Functionalized substrate to manipulate cell function and differentiation
a functionalized substrate and cell technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics and biotechnology, can solve the problem of relying primarily on the control of culture conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
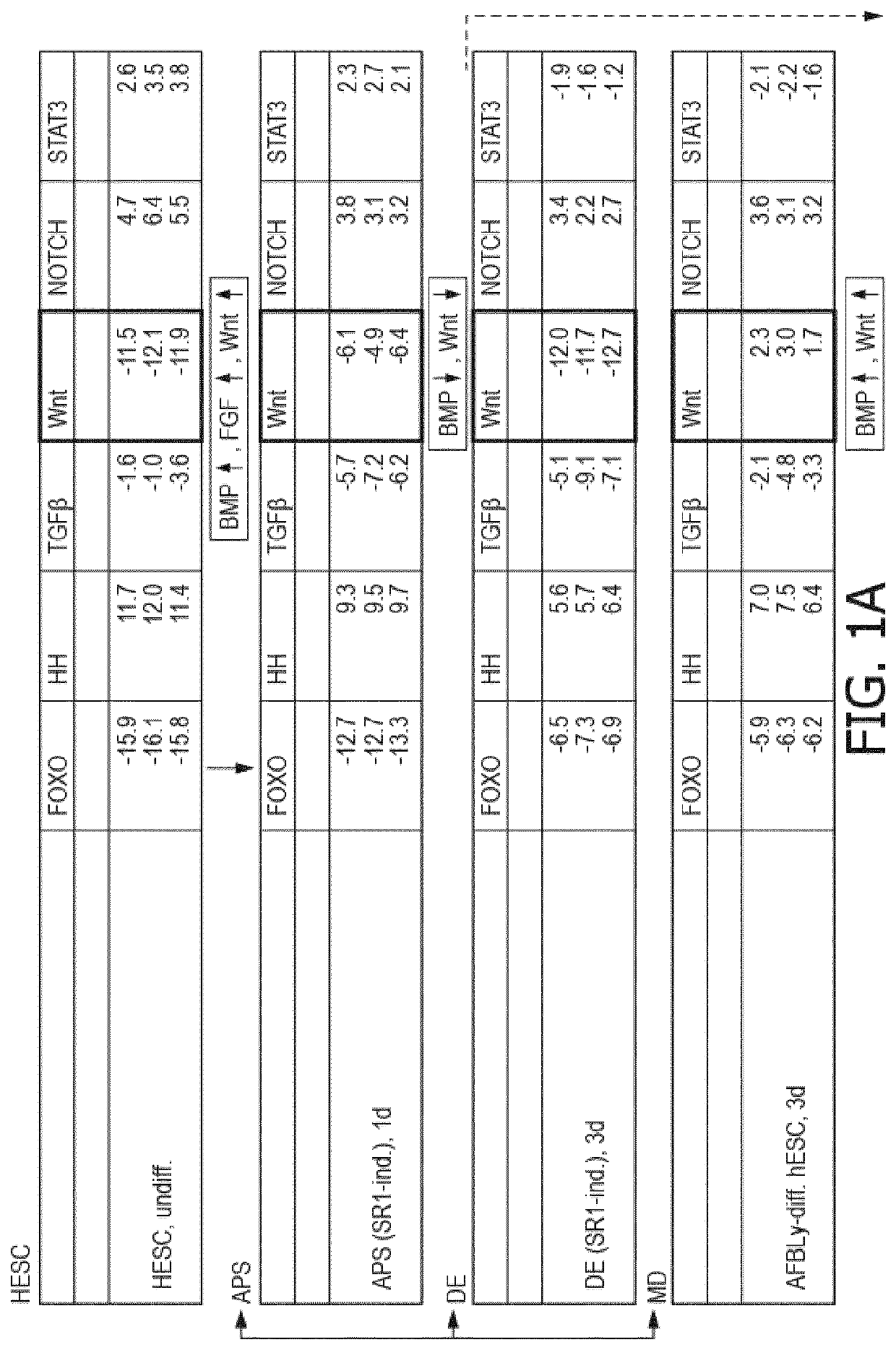
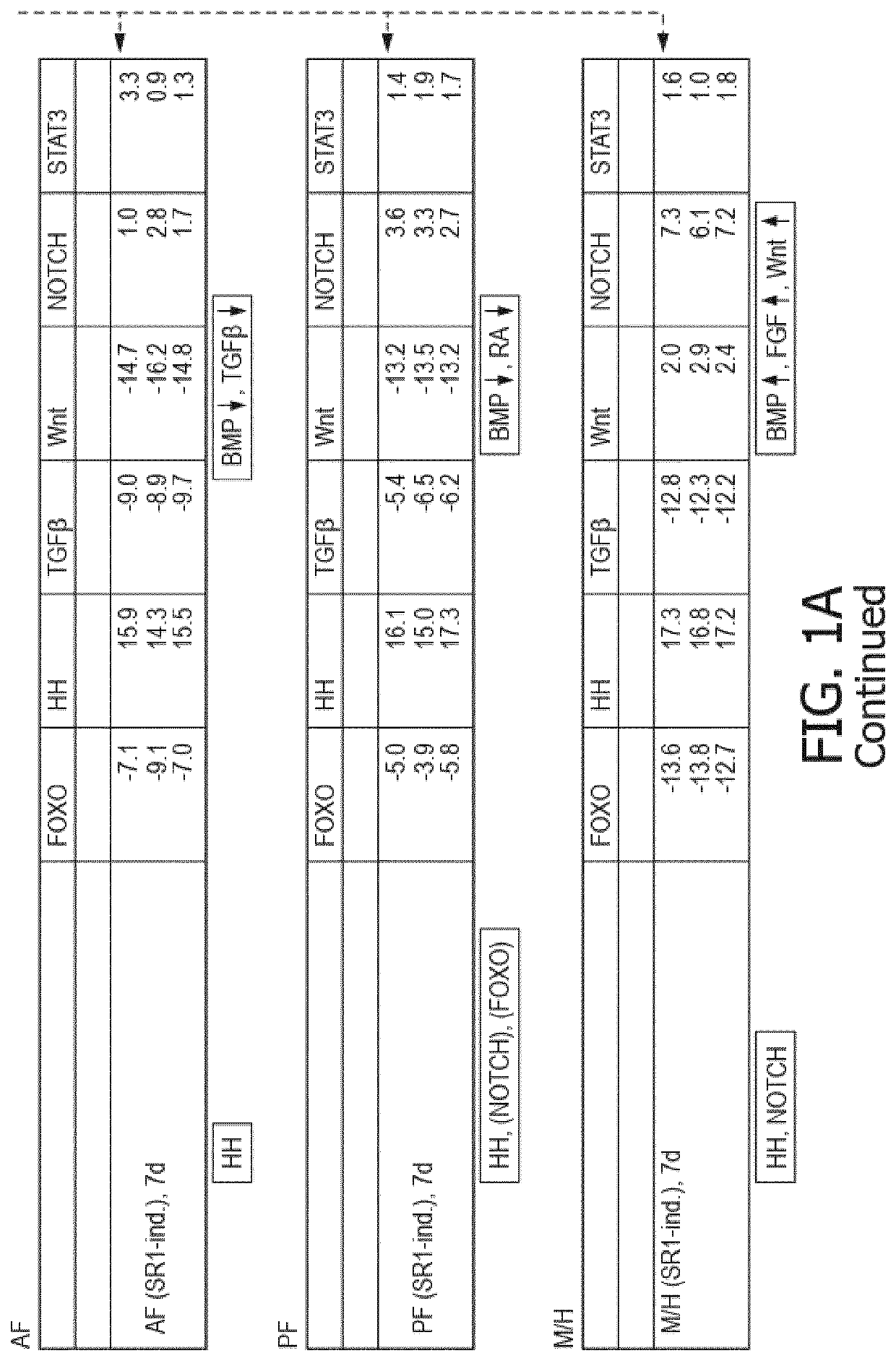
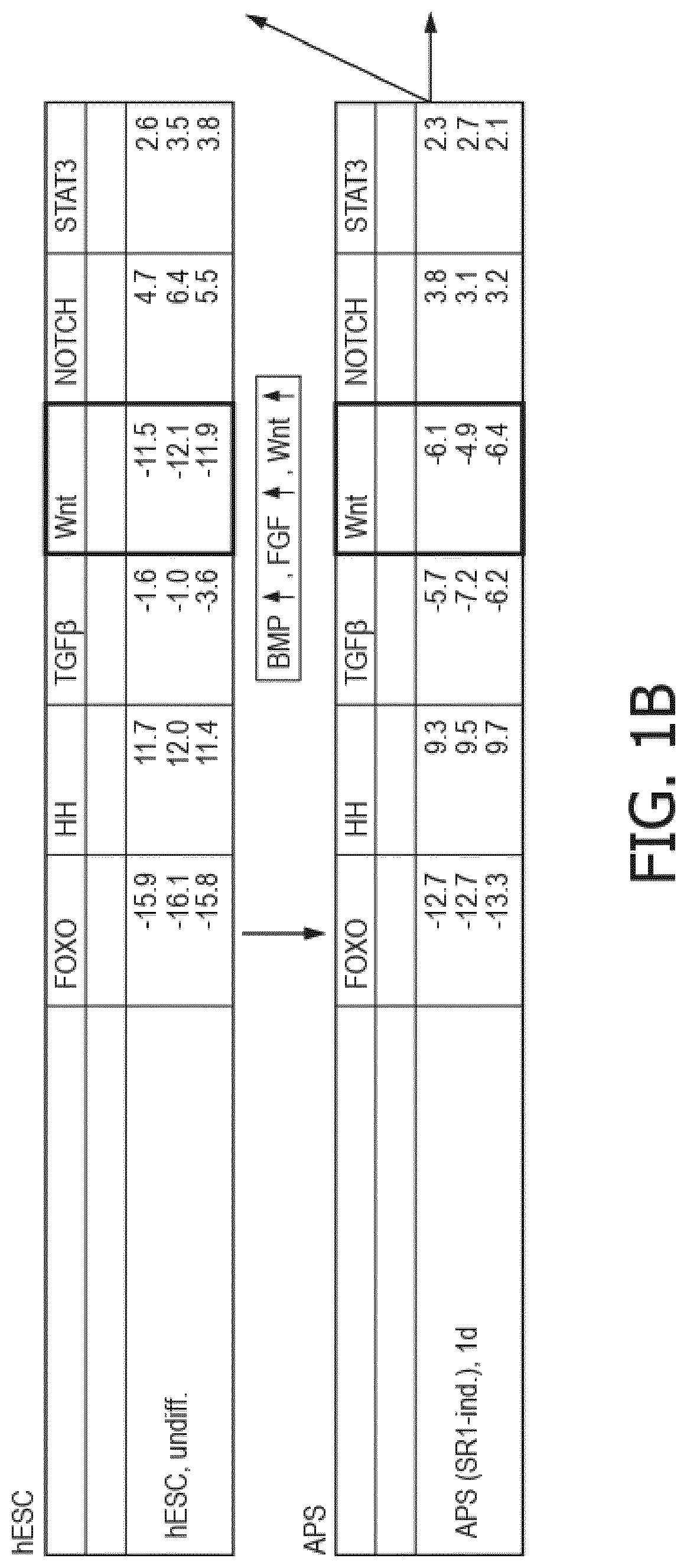
[0046]The following embodiments merely illustrate particularly preferred methods and selected aspects in connection therewith. The teaching provided herein may be used for constructing several test methods, test systems and / or test kits, e.g., to produce a cell culture, tissue and / or an organ. The following embodiments are not to be construed as limiting the scope of the present invention.
[0047]The extracellular microenvironment plays a significant role in influencing cellular behavior including maintenance of potency, cellular attachment, proliferation, metabolization, lineage-specific differentiation and remodeling. By manipulating the culture conditions in which cells including stem cells are cultivated, it is possible to influence cell behavior, restrict differentiation pathways and thereby produce cell cultures enriched in lineage-specific precursors, particular tissues or organs in vitro among others. Based on this understanding, one aspect of the invention relates to a substr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com