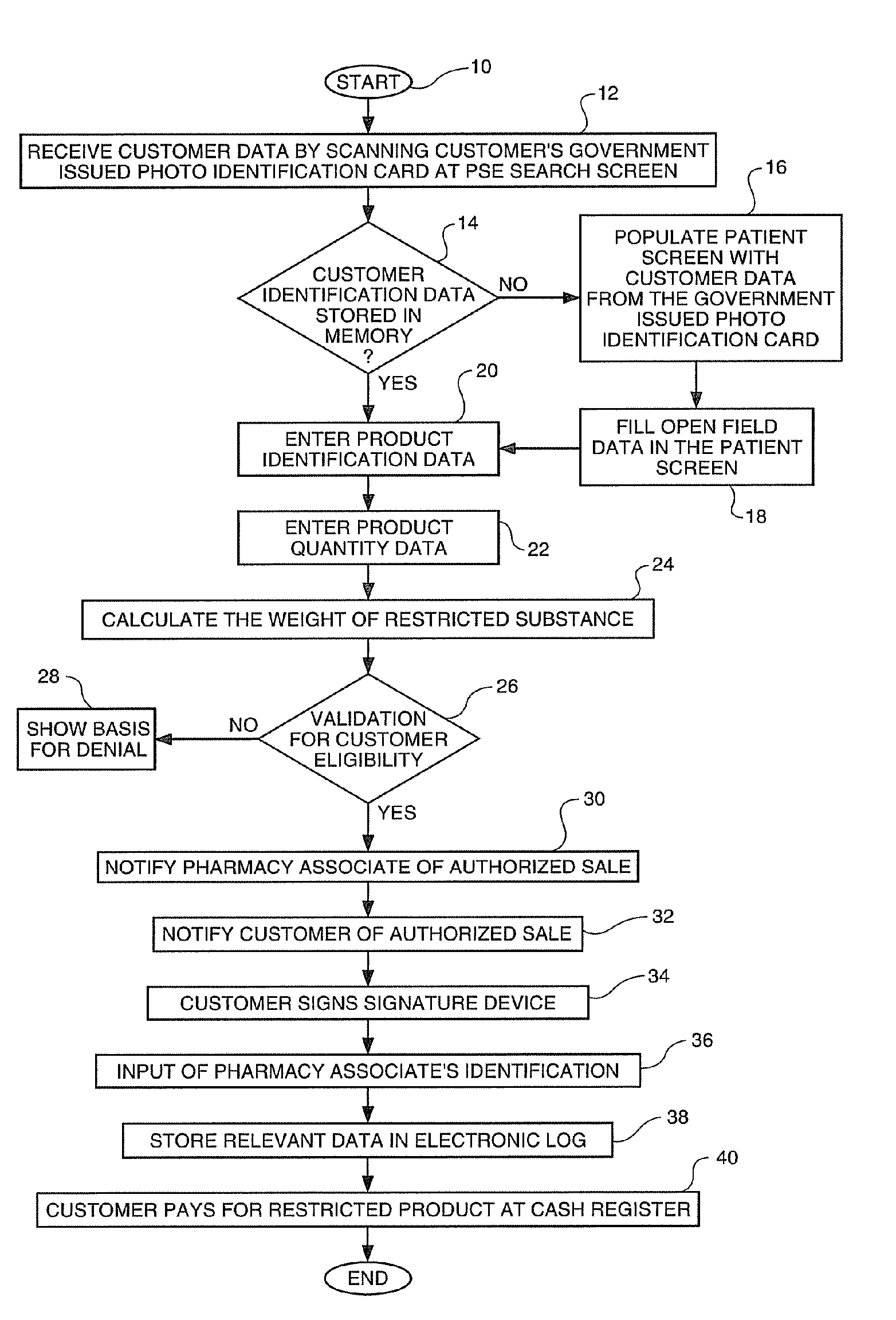
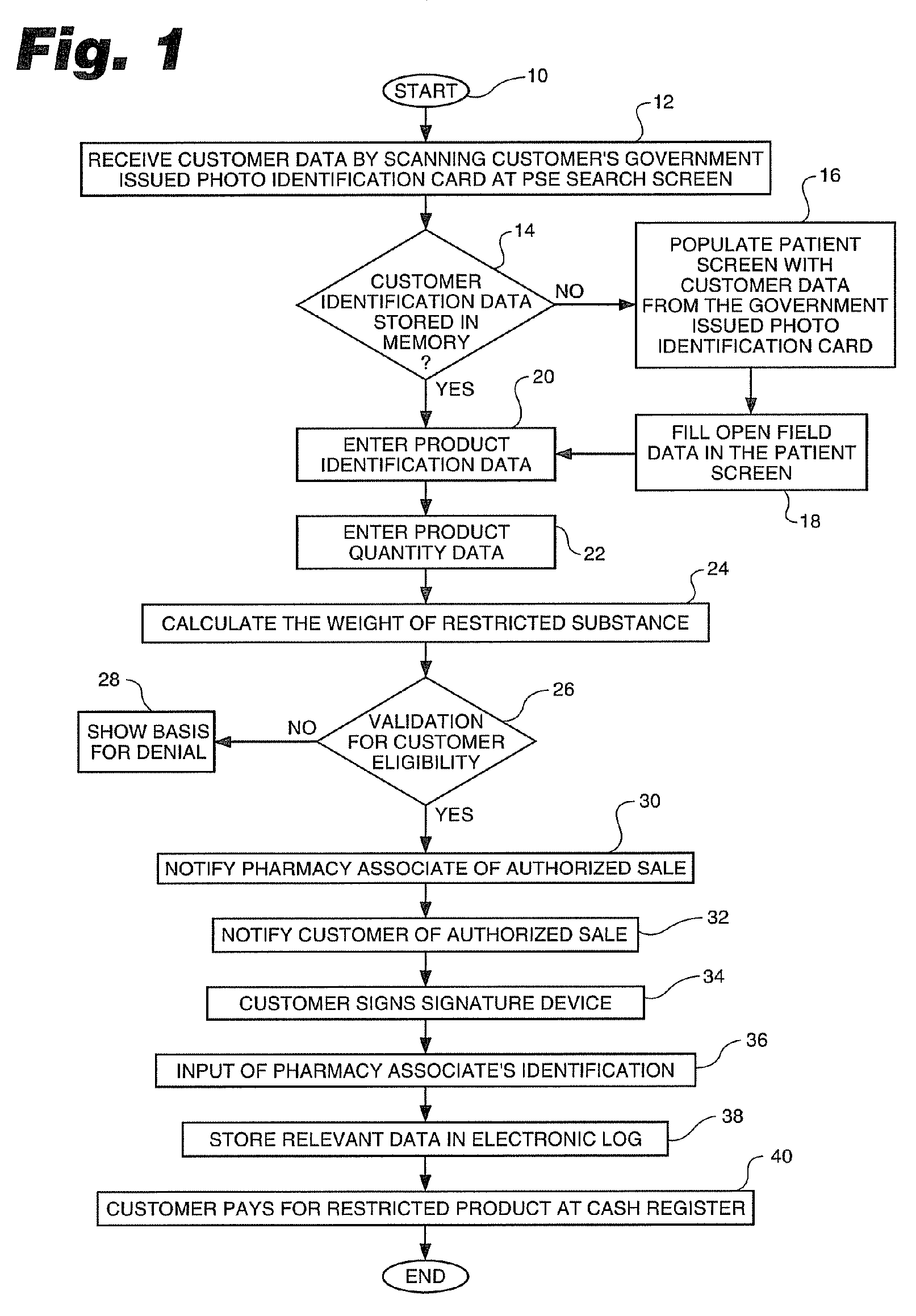
In an effort to control the production of illegal drugs such as methamphetamine, new statutes have placed restrictions on the sale of common cold remedies that contain pseudoephedrine and other precursors used in the production of these illegal drugs. Many common products, such as Sudafed® cold medicine, have been removed from store shelves and are now behind the counter at most pharmacies. These legal restrictions vary from state to state, but most restrict the amount of product that can be purchased by quantity and time. These legal restrictions also require creation of a customer log that often includes the customer's name, address, government-issued photo identification number and / or signature. Clearance of these restricted product sales and creation of the customer log are time consuming tasks that result in long lines during the winter season. The present invention is an automated process to speed up the authorization process and creation of the customer logs. The process can be applied to a single store or multiple stores. The invention also includes a clearance terminal especially adapted for this process.
Owner:WALMART APOLLO LLC
Antibody profiling sensitivity through increased reporter antibody layering
InactiveUS7695919B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune complex formationImmune complex deposition
A method for analyzing a biological sample by antibody profiling for identifying forensic samples or for detecting the presence of an analyte. In an embodiment of the invention, the analyte is a drug, such as marijuana, Cocaine (crystalline tropane alkaloid), methamphetamine, methyltestosterone, or mesterolone. The method comprises attaching antigens to a surface of a solid support in a preselected pattern to form an array wherein locations of the antigens are known; contacting the array with the biological sample such that a portion of antibodies in the sample reacts with and binds to the antigens in the array to form immune complexes; washing away antibodies that do form immune complexes; and detecting the immune complexes, to form an antibody profile. Forensic samples are identified by comparing a sample from an unknown source with a sample from a known source. Further, an assay, such as a test for illegal drug use, can be coupled to a test for identity such that the results of the assay can be positively correlated to the subject's identity.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
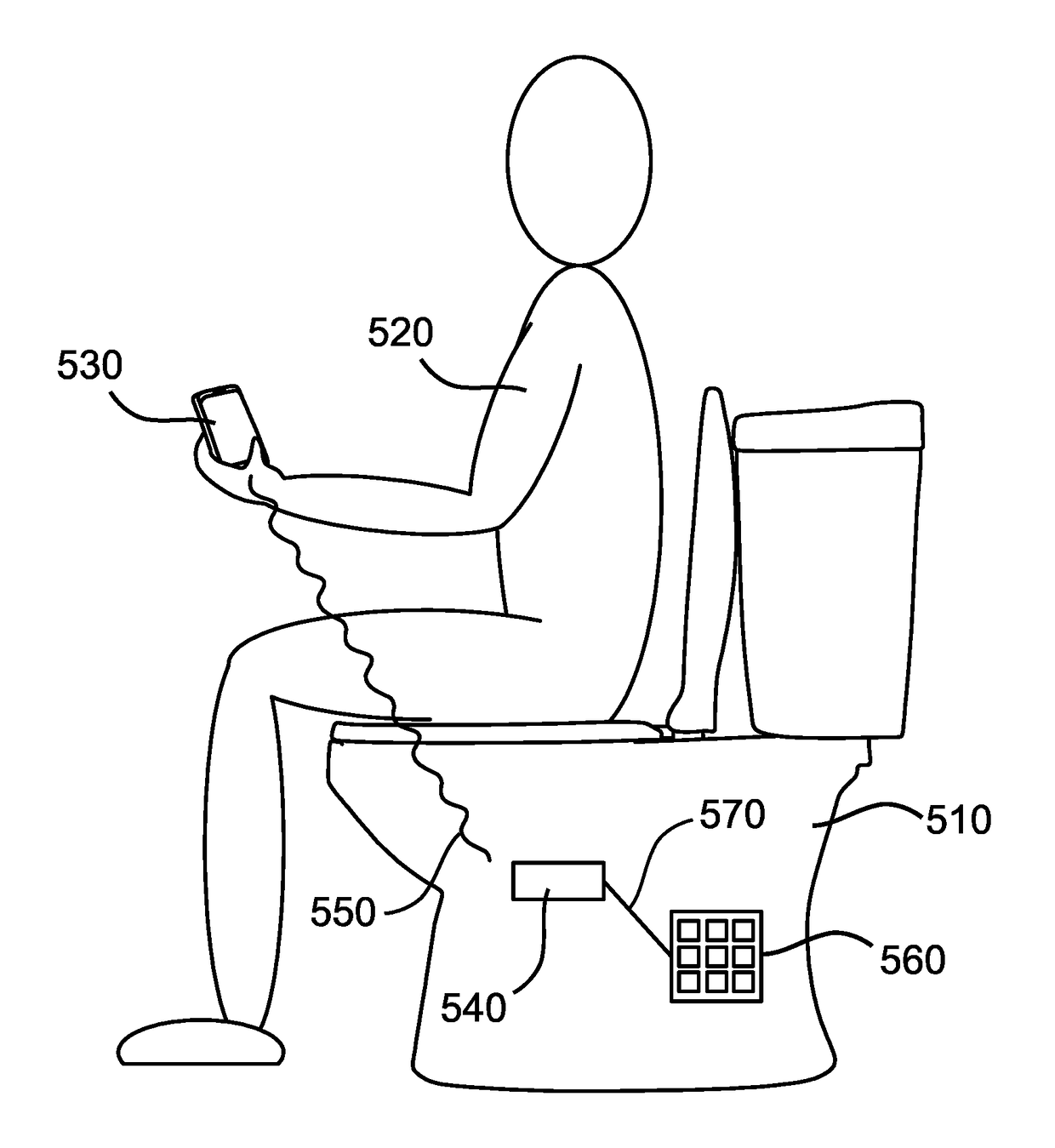
Toilet that detects drug markers and methods of use thereof
The present disclosure describes a method of detecting a drug marker in urine a urine sample using a toilet. The drug markers are fluorophores each of which emits a unique fluorescence spectra. Accordingly, the method does not detect the drug but rather, the drug marker. A user who has consumed the drug with its unique drug marker then urinates into the toilet and a urine sample is captured. The toilet includes a mechanism for fluid handling which diverts urine into a fluorescence spectrometer. The fluorescence spectrometer screens the urine for drug markers based on their unique fluorescent spectra. The toilet may include a controller which quantifies the drug marker. The fluorescent spectrometer may detect multiple drug markers in a single urine sample. This method may be used to confirm drug compliance, test for illicit drugs, identify amounts of drugs consumed, and other uses described herein.
Owner:MEDIC INC
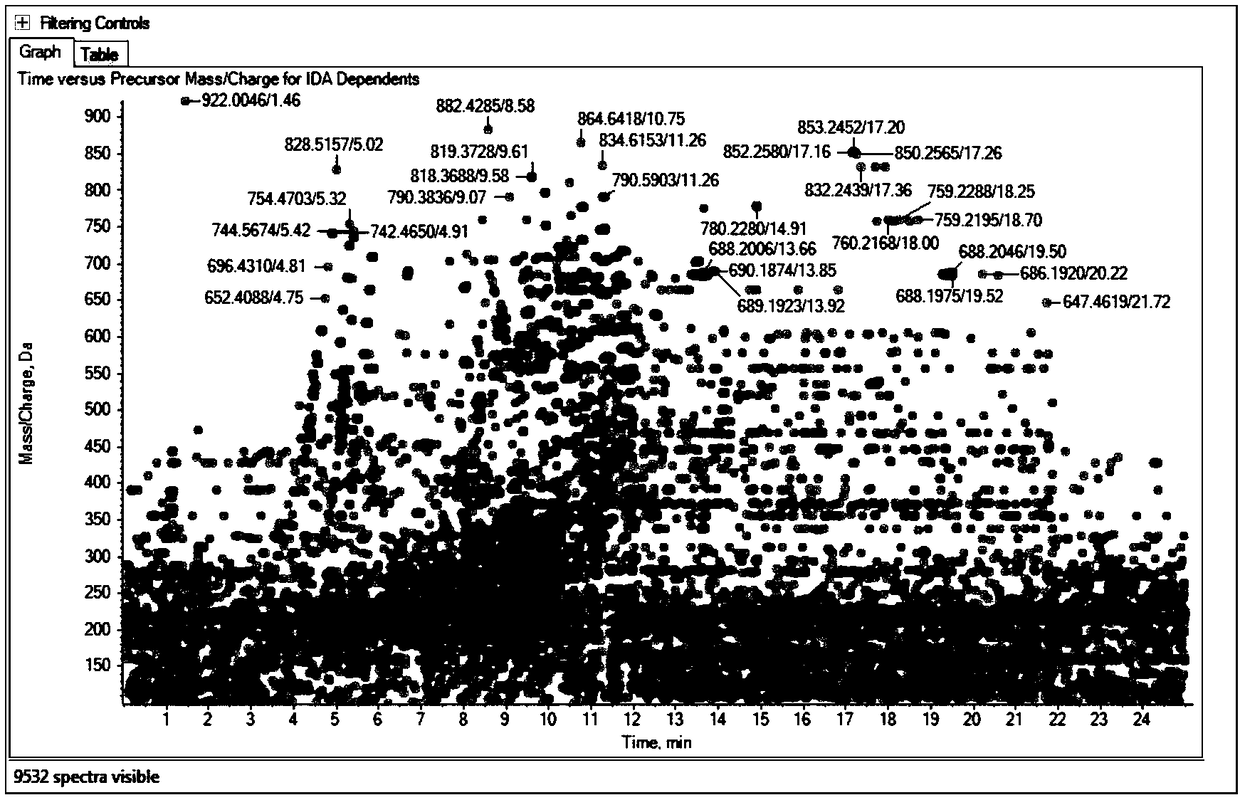
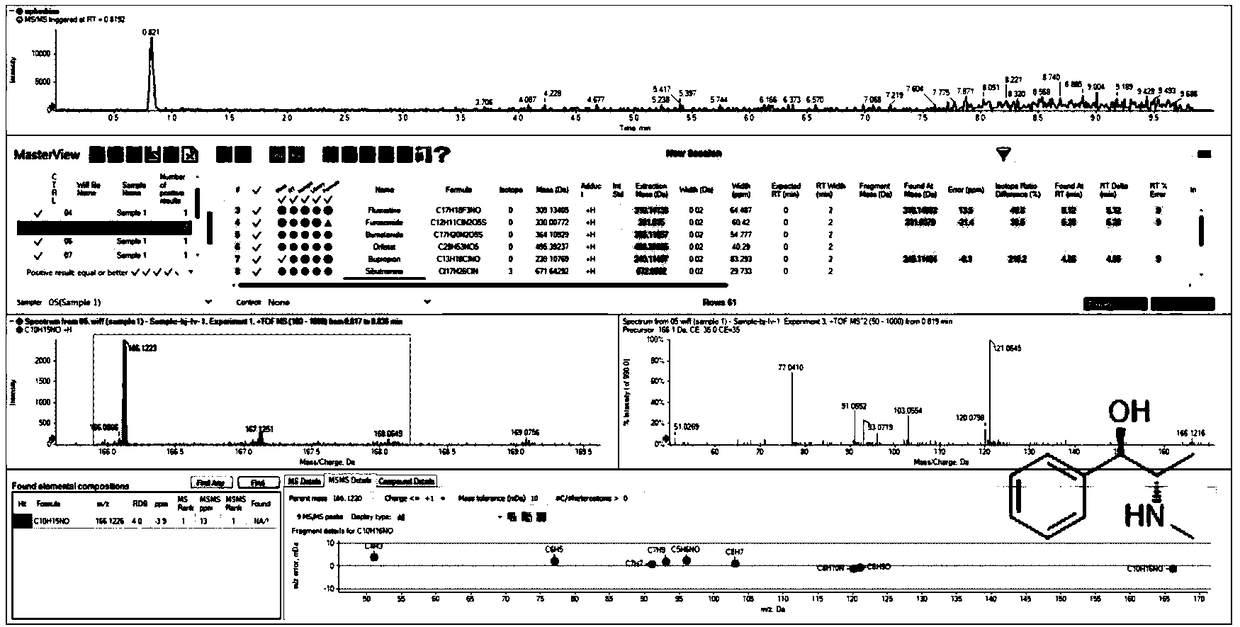
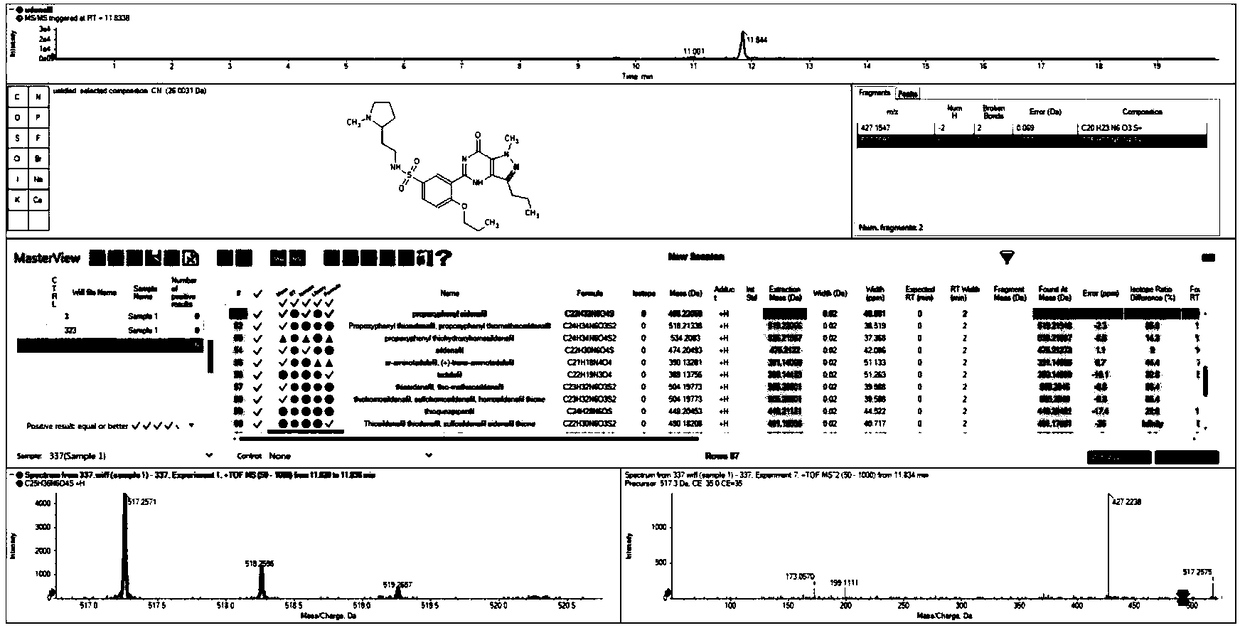
Non-target substance rapid detection method for illicit drugs in health food
InactiveCN108303486AReduce matrix effectImprove accuracyComponent separationSwath msAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a full-scan and high-throughput rapid screening detection method for illicit drugs in a health food. Data-dependent acquisition (IDA-MS) and data-independent acquisition (SWATH-MS) high-resolution mass spectrometry technologies are combined with Chemspider and an ACS compound structure database, illegally added western medicine ingredients in the health food are rapidly screened and analyzed according to the accurate parent ion and fragment molecular weights of primary mass spectrometry and secondary mass spectrometry and isotope peaks and other high-resolution mass spectrometry data information in the absence of a standard substance, and illicit drug ingredients in the health food are qualitatively identified under an unknown target substance condition in order toovercome the non-target substance detection problem of the health food. The method has the advantages of high-throughput analysis of the target substances, small matrix effect, high accuracy, simplicity in pretreatment, fastness, accuracy, small false negative error and small false positive error.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Use of N-aryl diazaspiracyclic compounds in the treatment of addiction
InactiveUS20060058328A1Reduces dopamine releaseReduce releaseBiocideNervous disorderMetaboliteSide effect
Compounds, compositions and methods for treating drug addiction, nicotine addiction, and / or obesity are disclosed. The compounds are N-aryl diazaspirocyclic compounds, bridged analogs of N-heteroaryl diazaspirocyclic compounds, or prodrugs or metabolites of these compounds. The aryl group can be a five- or six-membered heterocyclic ring (heteroaryl). The compounds are effective at inhibiting dopamine production and / or secretion, and accordingly are effective at inhibiting the physiological “reward” process that is associated with ingestion of nicotine and / or illicit drugs. The compounds and compositions can be administered in effective amounts to inhibit dopamine release, without resulting in appreciable adverse side effects (e.g., side effects such as significant increases in blood pressure and heart rate, significant negative effects upon the gastro-intestinal tract, and significant effects upon skeletal muscle).
Owner:BHATTI BALWINDER S +2
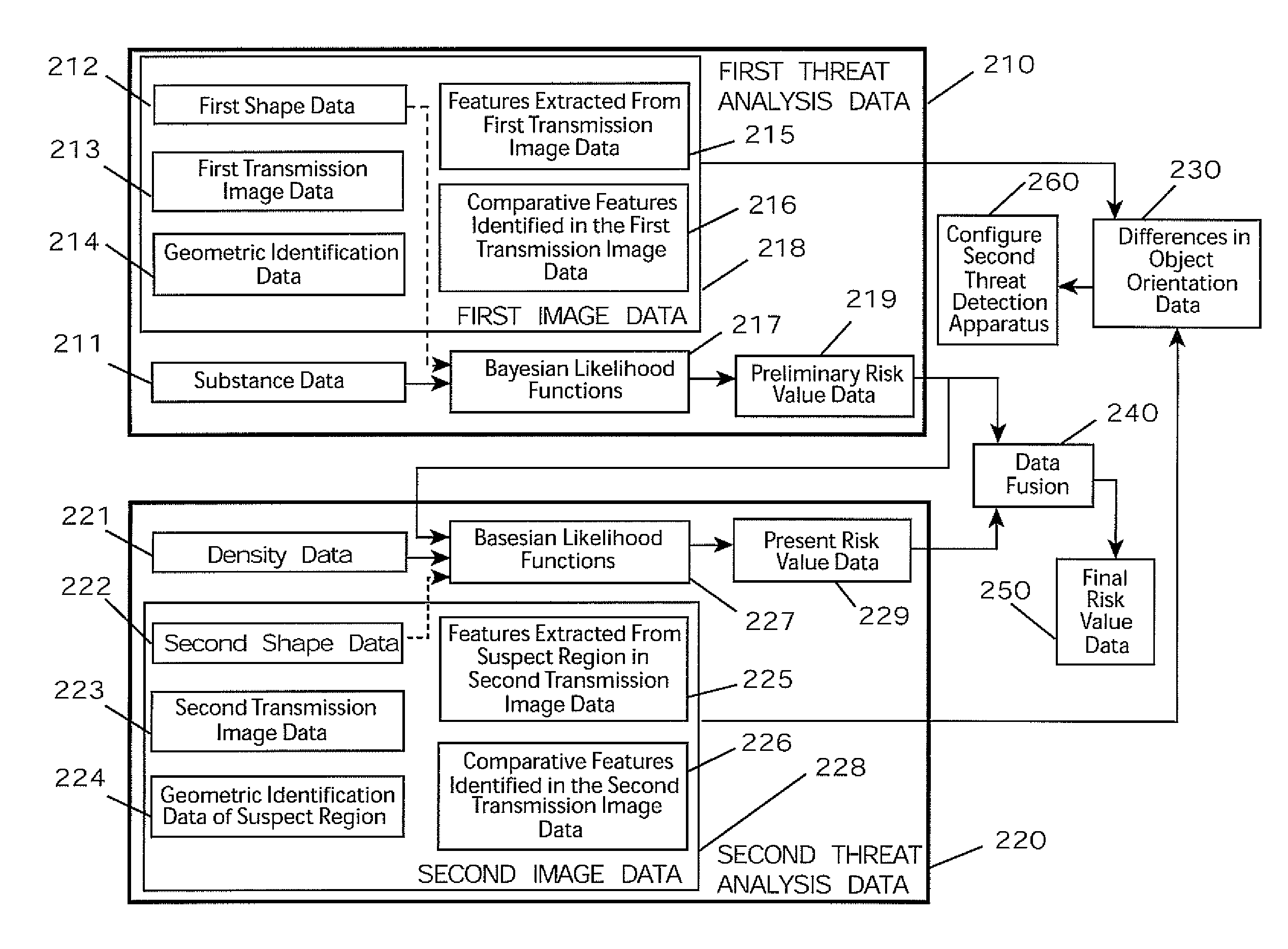
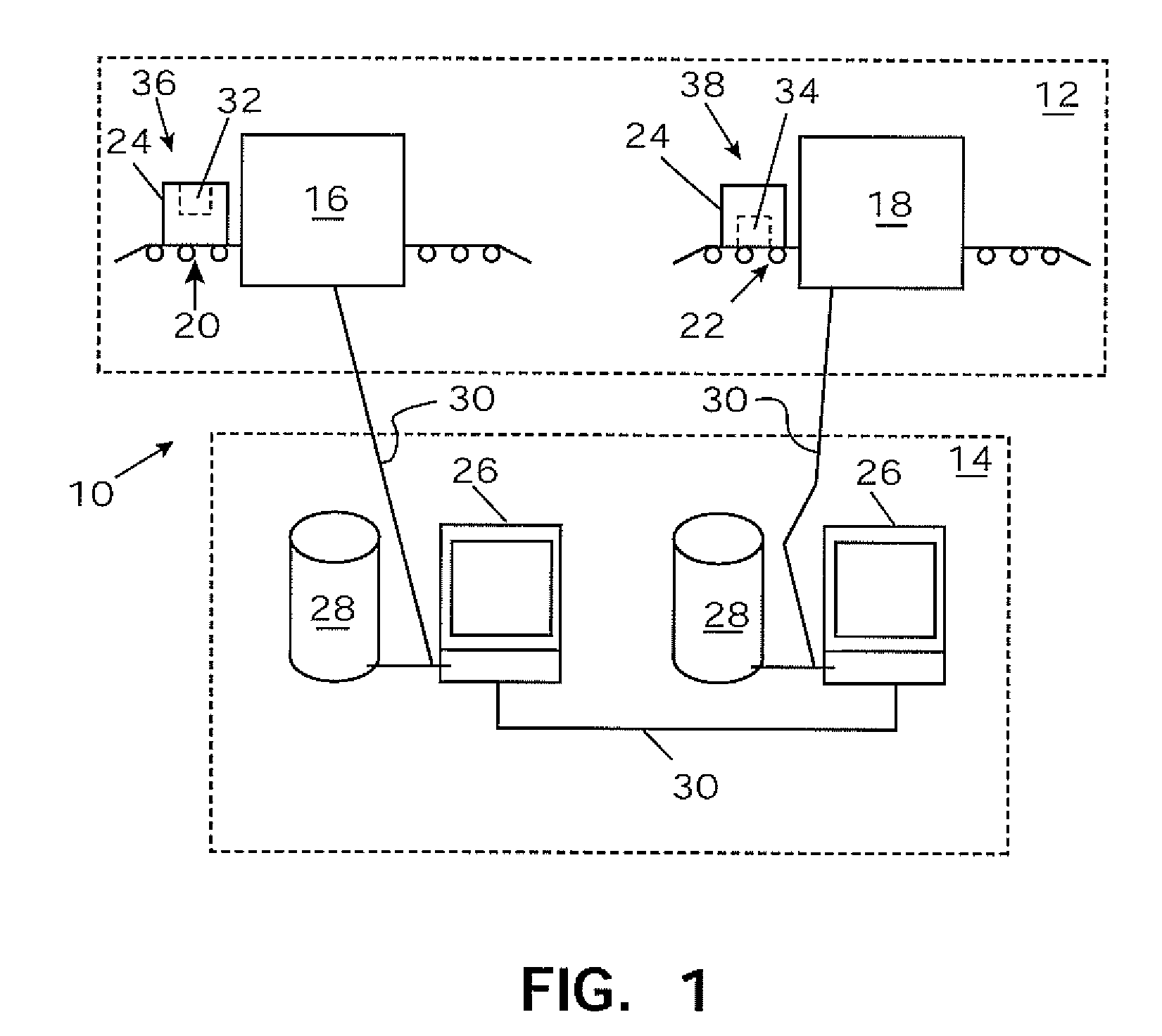
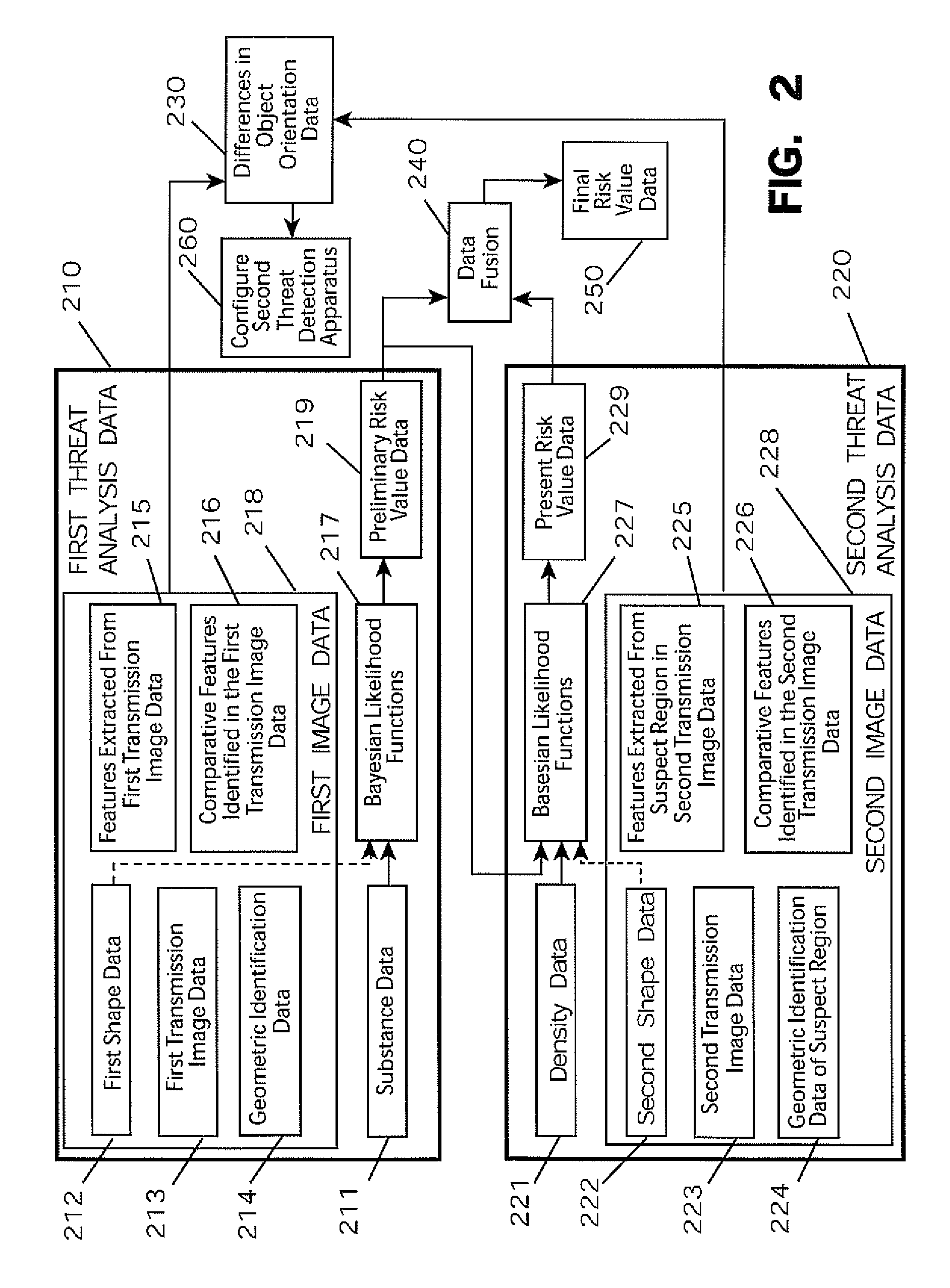
System and method for integrating explosive detection systems
ActiveUS20080056444A1Quickly and accurately and reliably identifyingOvercome disadvantagesRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusInternet privacyDangerous goods
An integrated detection system that includes a first threat detection apparatus and a second threat detection apparatus is provided. The first threat detection apparatus may identify one or more areas within an item of baggage that may contain threats. Example threats include, but are not limited to, explosives, weapons, illegal drugs, and hazardous matter, among others. The remaining areas are in theory deemed clear of threats. The second threat detection apparatus may be configured to inspect only the suspect areas of the item of baggage that was previously identified by the first threat detection apparatus. This improves throughput and lowers the false positive rate. A method for intelligently fusing the independent information obtained by the first and second threat detection apparatuses is also provided.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Antibody profiling sensitivity through increased reporter antibody layering
InactiveUSRE44031E1Analysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresImmune complex formationImmune complex deposition
A method for analyzing a biological sample by antibody profiling for identifying forensic samples or for detecting the presence of an analyte. In an embodiment of the invention, the analyte is a drug, such as marijuana, Cocaine (crystalline tropane alkaloid), methamphetamine, methyltestosterone, or mesterolone. The method comprises attaching antigens to a surface of a solid support in a preselected pattern to form an array wherein locations of the antigens are known; contacting the array with the biological sample such that a portion of antibodies in the sample reacts with and binds to the antigens in the array to form immune complexes; washing away antibodies that do form immune complexes; and detecting the immune complexes, to form an antibody profile. Forensic samples are identified by comparing a sample from an unknown source with a sample from a known source. Further, an assay, such as a test for illegal drug use, can be coupled to a test for identity such that the results of the assay can be positively correlated to the subject's identity.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
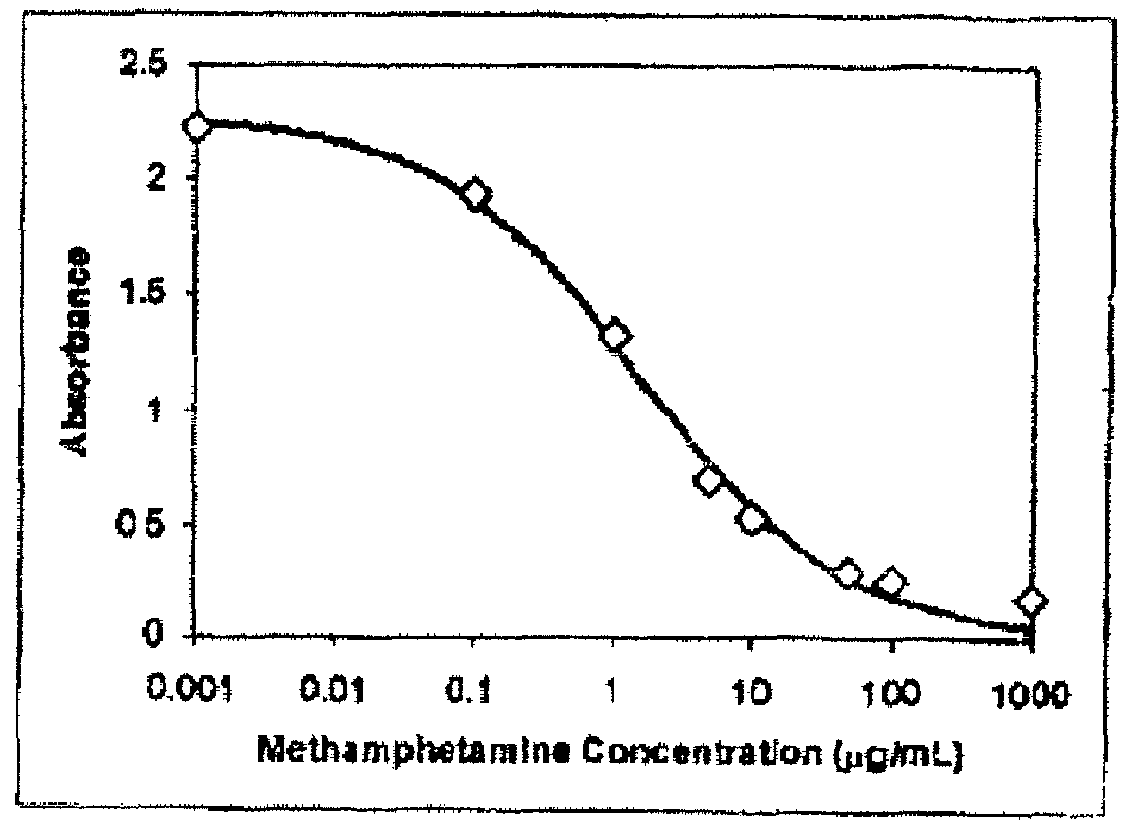
Reagent, A Kit, And A Method For Detecting And Identifying A Wide Range Of Illicit Drugs
ActiveUS20110117664A1Quick identificationImprove discriminationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistryOrganic solventEmulsion
A reagent for detecting and identifying a chemical substance. The reagent is an emulsion including a cobalt salt dissolved in water which also includes at least one organic solvent that is at least partly water-miscible and also including an organic compound which serves as an ion pair color changing indicator or a pH sensitive color changing indicator, the organic compound dissolved in an organic solvent only partly miscible with water. A two product kit for detecting and identifying a chemical substance is also taught. The kit includes the aforementioned reagent and a diazonium salt, typically a diazonium salt having electron withdrawing groups on its phenyl rings. A method for detecting and identifying a chemical substance using the two product kit is also discussed. The reagent, testing kit and method may be used for detecting and identifying controlled substances.
Owner:MISTRAL
Non-invasive disease diagnosis using light scattering probe
InactiveUS8031335B2Easy to detectShort test cycleRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansIllicit drugSmoking status
A method for non-invasive detection of a disease, a status of illicit-drug use, or smoking status includes transferring a body fluid obtained from a patient to a sensor comprising a nano-scale surface structure to allow the body fluid to come in contact with the nano-scale surface structure, illuminating the body fluid and the nano-scale surface structure by a laser beam, scattering the laser beam by the body fluid and the nano-scale surface structure to produce a scattered light, and analyzing the scattered light using a spectral analyzer to diagnose a disease, the status of illicit-drug use, or smoking status in the patient.
Owner:EXCELLENT CAPACITY LTD
Triple immune colloidal gold rapid detection card and its preparation and use method
InactiveCN102967707AImprove anti-interference abilityEasy to operateMaterial analysisAntigenControl line
The invention relates to an immune colloidal gold label rapid detection card, which applies the principle of competitive inhibition immunochromatography. During detection, first a sample to be detected is added into a sample adding hole. If the sample contains to-be-detected materials, antigens in the sample combine with colloidal gold-labeled specific monoclonal antibodies located on a gold label pad during side movement, thus inhibiting combination of the gold-labeled antibodies with corresponding antigen-BSA conjugates on NC film detection lines, and the detection lines (T lines) have no color, redundant gold-labeled monoclonal antibodies combine with redundant enzyme-labeled antibodies, and a control line (C line) present a color; and otherwise, the detection lines (T lines) are wine red, and the control line (C line) present a color. The rapid detection card provided in the invention can be applied to rapid, on-site and sensitive detection of Clenbuterol, Ractopamine and Salbutamol illicit drug residues in urine samples, tissue samples and the like.
Owner:WUXI FUYANG BIOTECH +1
Method and apparatus for conditioning honey bees
A method to condition honey bees to search for a non-rewarding producing target odor source enables bees to identify a number of chemical substances such as those associated with unexploded ordnances, land mines, and illicit drug laboratories. Further, the subject method can be used to increase pollination efficiency by conditioning the bees to search for a specific vapor from a target crop. The method includes conditioning the bees to the target odor by moving their hives into a staging area. The staging area is located at least two miles from the ultimate site to be searched. The target odor is applied to the hive. Bulk feeders containing the target odor are placed near the hive. The hives are reoriented to the bulk feeders for several days. The hives are then moved to the search site and feeding / conditioning trays containing the target odor are placed nearby. For the first, approximately 24 hours, the bees are fed from the feeding / conditioning trays. Thereafter, periods of feeding and starvation are alternated to encourage the bees to forage and identify the target source. There are several embodiments of the feeding / conditioning trays which present the target odor to the bee during conditioning. Additionally, an automated feeding controller is useful in the conditioning method.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MONTANA
Rapid classification of biological components
InactiveUS20050191692A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune complex depositionUnknown Source
A method is disclosed for analyzing a biological sample by antibody profiling for identifying forensic samples or for detecting the presence of an analyte. In an illustrative embodiment of the invention, the analyte is a drug, such as marijuana, cocaine, methamphetamine, methyltestosterone, or mesterolone. The method involves attaching antigens to the surface of a solid support in a preselected pattern to form an array wherein the locations of the antigens are known; contacting the array with the biological sample such that a portion of antibodies in the sample reacts with and binds to antigens in the array, thereby forming immune complexes; washing away antibodies that do form immune complexes; and detecting the immune complexes, thereby forming an antibody profile. Forensic samples are identified by comparing a sample from an unknown source with a sample from a known source. Further, an assay, such as a test for illegal drug use, can be coupled to a test for identity such that the results of the assay can be positively correlated to the subject's identity.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Liquid examination device and liquid examination method
InactiveUS20170299507A1Processing detected response signalMaterial analysis by optical meansReflected wavesIllicit drug
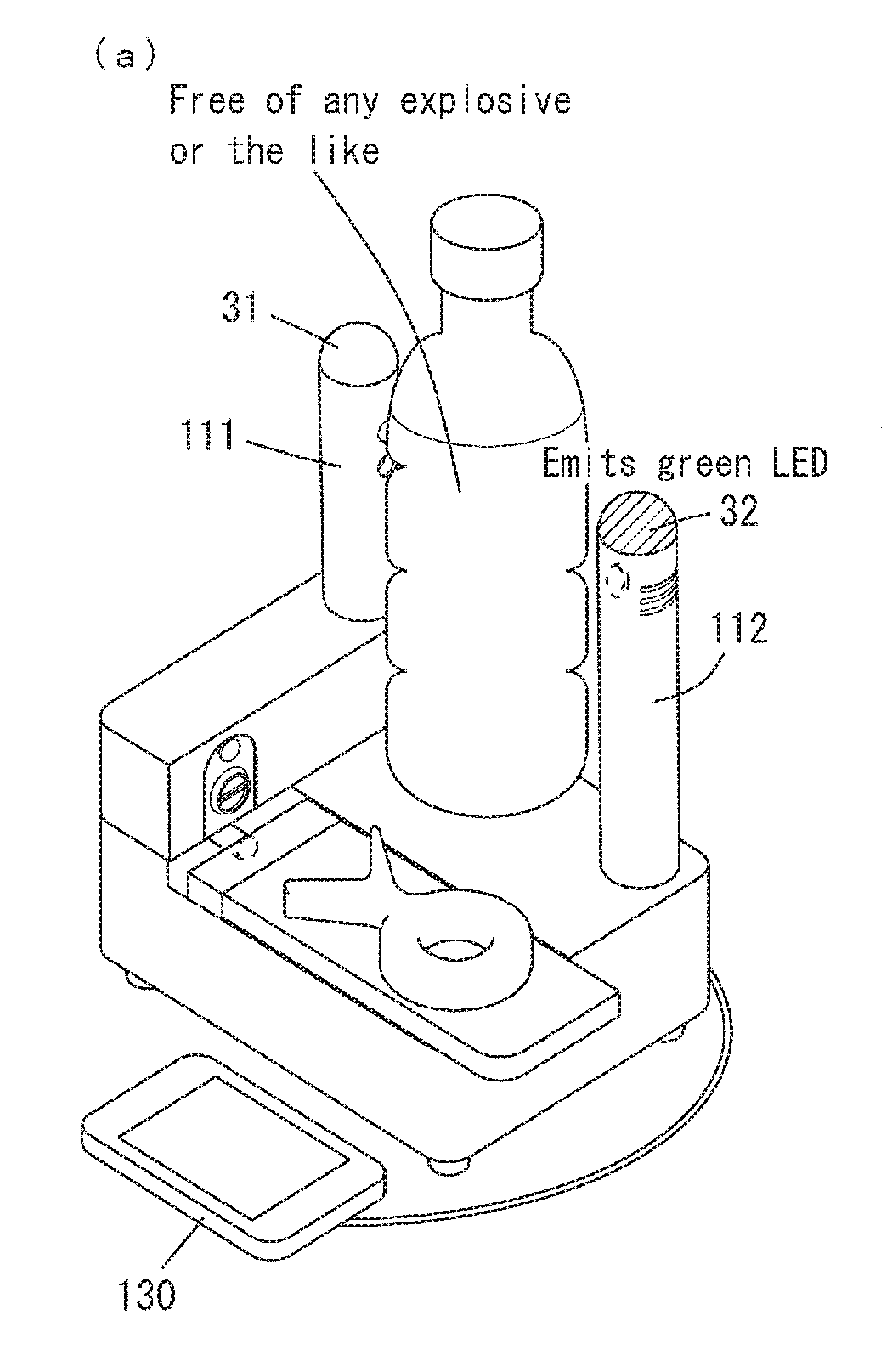
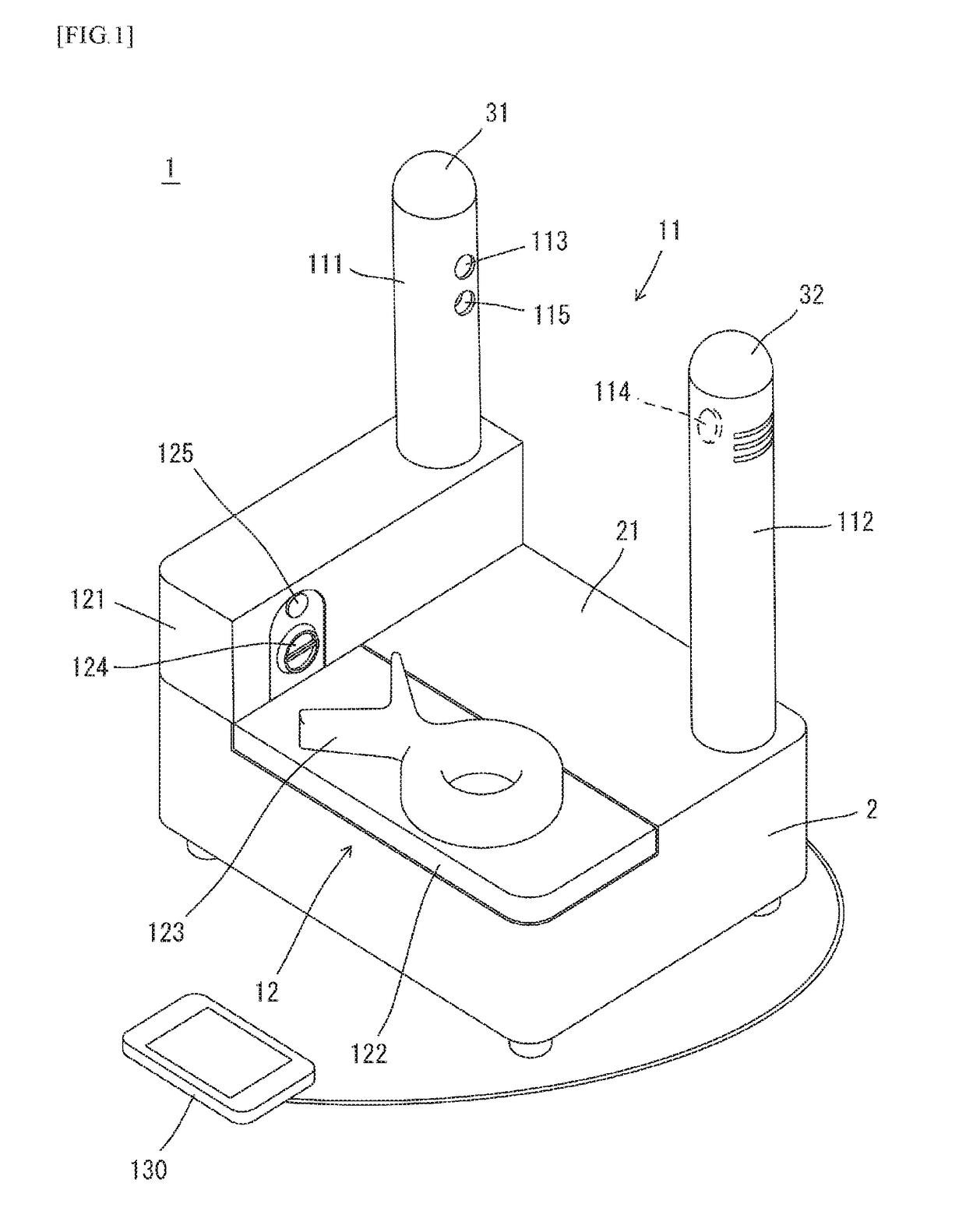
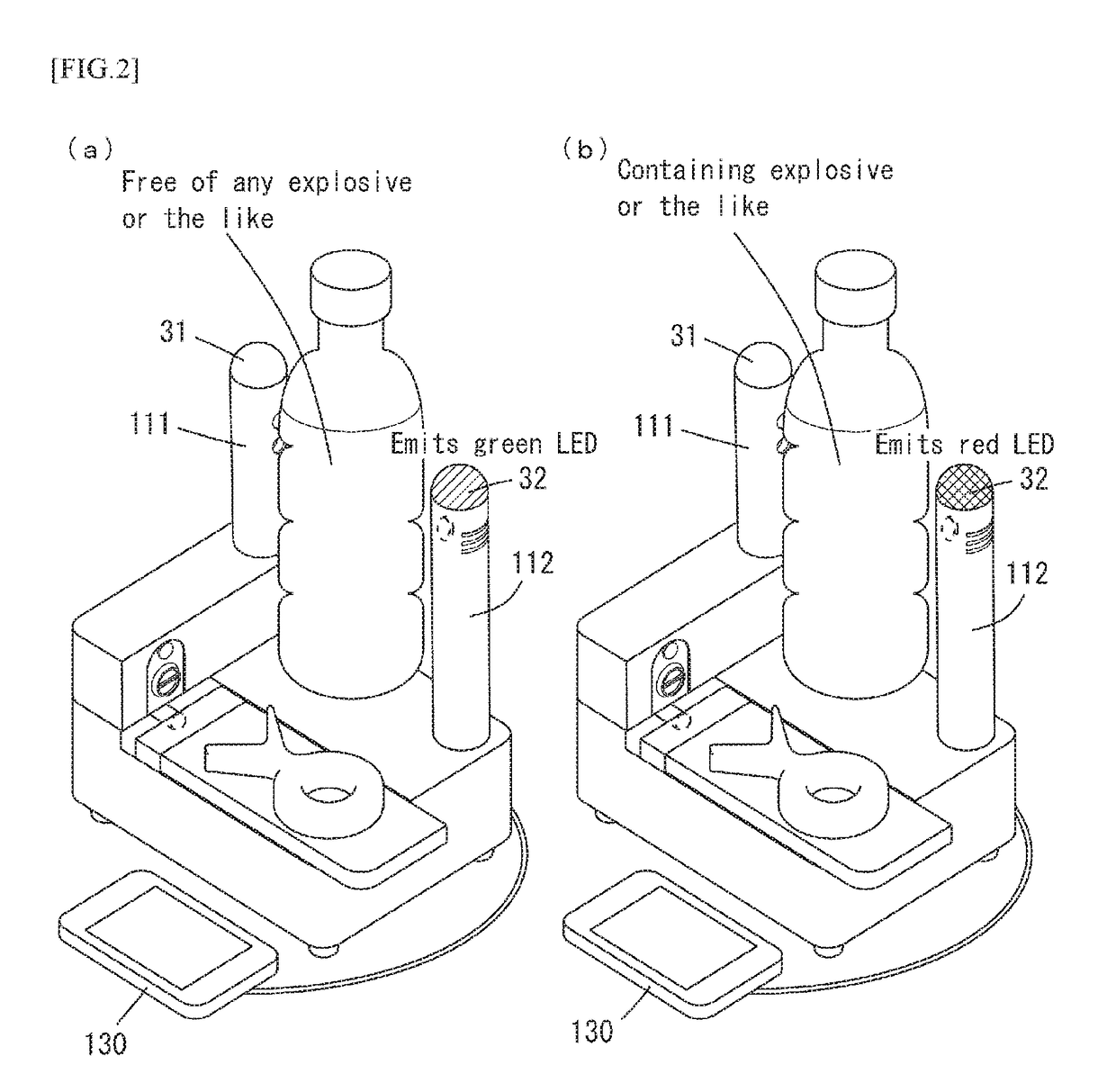
Provided is an examination technique that can quickly and reliably examine, from the outside of a container, whether a liquid which fills the container contains an explosive or the like, without being influenced by such things as the light transmissivity or size of the container, or the amount of liquid remaining in the container or the position of a label. In the present invention, a liquid examination device is formed by integrating the following: a near infrared-light examination device that examines whether a liquid which fills a container contains an explosive, an explosive raw material, and / or an illicit drug by projecting near infrared light into the liquid from outside of an optically transparent container, receiving the near infrared light which passed through the liquid or the near infrared light which was scattered by the liquid, and analyzing the absorption spectrum of such light; and an ultrasonic wave examination device that examines whether a liquid which fills a container contains an explosive, an explosive raw material, and / or an illicit drug by receiving the reflected waves of ultrasonic waves projected towards the liquid from outside of a metal container, and analyzing the ultrasonic wave speed of such waves.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
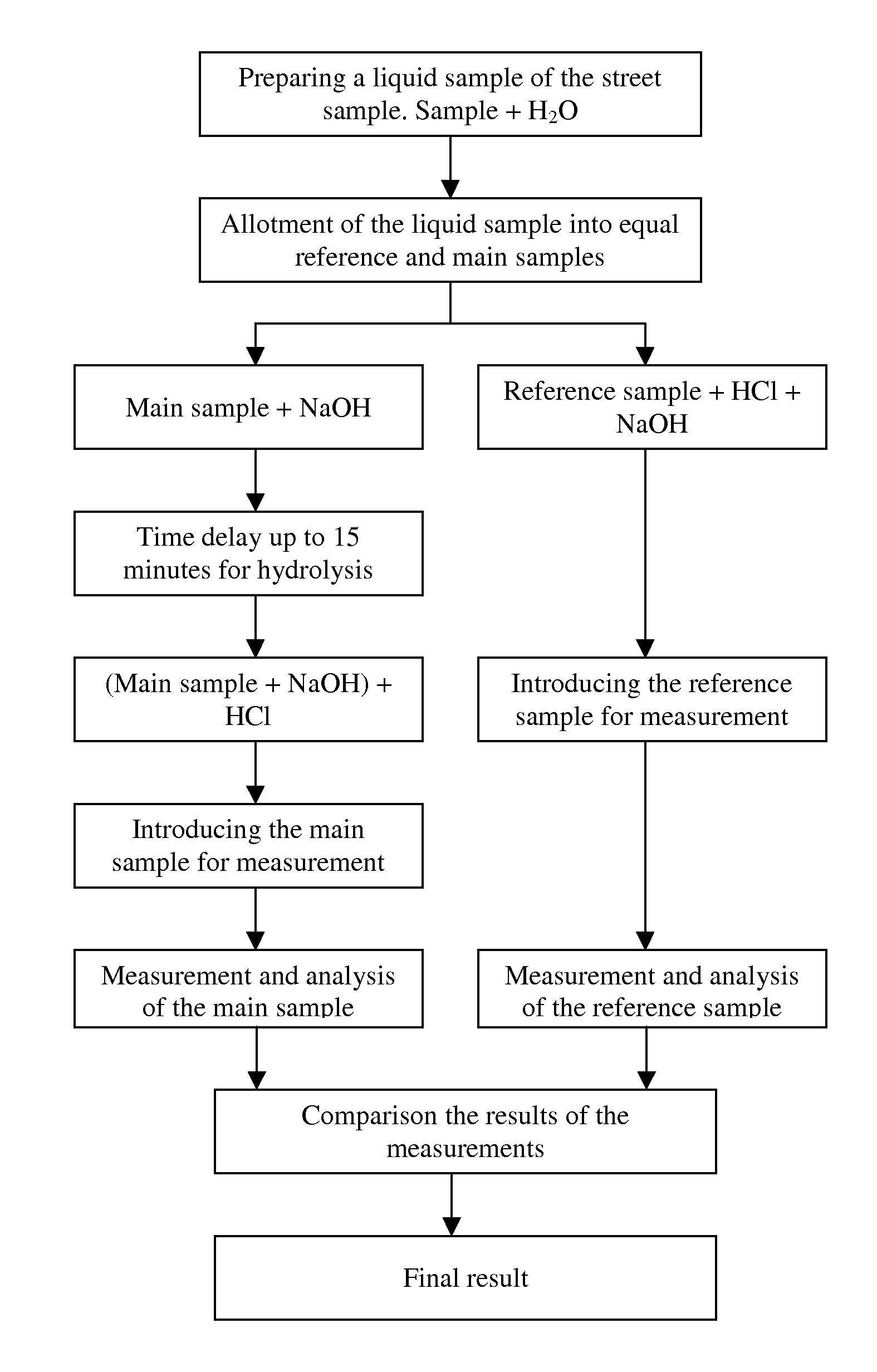
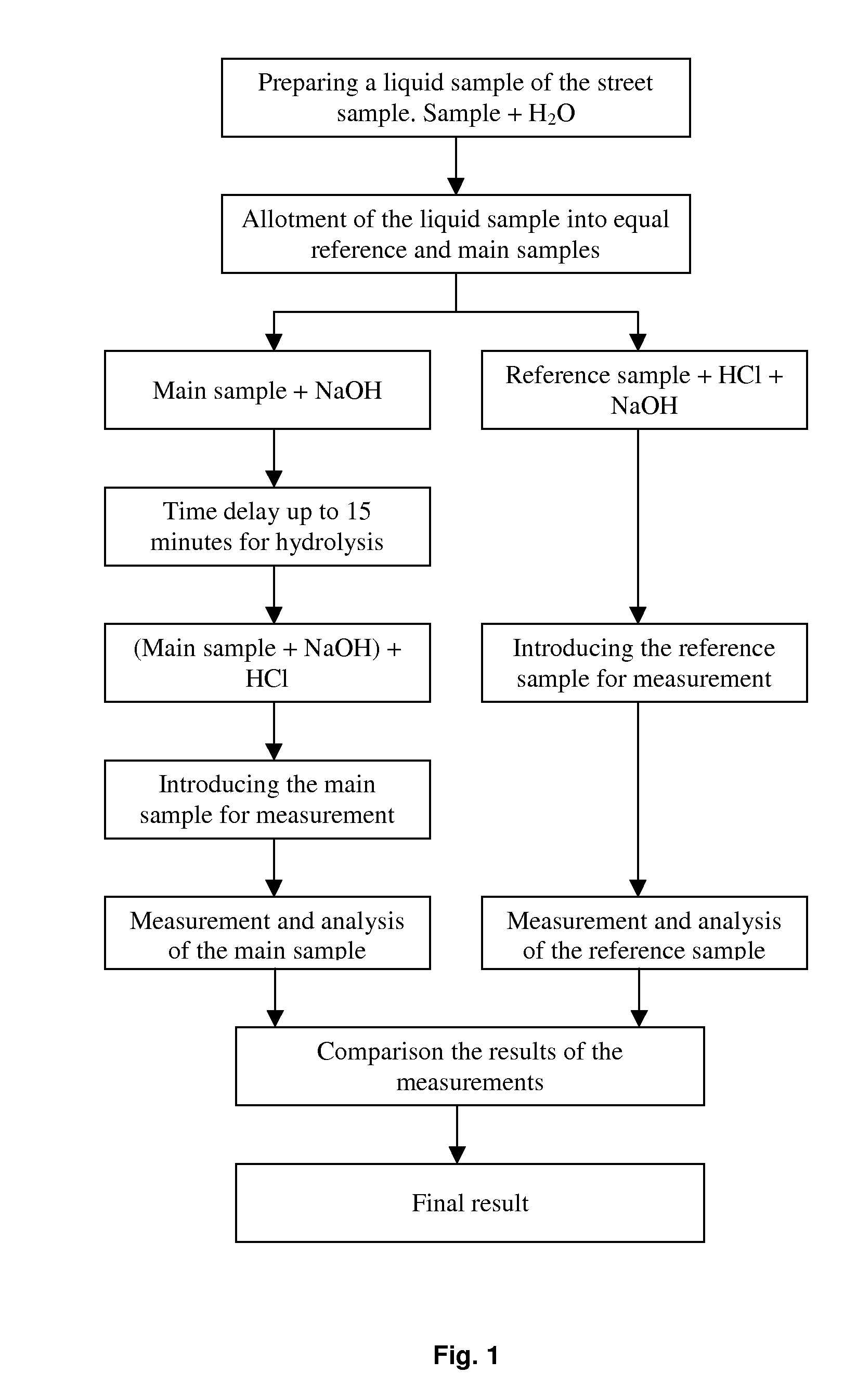
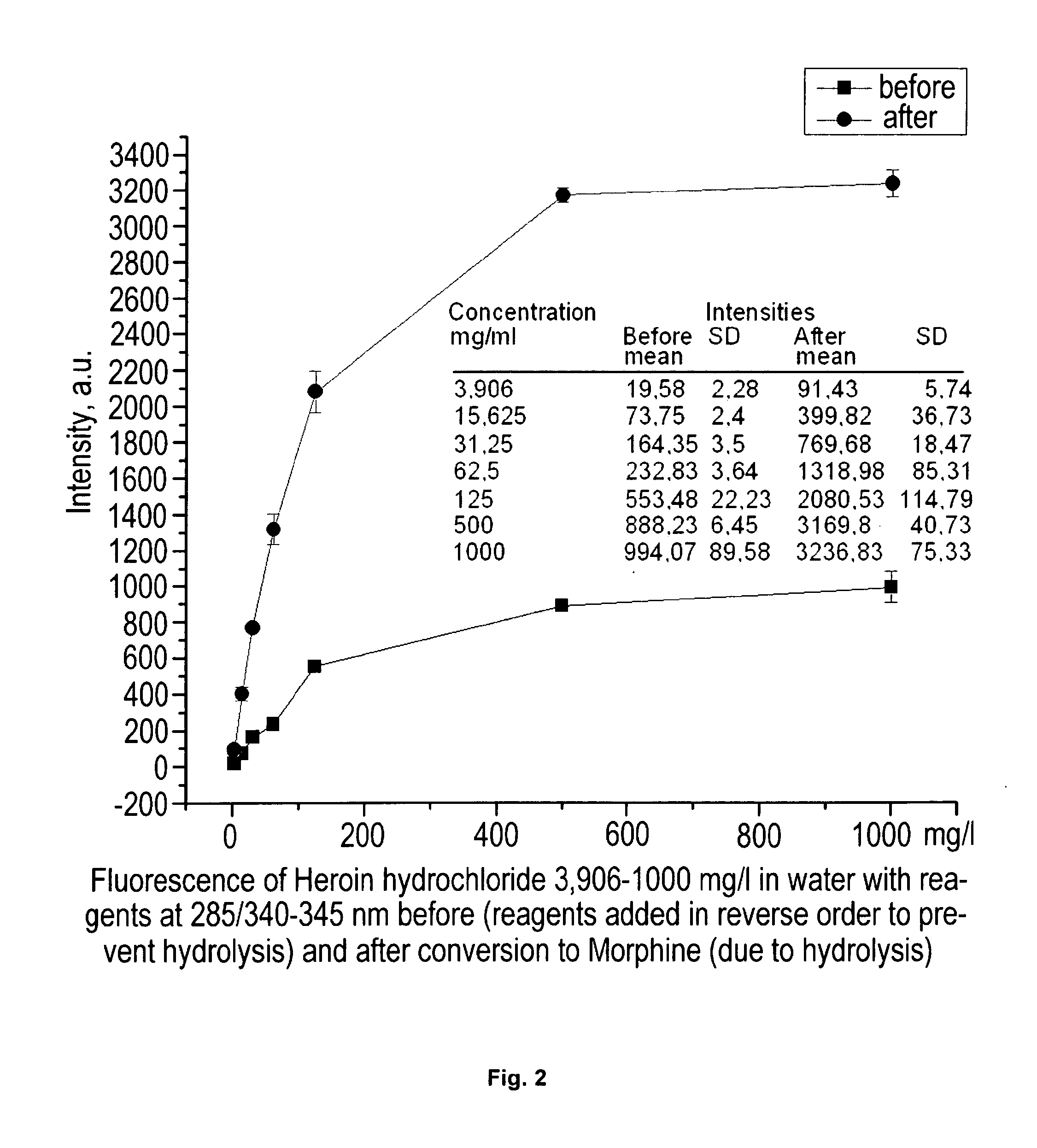
Method for on-site drug detection in illicit drug samples
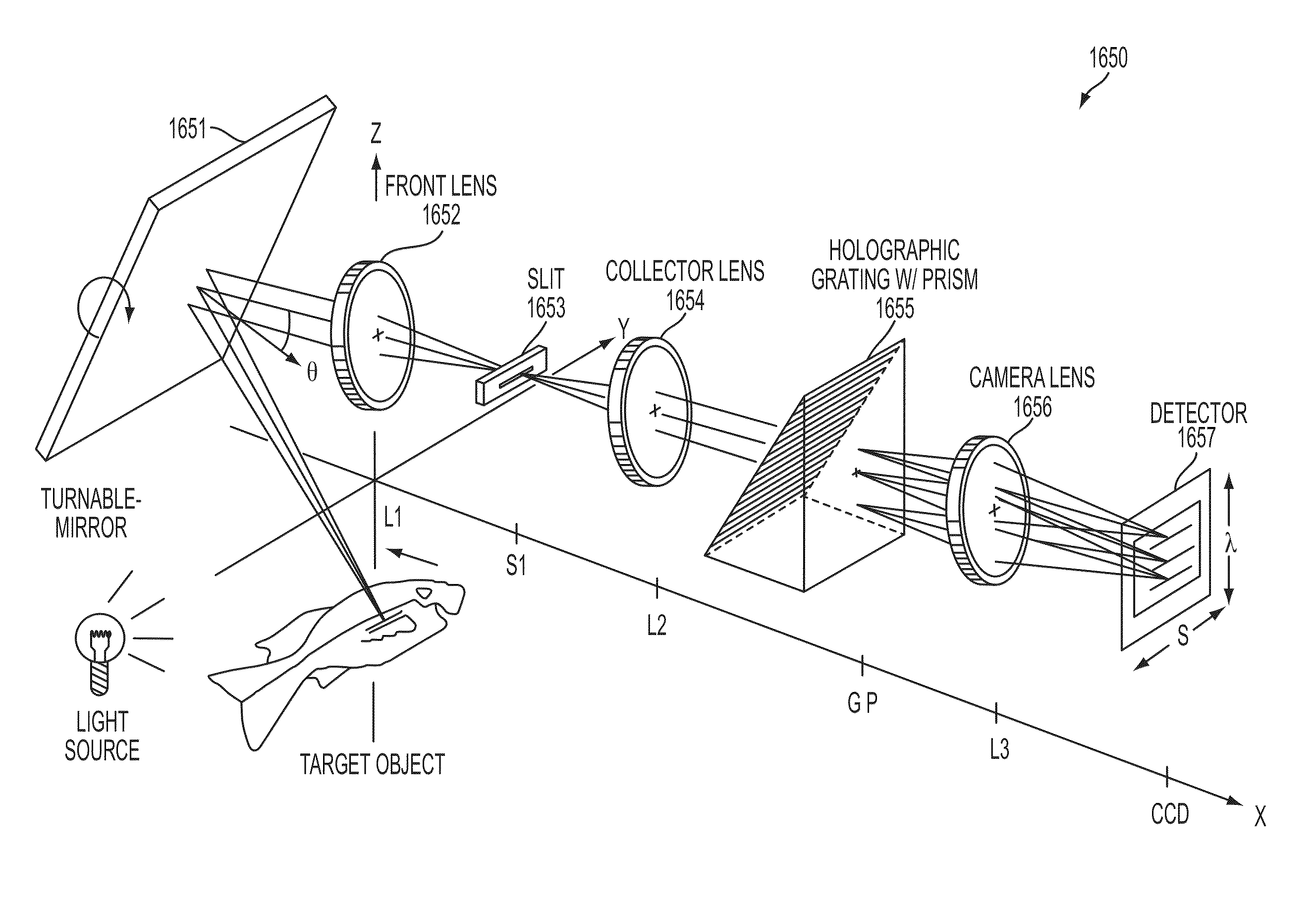
InactiveUS20110151570A1Reliable detectionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationReference sampleSpectral pattern
The invention is provided for detection of Heroin and Morphine in illicit drug samples, also for their differentiation. A liquid sample from a street sample is prepared and divided into two equal aliquots, one of them being reference sample, another being main sample. Both samples are treated with Hydrochloric acid and Sodium hydroxide, but those substances are added to the samples in the different sequence. After that the measurement of SFS of the reference sample is performed. Further the presence of specific spectral pattern of Morphine in the measured SFS of the reference, sample is detected and the value of SFS intensity at the specific spectral point is fixed (a reference value). After 15 minutes for acidification of the main sample, the analogous measurement and detection of the Morphine in the main sample are performed.
Owner:NARTEST
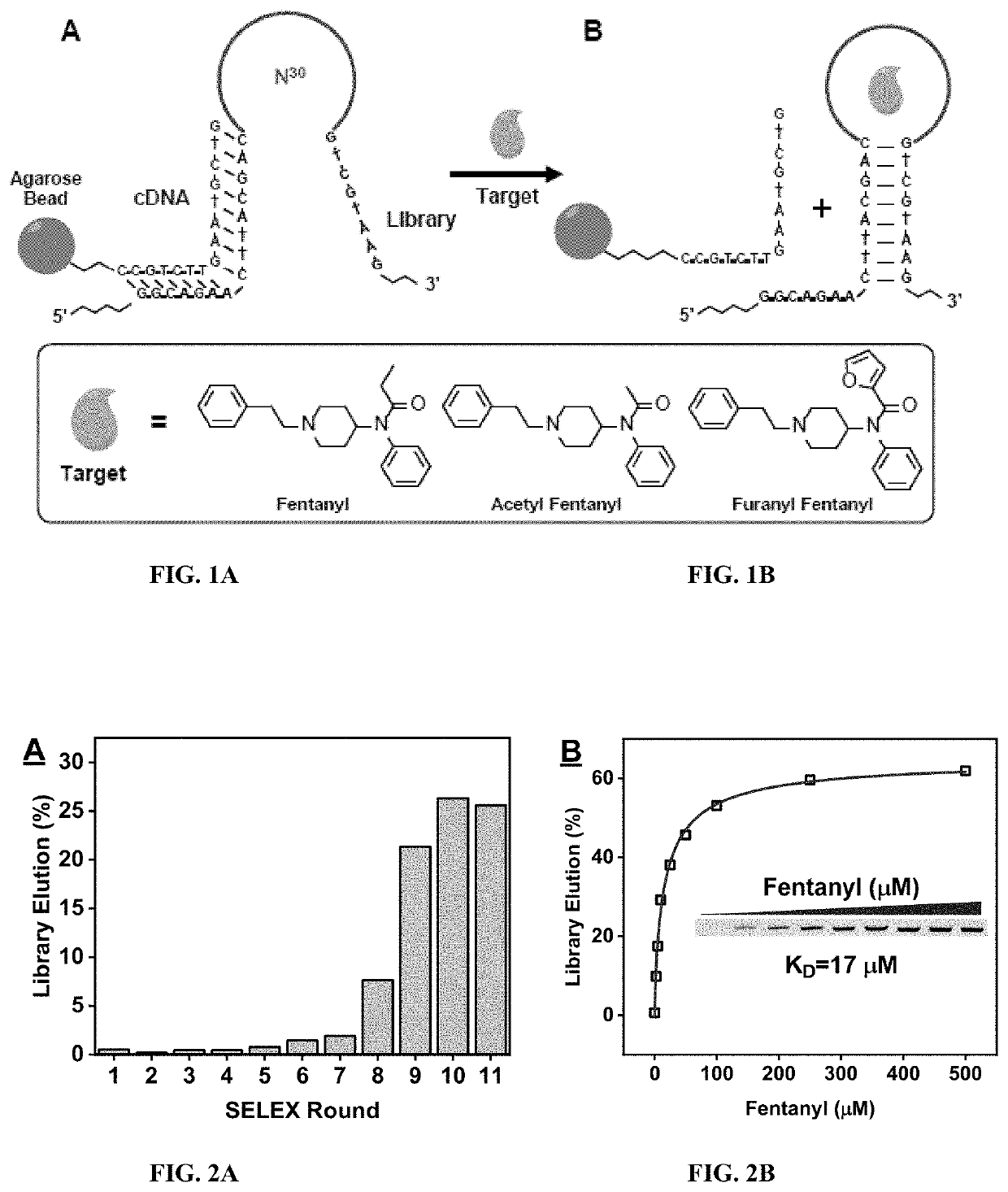
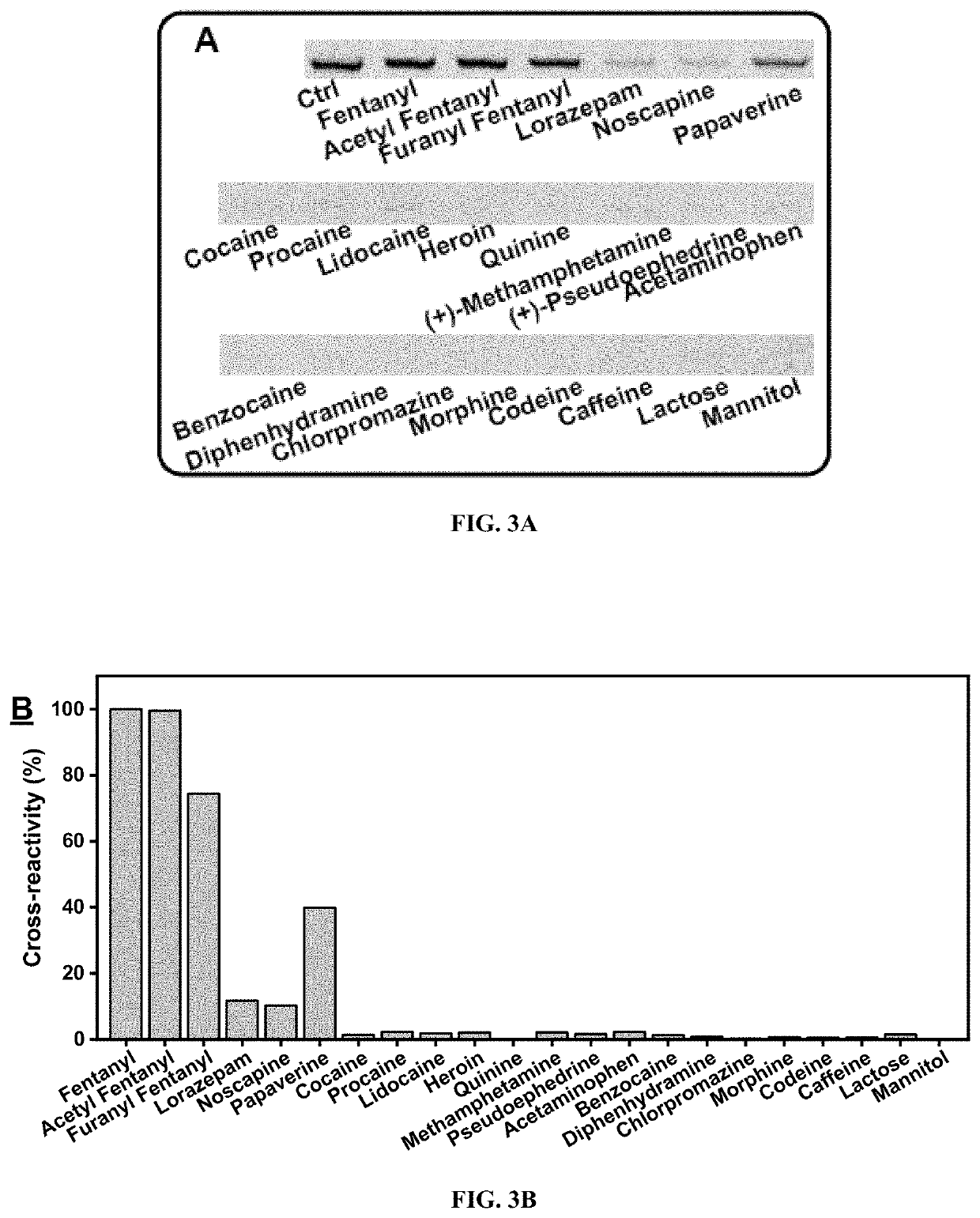
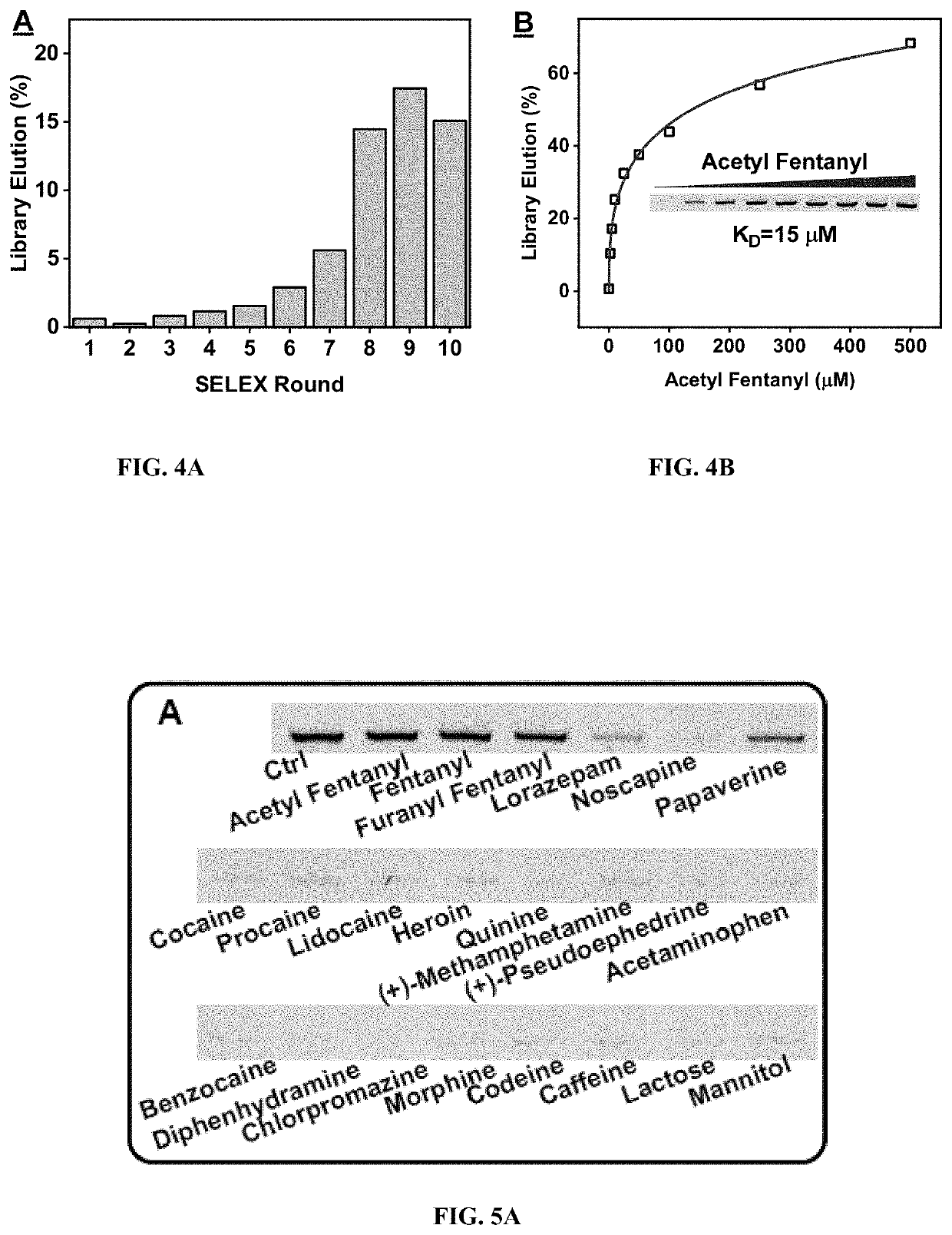
Aptamer-based sensors for detection of fentanyl opioids
The subject invention provides materials and methods for single-step fluorescence and electrochemical detection of small molecules, e.g., fentanyl and its analogs, in a sample. The subjection invention provides nucleic acids materials, e.g., aptamers (nucleic acid oligonucleotides) that can bind to fentanyl and its analogs with nanomolar affinity and high specificity against illicit drugs, adulterants, and cutting agents commonly existing in seized samples. The method for detecting fentanyl and / or its analogs in a sample comprises contacting the sample with an aptamer-based sensor selective for fentanyl and its analogs, and sensitively, specifically, and rapidly detecting fentanyl and / or its analogs in the sample.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Analysis method for simultaneously determining 11 drugs and metabolites thereof in domestic sewage
PendingCN111426768AMeet high-throughput analysis requirementsMeet the requirements for abuse monitoringComponent separationMetaboliteIllicit drug
Owner:ACADEMY OF FORENSIC SCIENCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com