Flapping rotor wing design method and microminiature flapping rotor wing designed according to the method
A design method and technology for aircraft, applied in aircraft, helicopters, motor vehicles and other directions, can solve the problems of complex structure, difficult miniaturization, low lift and body weight of aircraft, and achieve the effects of small size, simple structure and light weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
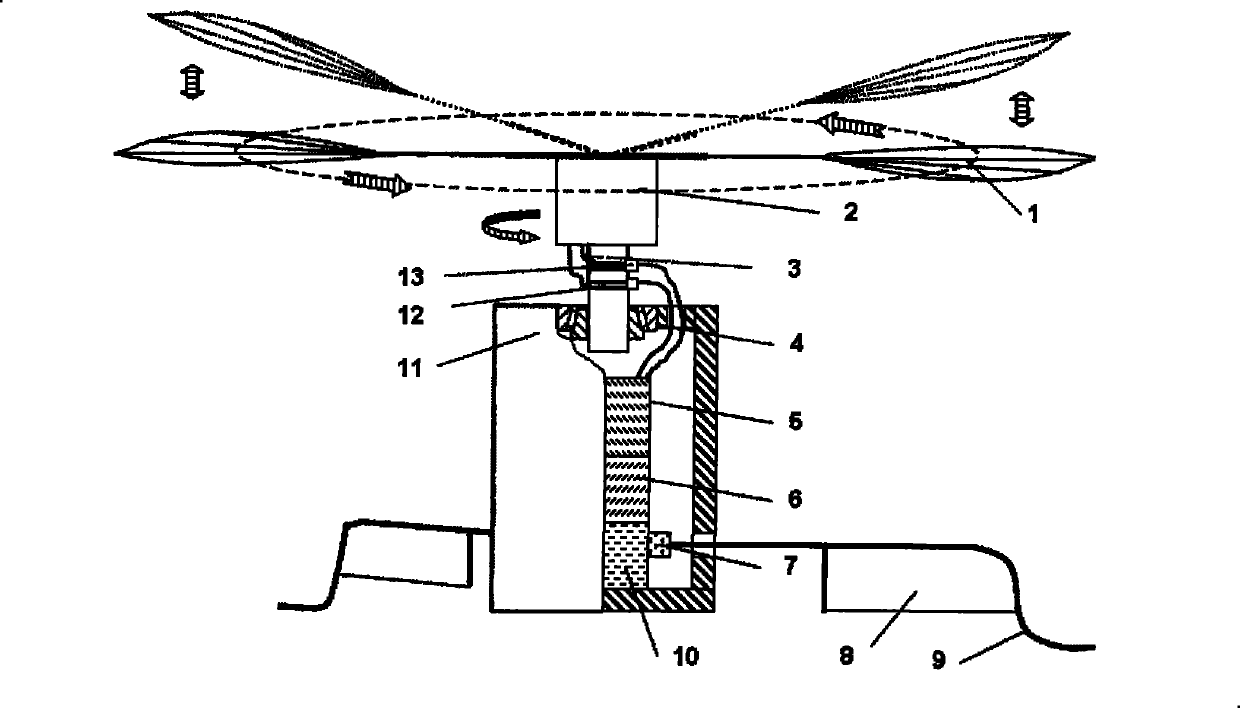
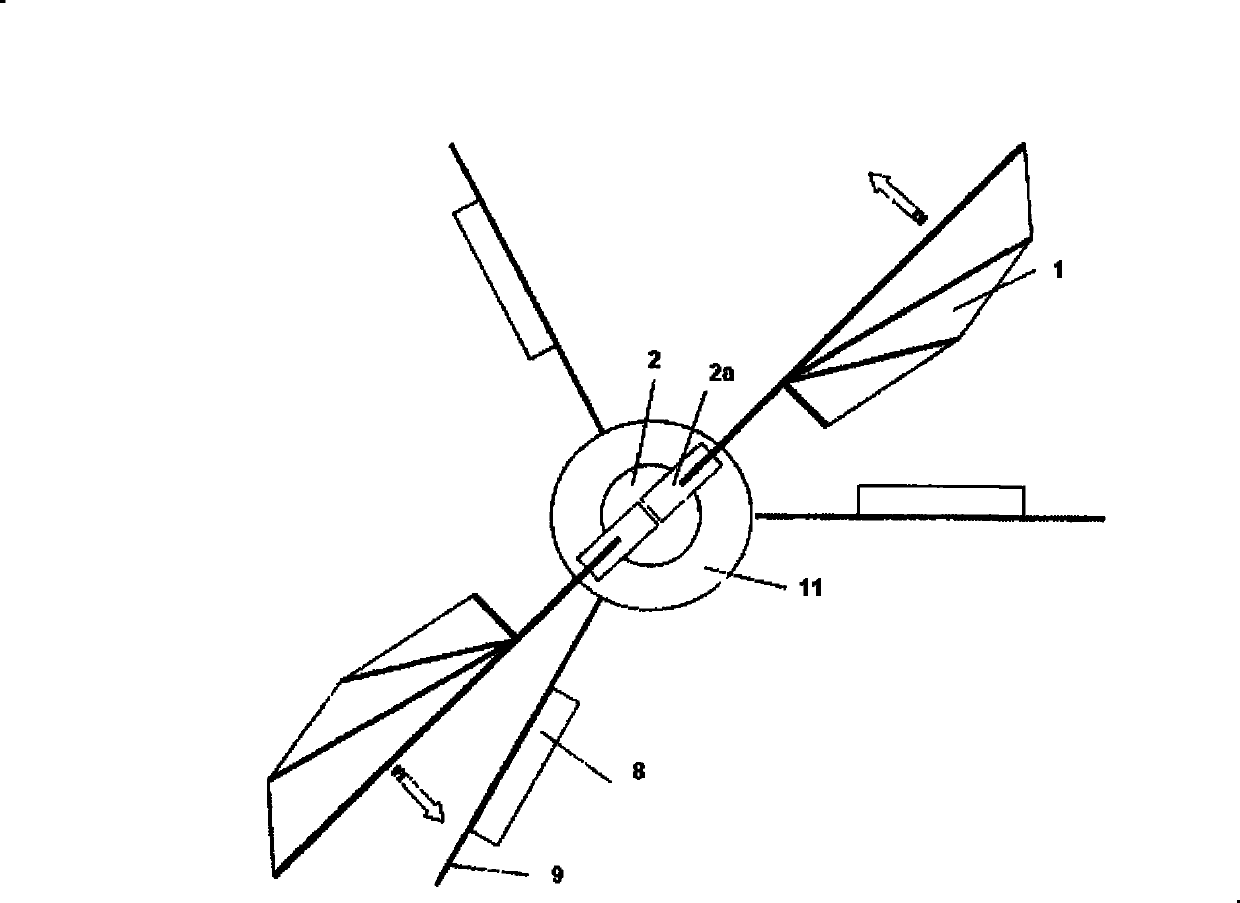
[0027] A micro flapping rotor aircraft of the present invention comprises a flapping wing 1, an electromagnetic drive mechanism 2, a connecting shaft 3 connecting the flapping wing and the body, a body shell 11, a control surface 8, an undercarriage 9, a power supply 5, and a controller 10 and electric steering gear 7.
[0028] The production steps of the flapping rotorcraft are as follows:
[0029] The first step is to make flapping wing 1. The polyvinyl chloride film used for ordinary packaging is selected as the material of the flapping wing surface, according to the attached image 3 The shown flapping wing shape trims the airfoil, and glues four reinforcing ribs la on the trimmed airfoil lb, and the reinforcing ribs are carbon fiber composite materials.
[0030] The second step is to make the electromagnetic driving mechanism 2 . The present invention adopts "W" electromagnetic driving mechanism. First, two U-shaped soft irons are juxtaposed together, and the magnetic ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A micro flapping rotor aircraft of the present invention comprises a flapping wing 1, an electromagnetic drive mechanism 2, a connecting shaft 3 connecting the flapping wing and the body, a body shell 11, a control surface 8, an undercarriage 9, a power supply 5, and a controller 10 and electric steering gear 7.
[0037] The first step is to make three flapping wings 1. The polyvinyl chloride film used for ordinary packaging is selected as the material of the flapping wing surface, according to the attached image 3 The shown flapping wing shape trims the airfoil, and glues four reinforcing ribs 1a on the trimmed airfoil lb, and the reinforcing ribs are carbon fiber composite materials.
[0038] In the second step, in order to increase the aerodynamic efficiency of the airfoil, the embodiment of the present invention uses a "3W" electromagnetic drive mechanism to drive three flapping wings, such as Figure 5 As shown, three U-shaped soft irons are placed close to the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com