Waste treatment systems
A waste treatment and stage technology, applied in the direction of energy wastewater treatment, waste fuel, sludge treatment, etc., to achieve effective treatment effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
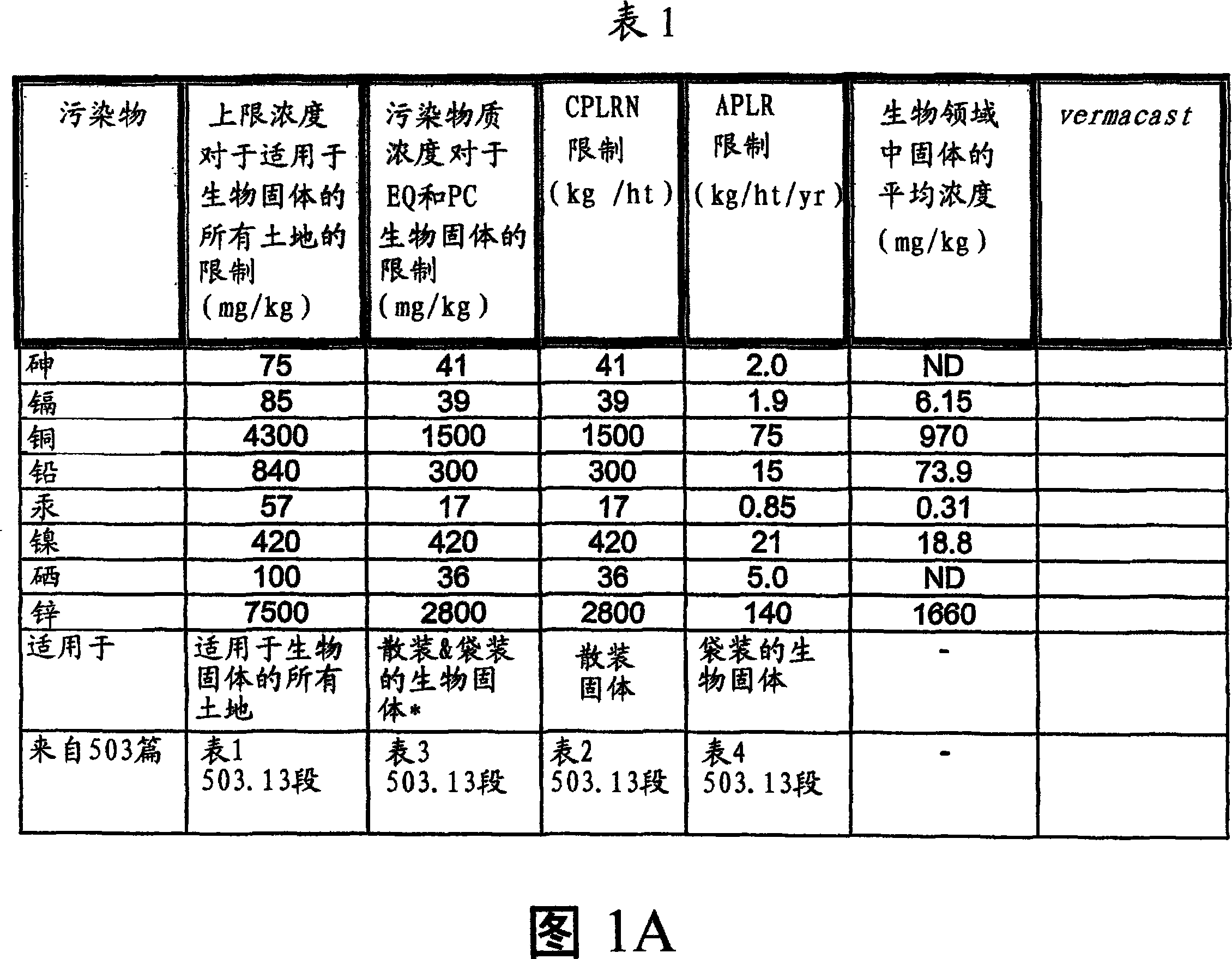
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] Described below is an exemplary waste disposal system that has been constructed. A mechanical strainer made by welding 1 / 4 inch by 2 foot flat steel bars spaced 3 / 4 inch apart for one strainer and 3 / 8 inch apart for a second strainer . The collection tank consisted of the bottom half of a 1500 gallon concrete tank purchased from Montano (Santa Fe, NM). The concrete pool is divided into two equal parts by placing a 1 / 4 inch steel bar in the middle of the concrete pool. A 30 degree "V" notch weir was cut to divide the panels, allowing the flow of septic from one side to the other. The larger bar screen is placed on the right side of the pool and the smaller bar screen is placed on the left or input side of the concrete pool. The collection tank was in fluid communication with the equalization tank, constructed on site using stabilized native soil, and a 30 mil PVC sleeve, commercially available from Snow Company (Albuquerque, NM). An earthen equalization tank 230 (see...
Embodiment 2
[0108] An exemplary waste treatment system includes a mechanical filter screen device in fluid communication with one or more collection basins via fluid conduits. The fluid collection tank is in fluid communication with an equalization tank of about 200 cubic meters through a fluid conduit. The equalization tank has a network of 50mm diameter PVC piping, spaced 50cm apart and in fluid communication with a blower / air compressor capable of delivering approximately 0.9m3 / min / 100m3 of received corrosion and / or or domestic sludge. The blower is controlled by a timing device and a low float. The equalization tank is in fluid communication with the 4 reed bases through 4 PVC sleeves with a diameter of 75 mm, which are equipped with 4 inflow pumps of 1.0-2.0 horsepower. The delivery of septic is controlled by a timing device that boosts each of the 4 pumps in series. Distribution of rot on the surface of the reed base was provided by a network of 100mm PVC casings arranged in a 7m...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Figure 20 shows a block diagram of a waste treatment system for treating domestic sludge and / or septage. Waste treatment system 500 includes centrifuge 510 in fluid communication with equalization vessel 520 via fluid conduit 515 . The centrifuge 510 is operated to remove inorganic and organic solids from the septage prior to delivering the septage to the equalization vessel 520 . The remainder of this article discusses the functions of the equalization vessel for illustration, such as aeration and mixing. Equalization vessel 520 is in fluid communication with hyacinth lagoon 530 . Hyacinth lagoon 530 is in fluid communication with trickle biofilter 540 via fluid conduits 545 and 546 . As discussed elsewhere in this paper, trickle flow biofilters are operated for nitrifying fluids. Hyacinth Lagoon 530 is also in fluid communication with constructed wetland 550 via fluid conduit 547 . As discussed elsewhere in this paper, structured wetlands are suitable for providin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com