Display apparatus, display apparatus driving method and electronic equipment
A technology for display devices and scanning devices, which is applied in lighting devices, logic circuit coupling/interfaces, and circuits using field effect transistors, and can solve problems such as loss of uniformity of the screen and achieve high-quality display images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
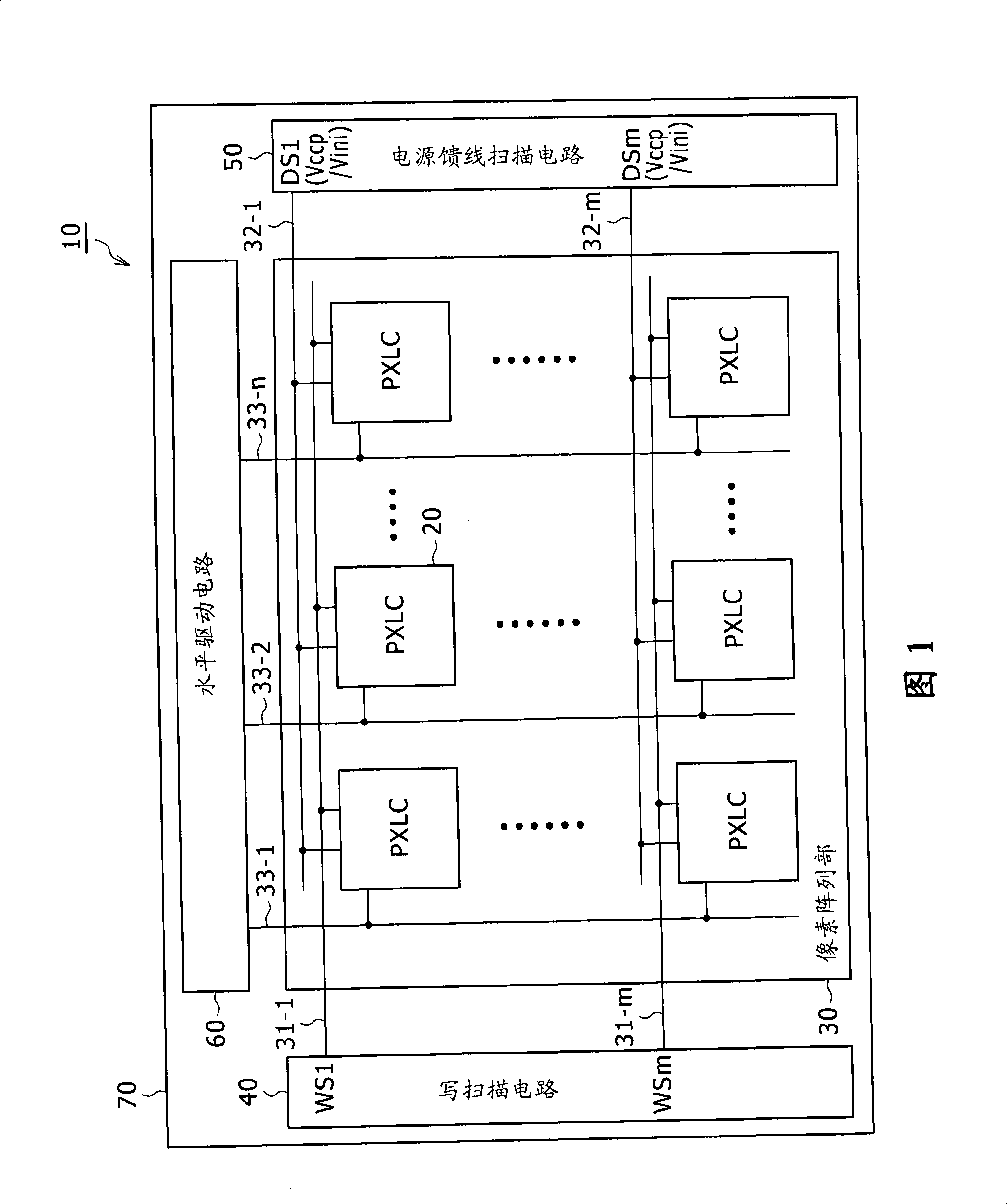
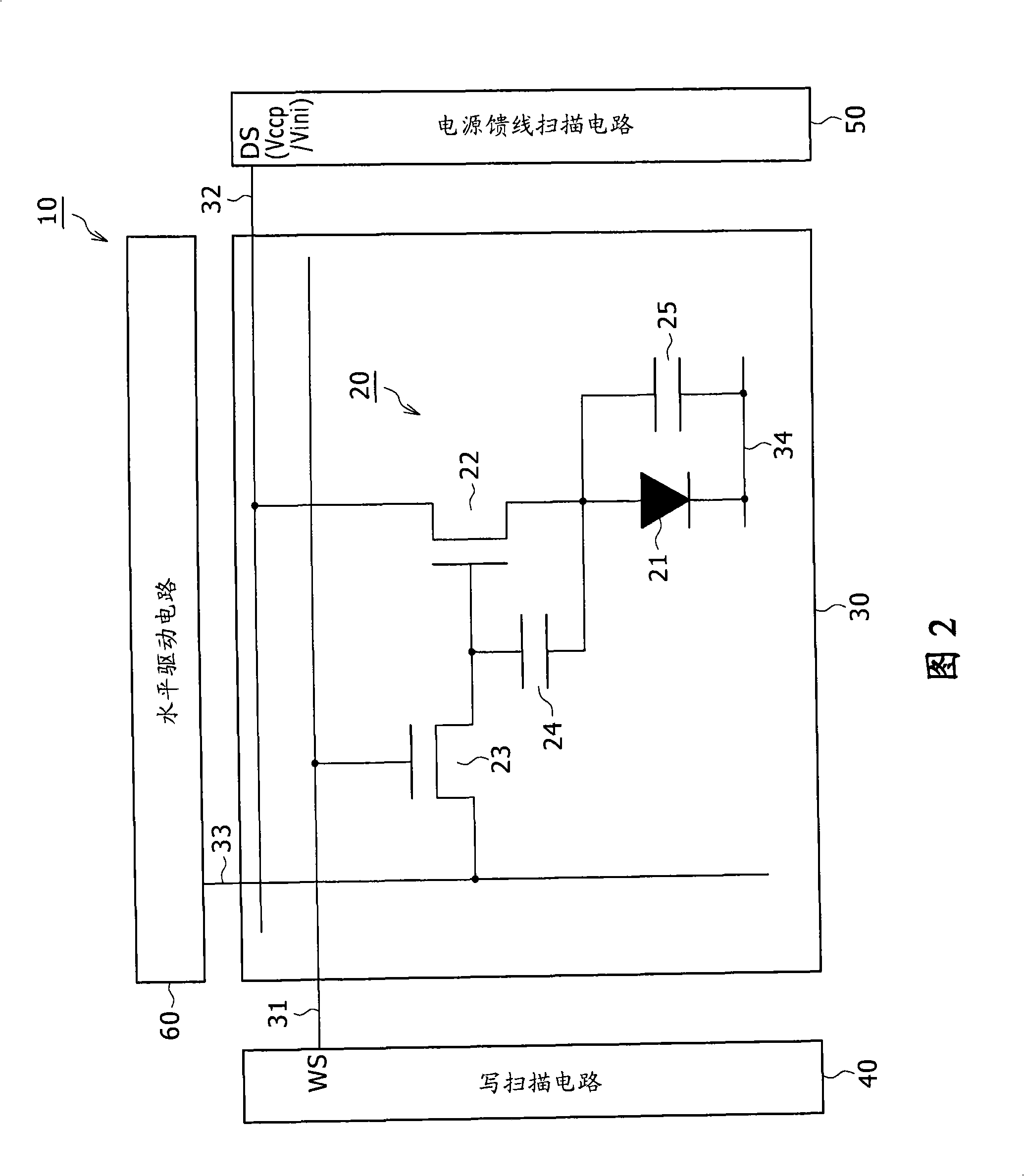
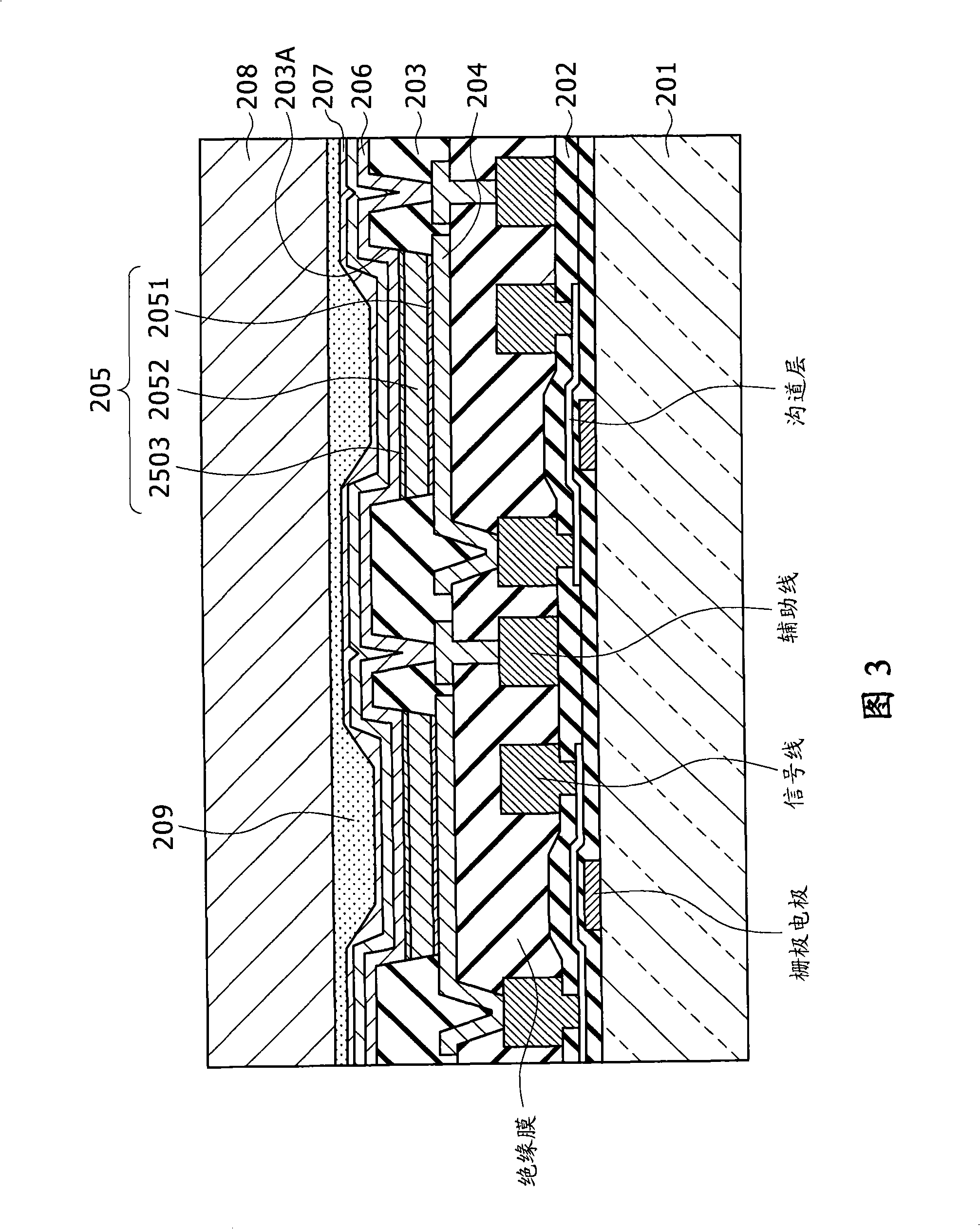
[0149] Figure 10 is a circuit diagram showing a typical configuration of the control device according to the first embodiment. As shown, the control device employs a last-stage buffer 50A connected to the power feeder 32 (ie, any one of the power feeders 32-1 to 32-m). The final-stage buffer 50A is a portion included in the power feeder scanning circuit 50 as a portion connected to the power feeder 32 connected to the pixel row of the pixel array section 30 .
[0150] The final-stage buffer 50A has a CMOS inverter configuration including a P-channel MOS transistor P11 and an N-channel MOS transistor N11. The source of the P-channel MOS transistor P11 is connected to a power supply line of a high first potential Vccp. The source of the N-channel MOS transistor N11 is connected to the power supply line of the low second potential Vini. The drain of the P-channel MOS transistor P11 is connected to the drain of the N-channel MOS transistor N11 through the drain common connecti...
no. 2 example
[0161] Figure 12 is a circuit diagram showing a typical configuration of the control device according to the second embodiment. Figure 12 shown with Figure 10 Elements that are the same as each corresponding element shown are denoted by the same symbols as the corresponding elements. Such as Figure 12 As shown, the control device employs a final stage buffer 50B connected to the power feeder 32 (ie, any one of the power feeders 32-1 to 32-m). The final-stage buffer 50B is a portion included in the power feeder scanning circuit 50 as a portion connected to the power feeder 32 connected to the pixel row of the pixel array section 30 .
[0162] The final-stage buffer 50B has a clocked inverter configuration including a P-channel MOS transistor P11, a P-channel MOS transistor P12, an N-channel MOS transistor N11, and an N-channel MOS transistor N12. The source of the P-channel MOS transistor P11 is connected to a power supply line of a high first potential Vccp. The sourc...
no. 3 example
[0175] Figure 14 is a circuit diagram showing a typical configuration of the control device according to the third embodiment. As shown in the drawing, the control device employs a final-stage buffer 50C connected to the power feeder 32 (ie, any one of the power feeders 32-1 to 32-m). The final-stage buffer 50C is a portion included in the power supply line scanning circuit 50 as a portion connected to the power supply line 32 connected to the pixel row of the pixel array section 30 .
[0176] The final-stage buffer 50C has a two-phase input inverter configuration including a P-channel MOS transistor P13 and an N-channel MOS transistor N13. The source of the P-channel MOS transistor P13 is connected to the power supply line of the high first potential Vccp. The source of the N-channel MOS transistor N13 is connected to the power supply line of the low second potential Vini. The drain of the P-channel MOS transistor P13 is connected to the drain of the N-channel MOS transis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com