Methods of production and use of liquid formulations of plasma proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
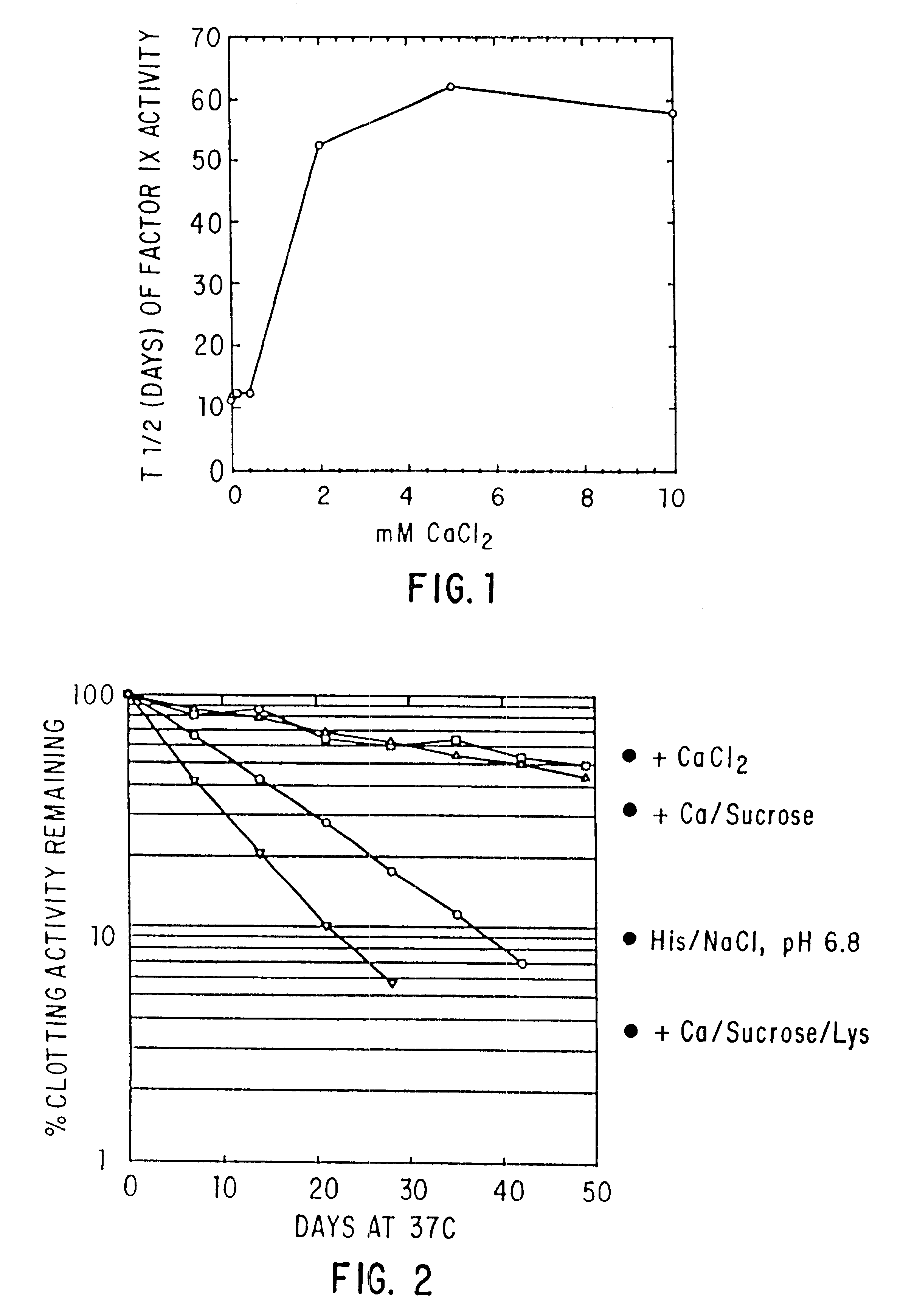
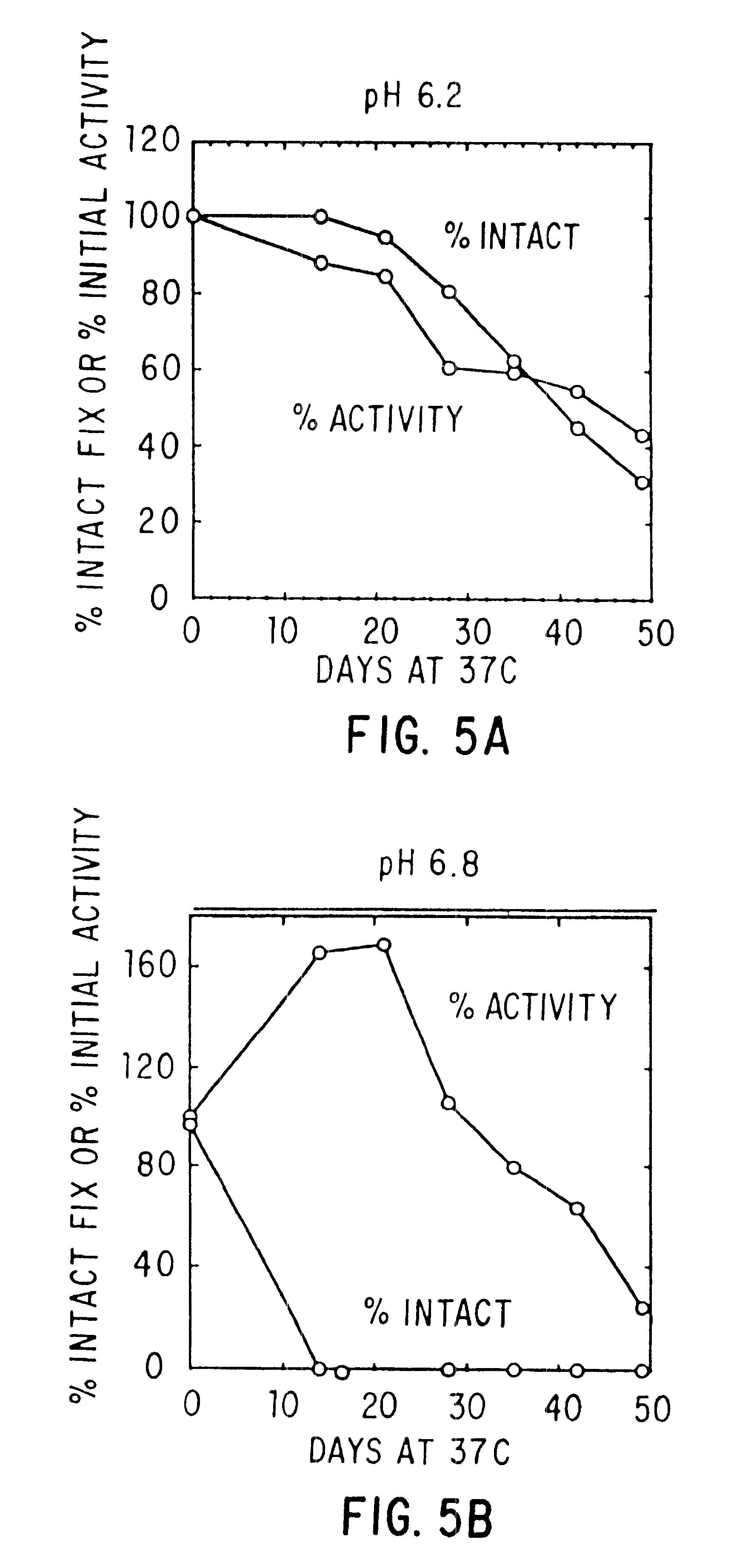
Effect of Buffer, Divalent Cations, and Other Excipients on the Stability of Coagulation Factor IX
CFIX-M (JHL) / DEAE was dialyzed into 0.01 M histidine, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 6.8 (histidine-saline) or was left in 0.02 M sodium citrate (NaCit), 0.11 NaCl, pH 6.8 (citrate-saline). An aliquot of the solution was mixed with an equal volume of 2X additive, prepared at twice the desired final concentration in the appropriate buffer (histidine-saline or citrate-silane). The formulated solutions were sterile filtered, aseptically dispensed into sterilized tubes, incubated at 37.degree. C. or 4.degree. C. for the designated length of time, and frozen until the end of the study, when the samples were thawed and assayed.
Factor IX coagulation assays were performed by a one-stage method using Kontakt brand APTT (Pacific Haemostasis) and congenital Factor IX-deficient plasma (George King or Universal Reagents). The standard was a lyophilized CFIX-SD concentrate. Working dilutions of Factor IX were prepar...
example 2
Effect of Various Excipients on Stability of Coagulation Factor IX in Histidine-saline
CFIX-M (JHL) in citrate-saline was diluted 1:10 in 0.01 M histidine, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 6.8 (histidine-saline) to give a final composition of 0.009 M histidine, 0.002 M citrate, 0.1 M NaCl, pH 6.8 (Buffer A) or was dialyzed against histidine-saline (Buffer B). Thereafter, the samples were treated as in Example 1, above, with the following changes:
(1) Samples were incubated at 37.degree. C., as indicated on the table below.
(2) Factor IX coagulation assays were performed on a Lancer Coagulyzer II.
Results
The stability of samples is shown in Table 2, below:
TABLE 2 In Vitro Half-life (T.sub.1 / 2 in Days) of Clotting Activity of Factor IX-M at 37.degree. C. NUMBER FORMULATION T.sub.1 / 2 (DAYS) 1 0.009M Histidine, 0.002M citrate, 0.1M NaCl, 2.2 pH 6.0 2 0.009M Histidine, 0.002M citrate, 0.1M NaCl, 4.2 pH 8.0 3 0.009M Histidine, 0.002M citrate, 0.1M NaCl, 5.0 pH 6.8 (Buffer A) 4 0.05M Glycine in Buffer A 2.8 5 0...
example 3
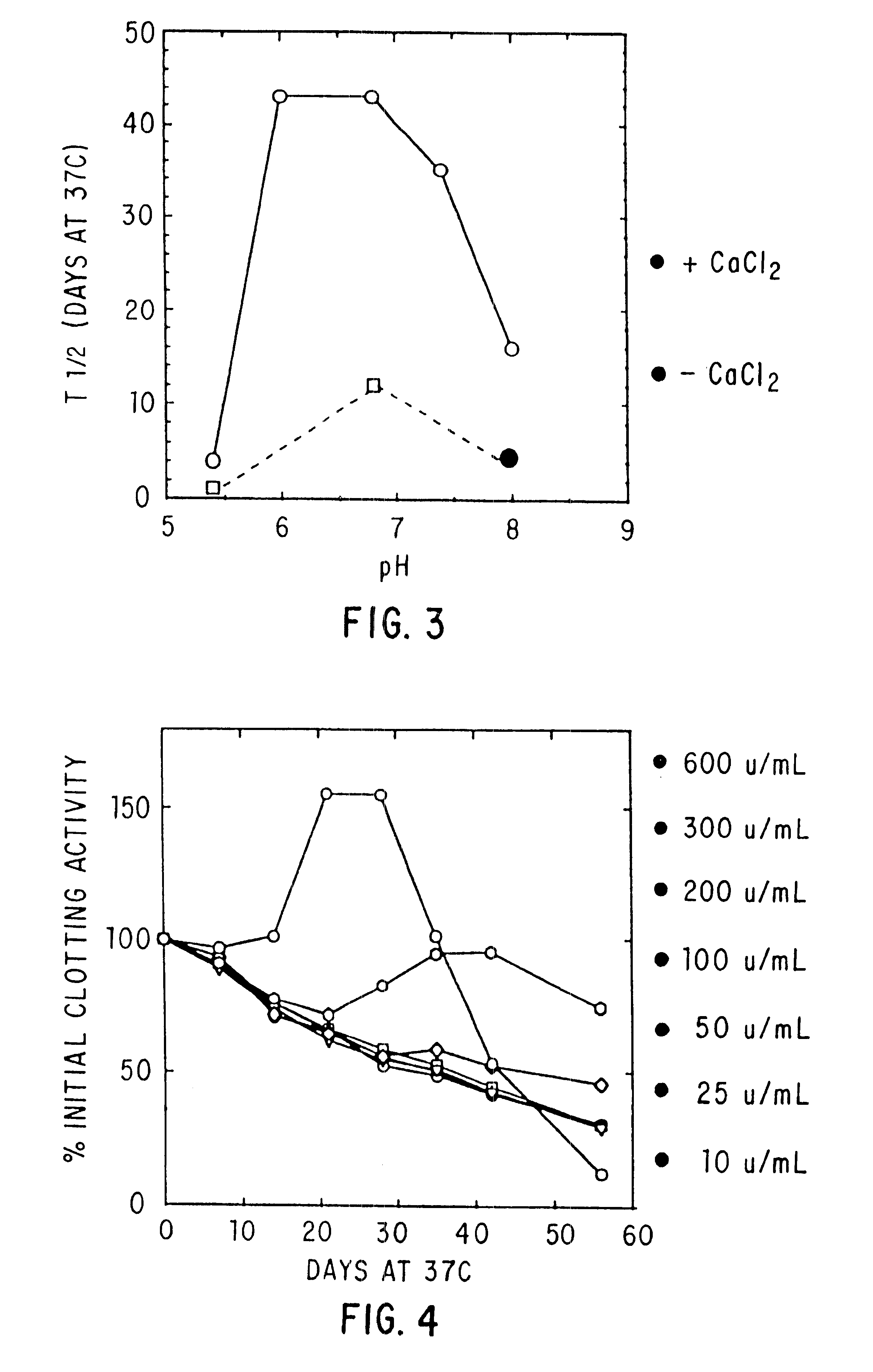
Effect of pH, Purity and Excipients on Stability of Coagulation Factor IX
Factor IX-M (JHL) with or without DEAE polishing, CFIX-SD, and ine in ARC formulation (ARC / A9) were treated as in Example 2 above.
Results
The stability of samples is shown in Table 3, below:
TABLE 3 In Vitro Half-life (T.sub.1 / 2 in Days) of Clotting Activity of Factor IX at 37.degree. C. T.sub.1 / 2 NO. FORMULATION pH FIX 37.degree. C. 1 0.01M Hist / 0.1M NaCl + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 6.8 DEAE 49 2 0.01M Hist / 0.1M NaCl 6.8 DEAE 12 3 Hist / NaCl + 20% Sucrose + 10 mM 6.8 DEAE 42 CaCl.sub.2 4 Hist / NaCl + 0.5M Glycine + 20% 6.8 DEAE 37 Sucrose + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 5 Hist / NaCl + 10 mM CaCl 6.8 CFIX-SD 18* 6 Hist / NaCl 6.9 CFIX-SD 7 7 Hist / NaCl + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 6.8 ARC / A9 17 8 Hist / NaCl 6.9 ARC / A9 2.5 9 Hist / NaCl + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 6.0 DEAE 43 10 Hist / NaCl + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 6.8 DEAE 43 11 Hist / NaCl + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 7.4 DEAE 35 12 Hist / NaCl + 10 mM CaCl.sub.2 8.0 DEAE 16 13 Hist / NaCl + 0.5M Lysine + 10 mM 6.8 DEAE 6 CaCl.sub.2 +...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com