Passivation method for shunt bug of non-crystal silicon film light voltage module
A technology of amorphous silicon thin film and photovoltaic module, applied in photovoltaic power generation, climate change adaptation, sustainable building, etc., can solve the problems of slow laser scribing, high cost, poor stability of amorphous silicon alloy, etc., and achieve less shunt defects, The effect of high output power and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The invention relates to a simple, low-cost and high-efficiency method for eliminating shunt defects, which is suitable for a see-through photovoltaic module containing a relatively thin amorphous silicon active absorption conversion layer.
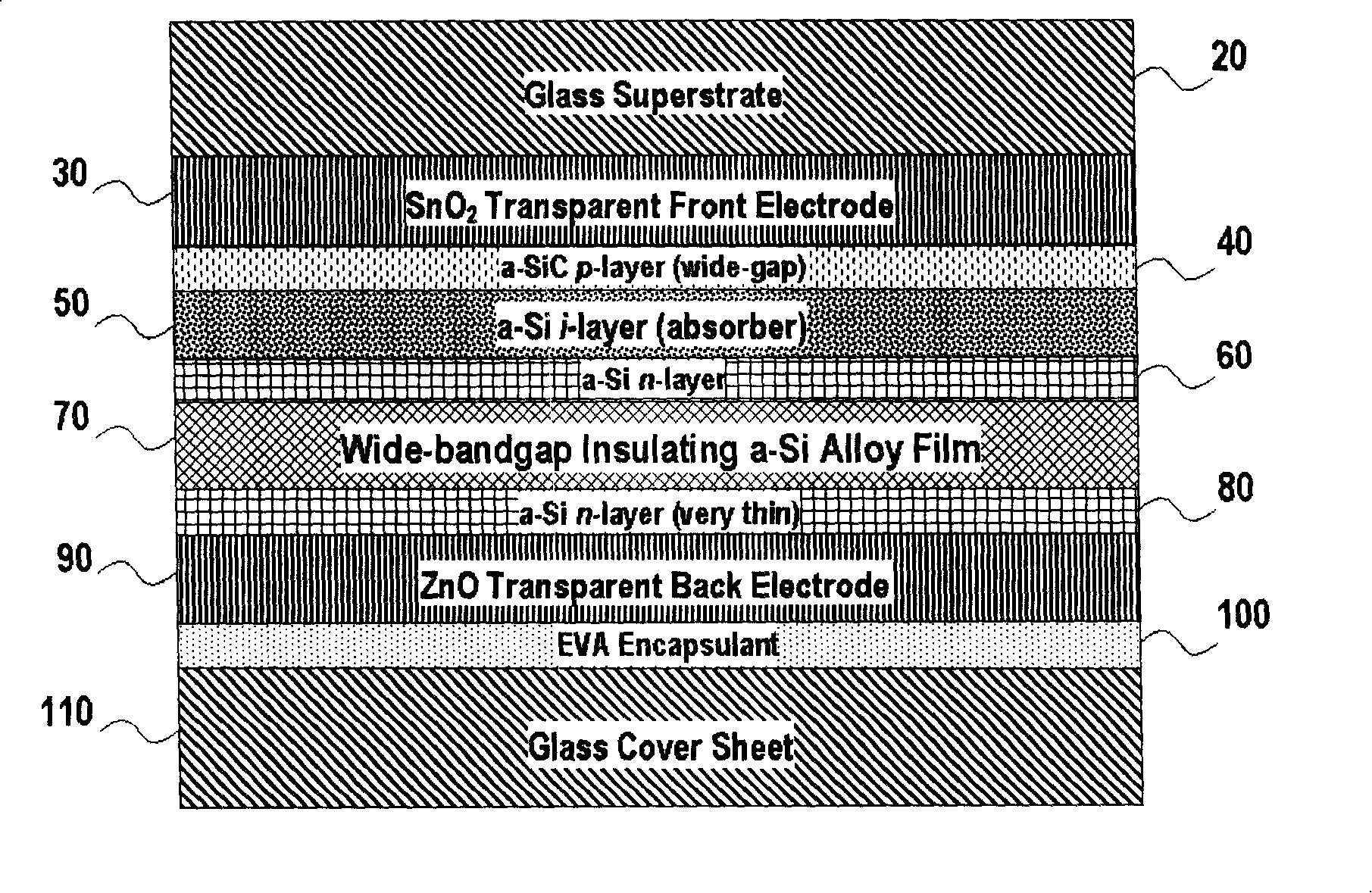
[0031] An implementation of the current invention, consisting of figure 2 explained. figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of a glass-encapsulated amorphous silicon solar cell based on figure 1 The p-i-n structure shown, but corrected. The only change in the device structure is that a first n-layer 60 based on amorphous silicon is added between the amorphous silicon i-layer and the wide-bandgap amorphous silicon-based shunt suppression layer 70 . In this p-i-n-"i"-n structure ( figure 2 40-50-60-70-80 in ), the shunt suppression "i" layer 70 and the second n-layer 80 form a double-layer suppression structure that acts as a shunt barrier, preventing any form of The diversion caused by the defect. The part that plays a role in t...
Embodiment 2
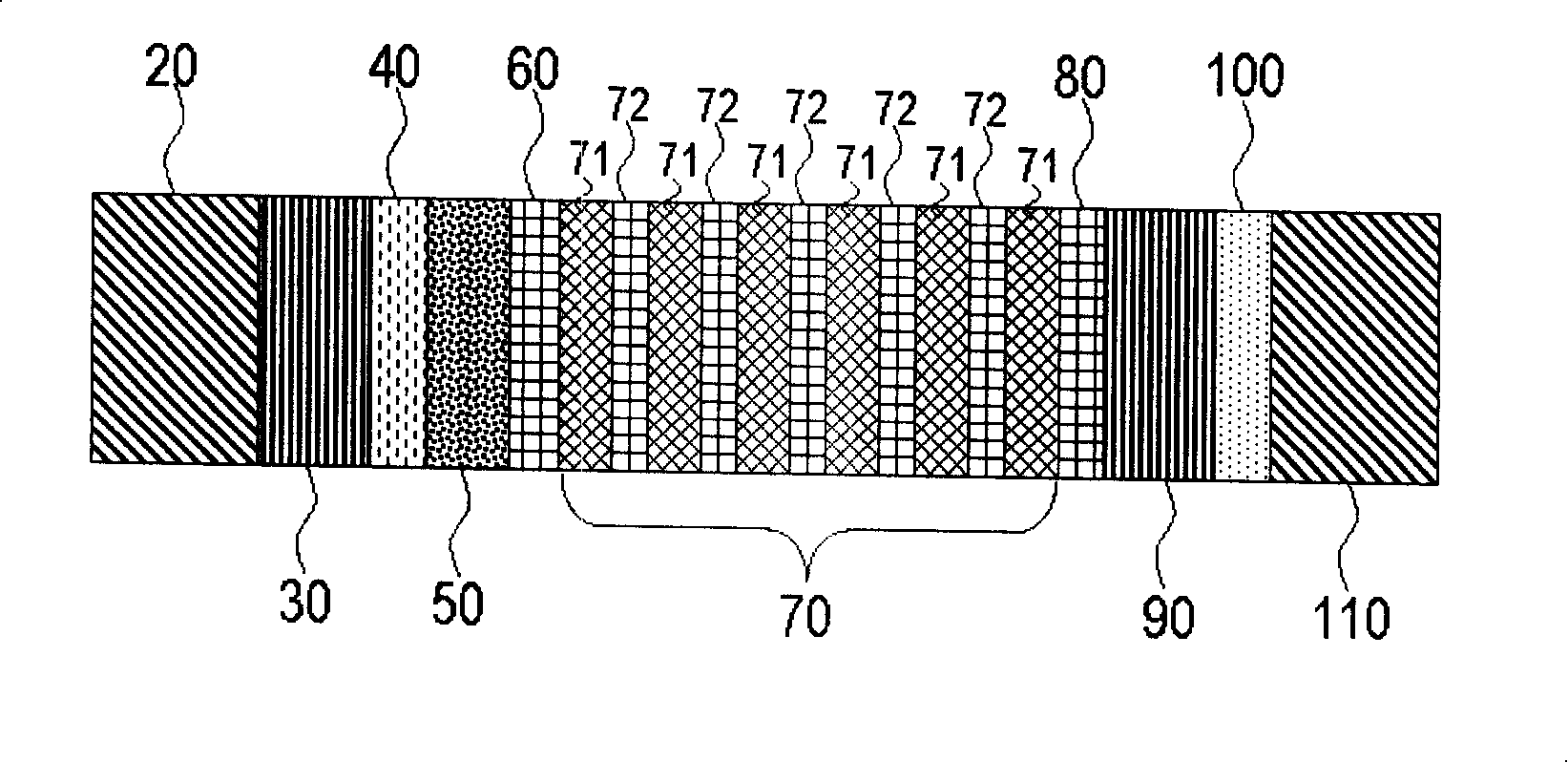
[0037] In fact, in order to make the building-integrated photovoltaic glass window more transparent, the amorphous silicon i-layer 50 needs to be made as thin as possible, but this will lead to more serious shunts. Therefore, the shunt suppression layer 70 based on amorphous silicon must be made as thick as possible to enhance its shunt prevention capability. However, for a given resistivity, if the shunt suppression layer "i" layer 70 is too thick, figure 2 A p-i-n-"i"-n-type device in will lose its energy conversion efficiency due to resistive losses in the "i" layer 70. To solve this problem, we can modify the shunt suppression structure of "i"-n (shunt suppression layer 70 and second n layer 80) by replacing a single thicker film layer with a series of thinner "i"-n bilayer films The shunt suppression layer 70. This concept is image 3 explained in. In this example, the shunt suppression layer 70, which plays the role of shunt passivation, is composed of many superimp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com