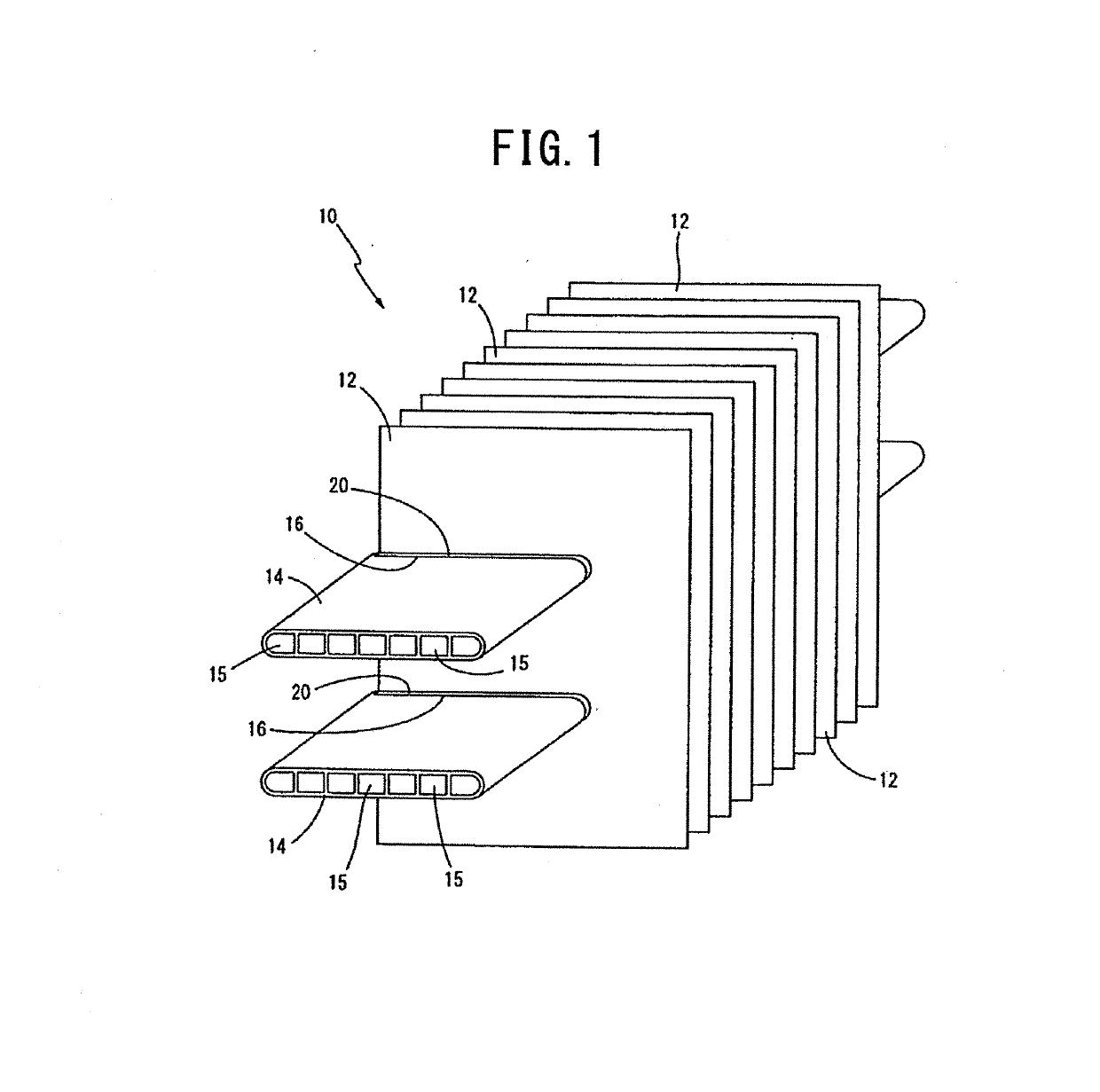
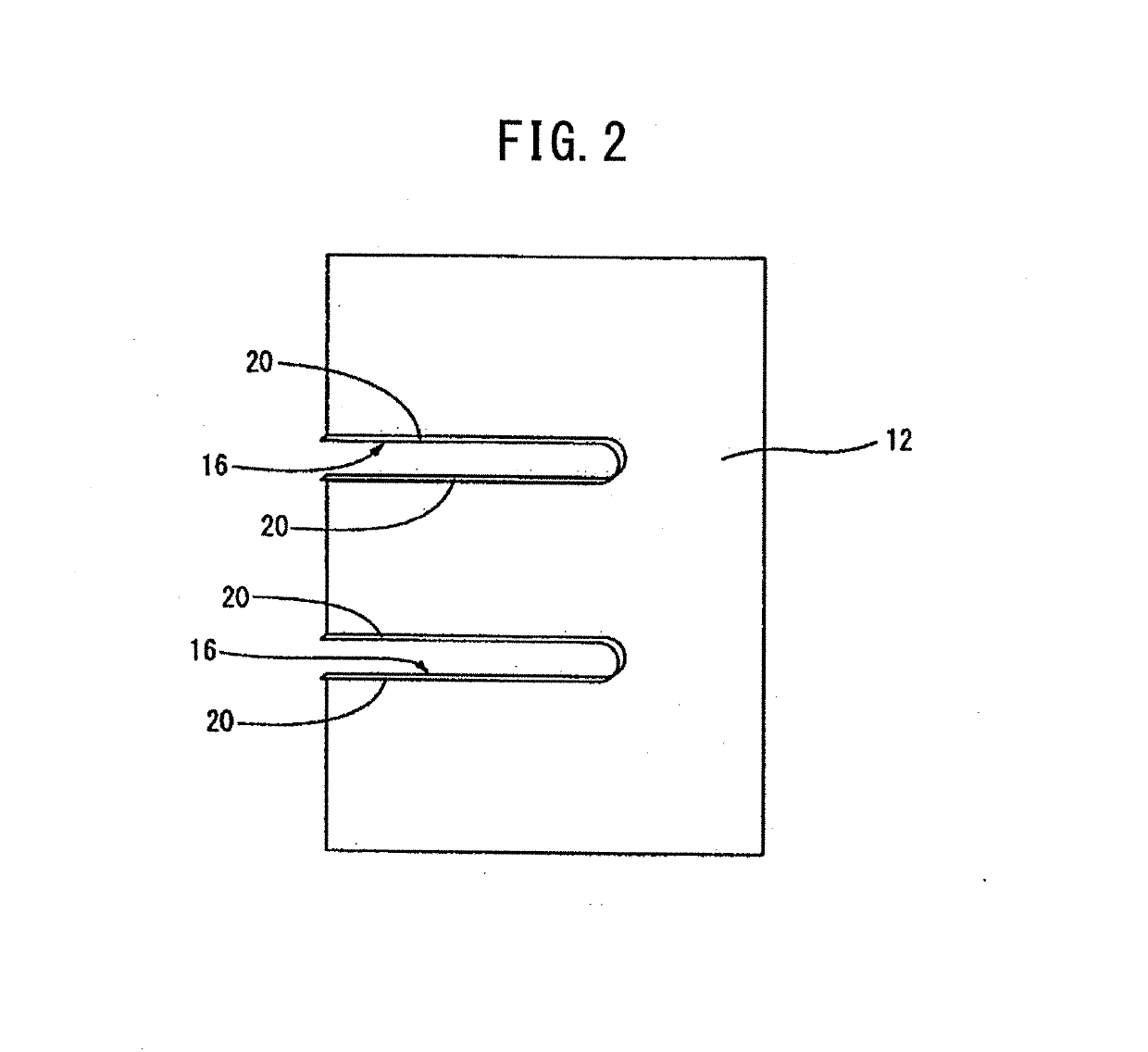
Aluminum alloy fin material, aluminum alloy brazing sheet, and heat exchanger
a technology of aluminum alloy brazing sheet and aluminum alloy, which is applied in the direction of soldering apparatus, manufacturing tools, light and heating equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reduced reduced clearance between tube surface and fin surface, and suppression of sheet thickness decrease, etc., to achieve low deterioration of rigidity in bonding and heating, small decrease in sheet thickness of fin material, and low deterioration of bondability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0123]Preferred embodiments of the present disclosure will be specifically described below based on Examples and Comparative Examples. However, the present disclosure is not limited thereto.
[0124]First, test materials having a thickness of 400 mm, a width of 1000 mm, and a length of 3000 mm were cast by a DC casting method using aluminum alloys having alloy compositions A1 to A23 set forth in Table 1. A casting rate was set to 50 mm / min at a cooling rate set to 1° C. / s. In the alloy compositions in Table 1, “-” indicates a value that is not more than a detection limit, and “balance” includes inevitable impurities. Then, the ingot cast by the DC casting method was faced to have a thickness of 380 mm, then heated to a temperature of 480° C. in a heating and retention step prior to hot rolling, retained at the temperature for 5 hours, and then subjected to a hot rolling step. In the hot rolling step, the ingot was rolled to have a thickness of 3 mm. A total rolling reduction in hot rou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| equivalent circle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| equivalent circle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com