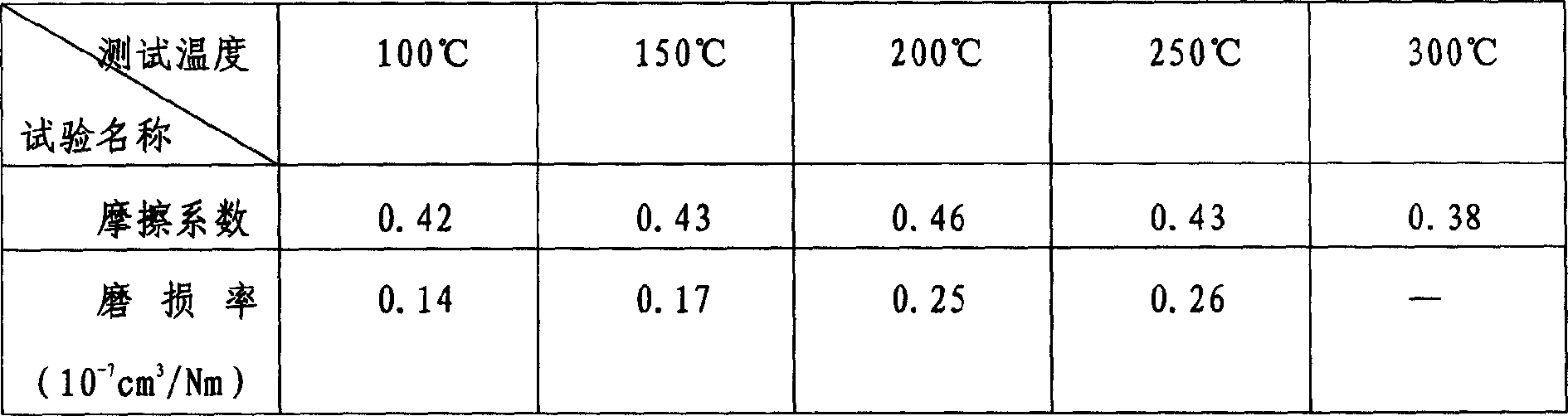
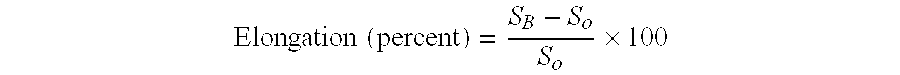Patents
Literature
1724 results about "Metal fibers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metallic fiber. Metallic fibers are manufactured fibers composed of metal, plastic-coated metal, metal-coated plastic, or a core completely covered by metal. Gold and silver have been used since ancient times as yarns for fabric decoration.
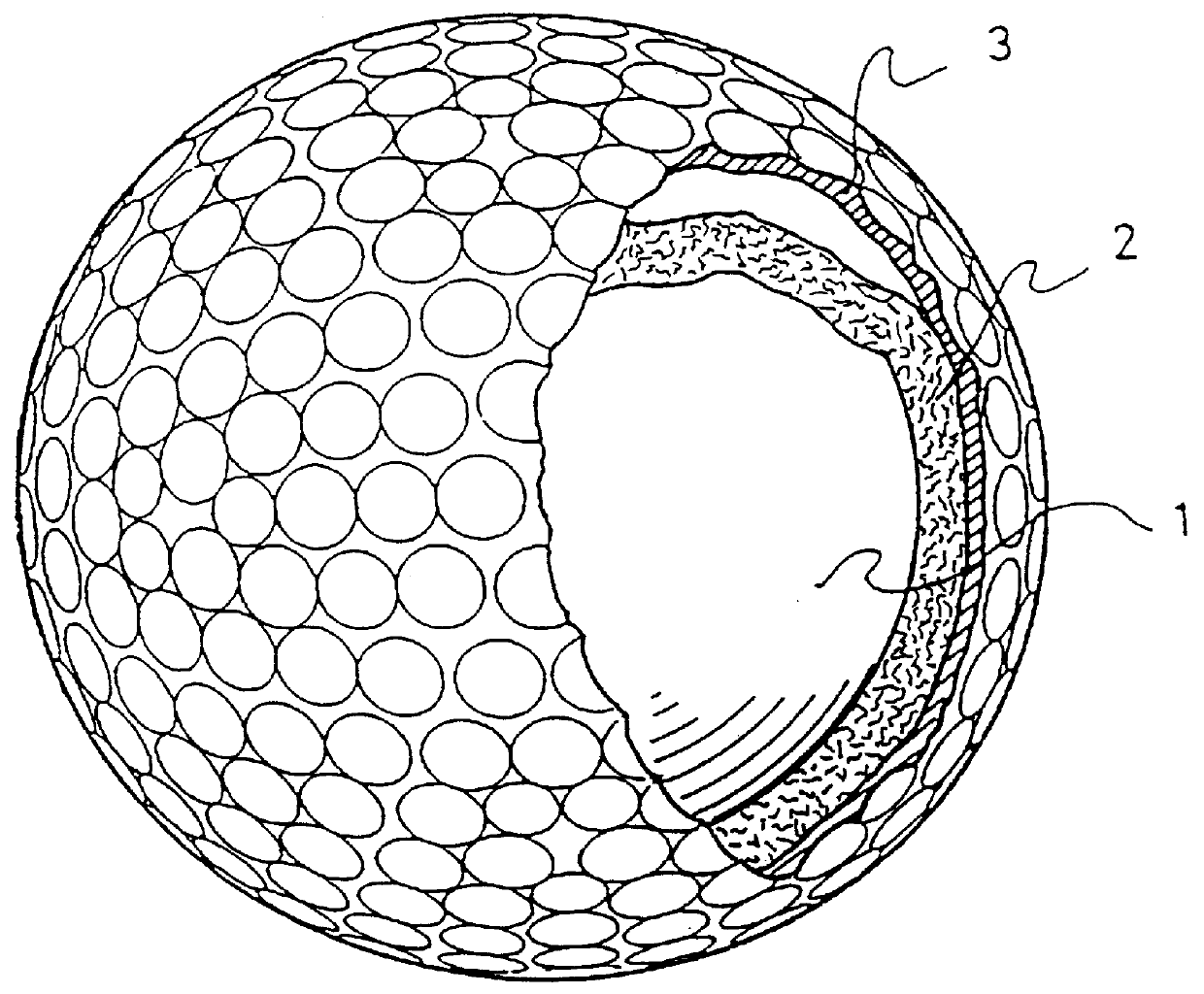
Golf ball with improved intermediate layer
A golf ball including an improved mantle composition which results in improved performance characteristics. The composition includes a soft, flexible resin, such as an elastomer, and a quantity of at least one hardness-enhancing material, such as a quantity of fibers or fiber segments, such as glass, carbon, aramid, and / or metallic fibers, and, optionally, at least one ionomer. The hardness-enhancing material can constitute about 1 to about 30 wt % of the intermediate layer. The composition of the intermediate layer enables the golf ball to maintain initial speed and distance of known golf balls, while improving upon spin rate and playability. Alternatively, spin rate and playability can be maintained, while improving upon the initial speed and distance.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
Formable light weight composites
ActiveUS20100040902A1Synthetic resin layered productsLaminationElectrical resistance and conductanceMetal fibers
The present invention relates to light weight composite materials which comprise a metallic layer and a polymeric layer, the polymeric layer containing a filled thermoplastic polymer which includes a thermoplastic polymer and a metallic fiber. The composite materials of the present invention may be formed using conventional stamping equipment at ambient temperatures. Composite materials of the present invention may also be capable of being welded to other metal materials using a resistance welding process such as resistance spot welding.
Owner:PRODIVE RES
Cnt-infused metal fiber materials and process therefor
A composition includes a carbon nanotube (CNT)-infused metal fiber material which includes a metal fiber material of spoolable dimensions, a barrier coating conformally disposed about the metal fiber material, and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) infused to the metal fiber material. A continuous CNT infusion process includes: (a) disposing a barrier coating and a carbon nanotube (CNT)-forming catalyst on a surface of a metal fiber material of spoolable dimensions; and (b) synthesizing carbon nanotubes on the metal fiber material, thereby forming a carbon nanotube-infused metal fiber material.
Owner:APPL NANOSTRUCTURED SOLUTIONS LLC
Method for producing metal fibers
InactiveUS20050000321A1Transportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusO-Phosphoric AcidMetal fibers
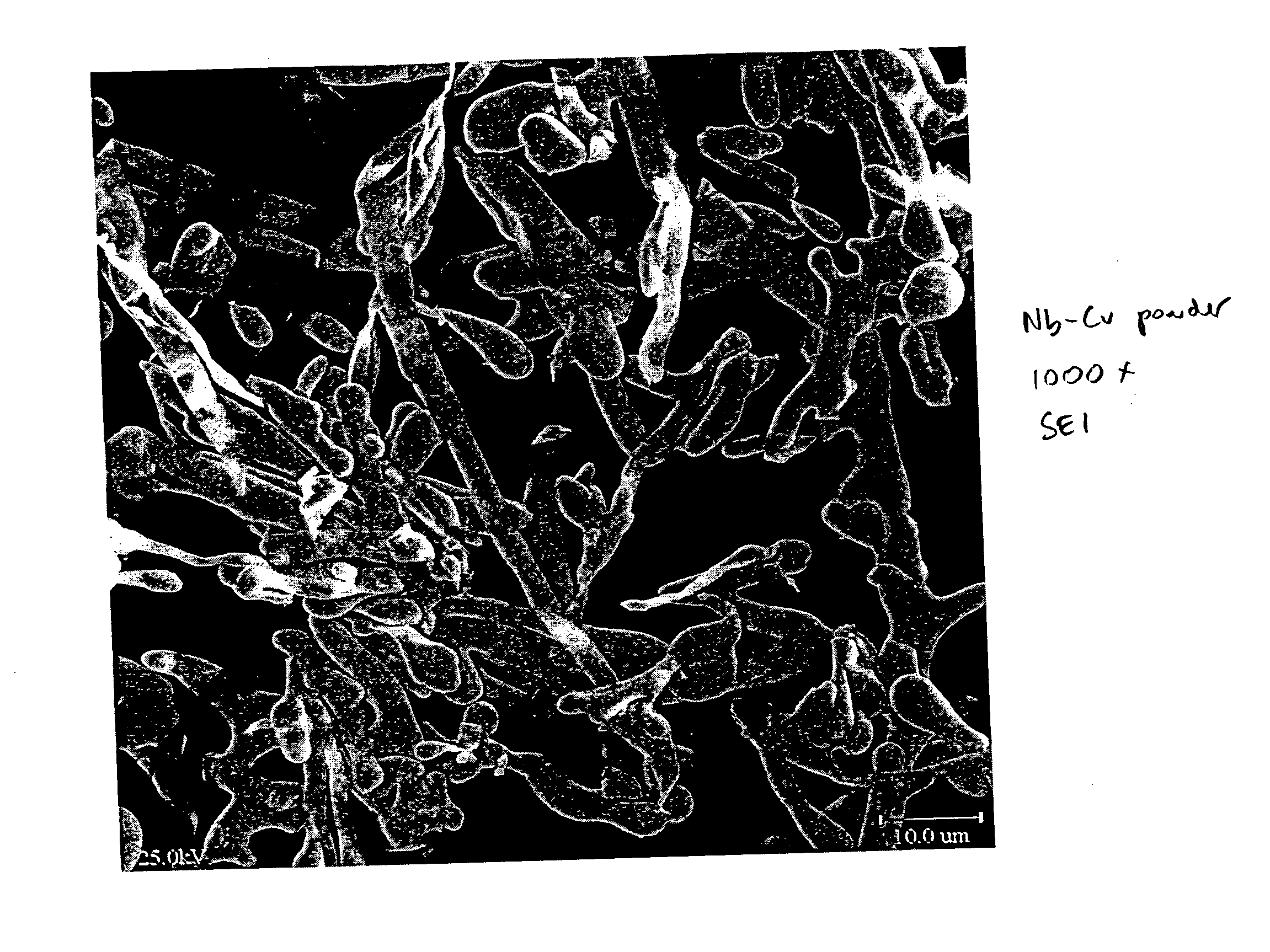
A method of producing metal fibers including melting a mixture of at least a fiber metal and a matrix metal, cooling the mixture to form a bulk matrix comprising at least a fiber phase and a matrix phase and removing at least a substantial portion of the matrix phase from the fiber phase. Additionally, the method may include deforming the bulk matrix. In certain embodiments, the fiber metal may be at least one of niobium, a niobium alloy, tantalum and a tantalum alloy and the matrix metal may be at least one of copper and a copper alloy. The substantial portion of the matrix phase may be removed, in certain embodiments, by dissolving of the matrix phase in a suitable mineral acid, such as, but not limited to, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid.
Owner:ATI PROPERTIES
Metallic fibers reinforced textile prosthesis
InactiveUS20050288775A1Improve mechanical propertiesOvercome deficienciesStentsSurgeryYarnMetallic materials
The present invention provides a composite yarn and an implantable prosthesis having at least portion made from a metallic material, component, or yarn. The composite yarn including a combination of a metallic component and a non-metallic component. The prosthesis includes a biocompatible fabric having a textile construction. A further aspect of the invention provides a method of making a implantable prosthesis constructed from a composite yarn of the present invention.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Non-intrusive coupling to shielded power cable
InactiveUS6980089B1Electric signal transmission systemsInterconnection arrangementsTransceiverPower cable
The invention describes a method and a device for transporting a signal over a power line. The inventive method includes inducing an alternating current (AC) voltage from the power line, powering a transceiver device with the induced AC voltage, communicating the signal with the transceiver device via the power line. The method further may include transmitting and / or receiving the signal with an end user via the transceiver device. The transceiver device may be a fiber optic-based device that transmits data to the end user over non-metallic fiber optic links. The method may filter the induced AC voltage, and separately filter the signal.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
Composite concrete
InactiveUS6080234AMaximum compactnessMaintain good propertiesSolid waste managementArmour platesPlasticizerMetal fibers
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 00122 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 24, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 24, 1997 PCT Filed Jan. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 22953 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 1, 1996An ultra-high performance composite concrete, with low cement and fiber content and having good mechanical properties as well as good impacts, shocks and projectile protection properties, includes hydraulic binder, aggregates, an admixture of metal fibers. Particularly, the composite concrete includes 70% to 85% of particles (A) having a particle size distribution which ranges from 0.01 to 3 mm up to particle size distribution which ranges from 0.01 to 0.50 mm; 2% to 10% of particles (B) having particle size of between 0.01 and 1 mu m; 3% to 20% of hydraulic binder; 0.1 to 3% of a dispersant or plasticizer; 0.05% to 8.5% of fibers; and, mixing water, wherein the percentages being weight percentages based on the sum of the weights of constituents a) to d).
Owner:LAFARGE MATERIAUX DE SPECIALITES
Flame retardant thermoplastic compositions having EMI shielding
ActiveUS20070105994A1Good physical propertiesConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPolysiloxane polycarbonate copolymerMetal fibers
A flame retardant thermoplastic composition having excellent physical properties that includes 20 to 90 wt. % of a polycarbonate resin; from 1 to 35 wt. % of an impact modifier; from 0.5 to 30 wt. % of a polysiloxane-polycarbonate copolymer including from 8 to 30 wt. % polydimethylsiloxane units or the equivalent molar amount of other diorganosiloxane units; from 0.5 to 20 wt. % of a phosphorus-containing flame retardant, and from 3 to 30 wt. % of metal fiber, each based on the total combined weight of the thermoplastic composition, exclusive of any filler. In one embodiment, a molded sample of the thermoplastic composition having a thickness of 3.0 mm (±10%) has an EMI shielding of at least 20 dB. In addition, a molded sample of the thermoplastic composition is capable of achieving UL94 V0 or V1 rating at a thickness of 1.5 mm (±10%). The compositions are useful in forming flame retardant articles having EMI shielding characteristics.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
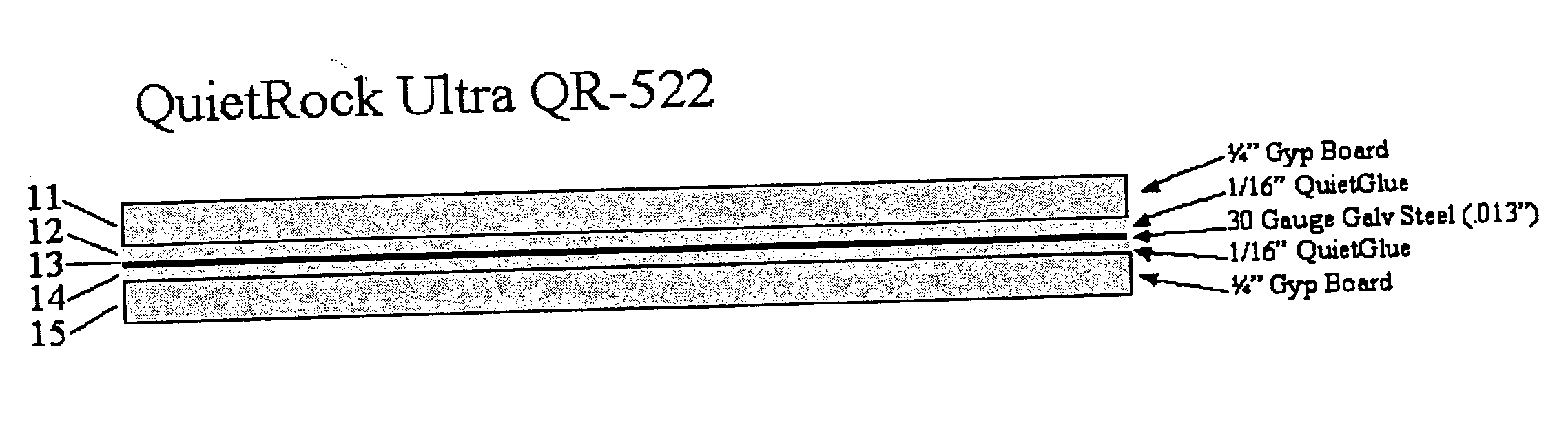
Acoustical sound proofing material and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20050050846A1Reduce transmission rateImprove abilitiesBuilding roofsCeilingsCelluloseUltrasound attenuation
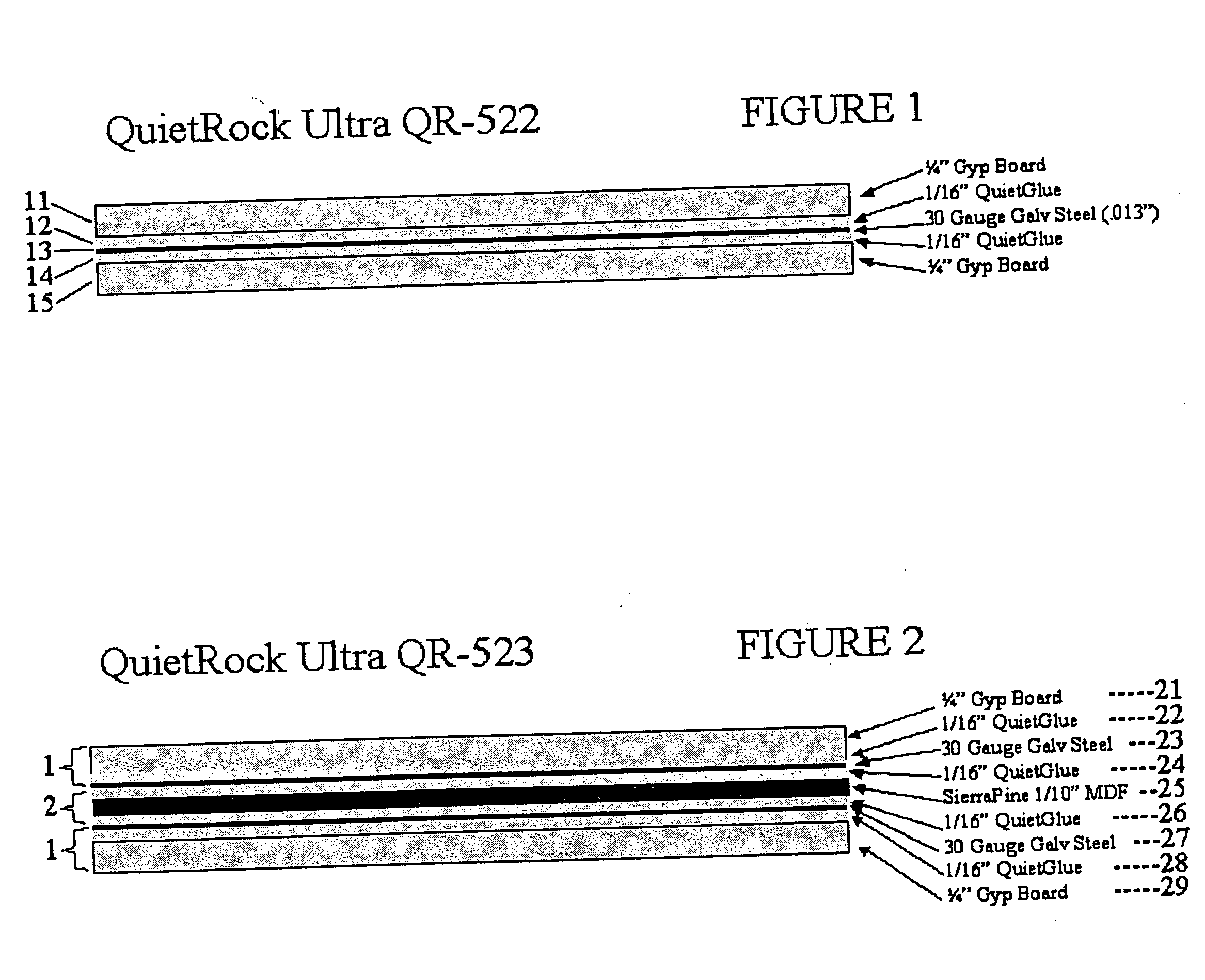
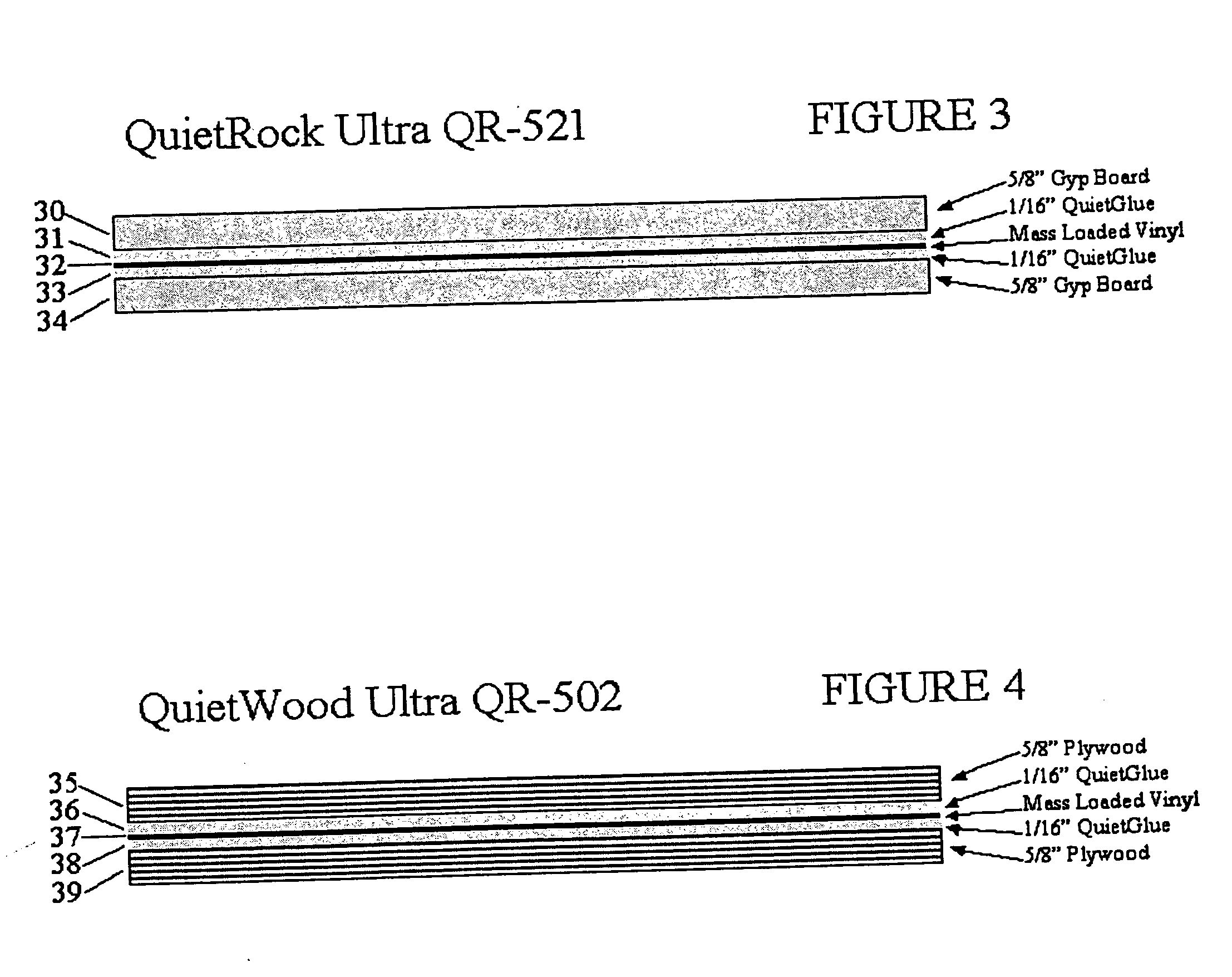
An improved acoustical damping wall (ceiling or floor) or door material comprises a laminar structure having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material which also functions as a glue and one or more constraining layers, such as metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminar structure; and one or more constraining layers are fabricated between the gypsum exterior. The resulting structure improves the attenuation of sound transmitted through the structure.
Owner:PACIFIC COAST BUILDING PRODS
Process of making fine and ultra fine metallic fibers
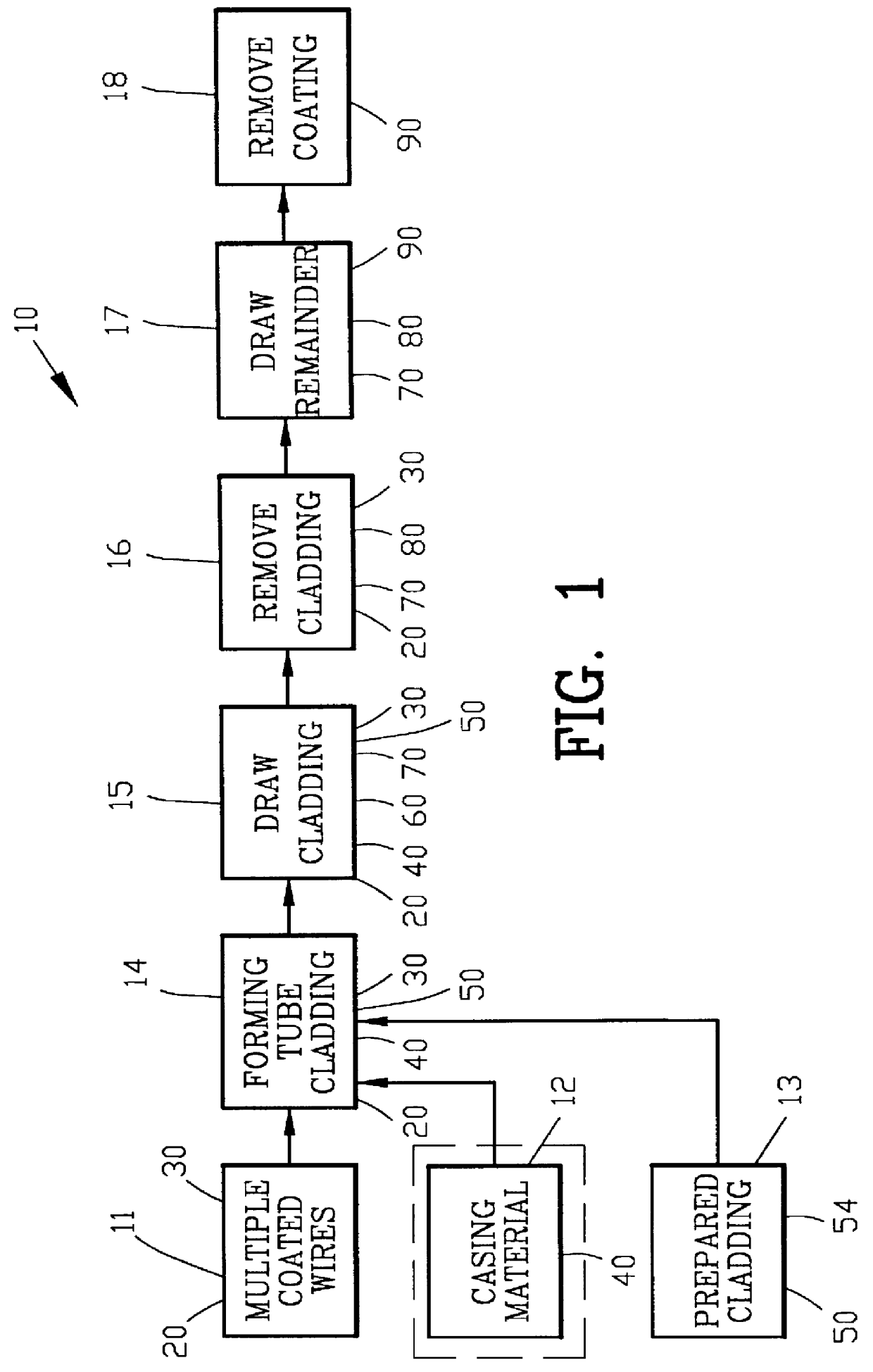
A process is disclosed for making fine metallic fibers comprising forming a continuous tube about a plurality of coated metallic wires for providing a first cladding. The first cladding is drawn for reducing the outer diameter and for diffusion welding the coating within the cladding. The tube is mechanically removed to provide a first remainder. The first remainder is drawn for reducing the diameter thereof to transform the plurality of metallic wires into a plurality of fine metallic fibers. In one example, the diffusion welded coating is removed for providing the plurality of fine metallic fibers. In another example, a plurality of the first remainders are assembled and a continuous tube is formed about a the first remainders for providing a second cladding. The second cladding is drawn for reducing the outer diameter. The tube is mechanically removed to provide a second remainder. The second remainder is drawn for reducing the diameter thereof to transform the plurality of fine metallic fibers into a plurality of ultra fine metallic fibers. The diffusion welded coating is removed for providing the plurality of ultra fine metallic fibers.
Owner:PALL CORP
Formable light weight composite material systems and methods
ActiveUS20110200816A1Attractive performance characteristicHigh strengthConductive materialSoldering apparatusElectrical resistance and conductancePolymer science
The present invention relates to filled polymeric materials including a polymer and a mass of metallic fibers distributed within the polymer, and to light weight composites which comprise at least a pair of metallic layers and a polymeric layer interposed between the pair of metallic layers, the polymeric layer containing the filled polymeric material. The composite materials of the present invention may be formed using conventional stamping equipment at ambient temperatures. Composite materials of the present invention may also be capable of being welded to other metal materials using a resistance welding process such as resistance spot welding. Preferred composite materials include one or any combination of the following features: metallic fibers that are ribbon fibers; a polymer selected from a polyolefin, a polyamide, or a combination thereof; or a metallic layer (e.g., one or both of the pair of metallic layers) having a surface facing the filled polymeric material that is untreated.
Owner:PRODIVE RES
Fire-resistant high performance concrete composition
InactiveUS6881256B2Improve fire resistanceSolid waste managementCeramicwareFiberCompressive strength
The invention concerns the use of organic fibers having a melting point lower than 300° C., an average length l more than 1 mm and a diameter Ø not more than 200 μm, in ultra high performance concrete for improving the concrete fire resistance, the amount of organic fibers being such that their volume ranges between 0.1 and 3% of the concrete volume after setting and the concrete having a compressive strength at 28 days of at least 120 Mpa, a bending strength of at least 20 Mpa, and a spread value in non-hardened state of at least 150 mm, the values being for a concrete preserved at 20° C., the concrete consisting of a particularly hardened cement matrix wherein metal fibres are dispersed.
Owner:BOUYGUES TRAVAUX PUBLICS SA +1
Carbon nano-tube enhanced cement-base composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101239800AResolve aggregationSolve the problem of tanglesSolid waste managementCarbon nanotubeMetal fibers
The present invention provides a carbon nano-tube reinforcing cement-based composite material and the preparing method thereof, which relates to an inorganic non-metal fiber-reinforced cement-based composite material and the preparing method thereof. The invention settles the problem that the carbon nano-tube is hard to uniformly dispersed in the cement substrate, and the carbon nano-tube reinforcing cement-based composite material of the invention is mainly composed of carbon nano-tube, dispersing agent, thickening stabilizing agent, cement blending material, superplasticiser, antifoaming agent and cement; the method of the invention comprises the following steps: slowly injecting the continuous phase mixed liquid of the thickening stabilizing agent into the carbon nano-tube disperse phase mixed liquid; adding the cement mixing material, mixing to uniform, heating and ultrasonic agitating, then vacuum discharging the bubble; then adding into the mixed liquid of the superplasticiser and the water for mixing to uniform, further eliminating the bubble with the antifoam agent; at last adding cement for mixing to uniform, adding the slurry into the oil mould and jolt ramming for molding; mode removing and standard maintaining to the prescribed lifetime. The carbon nano-tube in the product prepared by the method of the invention is uniformly dispersed in the cement substrate. The mechanical property and conductivity of the product is increased for several times.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Metal polyporous material with gradient pore structure and preparation thereof
The invention provides a metal porous material with a gradient pore structure, which is formed by at least two porous layers with different pore diameter. The pore diameter of the metal porous material gradually decreases or gradually increases with the thickness direction of the material; a bottom layer of the porous layers is a macropore layer used as a support body; a surface layer of the porous layers is a pore layer used as a filtering precision control layer; the material of the macropore layer is a composite wire gauze, a metal fiber felt or a powder sintered metal porous material; and the material of the pore layer is superfine metal powder or superfine metal fiber. A method for preparing the metal porous material comprises a step of using spraying, dipping or centrifugal coating method to manufacture at least one pore layer on the surface of the support body. Compared with the prior metal porous material in the same grade, the metal porous material with the gradient pore structure has the advantages of obviously raising permeability coefficient, well solving the contradiction between the pore diameter and relative permeability coefficient of the metal porous material and having a simple process.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Iron lithium phosphate material used for lithium ion battery and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1753216AReduce contentAvoid puffinessElectrode manufacturing processesLithium compoundsSodium-ion batteryMetal fibers
The invention relates to a LiFePO4 material for Li-ion battery and the making method thereof. The method controls diameter and length of C or metallic fiber at 100-300 nm and 10-20 mum, respectively and dopes ions with valences greater than +2-+4 in Li situ of LiFePO4, in the raw material composed of Li source, ion-doped compound, trivalent Fe source, phosphate radical, charcoal material, and C / metallic fiber, so as to make the LiFePO4 material, largely reducing the charcoal material content of the made LiFePO4 material on the premise of not reducing electron conductivity; and because the specific surface area of the charcoal material is selected at 30-80 sq m / g, effectively raising the tap density of material so as to bring a great convenience to the follow-up electrode smearing process. And the prepared LiFePO4 material has low cost and simple operating process, easy to large-scale production.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 18 RES INST
Automotiv non-asbestos high strength braking friction disk, and its prodn. method
InactiveCN1563735AImprove heat resistanceEnhancement effect is goodFriction liningHeat resistanceMetal fibers
The wearing piece of non-asbestos high srength material applies the high molecular compound, phenolic ressin as the agglomerant. The metal fiber or organic fiber is strengthen component. The stuffing applies regulator with frictional properties and barium sulfate, black lead, alumina as accessory ingredient. The production possesses excellent characteristic of physical chemical and mechanical and thermo-stability.
Owner:APPLIED PHYSICS INST OF GUANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
C/C and C/SiC composite material and metal connecting method
ActiveCN101143397AFirmly connectedSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesParticulatesMetal fibers
The invention is a method of binding compound materials of the C / SiC and C / C, which belongs to the technology field of binding heterogeneous materials. The processing procedures are as following: 1. The surface of the e compound materials of the C / SiC and C / Cis pretreated, which comprise the surface of the connecting are grinding, cleaning, vacuum biscuit firing, preparation of double-layer metal film and microvacum heat treatment and so on. 2. The transition layer of the connecting area surface gradient of the compound materials of the C / SiC is coated and sintered. 3. The compound materials with the gradient transition layer as the felted phase is brazed with the metal in vacuum. The invention is characterized in that the gradient transition layer is directly used as the materials that bind the compound materials with the metal; the gradient transition layer is double-layered or multilayered (sub-layered) structure; from the inner basal body to the outer part of the compound materials, the melting points of active brazing alloy adopted by each sub-layer gradually lower, the coefficient of heat expansion that adjust volume percentage composition gradually lower and the coefficient of heat expansion of the sub-layers gradually rise. The brazing ceramic metal connecting piece of the invention has good strength, air tightness and wide application field, which is suitable for various non-metallic fibers, such as ceramics of SiC, Si3N4, Al2O3, AlN and so on and applicable for connecting the ceramic matrix compound materials with particulate reinforced with the metal.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Fluid filter and method of making
InactiveUS6096212AIncrease surface areaIncrease capacityLoose filtering material filtersCartridge filtersFilter mediaMetal fibers
A fluid filter assembly and method of making is disclosed for filtering a fluid. The fluid filter assembly comprises a first filter component including a filter media comprising a matrix of metallic fibers. A second filter component includes a filter support. A sinter bond bonds the matrix of metallic fibers of the filter media to the second filter component.
Owner:USF FILTRATION & SEPARATIONS GROUP
Polycarbonate composition and articles formed therefrom
ActiveUS20130309474A1Speed up the flowImprove aestheticsSynthetic resin layered productsConductive materialPolysiloxane polycarbonate copolymerCarbon fibers
A composition includes at least one poly(aliphatic ester)-polycarbonate copolymer, a polysiloxane-polycarbonate copolymer, and an electromagnetic shielding agent (such as metal fibers). The composition exhibits excellent impact properties and electromagnetic shielding properties when formed into an article. Another composition includes at least one poly(aliphatic ester)-polycarbonate copolymer, a polysiloxane-polycarbonate copolymer, and carbon fibers. This composition has excellent impact properties when formed into an article.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
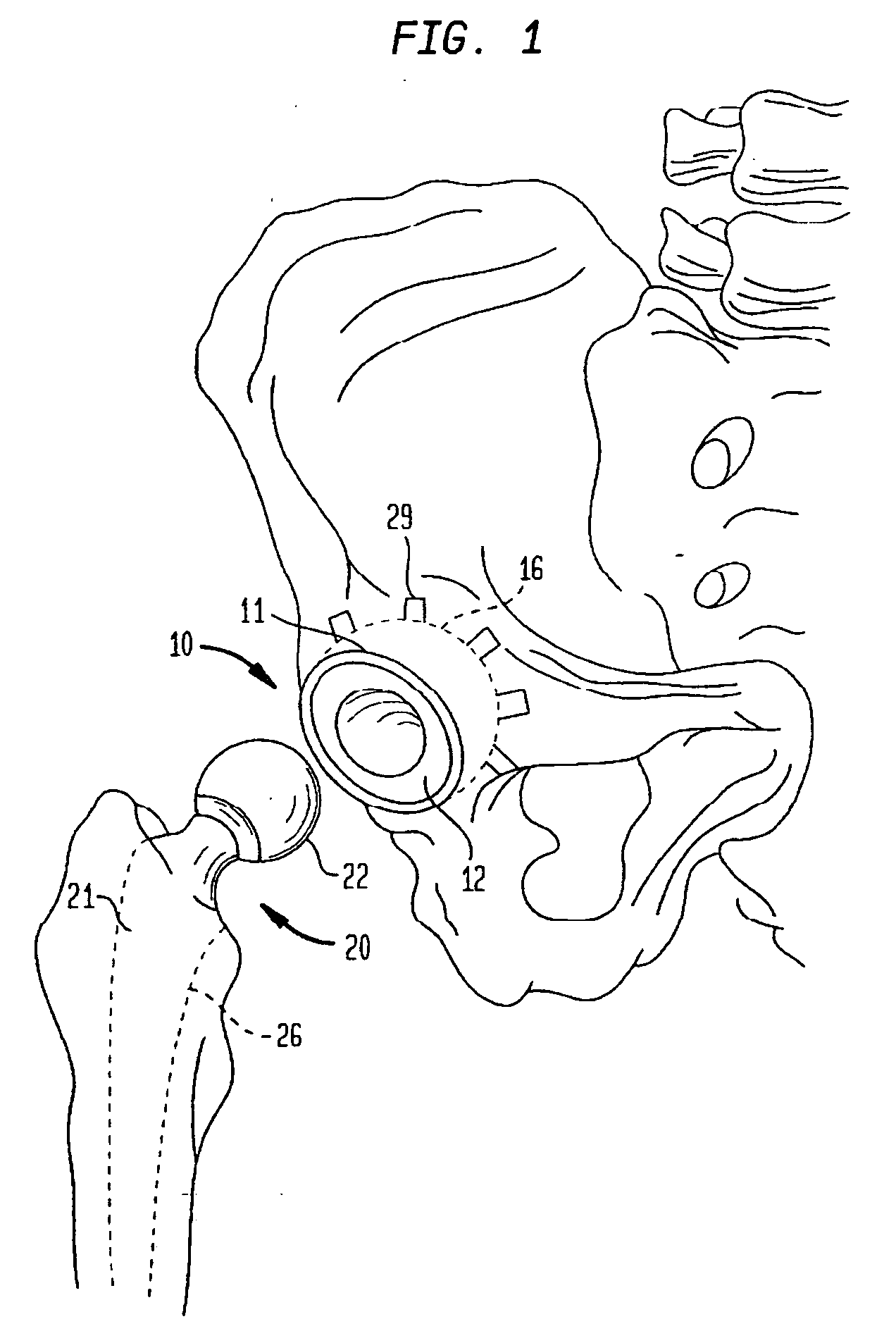
Medical device for insertion into a joint
The present invention relates to implants used for alleviating and / or preventing conditions relating to damaged joints involving articulating surfaces. The implants comprise fibre of polymer and / or metal, and can be used as an artificial joint, as part of an artificial joint or as an artificial joint spacer made to replace the missing cartilage or to improve the slidability between two natural and / or artificial components of the body, or between a natural and artificial component. The product of the invention can be used to partly or entirely coat medical products or to make up implant partly or entirely.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Anion generator for incorporation into lighting apparatuses and other appliances
InactiveUS20060078460A1To promote metabolismRestore balanceMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceLight equipmentEffect light
A negative ion generator for improving the air quality of a room or space and may be conveniently incorporated into a lighting apparatus, appliance or other house item. The anion generator includes a metal fiber brush which reduces or eliminates ozone production. The lighting apparatus may take a variety of forms and may also include a photocatalyst coating to further purify the air.
Owner:RYU JASON +1
Vehicle body, chassis, and braking systems manufactured from conductive loaded resin-based materials
InactiveUS20080036241A1Effective vehicle brake systemReduce weightVehicle seatsNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialMetal fibersElectroplating
Vehicle body, chassis, and braking components are formed of a conductive loaded resin-based material. The conductive loaded resin-based material comprises micron conductive powder(s), conductive fiber(s), or a combination of conductive powder and conductive fibers in a base resin host. The percentage by weight of the conductive powder(s), conductive fiber(s), or a combination thereof is between about 20% and 50% of the weight of the conductive loaded resin-based material. The micron conductive powders are metals or conductive non-metals or metal plated non-metals. The micron conductive fibers may be metal fiber or metal plated fiber. Further, the metal plated fiber may be formed by plating metal onto a metal fiber or by plating metal onto a non-metal fiber. Any platable fiber may be used as the core for a non-metal fiber. Superconductor metals may also be used as micron conductive fibers and / or as metal plating onto fibers in the present invention.
Owner:INTEGRAL TECHNOLOGY INC
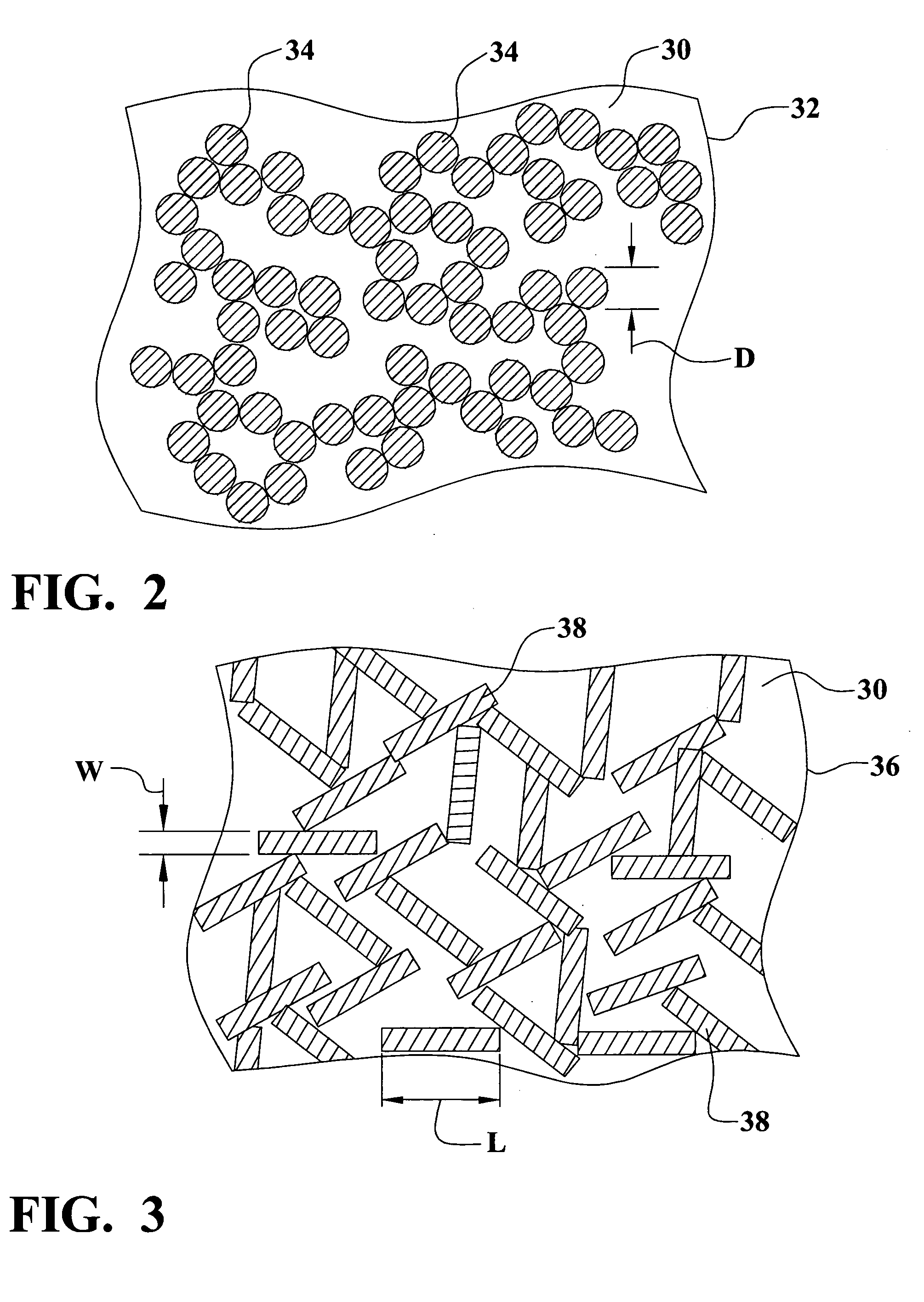
Porous metallic scaffold for tissue ingrowth
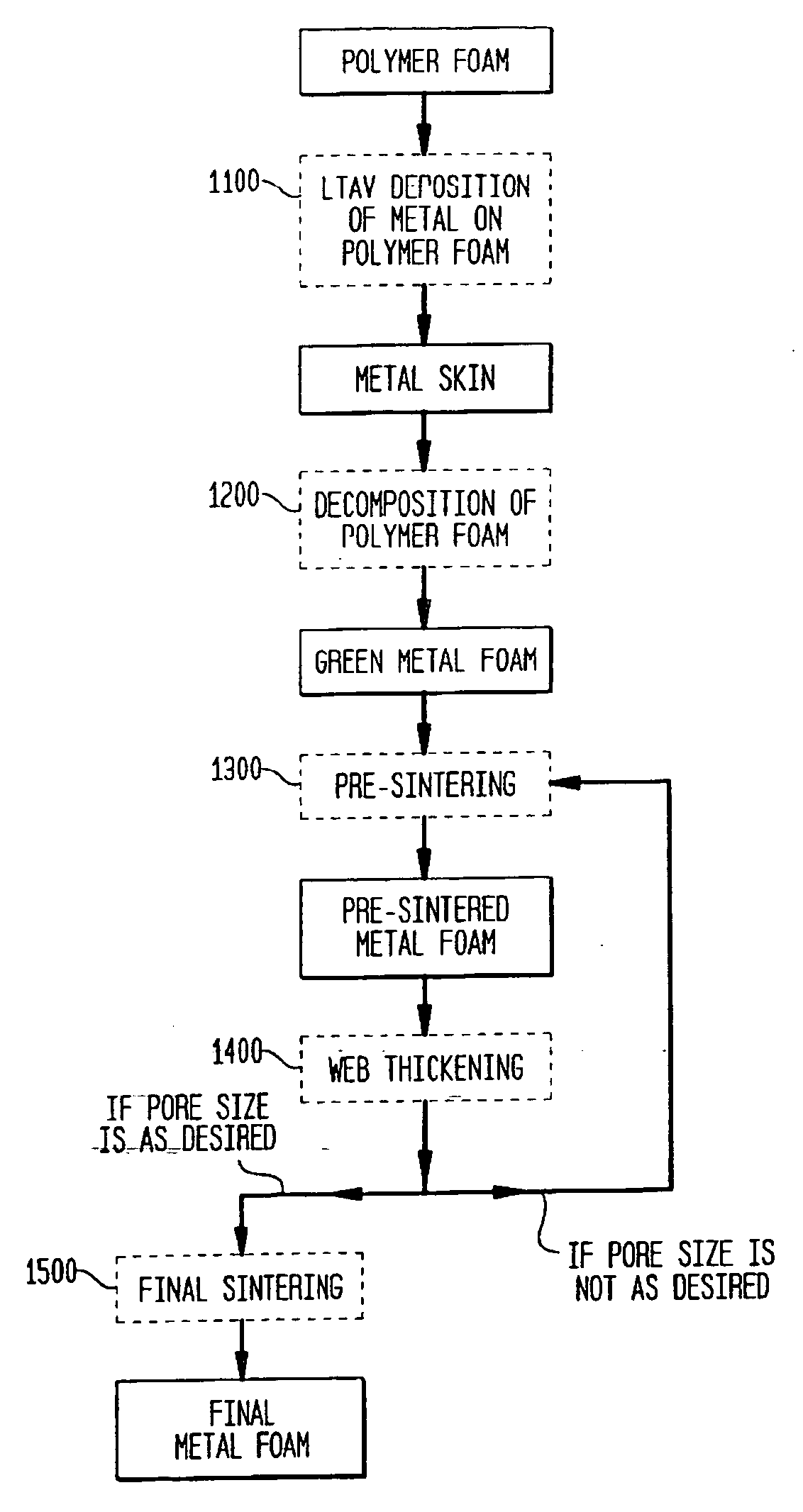
The invention relates to implantable medical devices, particularly, to porous structures for such devices. In one aspect, the invention provides a porous metal scaffold comprising a porous metal network having pores defined by metal webs, the metal webs covered with at least one layer of metal particles bonded to the metal webs. In other aspects, the invention provides methods of forming porous scaffolds. In one such aspect, the method includes providing a polymer foam; forming a skin of biocompatible metal on the polymer foam by low temperature arc vapor deposition; and heating the polymer foam and the metal skin above the decomposition temperature of the polymer foam in an inert gas atmosphere; thereby the polymer foam decomposes producing a green metal foam. In yet other aspects, the invention provides methods of improving stability of porous scaffolds.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
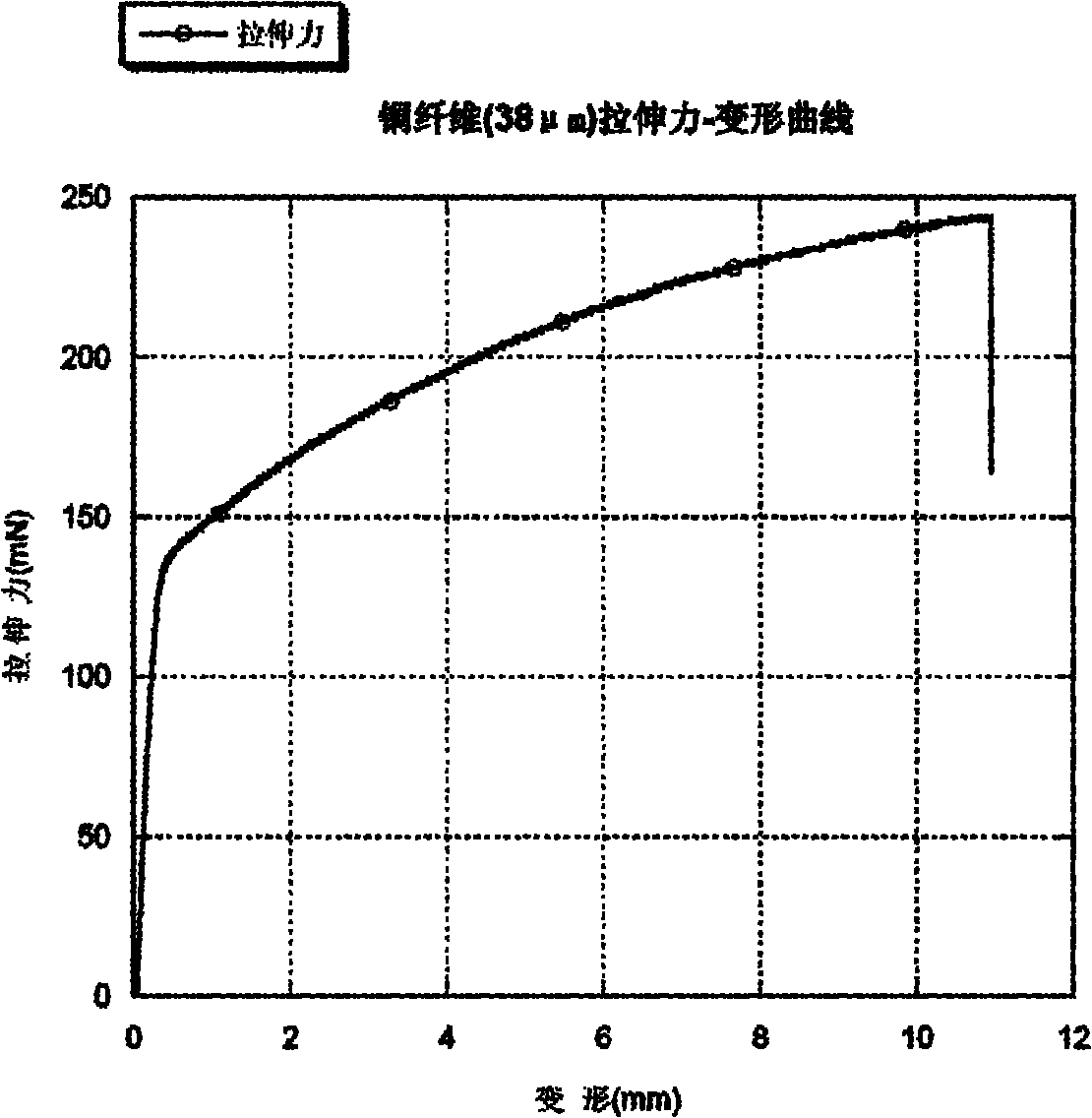
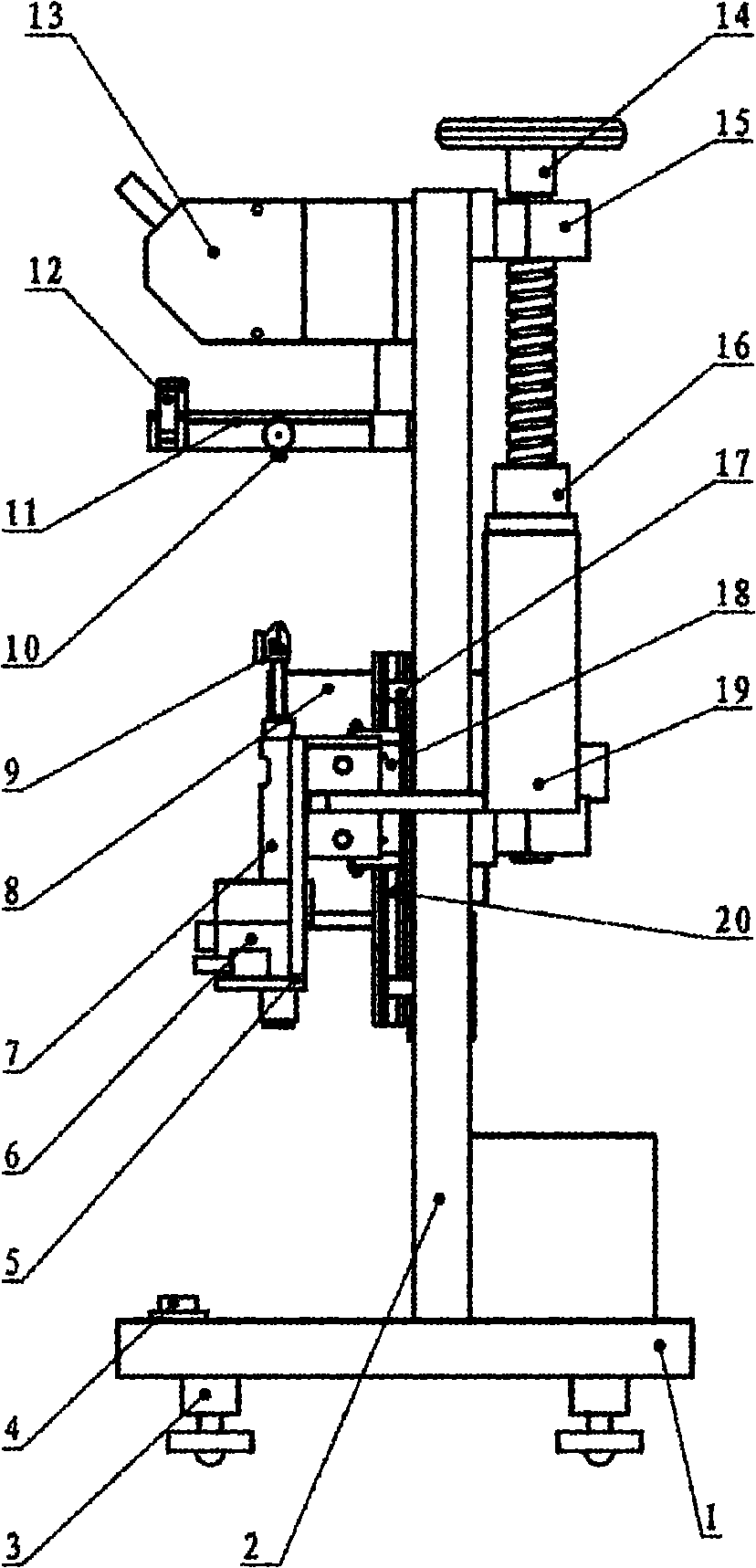
Method and device for testing micro-tensile mechanical properties of metal fiber
ActiveCN101949797AAdjust the measuring rangeAdjust measurement sensitivityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansTest sampleStress–strain curve
The invention discloses a method and a device for testing micro-tensile mechanical properties of a metal fiber. Being different from the existing tensile tester, the invention is characterized in that a force transducer is composed of a non-contact photoelectric displacement transducer and an elastic element, the force transducer can be used for measuring both the tensile force of a fiber and the displacement of the gripped end of the fiber and helping automatically and accurately obtain the tensile force-deformation curve of a test sample in real time so as to obtain the stress-strain curve of the test sample, and parameter values characterizing the micro-tensile mechanical properties of the metal fiber can be obtained by analyzing the stress-strain curve. By using the optical non-contact measurement method, the invention avoids the interference generated by the traditional contact measurement, and enables the measuring system to be more stable. Besides, the whole device has the advantages of ingenious structure, simple and convenient operation and stable performance, thereby being applicable to testing the micro-tensile mechanical properties of various single fibers (especially metal fibers).
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Formable light weight composites
ActiveUS7927708B2Synthetic resin layered productsLaminationElectrical resistance and conductanceMetal fibers
The present invention relates to light weight composite materials which comprise a metallic layer and a polymeric layer, the polymeric layer containing a filled thermoplastic polymer which includes a thermoplastic polymer and a metallic fiber. The composite materials of the present invention may be formed using conventional stamping equipment at ambient temperatures. Composite materials of the present invention may also be capable of being welded to other metal materials using a resistance welding process such as resistance spot welding.
Owner:PRODIVE RES
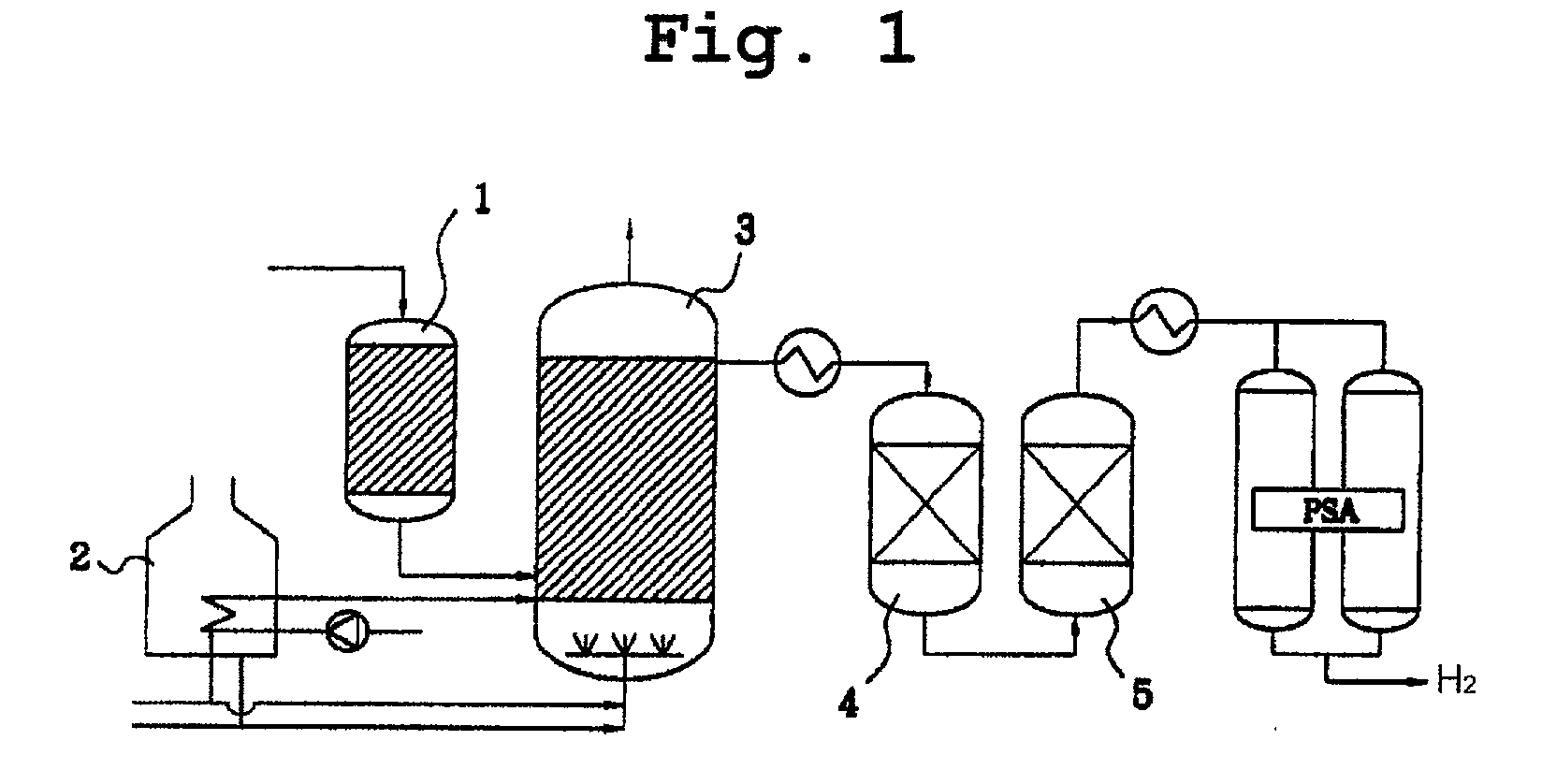
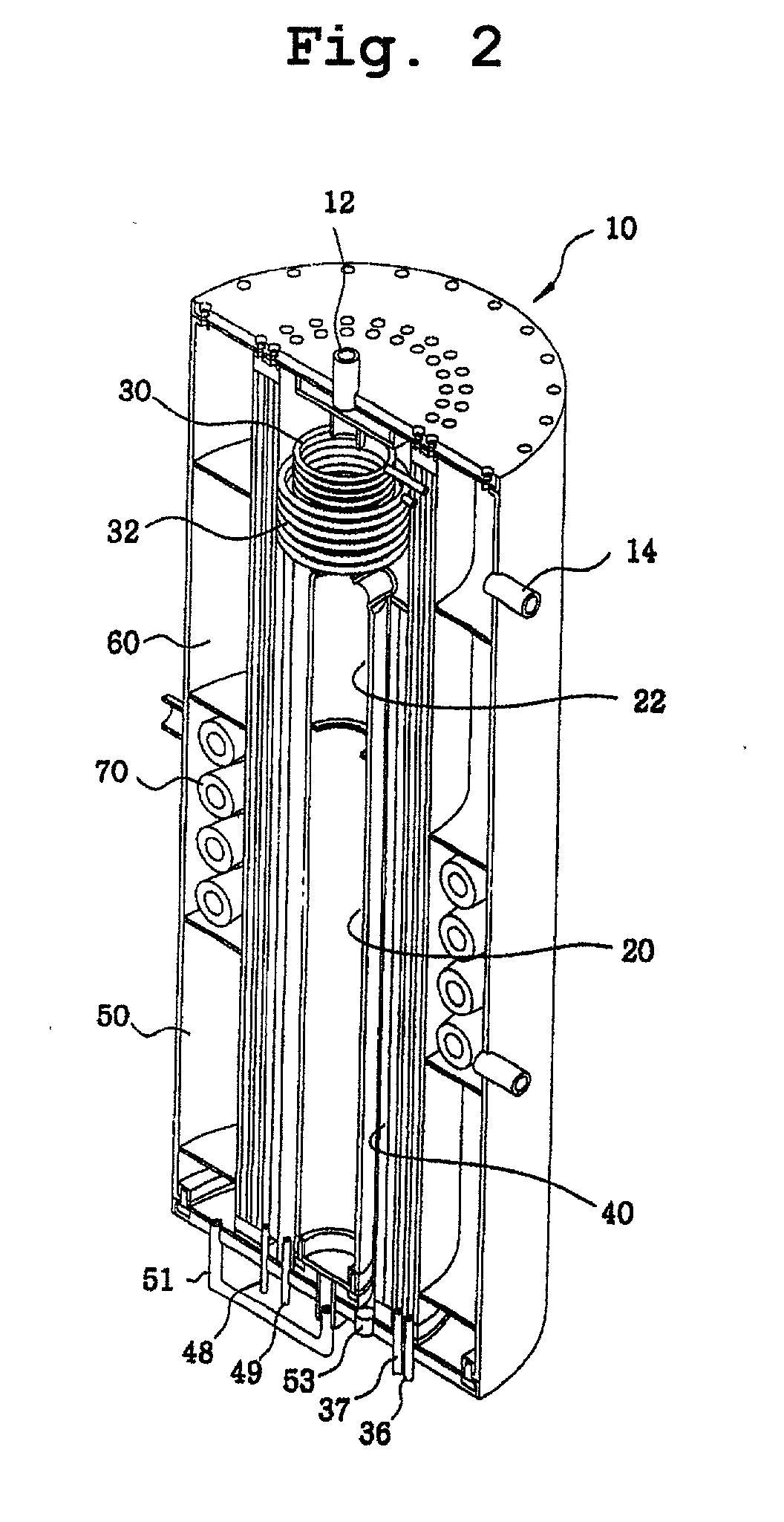
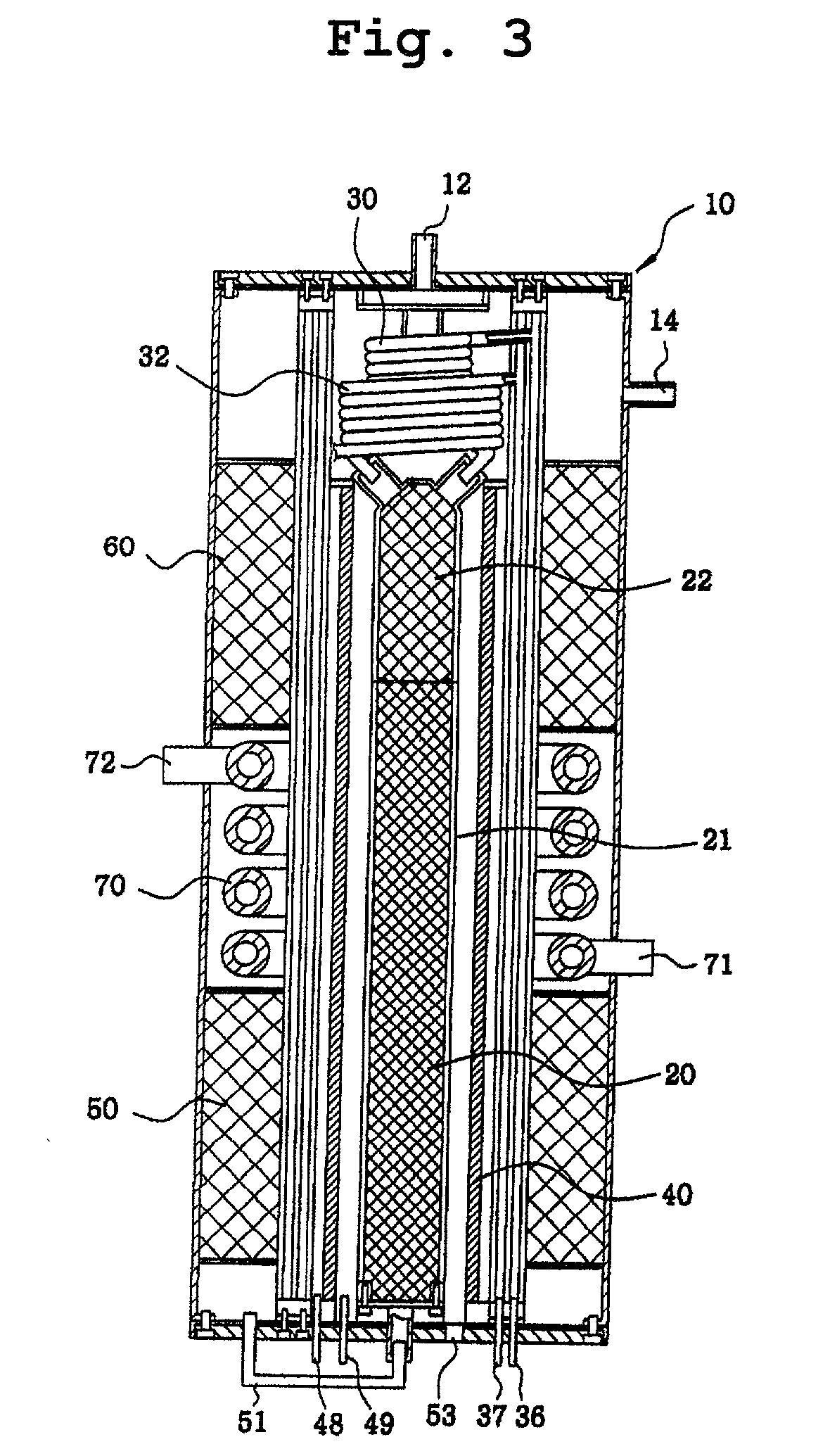
Compact steam reformer
Disclosed is a compact steam reformer which integrally comprises a housing; a reforming reactor having an upper mixing compartment for mixing natural gas and steam and a lower compartment for accommodating a catalyst bed; a natural gas feeding coiled pipe through which natural gas is introduced while being heated; a steam generating coiled pipe in which pure water is converted to steam by the exhaust; a metal fiber burner for heating the reforming reactor; a high-temperature converter for primarily removing carbon monoxide from a synthetic gas; a low-temperature converter for secondarily reducing the carbon monoxide level of the synthetic gas; and a heat exchanger, provided between the high-temperature converter and the low-temperature converter, for cooling the gas effluent from the high-temperature converter. The steam reformer enjoys the advantage of being easy to install in situ and being fabricated at low cost. Also, the cylindrical metal fiber burner can provide heat uniformly over the reforming reactor without a temperature gradient, thereby maximizing the reforming efficiency. The reformer has such a structure as to utilize the heat of the burner exhaust in generating steam, bringing about an effect of reducing the cost of the reformer because no additional steam generators are required.
Owner:KOREA GAS CORPORATION +2
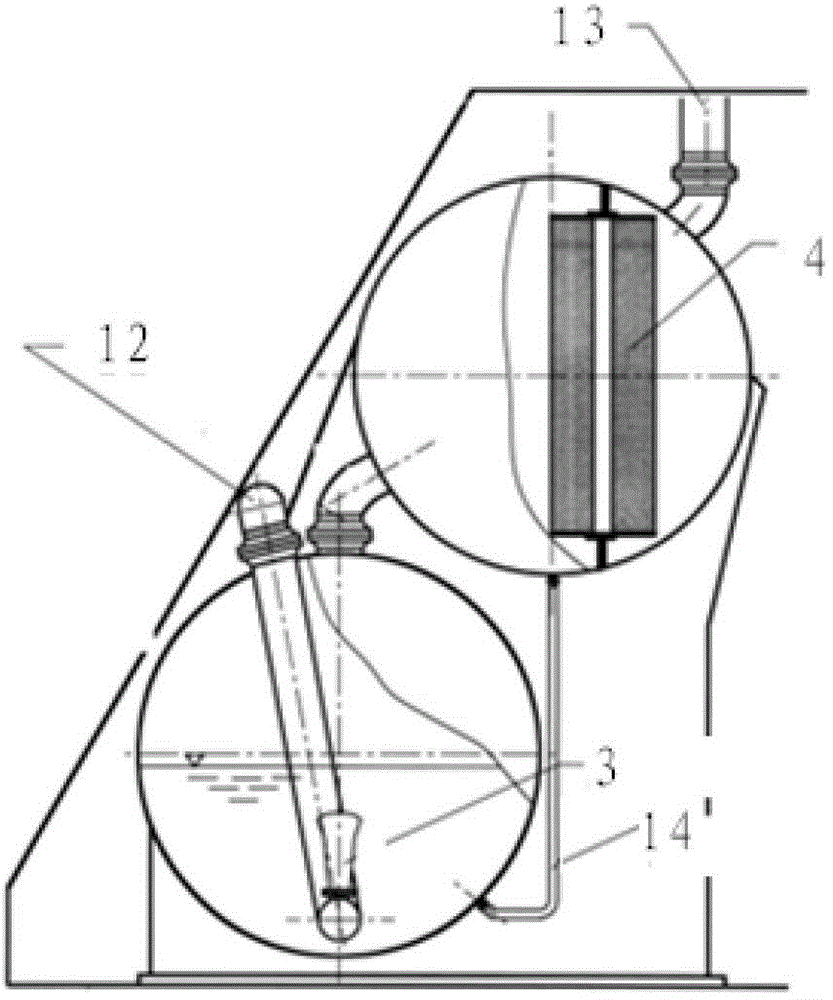
Containment filtering and discharging system
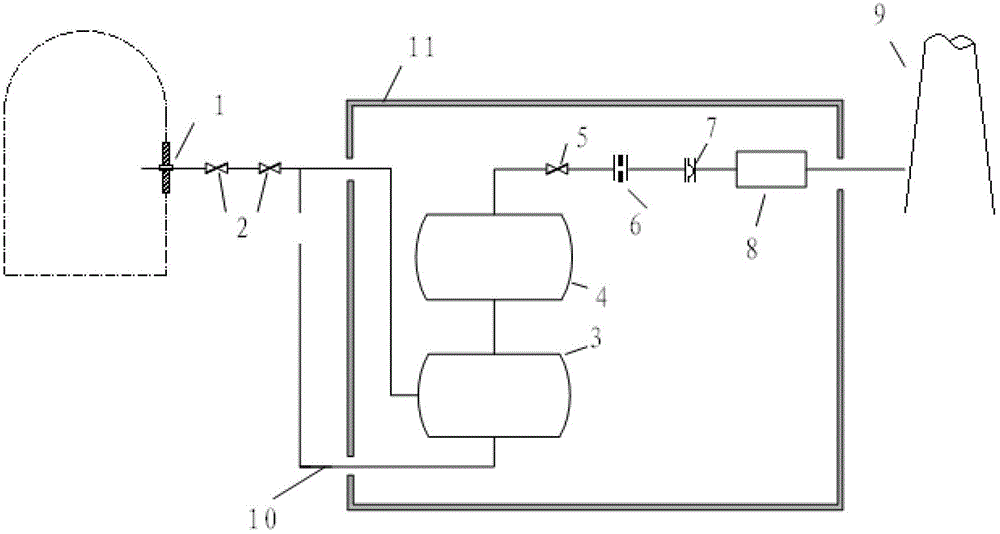
InactiveCN102723114AImprove filtering effectAccumulated radioactivityNuclear energy generationEmergency protection arrangementsLiquid wasteRadioactive agent
The invention relates to a containment filtering and discharging system. As a shielding plant (11) is arranged outside a containment, a discharging and filtering sub system is arranged in the shielding plant (11), a water washing filter (3) and a metal fiber filter (4) connected with each other in sequence are arranged in the discharging and filtering sub system and the water washing filter (3) is provided with a waste liquid returning pipeline (10), gases discharged by the containment are doubly filtered by the water washing filter (3) and the metal fiber filter (4), and the waste liquid accumulated in the water washing filter (3) self-flows into the containment through the waste liquid returning pipeline (10) under the effect of gravity force. Therefore, according to the invention, serious accidents occurred in pressurized-water reactor nuclear power stations are eased, overpressure failure of the containment is prevented, radioactive substances released to the environment are reduced, safeties of the surrounding environment and personnel are protected, and the safety of the nuclear power stations are greatly improved.
Owner:CHINA NUCLEAR POWER ENG CO LTD
Electrically conductive thermoplastic polymer composition
InactiveUS6936191B2Improve conductivityReduce the amount requiredNon-insulated conductorsConductive materialMetal fibersThermosetting polymer
Disclosed is an electrically conductive thermoplastic polymer composition comprising a thermoplastic polymer and a synergistic combination of metal fibers and metal-coated fibers, structures made therefrom, and a process to make said compositions and structures.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
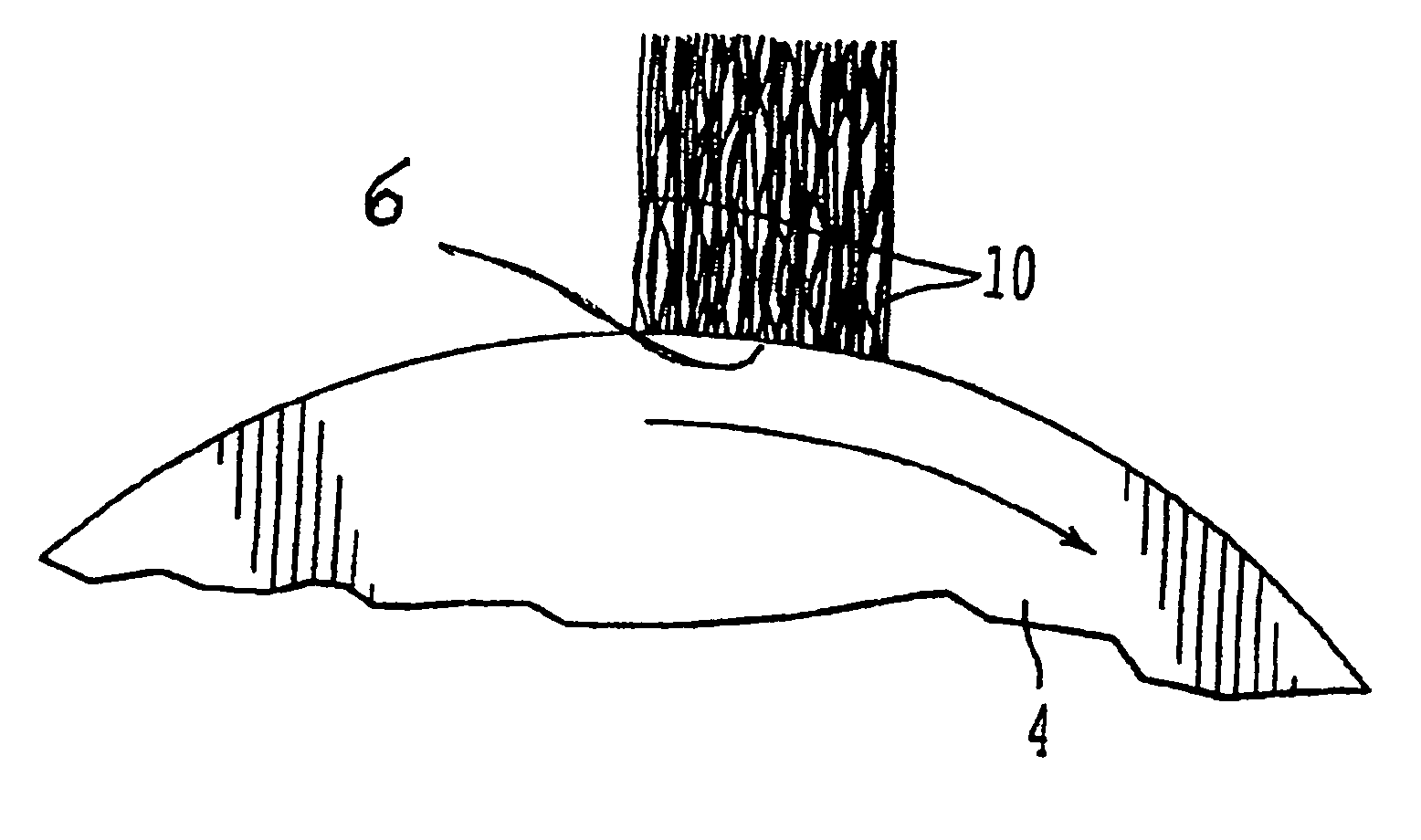
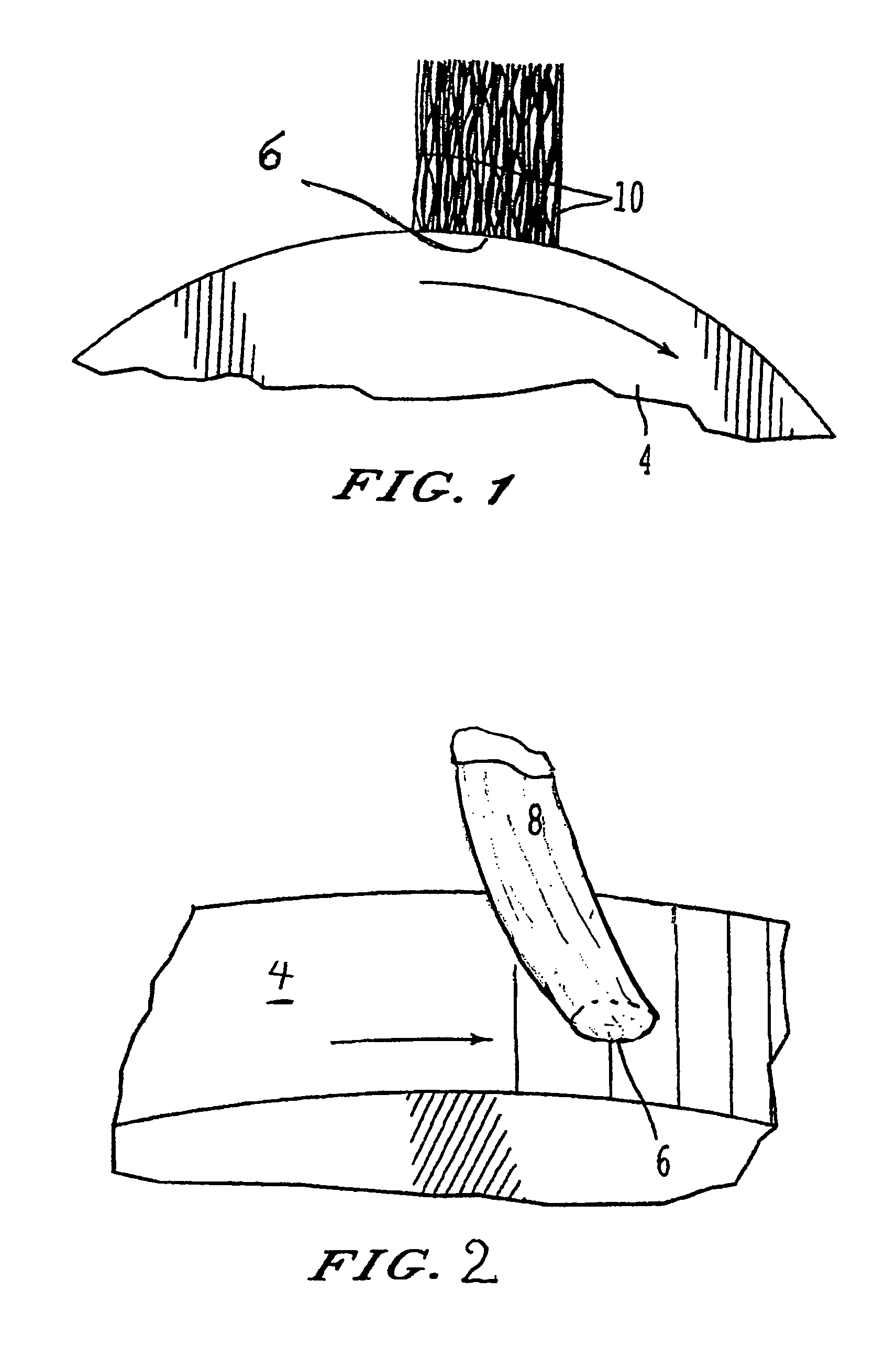
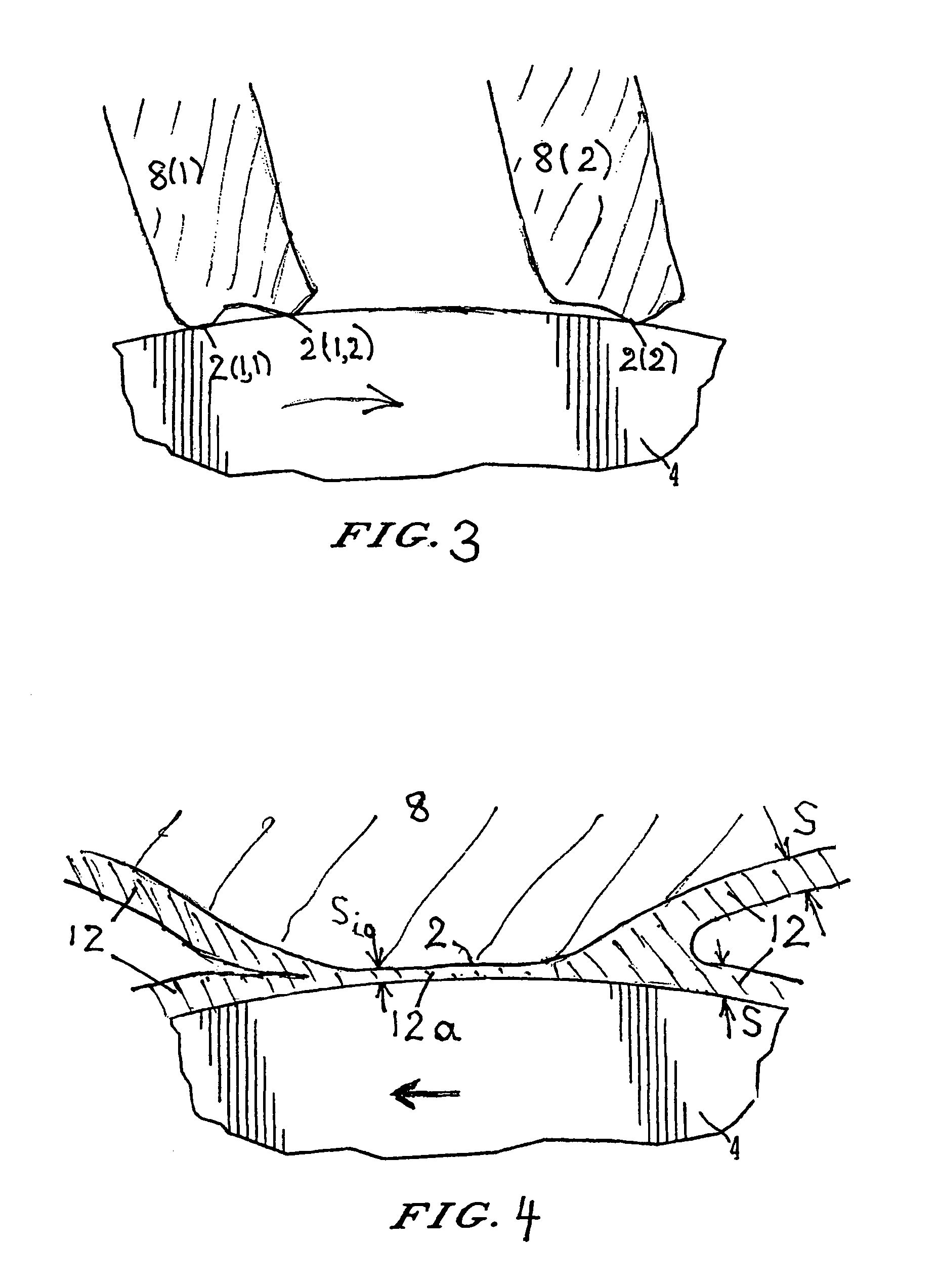
Metal fiber brush interface conditioning
ActiveUS7622844B1Increase achievable brush current densityIncrease sliding speedRotary current collectorDynamo-electric machinesMetal fibersElectron
An electrical brush having at least one conductive element and at least one conditioning material coated on the at least one conductive element wherein the conditioning material has a composition and thickness on the conductive element such that, as deposited on a moving contact surface in the course of brush operation, the conditioning material can have an average film thickness S<˜1 μm so that current can be conducted by means of electron tunneling through a film thickness of the deposited conditioning material of Si≦12 nm thickness over a fractional area fC, greater than 0.01 of a foot print of the conductive element in a current conductive area.
Owner:ALEXSAVA HLDG
Process for bonding workpieces
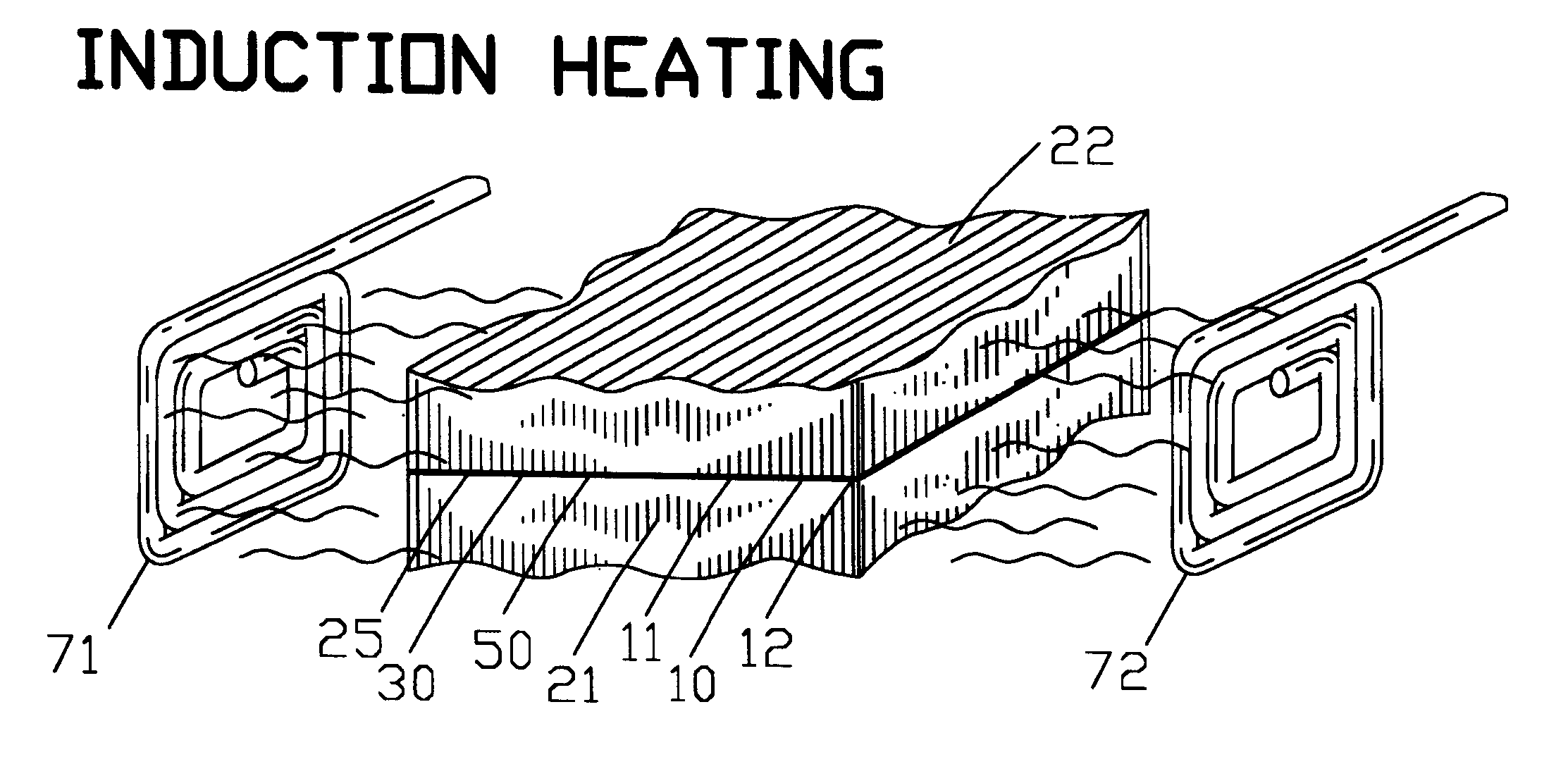
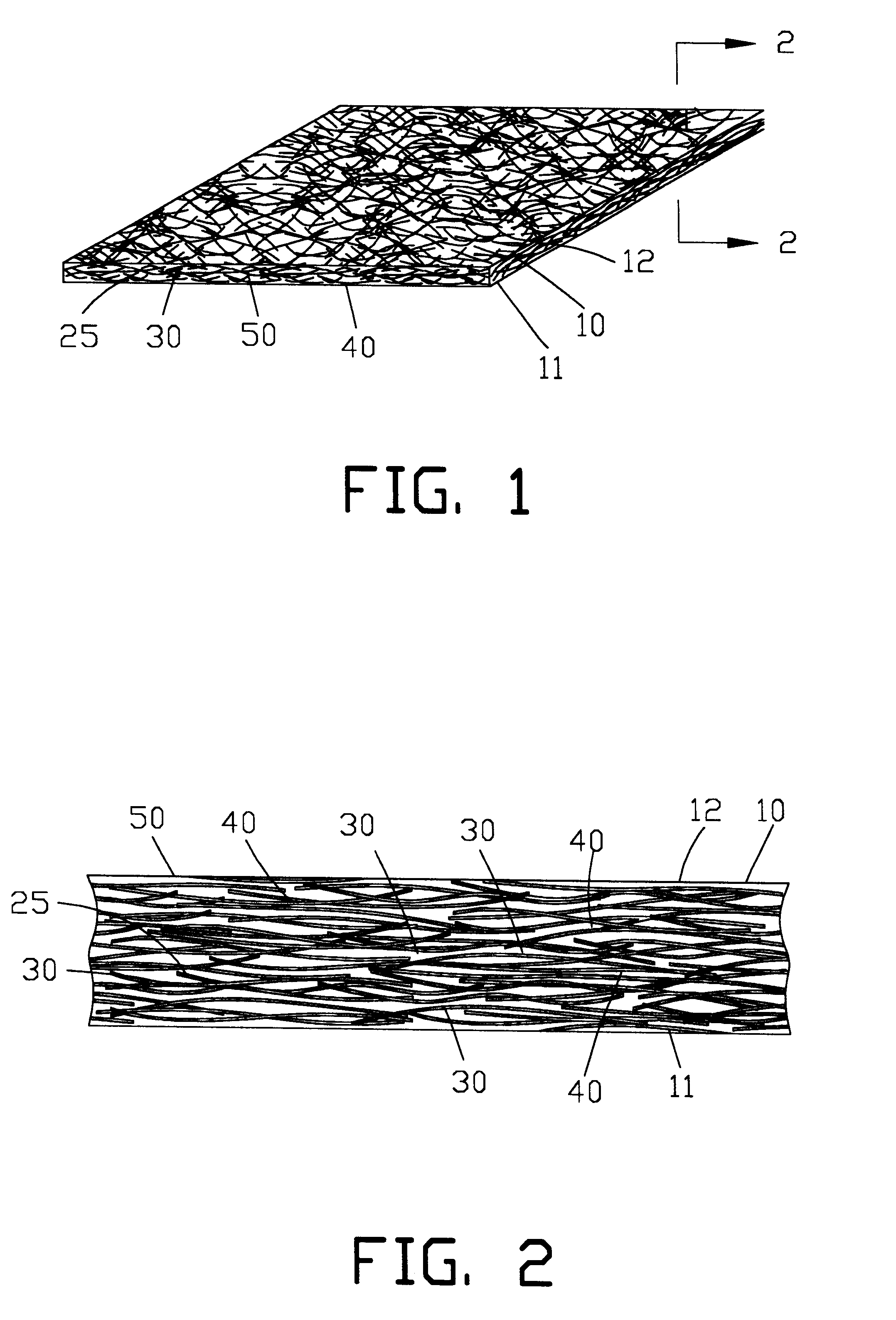
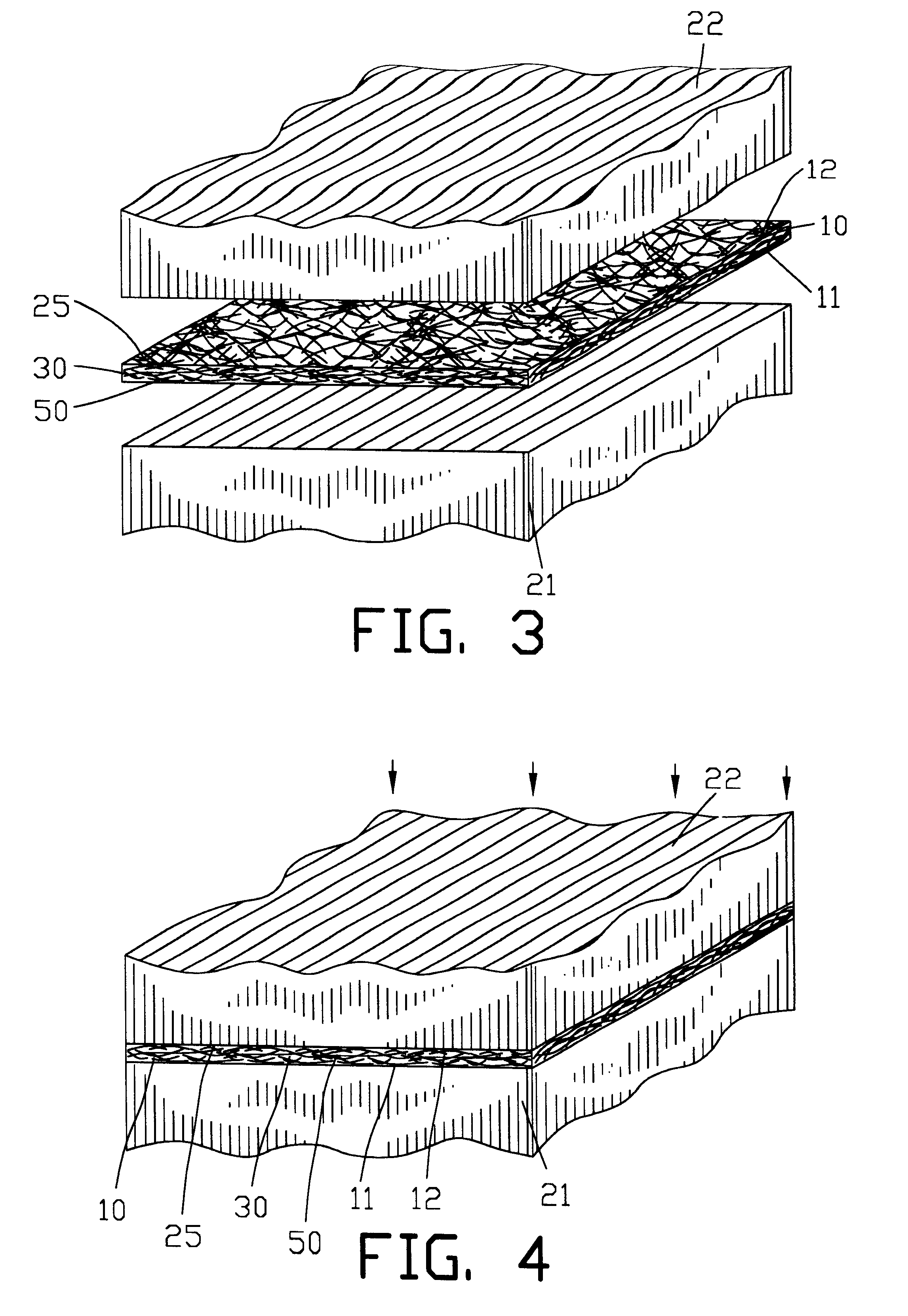
InactiveUS6291806B1Economical to useDrying solid materials with heatHigh frequency current welding apparatusMetal fibersMaterials science
Owner:USF FILTRATION & SEPARATIONS GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com