Integration of Thermochemical Heat Storage System with Waste heat Recovery Systems
a heat storage system and thermochemical technology, applied in indirect heat exchangers, lighting and heating apparatus, heating types, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the operation capabilities of those systems, no efficient and cost-effective heat preservation means, and limited practicability of waste heat from refrigeration systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015]In the description which follows, like parts are marked throughout the drawing with the same reference numerals respectively.
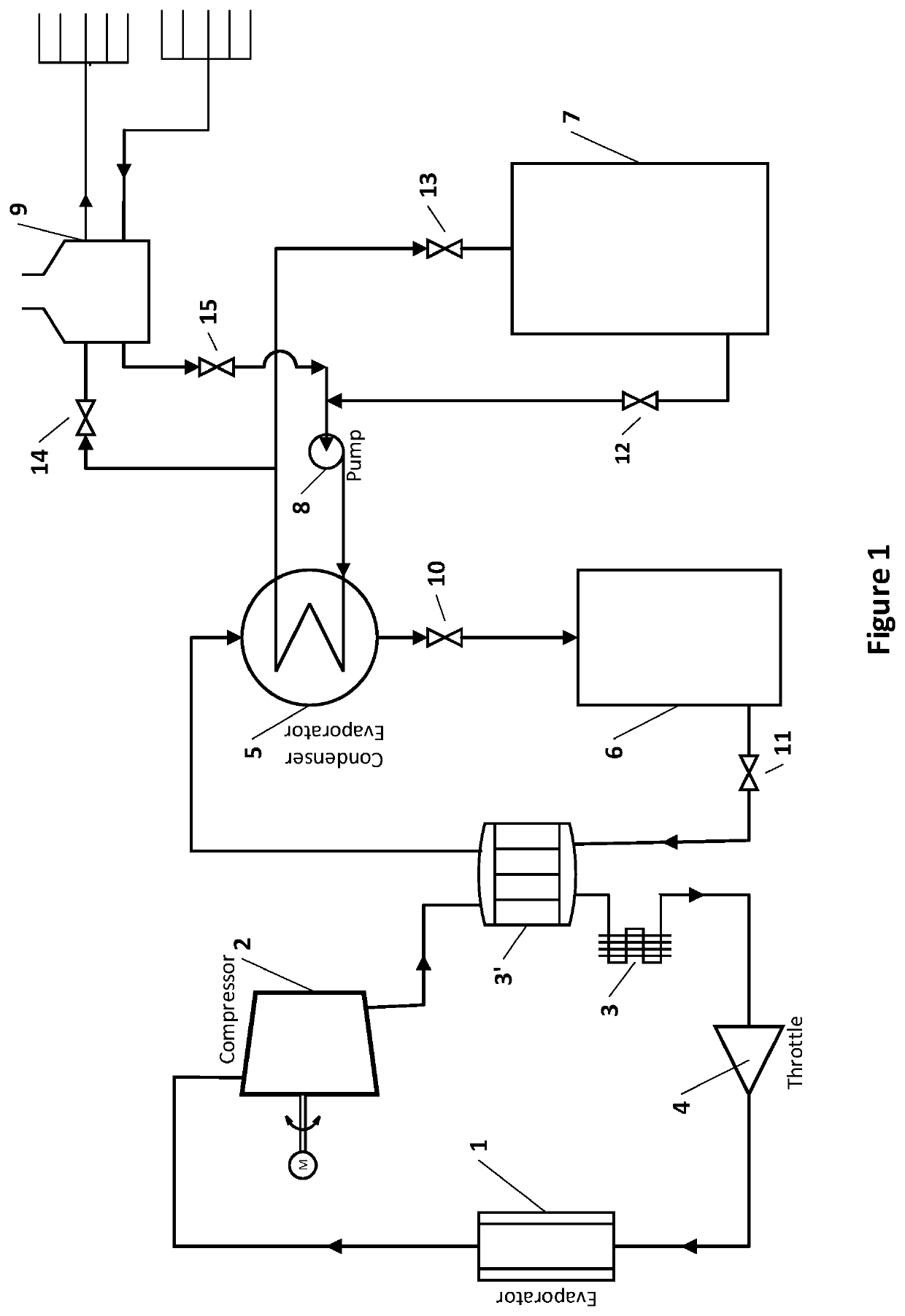
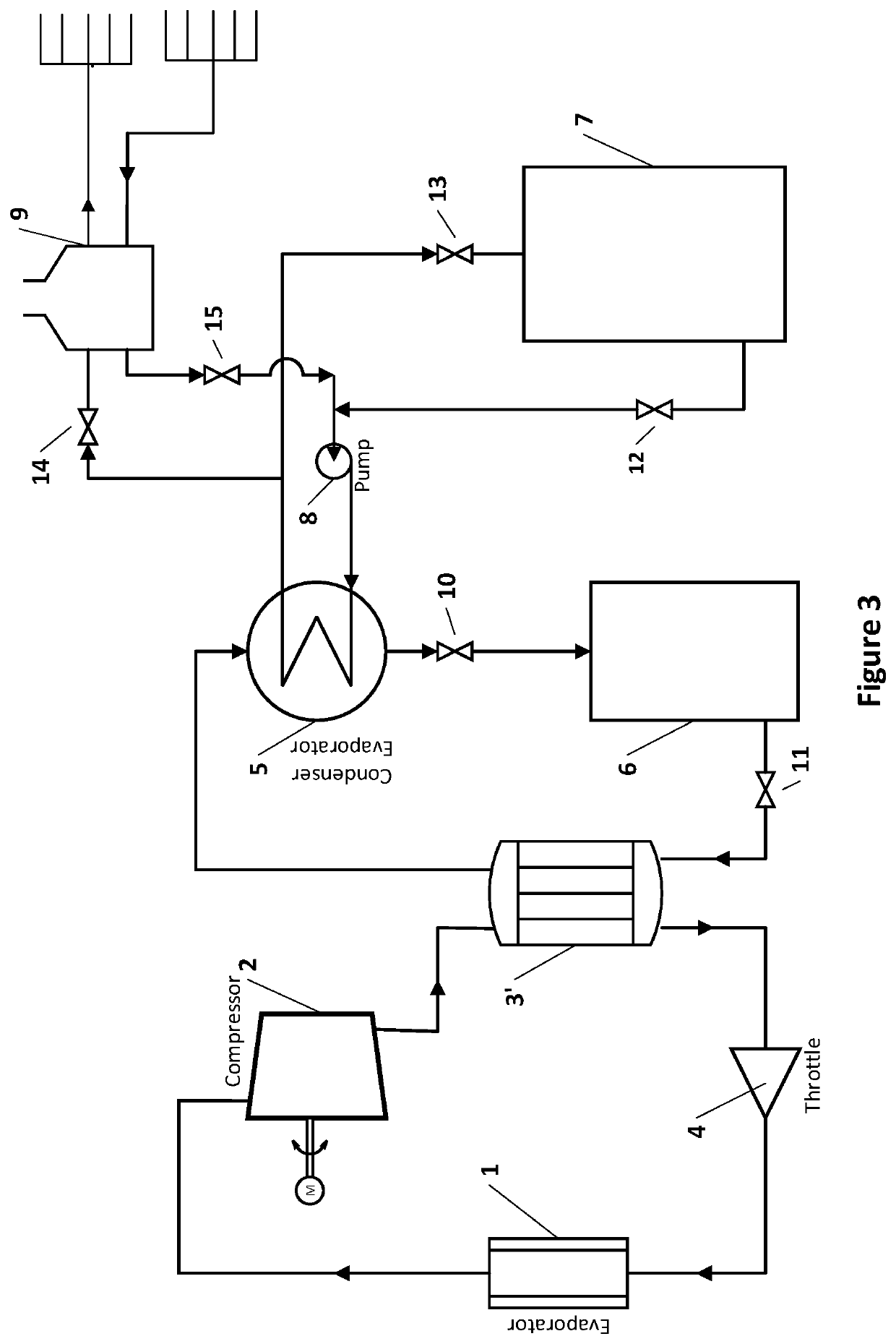
[0016]Referring now to FIG. 1 of the drawing, the waste heat recovery system of the present invention includes an integration of four subsystems: a conventional air conditioning or refrigeration system, a waste heat transfer system, a thermochemical storage system and a waste heat utilization system.
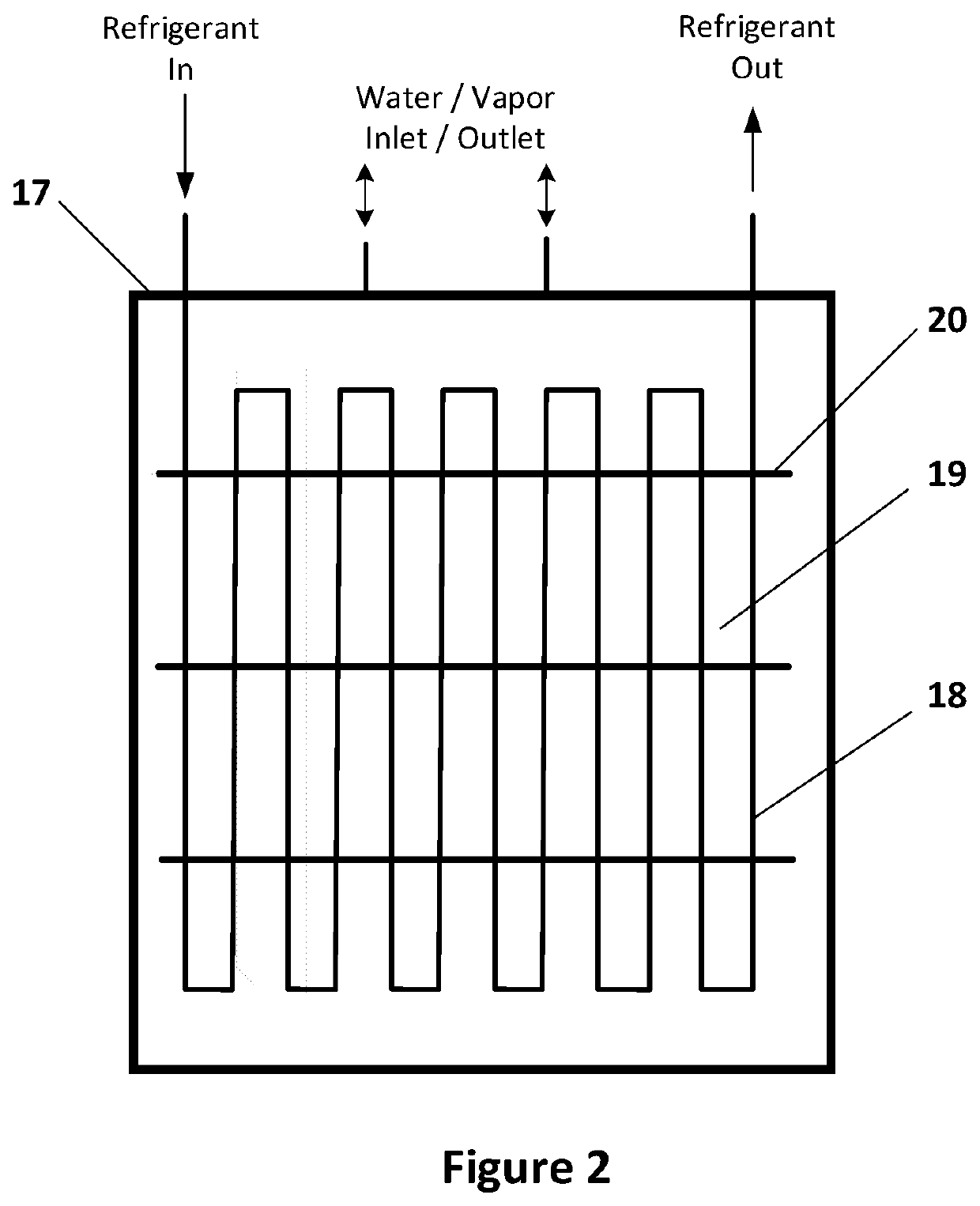
[0017]The conventional air conditioning or refrigeration system consists of an evaporator 1, a compressor 2, a condenser 3, and a throttle 4, they are suitably sized and interconnected to provide air conditioning for a residential house or refrigeration for a commercial establishment such as a show case in a supermarket or refrigeration for an industrial process such as food processing. Air to be conditioned is brought into heat exchanger relation with the evaporator 1 by means of suitable circulation equipment (not shown) into the area being conditioned. An ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com