Sampling method for non-damage fixed position observation of plant stomata in field experiment
A field-tested, non-invasive technology, applied in the field of plant physiology and ecology research, which can solve the problems of complex operation, limited dynamic characteristics, inability to use stomatal opening and closing conditions or the changing law of opening degree, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1 Observation of Stomata of Munage Grape
[0042] In August 2008, in the grape corridor of Dahan Village, Tuohula Township, Wensu County, Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, in the study of the effects of soil and foliar fertilization on the photosynthetic characteristics of Munage grapes, the stomata of Munage grape leaves were sampled. . The method is to select leaves with normal photosynthetic function on the sunny side (usually the third or fourth leaf from the base of the branches) according to different soil fertilization treatments and foliage spray treatments. Since the test site is on the roadside of the village, there is a lot of dust The dust on the surface of the blade is cleaned by blowing, wiping, brushing and other means. On the part near the main vein of the leaf, carefully apply the nail polish film, the area is less than 1cm 2 , use mouth blowing to speed up drying, use 15mm×15mm transparent plastic tape to remove the dried nail polish film, quickly ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Observation of Stomata of Red Globe Grape
[0044] In August 2008, in Hongqipo Farm, Aksu District, Xinjiang, in the study of the effect of soil and foliar fertilization on the photosynthetic characteristics of Red Globe Grape, the stomatal sampling of Red Globe Grape leaves was studied. The method is to select the leaves with normal photosynthetic function on the sunny side (the third or fourth leaf from the base of the branch) according to different soil fertilization treatments and spray fertilizer treatments on the leaves, first blow and wipe the surface of the leaves, and place them near the main veins of the leaves. Parts, carefully apply nail polish film, the area is 5mm×5mm, use ear washing ball to blow air to speed up drying, use transparent plastic tape (15mm×15mm) to remove the dried nail polish film, quickly paste it on the glass slide, each The slides are all numbered, including the treatment name, time, etc., and more than 3 repeated samples are ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Observation on daily changes of stomata in Wensu red grapes
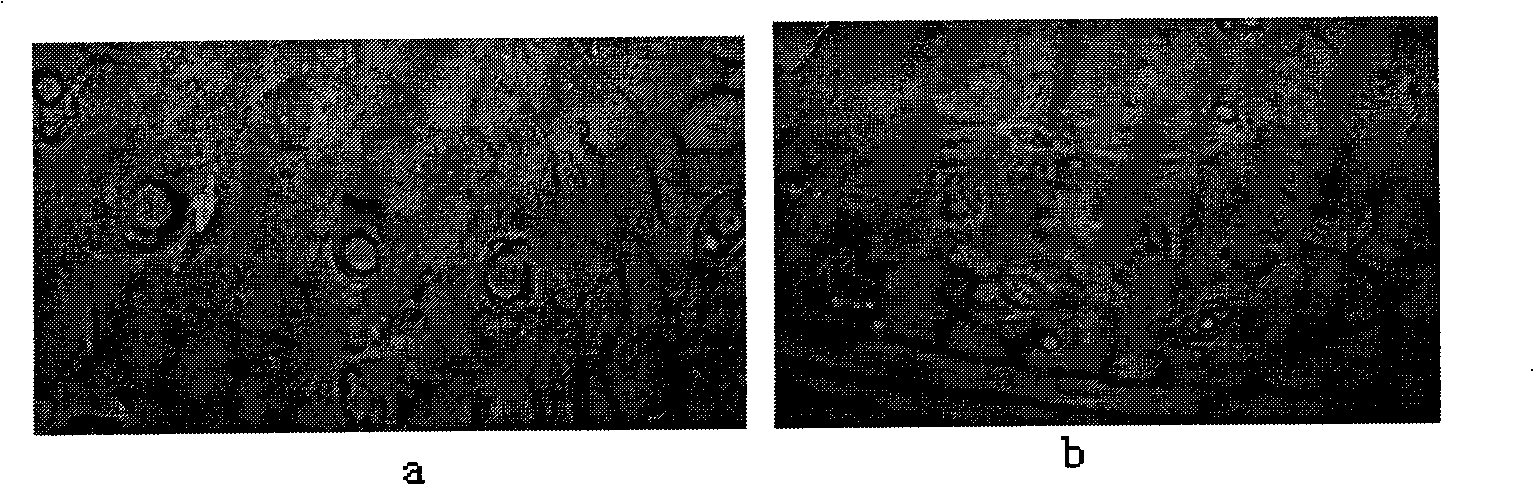
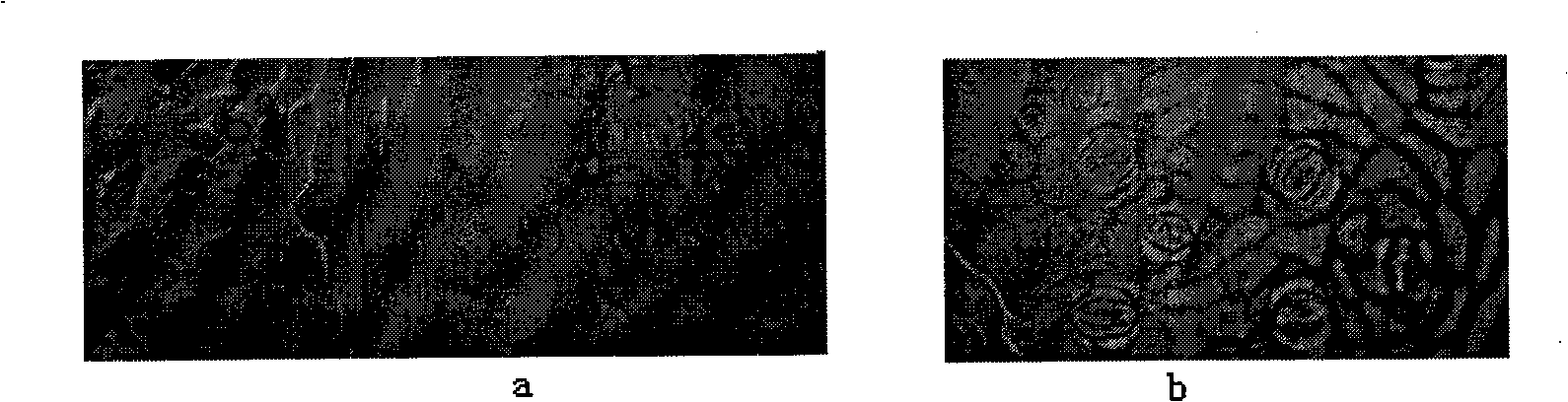
[0046] In August 2008, in Wensu County, Aksu Prefecture, Xinjiang, in the research on the selection of Wensu red grape varieties, the stomatal sampling research of Wensu red grape leaves was carried out, especially for the trophic variant lines with obvious different fruit morphology. Changes and other characteristics, in order to provide a basis for variety selection. The method is the same as in example 2, see the result Figure 3-5 , image 3 The left and right pictures are respectively 10:00 and 12:00 Beijing time; Figure 4 14:00 and 16:00 respectively; Figure 5 Stomatal characteristics of Wensu red grapes at 18:00 and 20:00 respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com