Technology for preparing ultrafine nano metal oxide materials
A nano-oxide and nano-metal technology, applied in the field of preparation of nano-metal oxide materials, can solve the problems of complex preparation process conditions of nano-oxide materials, poor controllability of nano-size, and high preparation cost, and achieve fast price and operation method. Simple, high specific surface area effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
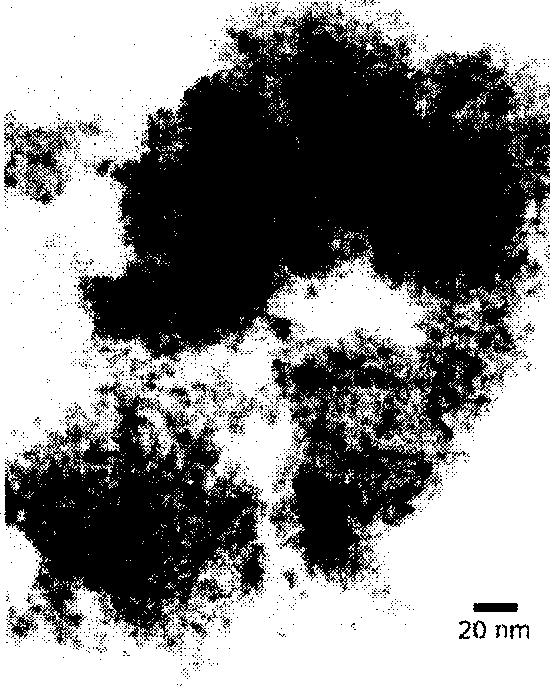
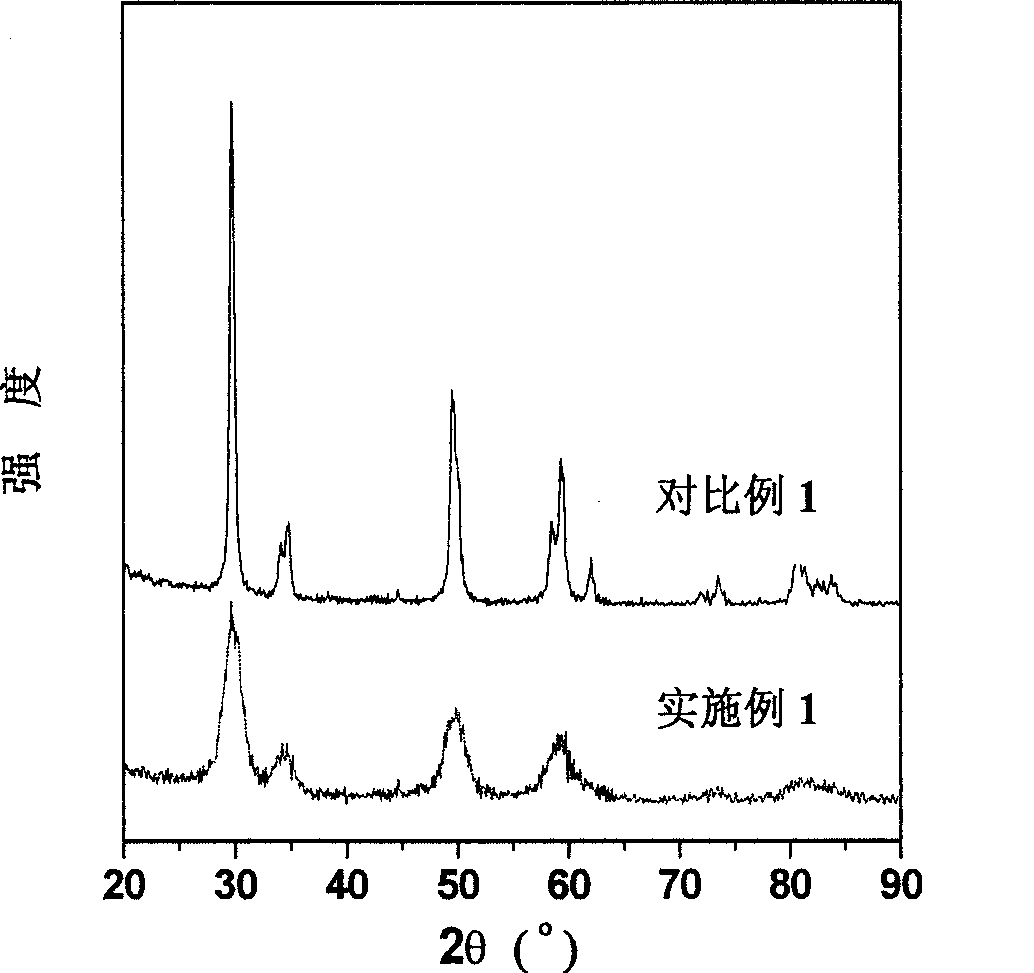
[0021] According to Example 3, a loose powder gel, that is, an oxide precursor, was prepared. Afterwards, the oxide precursor was calcined at 800° C. for 3 hours under normal pressure with nitrogen protection at a flow rate of 30-50 ml / min to obtain a black carbon-containing oxide intermediate. Finally, the black carbon-containing oxide intermediate was roasted in the air at 400°C for 3 hours to obtain zirconium-cerium oxide. Characterized by XRD, TEM and BET, the prepared cerium-zirconium oxide was a nanomaterial with a high specific surface area, see Schedule 1 and the attached figure 1 , attached figure 2 , attached Figure 4 .
Embodiment 2
[0025] Weigh 32.37g Ce(NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O, 8.00g Zr(NO 3 ) 4 ·5H 2 O and 16.16g of malic acid were mixed and dissolved in an appropriate amount of deionized water to obtain a precursor solution. Then, under the condition of stirring, heat it with an electric furnace with controlled current, carefully evaporate to a viscous sol, and dry it at about 100°C for 10 to 14 hours to obtain a loose powder gel, that is, the oxide precursor. Afterwards, the oxide precursor was calcined at 600° C. for 3 hours under normal pressure with nitrogen protection at a flow rate of 30-50 ml / min to obtain a black carbon-containing oxide intermediate. Finally, the black carbon-containing oxide intermediate was roasted at 400°C in the air for 3 hours to obtain cerium-zirconium oxide. Characterized by XRD, TEM and BET, the prepared cerium-zirconium oxide was a nanomaterial with a high specific surface area, see Schedule 1 and the attached Figure 1~3 .
Embodiment 3
[0029] Weigh 7.30g Ce(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O, 28.87g Zr(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O and 17.66g of citric acid were mixed and dissolved in an appropriate amount of deionized water to obtain a precursor solution. Then heat it with a water bath under the condition of stirring, carefully evaporate to a viscous solution, and dry it at about 100°C for 10 to 14 hours to obtain a loose powdery gel, that is, the oxide precursor. Afterwards, the oxide precursor was calcined at 600° C. for 3 hours under normal pressure with nitrogen protection at a flow rate of 30-50 ml / min to obtain a black carbon-containing oxide intermediate. Finally, the black carbon-containing oxide intermediate was roasted in the air at 400°C for 3 hours to obtain zirconium cerium oxide. Characterized by XRD, TEM and BET, the prepared zirconium cerium oxide was a nanomaterial with a high specific surface area, see Schedule 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com