Covalently attached nile blue derivatives for optical sensors
A technology of Nile blue and its derivatives, applied in the field of clinical laboratory equipment, can solve problems such as long response time and inability to use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
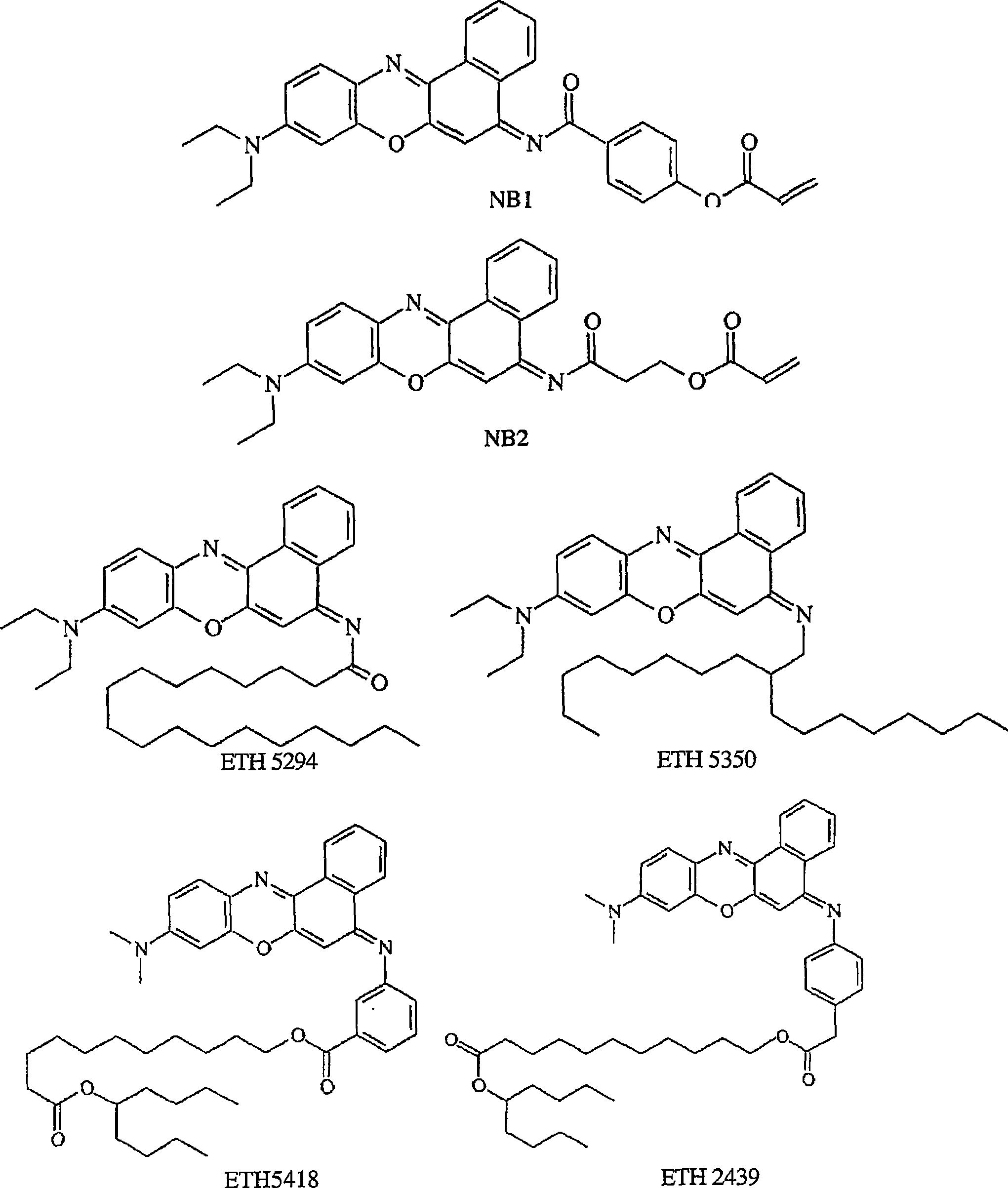
[0068] Synthesis of NB1. Procedure: 13.8 g (0.1 mol) of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid were dissolved in the following mixture: a mixture of 25 ml carbon tetrachloride and 9.2 g NaOH in 55 ml water. Then 0.12 mole of acryloyl chloride was added dropwise to the cold mixture. After stirring at room temperature for 6 hours, the reaction mixture was neutralized with dilute hydrochloric acid. The resulting precipitate was filtered, washed with warm water, dilute hydrochloric acid and water. The crude product was recrystallized from ethanol. A white solid powder was obtained (yield 90%).
[0069] Step 2: 9.6 g (0.05 mol) of 4-acryloyl hydroxybenzoic acid was reacted with 30 ml of thionyl chloride containing a few drops of N,N-dimethylformamide at 45-50 ° C for 10 hours, and then Excess thionyl chloride was removed under 20°C to obtain the corresponding acid chloride (yield 85%).
[0070] Step 3: Add 317 mg (1 mmol) basic Nile blue in 13 mL CH 2 Cl 2 To the solution in , add dissolved ...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Synthesis of NB2. 2-Carboxyethyl acrylate (0.736 g) and basic Nile blue (0.529 g) were dissolved in 30 mL of anhydrous CH with stirring at room temperature. 2 Cl 2 Add Et to the solution 3 N (0.8 g). Then 0.612 g of BOP-Cl was added. The mixture was refluxed for 24 hours. The reaction mixture was washed with 10 mL saturated NaHCO 3 Wash with water. The organic phase is obtained after separation and evaporation of the solvent. The residue was purified by flash chromatography (1:5 EtOAc:Hexanes). A solid was obtained after evaporation of the solvent in 31% yield. The structure of NB2 is passed 1 Confirmed by HNMR.
Embodiment 3
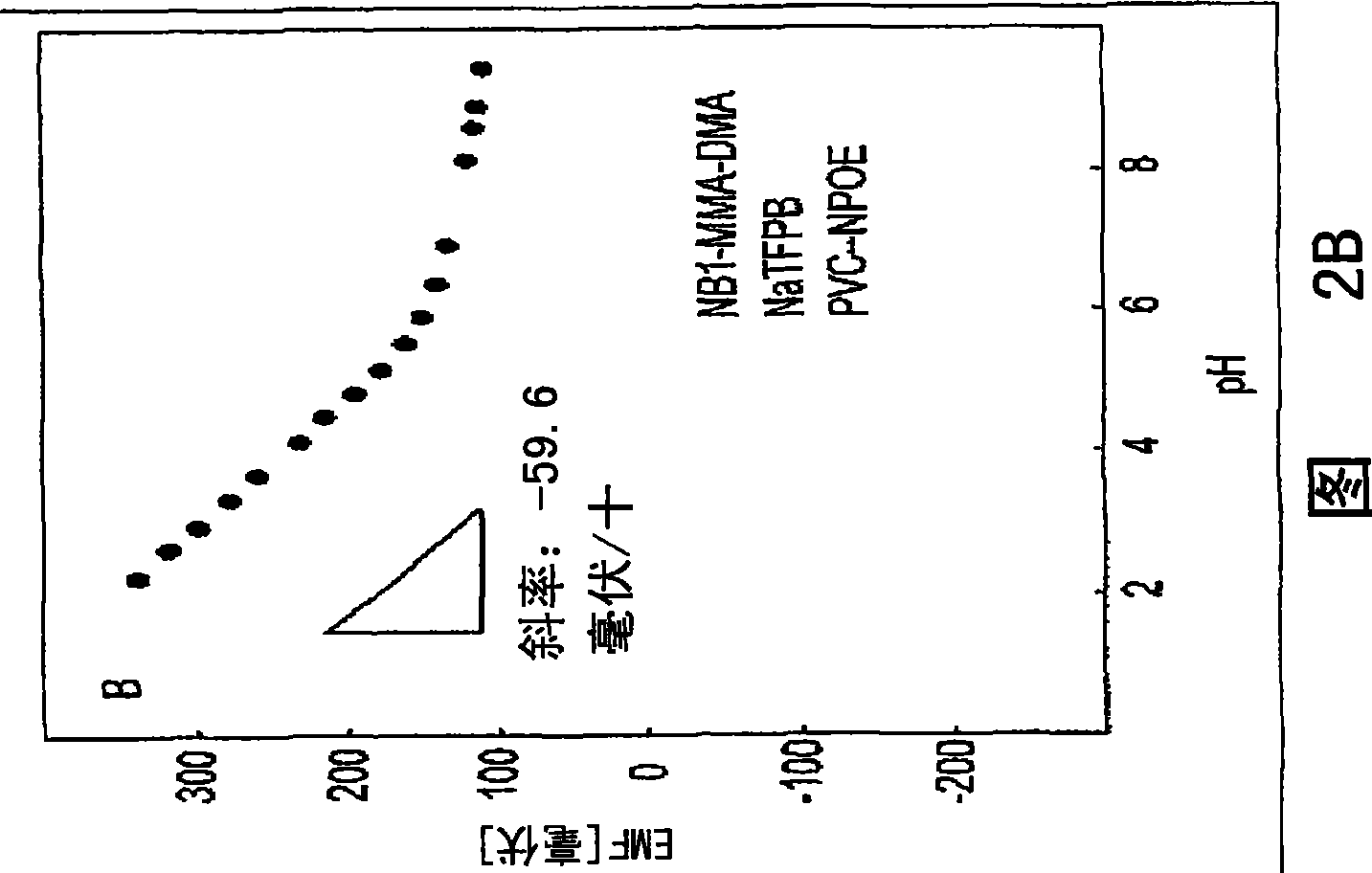
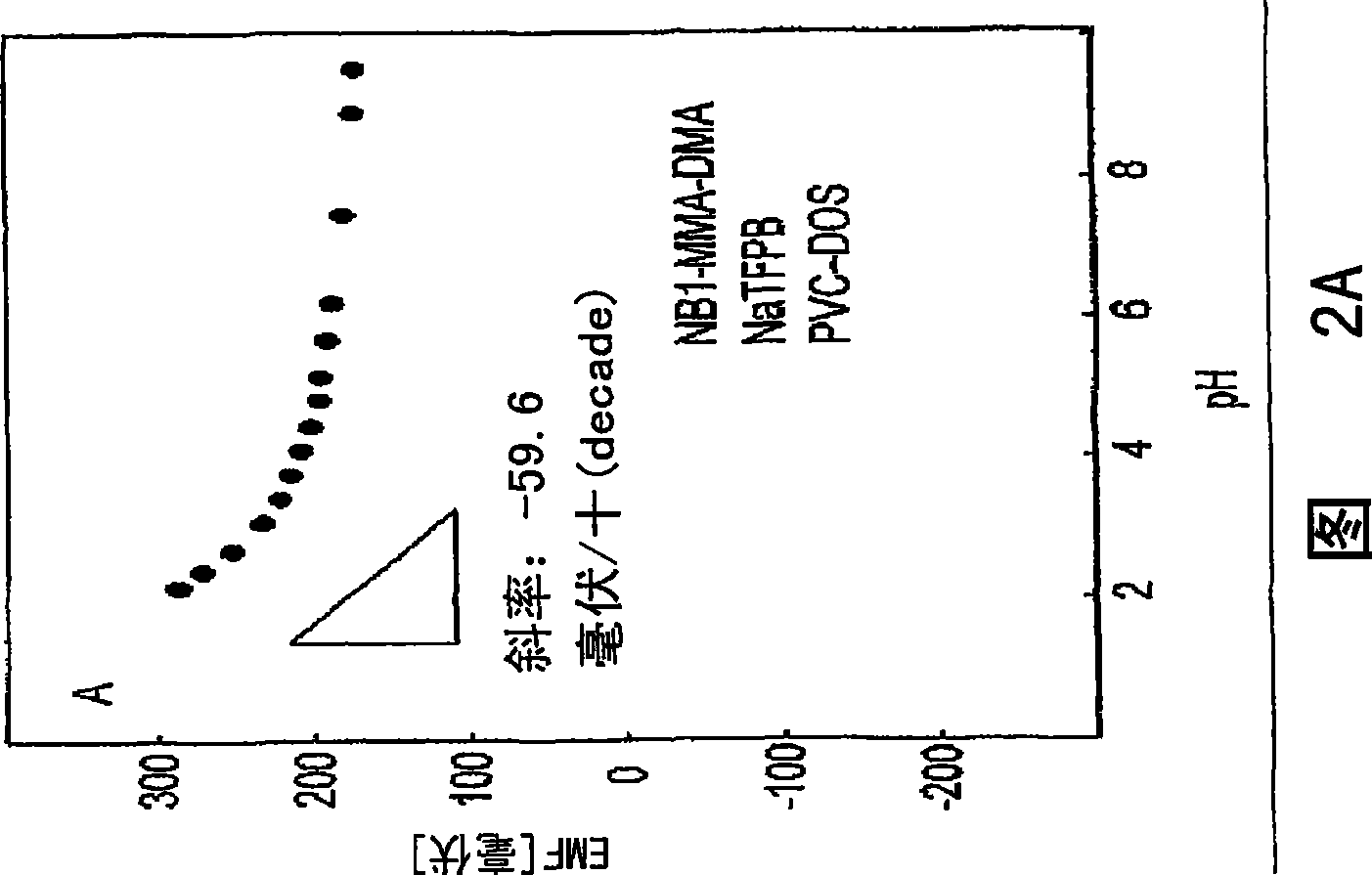
[0075] Polymer synthesis and characterization. All polymers were synthesized by thermally initiated free-radical solution polymerization. The amounts of methyl methacrylate and n-decyl methacrylate were the same as previously reported (16, 20). For polymers containing grafted ionophores, 1 wt% Nile blue derivative (20 mg), 0.78 g MMA and 0.20 g DMA were dissolved in anhydrous EtOAc. The solution was N 2 After purging for 20 minutes, 5.1 mg of AIBN was added. Stirring of the homogeneous solution was continued and the temperature was raised to 90°C where it was maintained for 16 hours. After the reaction was complete, the solvent was evaporated and the polymer was redissolved in 10 ml of dioxane.
[0076] With vigorous stirring, an aliquot of the polymer solution (2 mL) was added to 100 mL of distilled water. The precipitate was collected, dissolved in 25 mL of dichloromethane, and washed with anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 Remove water, then filter. The solvent was evaporated and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com