Method for forming lithium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery and chemical formation method technology, which is applied in the manufacture of secondary batteries, electrochemical generators, and electrolyte batteries, can solve problems such as poor cycle performance, thick lithium-ion secondary batteries, and low battery capacity, and achieve Increased thickness yield, good cycle performance, and high-capacity effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] This example illustrates the preparation of a lithium ion secondary battery.
[0035] (1) Preparation of positive electrode
[0036] 100 g of the positive active ingredient LiCoO 2 , 2 grams of binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), 3 grams of conductive agent acetylene black were added and mixed with 40 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone, and then stirred in a vacuum mixer to form a uniform positive electrode slurry.
[0037] The slurry was evenly coated on an aluminum foil, then dried at 150°C, rolled, and cut to obtain a positive electrode with a size of 328×42 mm, which contained 5.5 grams of active ingredient LiCoO 2 .
[0038] (2) Preparation of negative electrode
[0039] Mix 100 grams of natural graphite, a negative electrode active ingredient, 1 gram of binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), and 40 grams of N-methylpyrrolidone, and then stir in a vacuum mixer to form a uniform negative electrode slurry.
[0040] The slurry was evenly coated on the copper foil, th...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This embodiment illustrates the formation method of the lithium ion secondary battery provided by the present invention
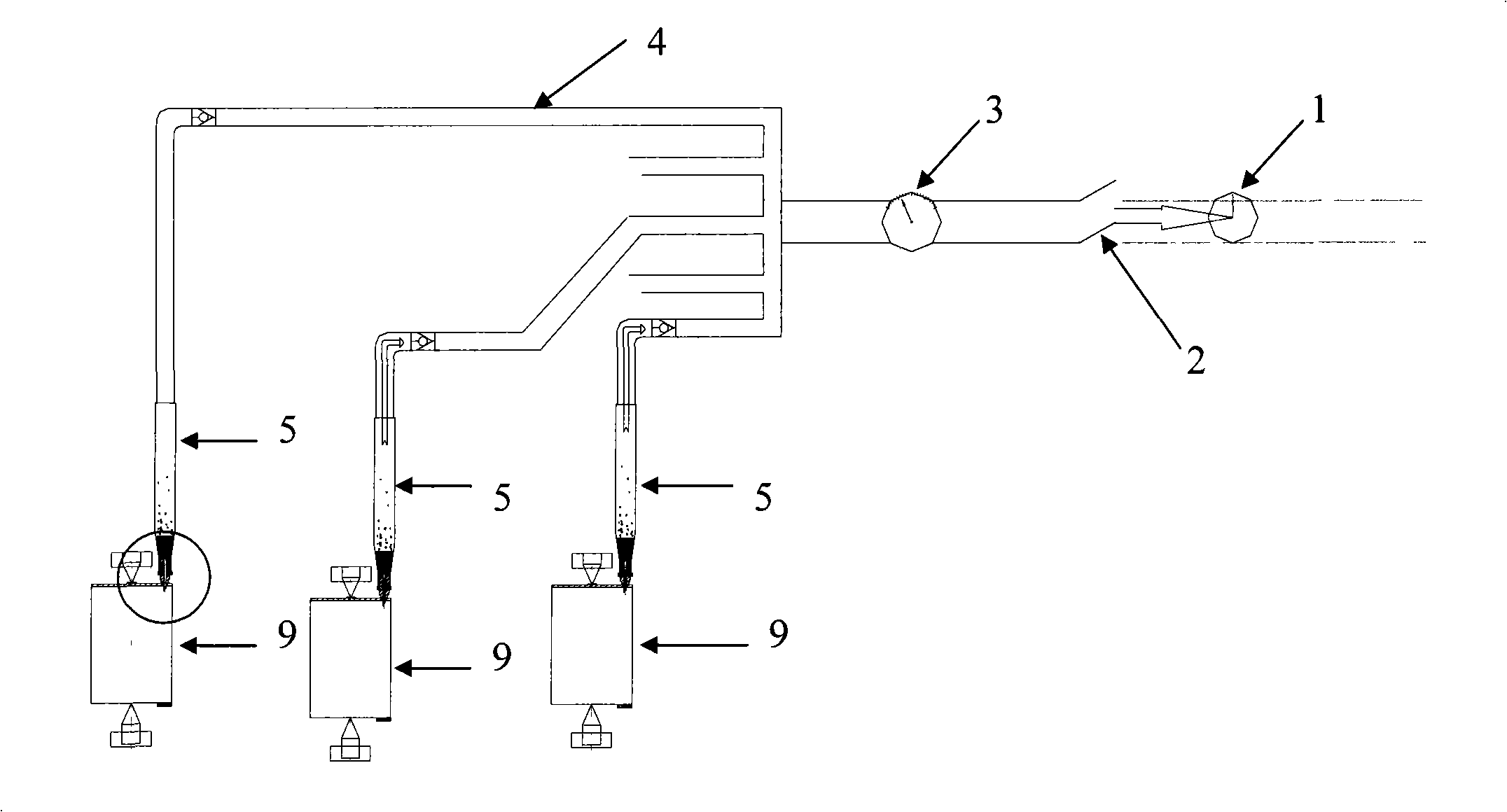
[0045] prepared as figure 1 The negative pressure charging device.
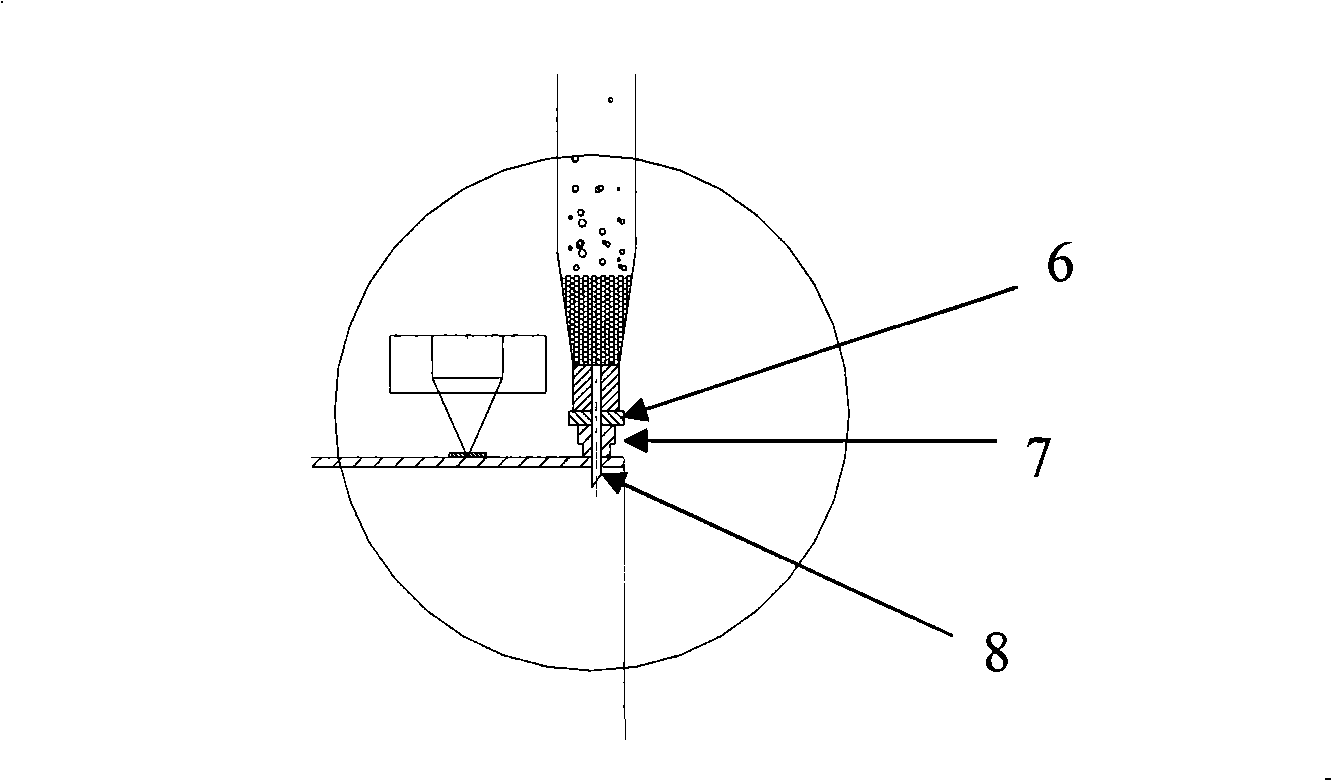
[0046] The 20 batteries after liquid injection prepared according to the method of Example 1 were respectively loaded in such as figure 1 On the negative pressure charging device shown. The connection method is to penetrate the needle 8 sealed in the rubber block 7 into the liquid injection hole of the battery 9, make the rubber block 7 closely contact with the liquid injection hole and fix the needle 8 in the rubber block 7, and pass The fastening rubber ring 6 fixes the rubber block 7 and the needle 8. The needle 8 is airtightly connected with the syringe 5, and the syringe 5 is connected in series with the vacuum pump 1 through the vacuum pipeline 4, and a vacuum gauge 3 and a vacuum valve 2 are connected in series on the vacuum pipeline 4. The connection between the vacuum p...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This embodiment illustrates the formation method of the lithium ion secondary battery provided by the present invention
[0050] According to the method of Example 2, the battery after liquid injection obtained in Example 1 is formed. The difference is that, under normal pressure, the battery is first charged to 3.4 volts with a constant current of 0.01C, and then the battery is charged at a vacuum degree of At 0.05 MPa, the battery was continuously charged to 4.0 volts at a constant current of 0.01 C, and the subsequent charging steps and conditions were the same as in Example 2. The formed lithium ion battery is obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com