Method of filling redundancy for semiconductor manufacturing process and semiconductor device
A filling method and technology of manufacturing process, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device components and other directions, can solve problems such as adverse side effects, reduce device performance, increase parasitic capacitance, etc., to reduce power consumption, Reduce the number of redundant metals, the best effect of redundant layout distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] In order to make the present invention easier to understand, the following descriptions will be written in the form of embodiments or examples, together with the accompanying drawings. However, these embodiments or examples are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Any changes and further modifications will be described in the embodiments, or can be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art based on the content disclosed in the present invention. Furthermore, the presence of one or more adjacent elements does not imply that there are no intervening elements present. Furthermore, reference numerals may appear repeatedly in these embodiments, but it does not mean that the characteristics of one embodiment can be applied to another embodiment, even if they have the same reference numerals.
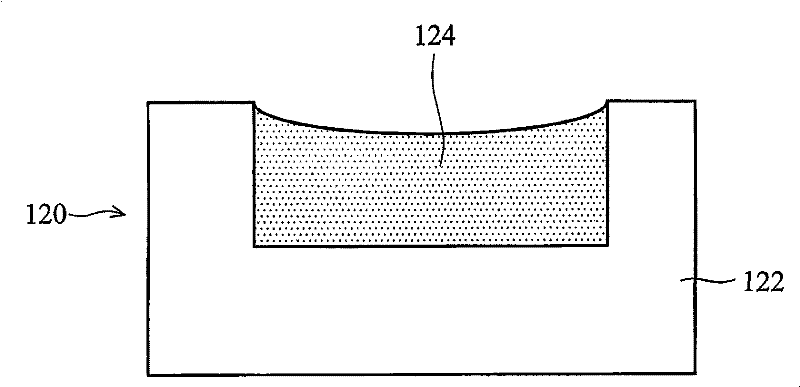
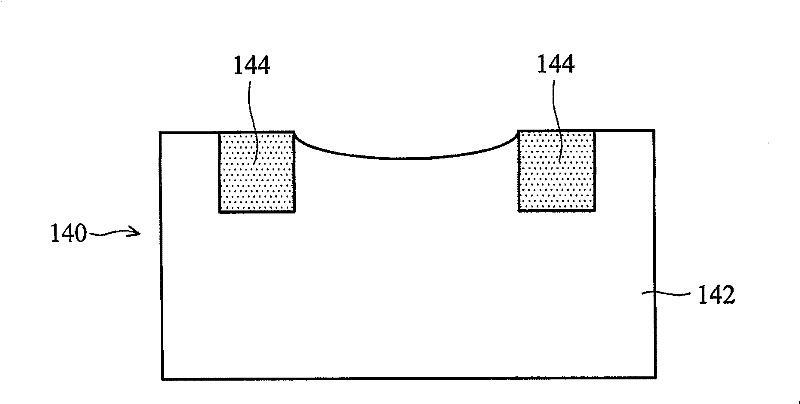
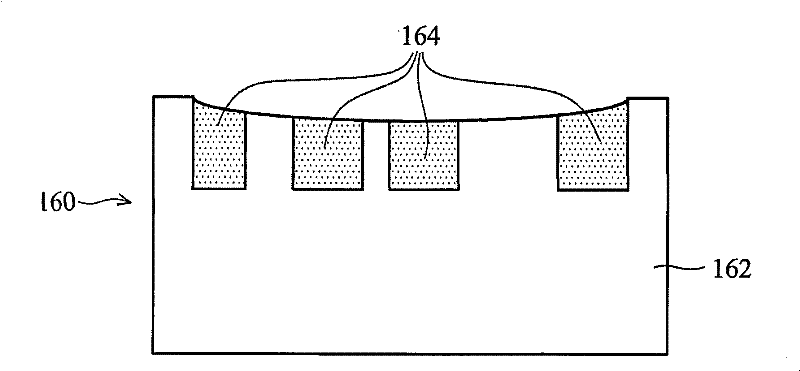
[0035] FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view 100 of four semiconductor wafers showing dishing and erosion phenomena caused by chemical mechanical polishing. exi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com