VARYING ENERGY BARRIERS OF MAGNETIC TUNNEL JUNCTIONS (MTJs) IN DIFFERENT MAGNETO-RESISTIVE RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY (MRAM) ARRAYS IN A SEMICONDUCTOR DIE TO FACILITATE USE OF MRAM FOR DIFFERENT MEMORY APPLICATIONS
a technology of random access memory and magnetic tunnel junction, which is applied in the field of magnetic tunnel junctions (mtjs) employed in mram, can solve the problem of allowing the realization of desired performance differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029]With reference now to the drawing figures, several exemplary aspects of the present disclosure are described. The word “exemplary” is used herein to mean “serving as an example, instance, or illustration.” Any aspect described herein as “exemplary” is not necessarily to be construed as preferred or advantageous over other aspects.
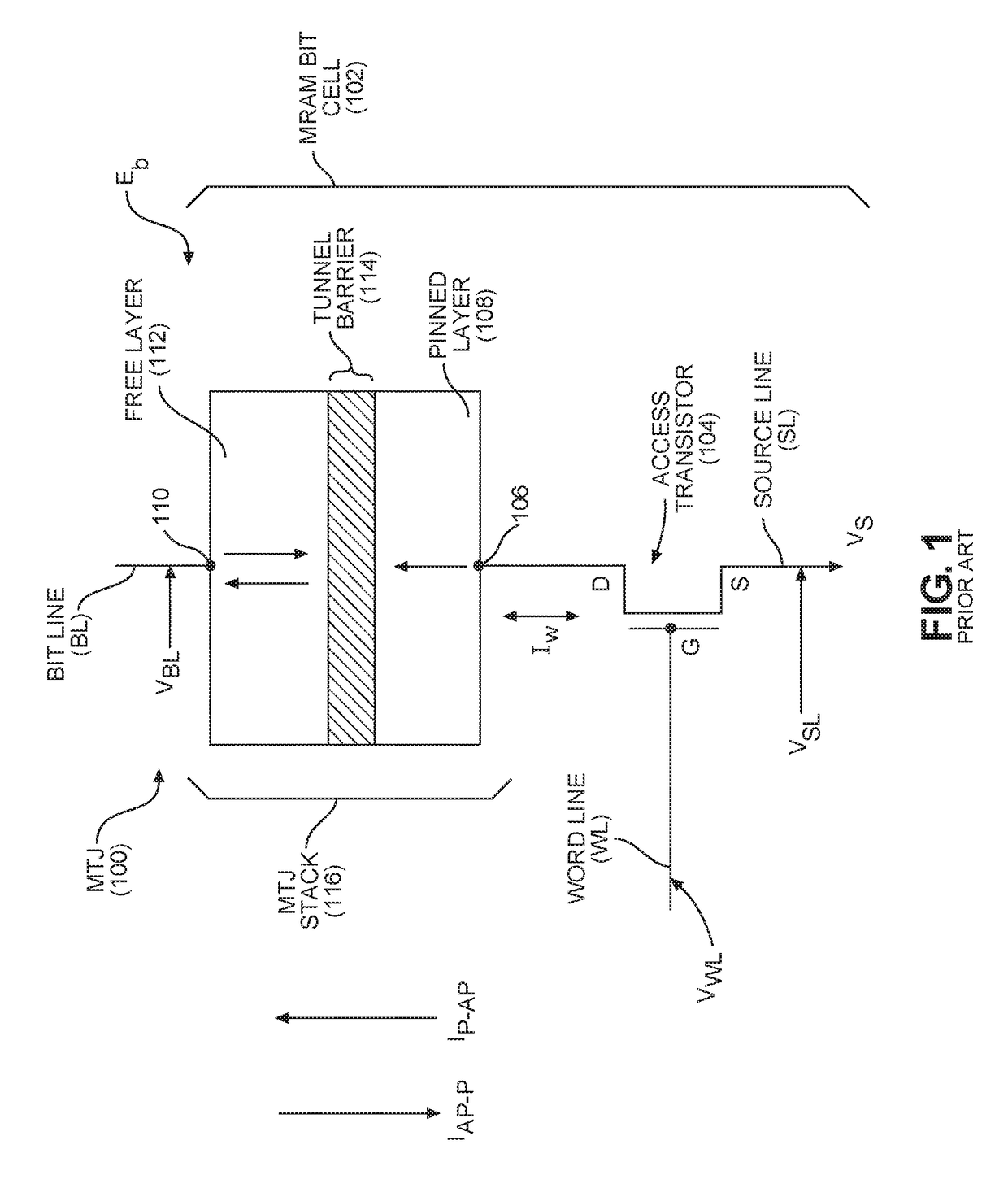
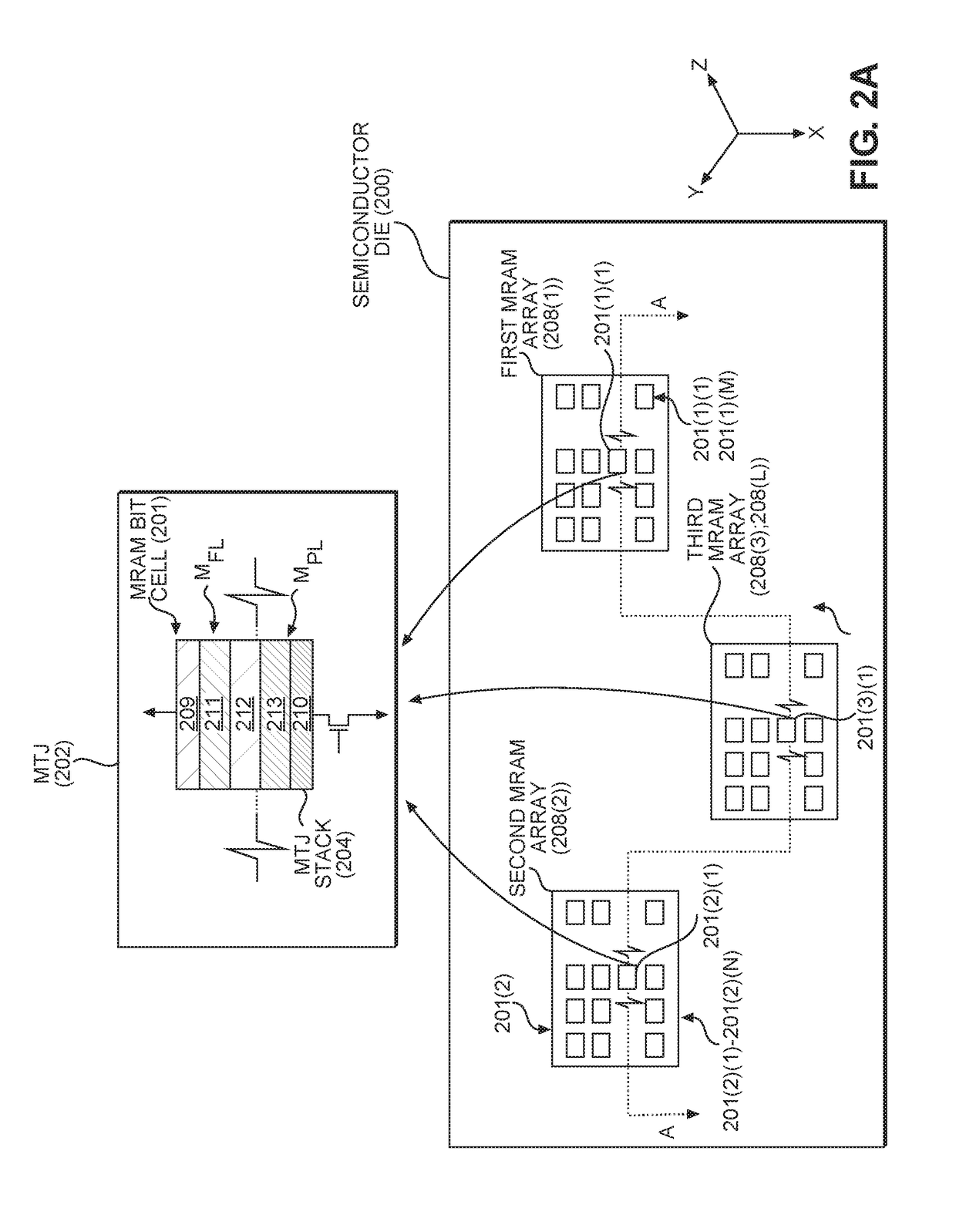
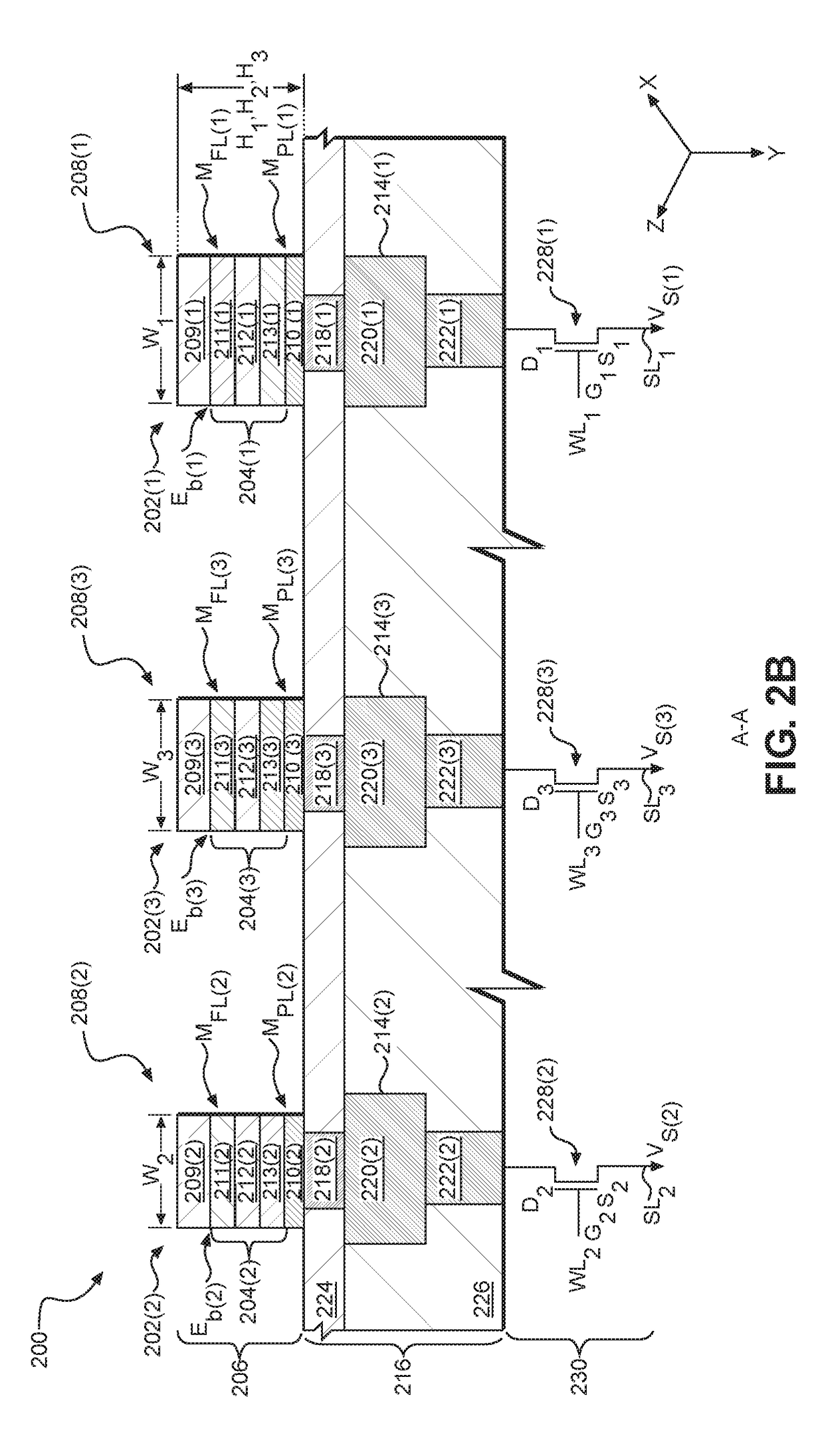
[0030]Aspects disclosed in the detailed description include varying energy barriers of magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) in different magneto-resistive random access memory (MRAM) arrays in a semiconductor die to facilitate use of MRAM for different memory applications. Different memory applications may require different tradeoffs between access times and data retention performance as an example, where using MTJ stacks having the same energy barrier in these different memory applications may not allow the desired differences in performance to be realized. Thus, in this regard, in exemplary aspects disclosed herein, to facilitate use of MRAM for differe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com