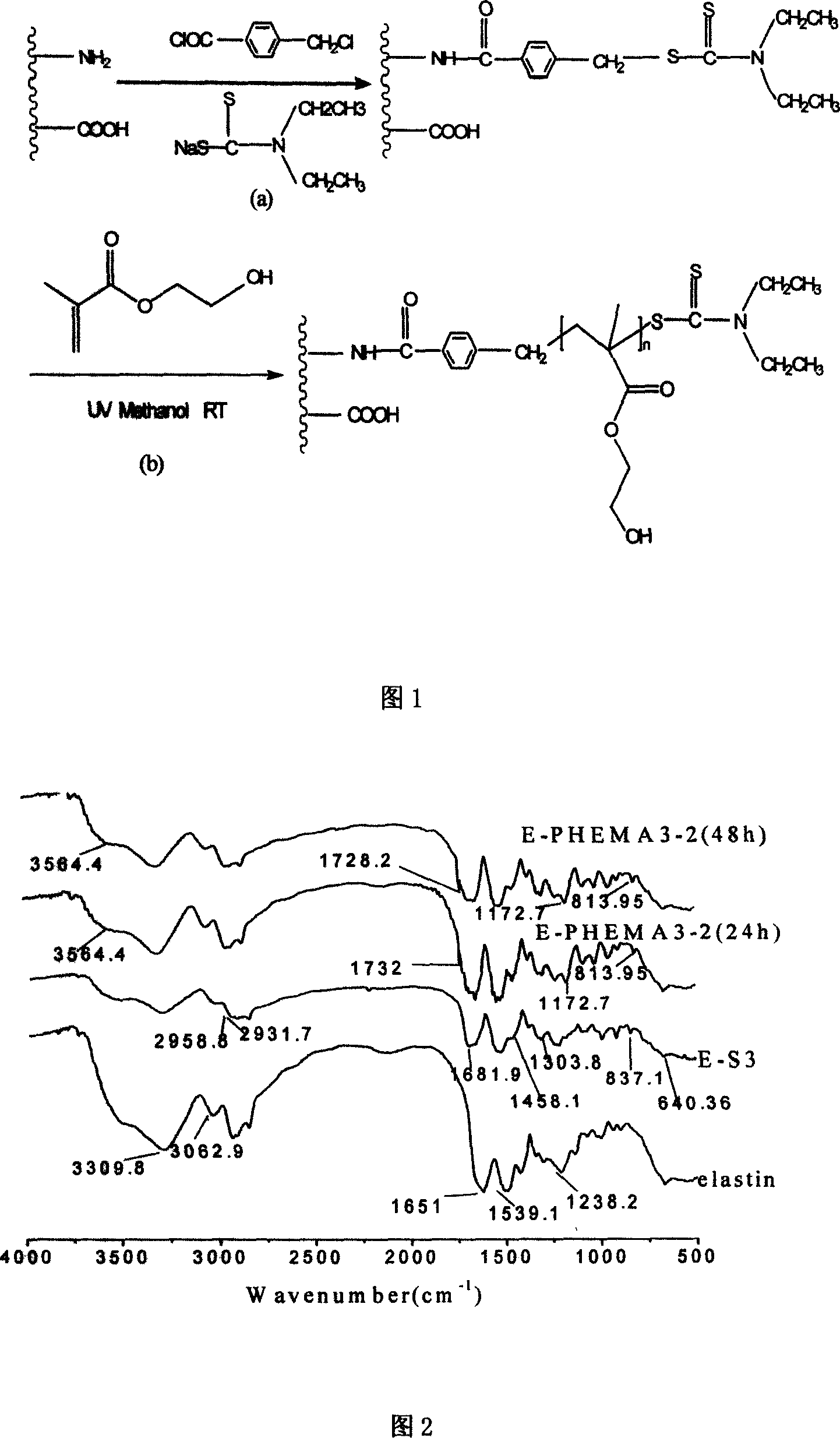
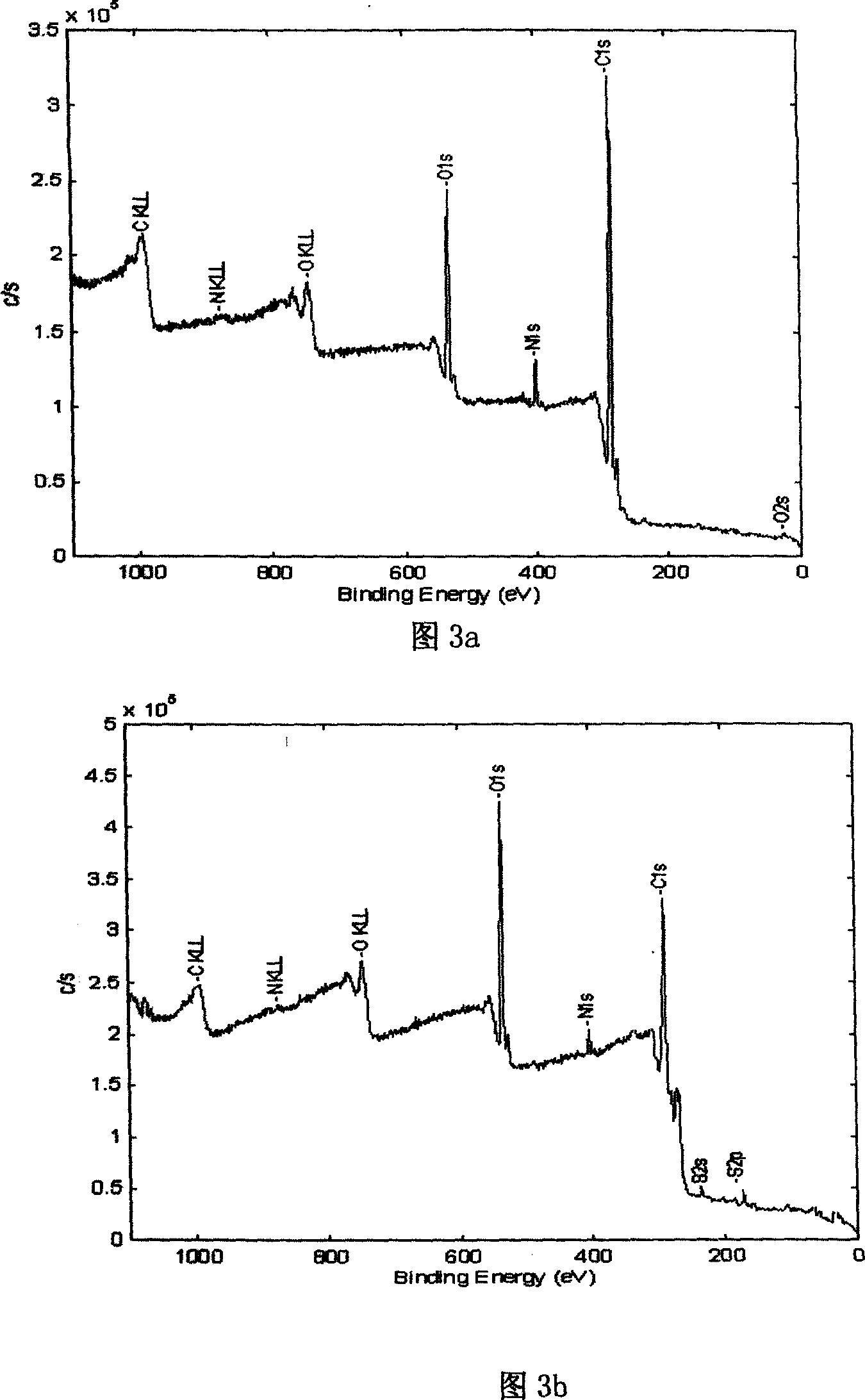
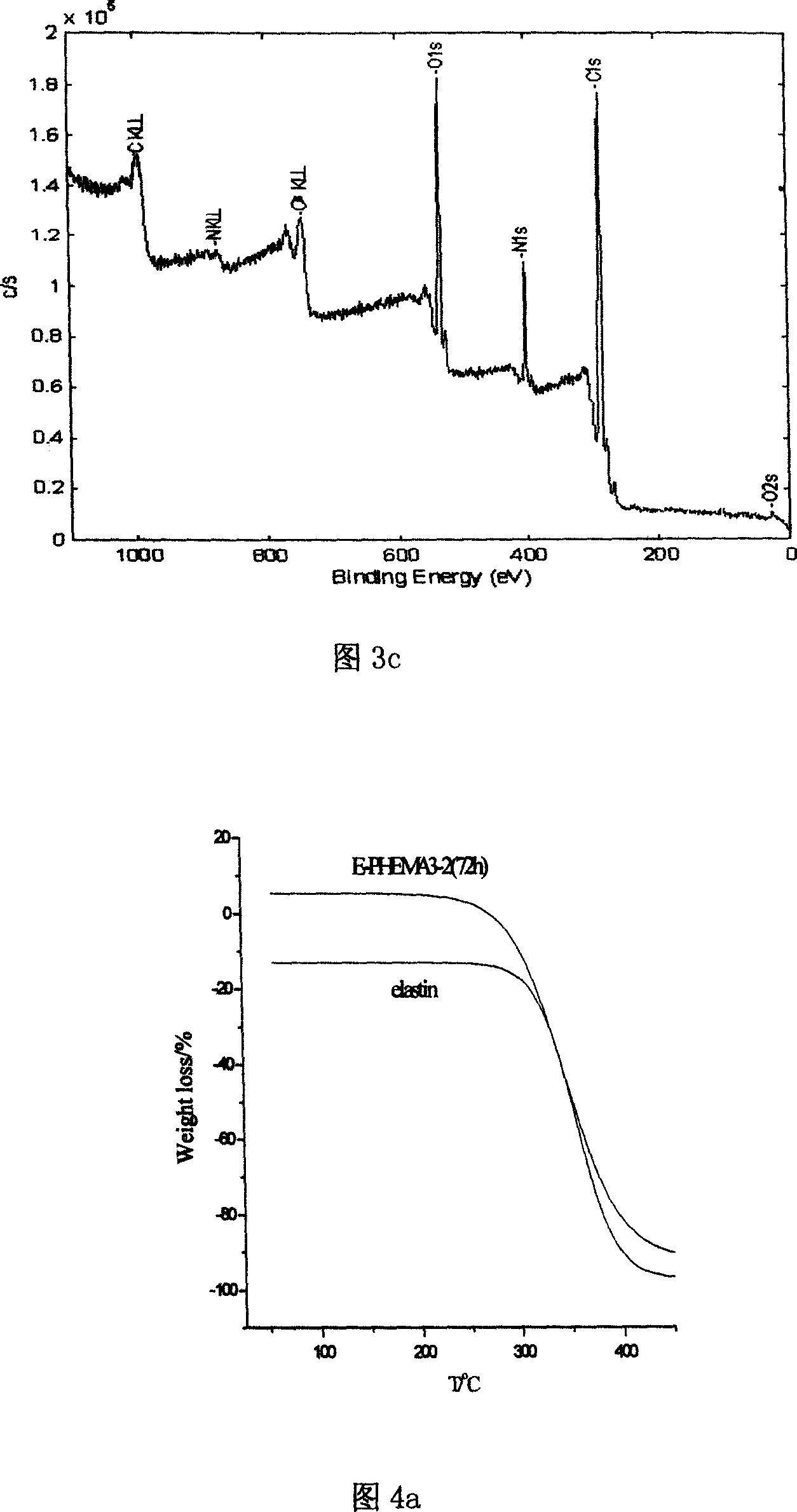
Method of modifying elastin by initiation transition termination agent
An elastin and terminator technology, which is applied in the field of elastin modification by initiating transfer terminators, and can solve problems such as no research reports.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0034] (1) 3 g of unswollen elastin, 1.36 g of triethylamine, and 2.03 g of p-chloromethylbenzoyl chloride were reacted at 20° C. for 15 h, and the product was fully washed and dried to obtain chlorinated elastin.
[0035] (2) 1.5g of chlorinated elastin and 3.84g of sodium diethyldithiocarbamate were reacted at 20°C for 15h, and the product was fully washed and dried to obtain vulcanized elastin, which is a macromolecular thioiniferterminator.
[0036] (3) in N 2 Add 11.2mL of β-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 11.2mL of anhydrous methanol and 0.50g of macromolecular thio-iniferter under protection, put the reaction bottle into a 250W UV lamp reaction box, and react at 20°C for 15h. The product is fully washed and dried to obtain polymethacrylate-β-hydroxyethyl ester modified elastin polymer.
example 2
[0038] (1) 4 g of unswollen elastin, 20 g of triethylamine, and 57.14 g of p-chloromethylbenzoyl chloride were reacted at 35° C. for 12 h, and the product was fully washed and dried to obtain chlorinated elastin.
[0039] (2) 2.5g of chlorinated elastin and 44.53g of sodium diethyldithiocarbamate were reacted at 25°C for 18h, and the product was fully washed and dried to obtain vulcanized elastin, a macromolecular thioiniferterminator.
[0040] (3) in N 2 Add 50mL of β-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 60mL of anhydrous methanol and 1.50g of macromolecular thioiniferter under protection, put the reaction bottle into a 300W UV lamp reaction box, and react at 40°C for 48h, and the product passes through Fully washed and dried to obtain polymethacrylate-β-hydroxyethyl ester modified elastin polymer.
example 3
[0042] (1) 5 g of unswollen elastin, 40 g of triethylamine, and 74.75 g of p-chloromethylbenzoyl chloride were reacted at 35° C. for 24 h, and the product was fully washed and dried to obtain chlorinated elastin.
[0043] (2) 4 g of chlorinated elastin and 115.78 g of sodium diethyldithiocarbamate were reacted at 30°C for 24 hours, and the product was fully washed and dried to obtain vulcanized elastin, which is a macromolecular thio-iniferterminator.
[0044] (3) Add 60mL of β-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, 90mL of anhydrous methanol and 3g of macromolecular thio-iniferter under the protection of Ar, put the reaction bottle into a 400W UV lamp reaction box, and react at 35°C After 96 hours, the product was fully washed and dried to obtain an elastin polymer modified by polymethacrylate-β-hydroxyethyl ester.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com