Semiconductor array laser light beam reshaping structure
A beam shaping and semiconductor technology, which is applied in the laser field, can solve the problems of large divergence angle, short working distance, and underutilization of the beam, and achieve the effect of small divergence angle, large spot diameter and long working distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
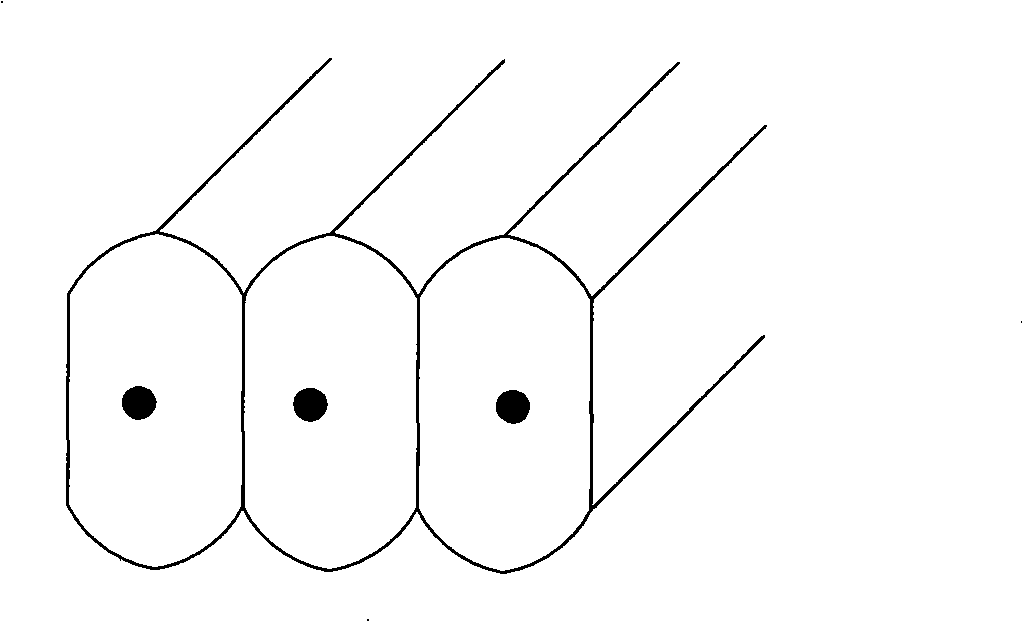
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, the optical element structure is a semiconductor laser array 101 , a collimating lens array 102 , a cylindrical mirror 103 and a beam changing prism 104 arranged in sequence.
[0033] The laser light is emitted from the semiconductor laser, and first passes through the collimating lens array to shape the beam in a 10° direction. The focal length of the lens is as large as possible, and it is close to the limit of the size of the collimated beam at an angle of 10°, that is, it is smaller than and close to the center distance between two chips. , to maximize the spot size. After further compressing the long-axis direction of the output beam of the semiconductor laser by a prism, a prism pair or a grating, it can be coupled directly or through a converging lens to a multimode fiber, a high-power fiber or directly used in an end-pumped laser.
Embodiment approach 2
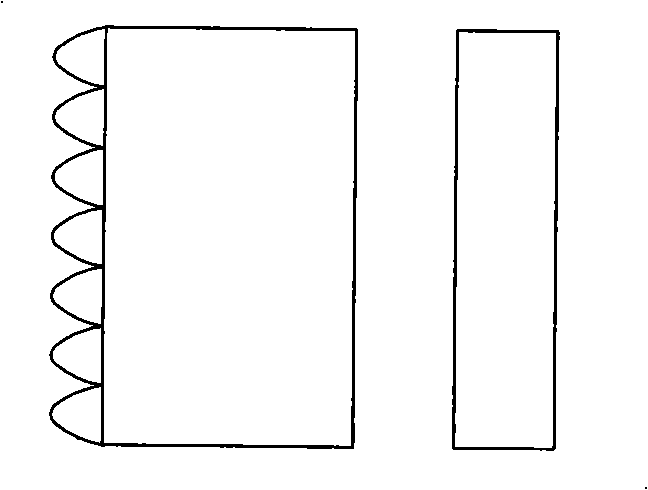
[0035] Such as figure 2 As shown, the optical element structure is a semiconductor laser array 201 , a collimating lens array 202 , a cylindrical mirror 203 , a pair of beam changing prisms 204 and 205 , a coupling lens 206 and an optical fiber 207 .
[0036] Whether the coupling lens 206 is needed depends on the specific conditions of the diameter of the compressed beam.
Embodiment approach 3
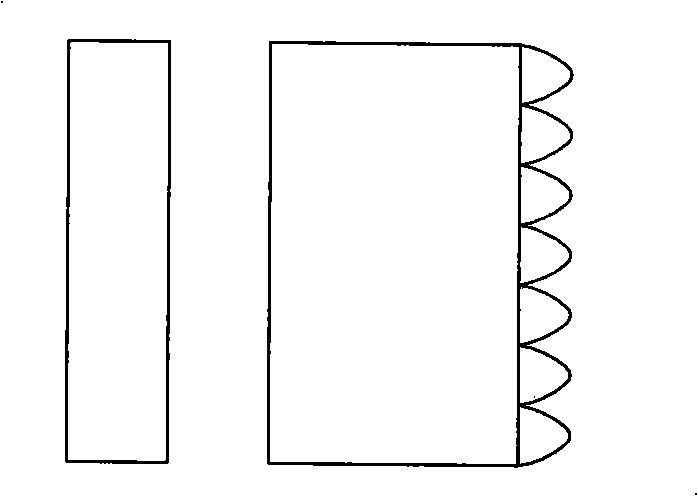
[0038] Such as image 3 As shown, the optical element structure is a semiconductor laser array 301 , a cylindrical mirror 302 , a beam changing grating 303 , a coupling lens 304 and an optical fiber 305 arranged in sequence.
[0039] After the laser light emitted by the semiconductor laser is collimated and compressed by the cylindrical mirror 302 and the variable beam grating 303 , it can be coupled into the optical fiber 305 through a coupling lens or directly.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com