Improved preparation of molecular imprinted polymers
A technology of molecular imprinting and polymers, which is applied in the field of pharmaceutical preparations that bind target molecules such as cholesterol, bile acids and bile salts, and can solve the problems of undisclosed separation of inefficient or non-conjugates, undisclosed, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
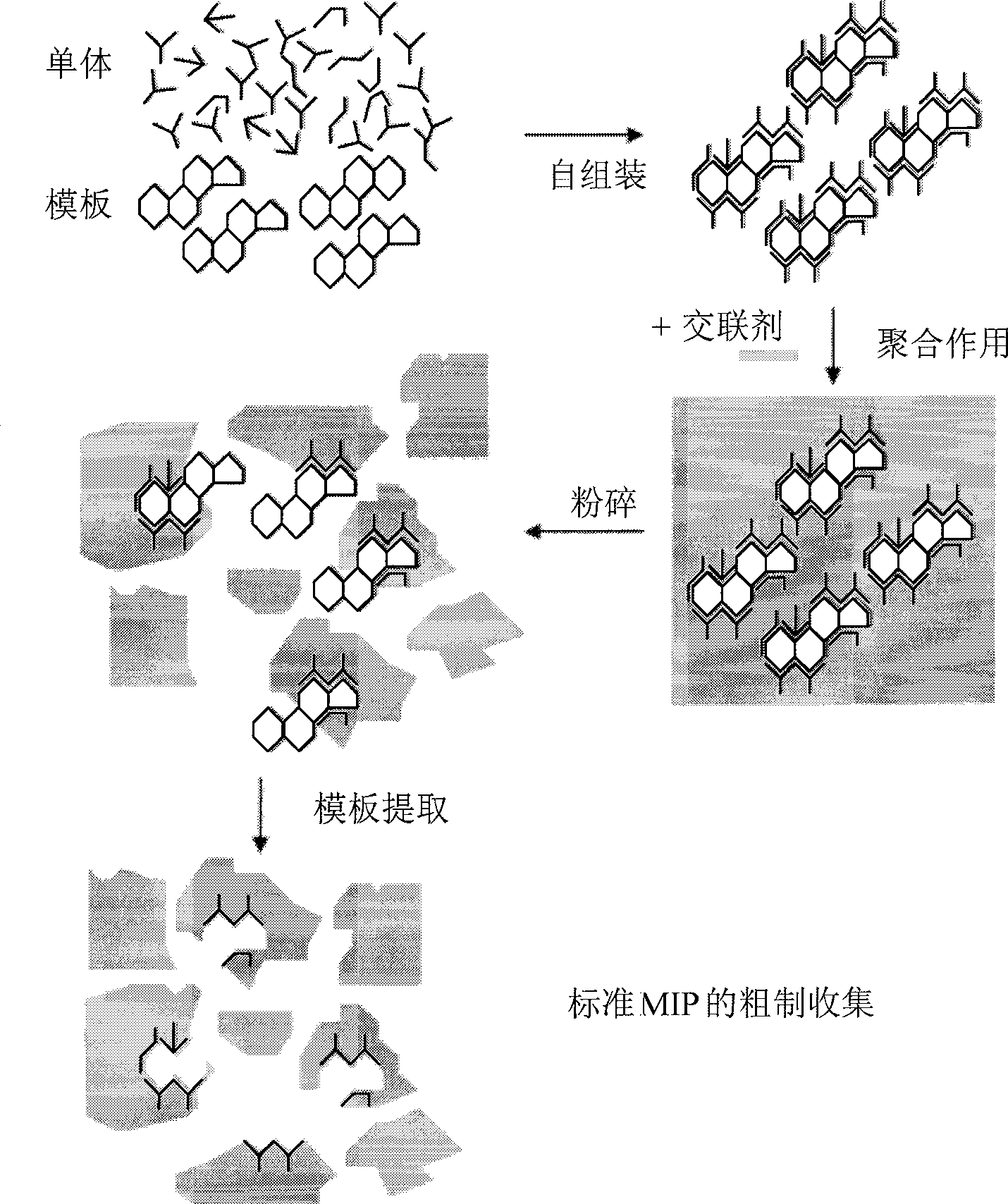
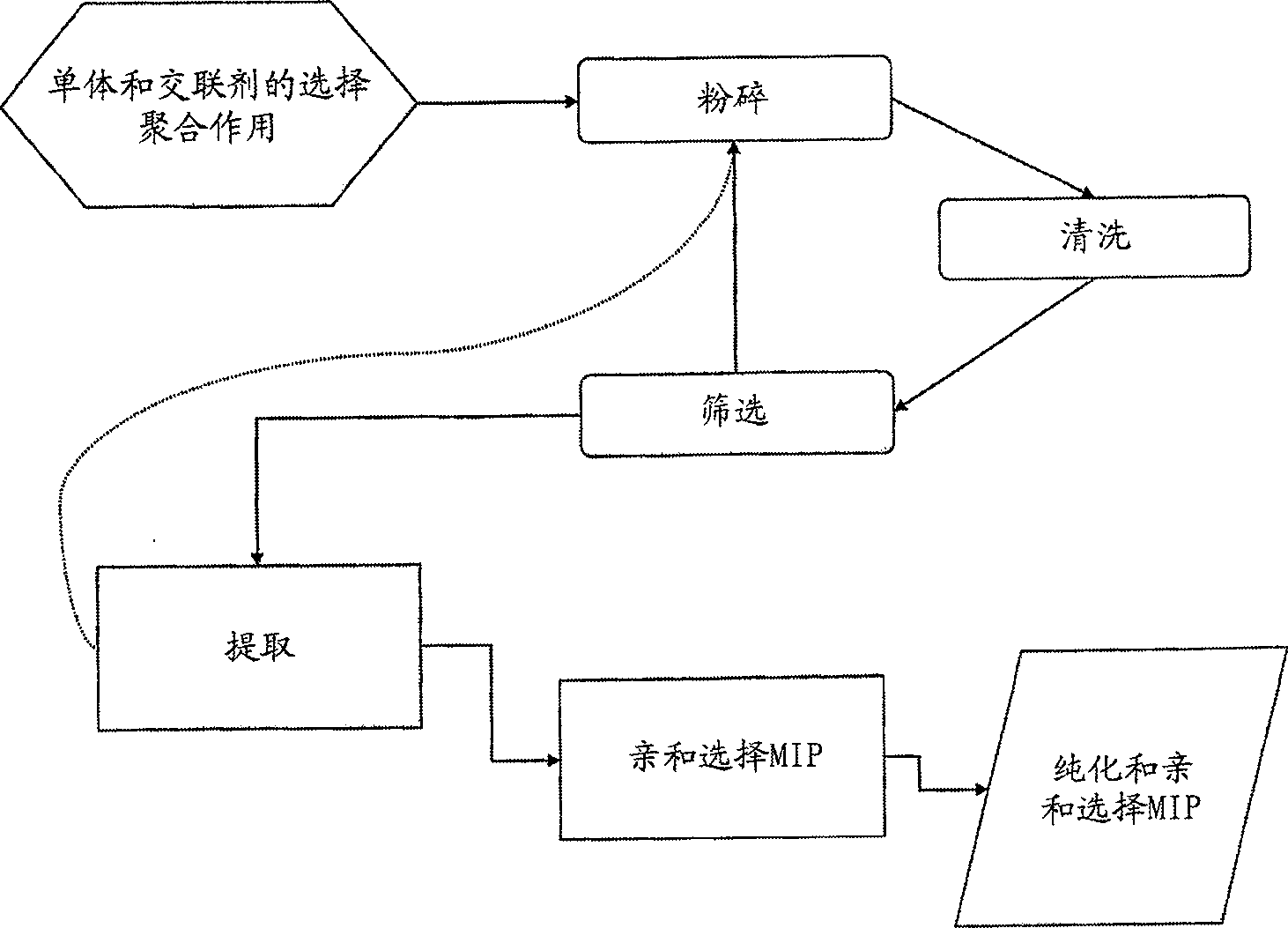
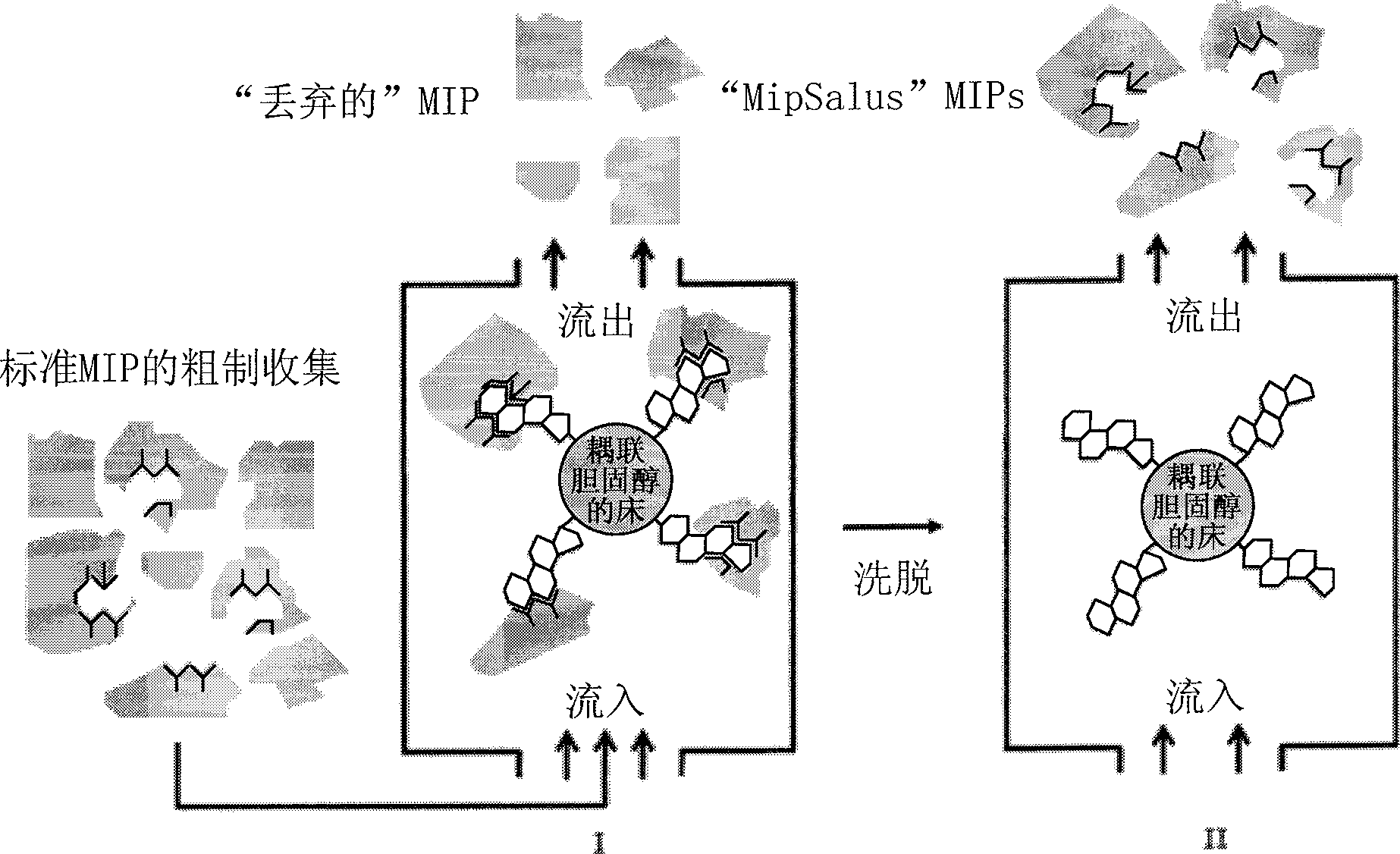
[0133] Therefore, it is evident from the above that the second aspect of the present invention derives a method for the preparation of a MIP having high binding capacity and specificity for a target molecule, which method comprises: Raw MIP (i.e. polymeric cross-linked MIP that does not substantially extract the template or does not adopt the structure of the micronized MIP) of the template molecule composed of the material, undergoes a first step of micronization so that the resulting MIP particles are small enough to remove / extract the template molecule, removing / extracting substantially all of the template molecules, optionally subjecting the MIP thus obtained to a second micronization step, wherein said first and optionally second micronization steps result in a MIP having an average diameter of at most 25 μm . After these processes, the resulting MIPs have a higher ratio of volume to exposed binding sites. Usually it is sufficient (easiest) to use only the first microniz...
Embodiment 1
[0183] Fluorescein-templated MIP
[0184] In a 100ml flask, 1.4ml methacrylic acid (MAA) monomer, 9.5ml ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA), 50mg fluorescein and 10ml tetrahydrofuran (THF) were placed in a hot water bath (about 40°C) Mix for 30 minutes. 2 g of 1,1-azobis(cyclohexane-carbonitrile) (ACHCN) were added slowly. After dissolution the solution was purged with argon (THF sat'd) for 15 minutes. Polymerization was initiated by continuous UV light (365 nm, 9 W) irradiation for 48 h. The resulting polymer was yellow and brittle and was micronized by hand in a mortar to a particle size between 10 and 25 μm. The powder was refluxed in THF for 30 minutes, washed in ethanol / THF (75:25) and filtered several times. Air-dried white powder.
Embodiment 2
[0186] MIP templated with cholic acid
[0187] In a 100 ml flask, 1.4 ml methacrylic acid (MAA) monomer, 9.5 ml ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA), 2 g cholic acid and 12 ml tetrahydrofuran (THF) were mixed in a hot water bath for 30 minutes. 0.2 g of 2,2'-azobisisobutyronitrile / 2,2'-azobis-(2-methylpropionitrile) (AIBN) was added slowly. After dissolution the solution was purged with argon (THF sat'd) for 15 minutes. Polymerization was initiated by continuous UV light (365 nm, 9 W) irradiation for 24 h in an ice bath. The resulting polymer was yellow rigid and micronized by hand in a mortar to a particle size between 25 and 50 μm. The powder was refluxed in THF for 30 minutes, washed and filtered 4 times in ethanol / THF (75:25). The white powder was air dried overnight.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com