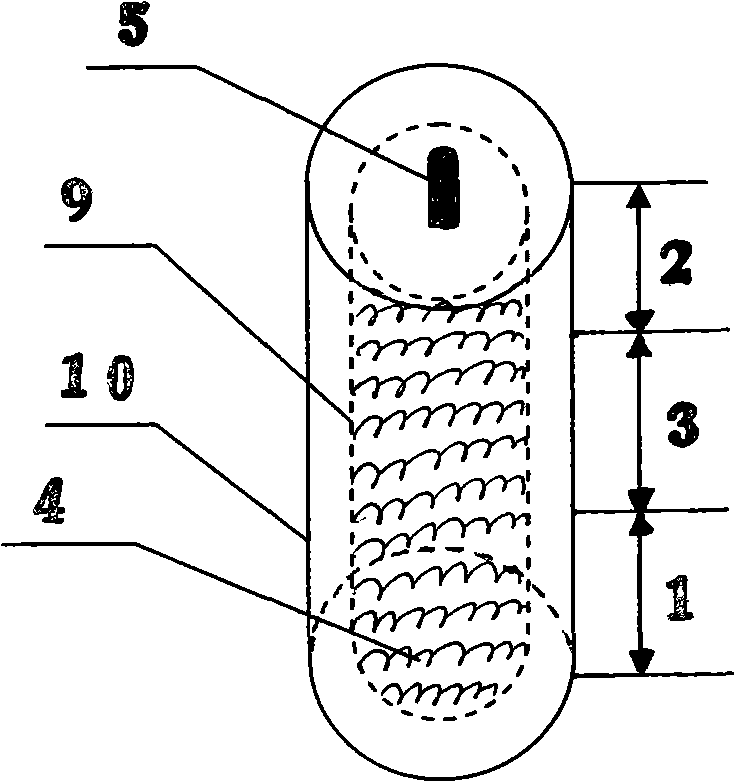
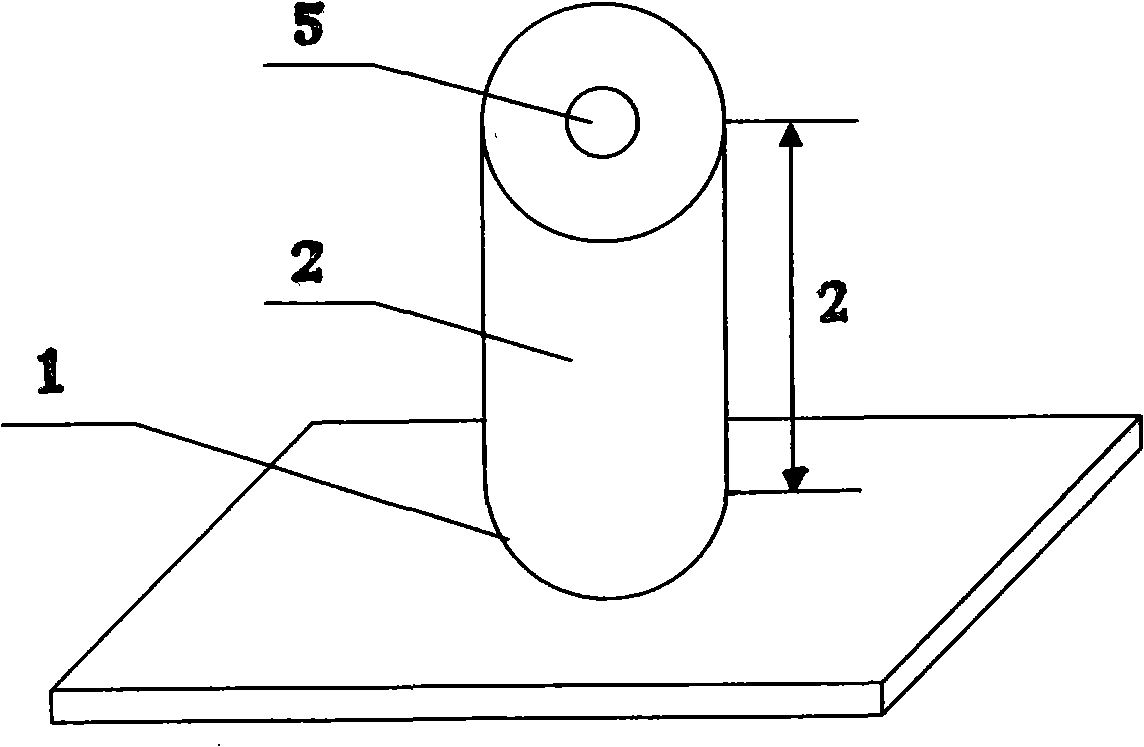
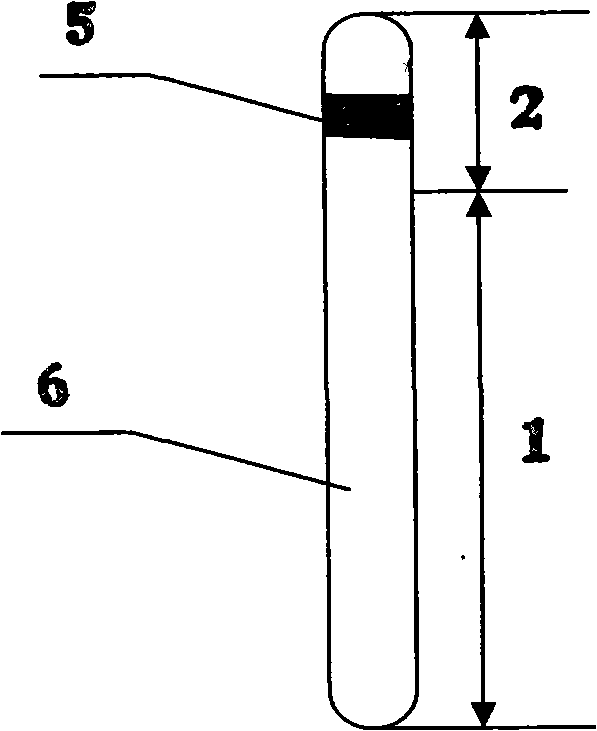
Supercritical phase-change intensified heat diffusion method and its heat-transfer medium and applications
A technology for enhancing heat transfer and supercritical phase, which is applied in heat transfer modification, heat exchange equipment, lighting and heating equipment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The supercritical phase change enhanced heat transfer method and the heat transfer medium involved in this embodiment are suitable for application fields: building heating, engine cooling, liquid cooling of electronic devices, temperature control of machinery and medical equipment, aerospace, and military affairs.
[0031] Basic supercritical heat transfer medium: carbon dioxide, critical temperature 31.3°C, critical pressure 7.29MPa, working temperature range: 30-100°C, working pressure range: 8-15MPa,
[0032] Different auxiliary phase change heat transfer substances are adopted in the following different embodiments:
Embodiment 11
[0034] The auxiliary phase change heat transfer material is a liquid-gas phase change material, which is a mixture of methanol and ethanol. In this embodiment, the volume ratio of each component of the supercritical heat transfer medium composed of the basic heat transfer medium and the auxiliary phase change heat transfer material is:
[0035] Water: 100, vaporization temperature is 100°C;
[0036] Methanol: 30, vaporization temperature: 64.7°C;
[0037] Ethanol: 40, vaporization temperature: 78.3°C;
[0038] The heat transfer method using this enhanced heat transfer medium is: adding methanol and ethanol to carbon dioxide as a heat transfer medium. At the heating end, as the temperature rises, carbon dioxide becomes a supercritical fluid, which contains water, methanol, and ethanol. Fog beads, the mist beads themselves play a role in enhancing heat transfer. After the temperature rises, methanol and ethanol are vaporized. When the fluid enters the condensation end, the eth...
Embodiment 12
[0040] In this embodiment, the solid-solid phase change material is used as the auxiliary phase change heat transfer material, and 2,2-dimethylol propanol (PG) is used as the material.
[0041] The volume ratio of each component of the heat transfer medium is:
[0042] Carbon dioxide: weight 1000 grams
[0043] 2,2-Dimethylolpropanol (PG): 100g, phase transition temperature: 81.76°C, transition enthalpy: 172.458J / G;
[0044] Working temperature range: 30-100°C, working pressure range: 8-15MPa,
[0045] The enhanced heat transfer method is: adding a solid-solid phase change material to carbon dioxide as an auxiliary phase change heat transfer material. At the heating end of the heat exchange system, when the carbon dioxide is heated to 81.76°C, PG begins to undergo endothermic phase change. When the temperature is low It starts to release heat at 81.76°C, so as to realize heat transfer and temperature control by solid-solid phase change;
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Critical temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Critical pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Phase transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com