Cutting method of fragile material substrate
A brittle material substrate and cutting method technology, applied in glass cutting devices, stone processing equipment, fine working devices, etc., can solve the problem of uncertainty of the initial micro-crack direction, reduce laser power, ensure cutting speed, and ensure cutting quality effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0021] Example 1 Liquid crystal glass cutting using liquid nitrogen as cooling medium
[0022] In the first step, a liquid crystal glass substrate with a thickness of 0.7mm and a size of 2850×3050mm is provided.
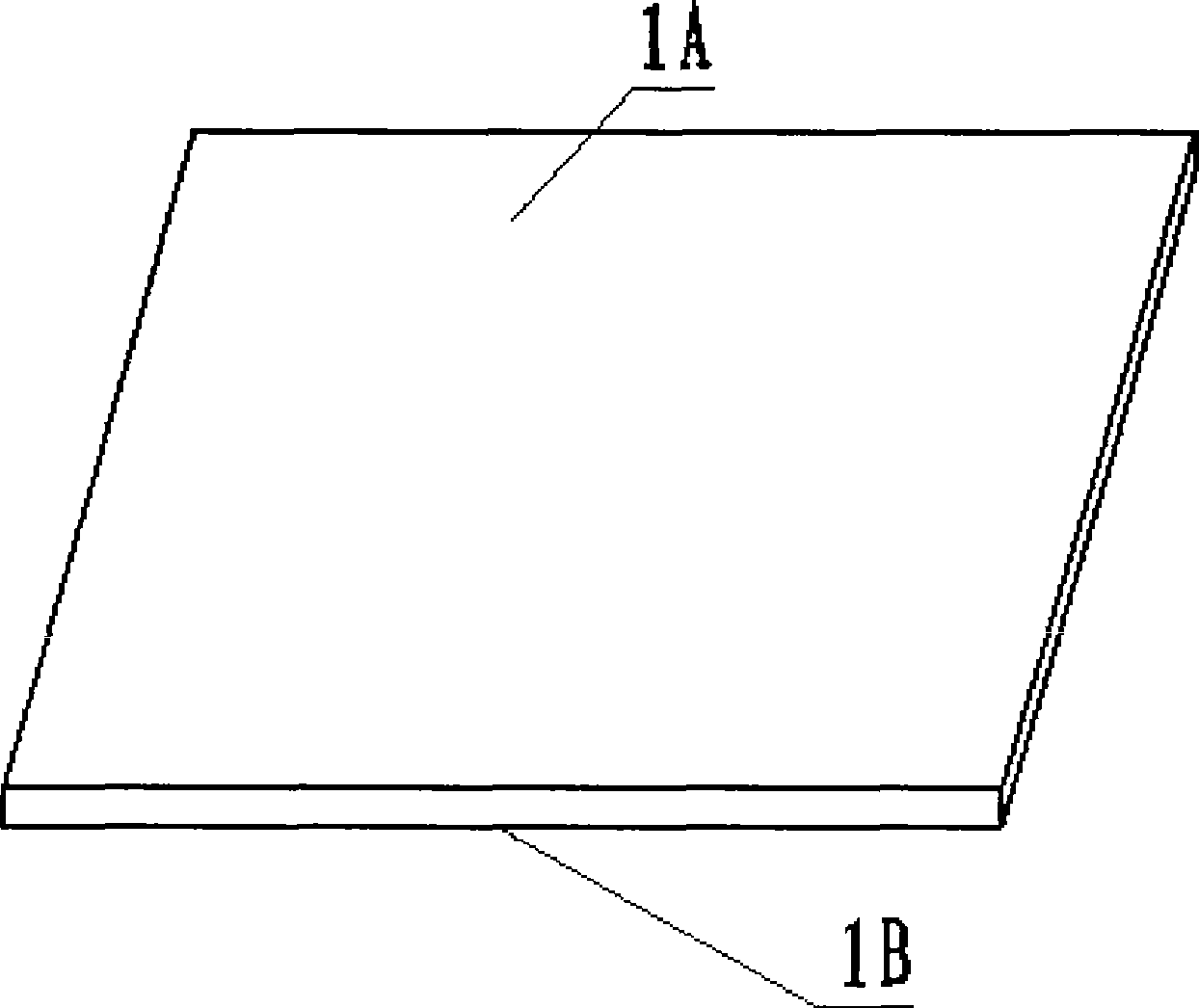
[0023] The second step, such as figure 1 shown. One surface 1A of the liquid crystal glass substrate is selected as the laser irradiation heating surface, and this plane is called the main surface.
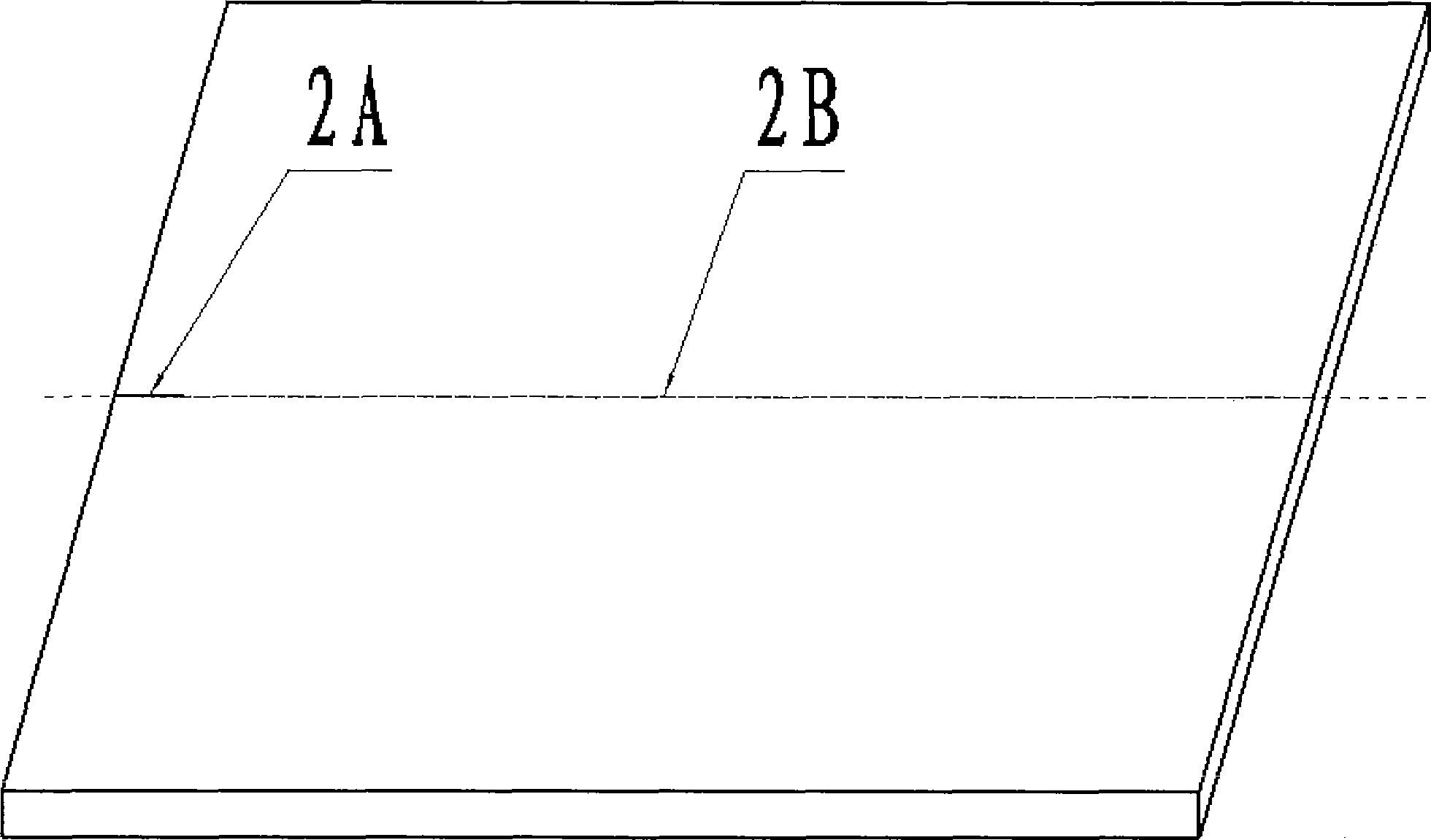
[0024] The third step, such as figure 2 shown. A slit with a length of 10 mm and a width of 0.1 mm is produced along the cutting direction along the edge of the main surface, and this slit is a penetrating initial slit.
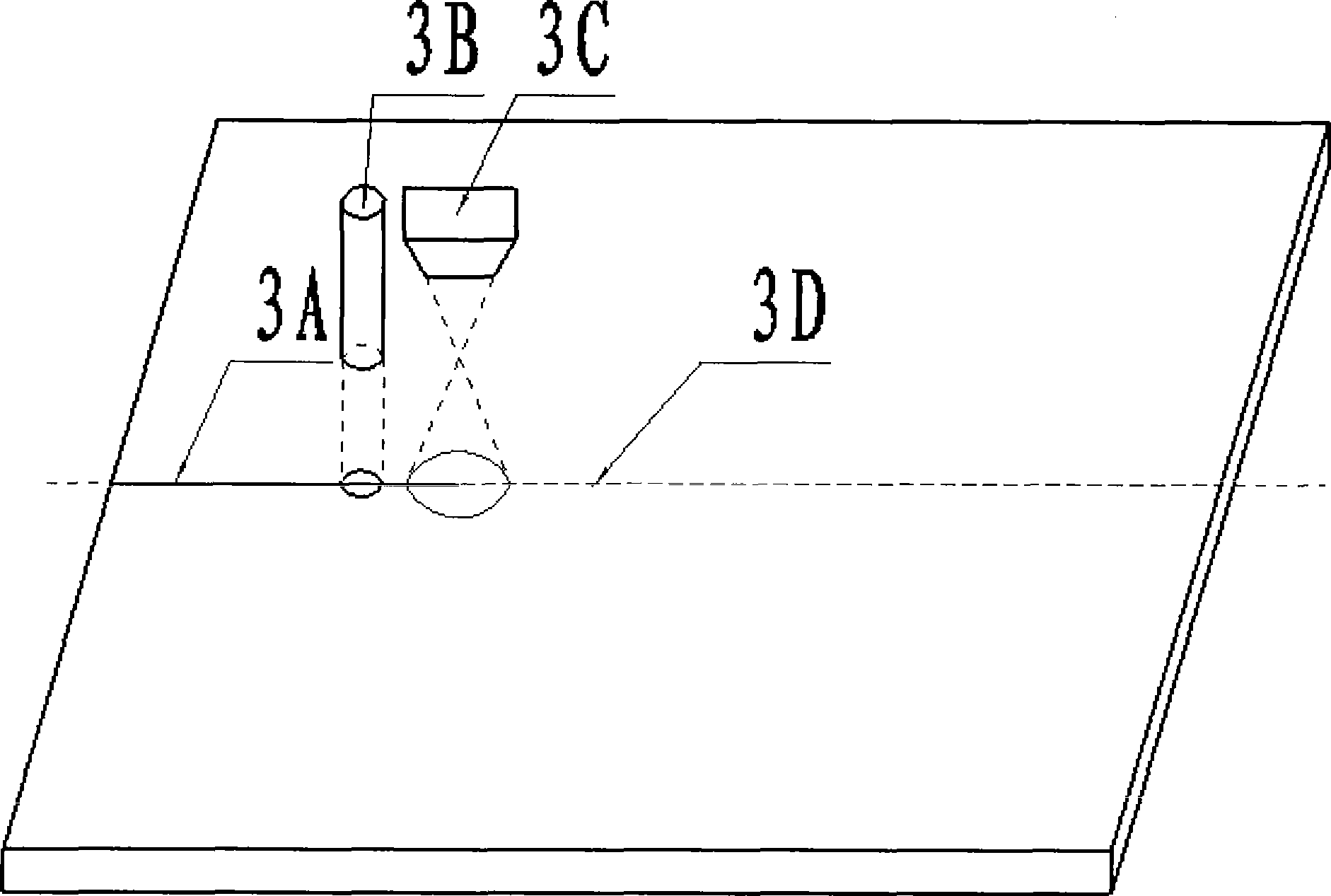
[0025] Here, a carbon dioxide laser with a wavelength of 10.6 μm is used. The distance between the laser head and the glass substrate is 30 cm. It is irradiated on the liquid crystal glass to form a circular spot with a diameter of 0.1 mm, and a penetrating laser spot with a length of 1 cm and a width of 0.1 mm is cut out. initial gap.
[0026] T...
example 2
[0030] Example 2 Ultra-clear glass cutting using jet water as cooling fluid
[0031] The first step is to provide an ultra-clear glass substrate with a thickness of 1.8mm and a size of 200×400mm.
[0032] The second step, such as figure 1 shown. One surface of the liquid crystal glass substrate is selected as the laser irradiation heating surface, which is called the main surface, which is the plane pointed by 1A here; the opposite side of 1A is 1B, which is called the secondary surface here.
[0033] The third step, such as figure 2 shown. A slit with a length of 10 mm and a width of 0.1 mm is produced along the cutting direction along the edge of the main surface, and this slit is a penetrating initial slit.
[0034] Here, a carbon dioxide laser with a wavelength of 10.6 μm is used. The distance between the laser head and the glass substrate is 30 cm. It is irradiated on the liquid crystal glass to form a circular spot with a diameter of 0.1 mm, and a penetrating laser ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com