Method of replenishing indium ions in indium electroplating compositions
A composition and technology of indium ions, applied in the field of supplementing indium ions, can solve problems such as inability to accurately know the concentration of additives
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
[0064] Embodiment 1 (comparative example)
[0065] Prepare the following aqueous indium compositions:
[0066] Table 1
[0067] components
content
Indium ion ( 3+ ) (from indium sulfate)
60g / L
30g / L
Imidazole-epichlorohydrin copolymer 1
100g / L
water
to the desired volume
pH
1
[0068] 1. Lugalvan TM IZE, obtained from BASF (IZE contains 48-50 wt% copolymer)
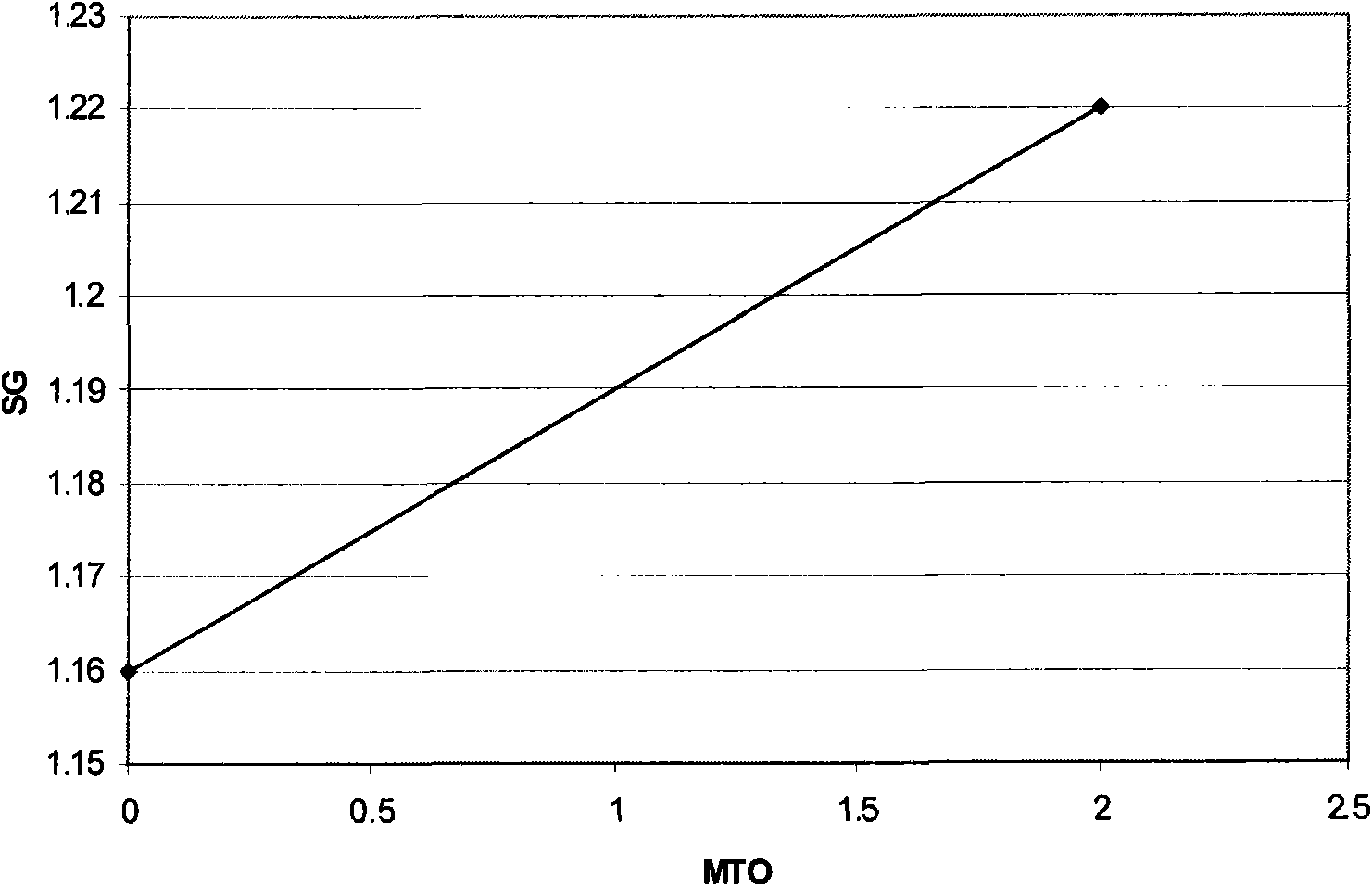
[0069] The indium composition was used to deposit an indium layer on a copper plate. The indium electroplating composition was maintained at a pH of 1 and a temperature of 60°C. The pH was adjusted with KOH. The initial S.G. was measured to be 1.16. The specific gravity is measured with a conventional gas density meter. The composition was continuously stirred during indium metal plating. The cathode current density is maintained at 10A / dm 2 , and the indium deposition rate was 1 μm in 20 seconds. A copper ...
Embodiment II
[0072] The following aqueous indium electroplating compositions were prepared:
[0073] Table 2
[0074] components
content
Indium ion ( 3+ ) (from indium sulfate)
60g / L
30g / L
Imidazole-epichlorohydrin copolymer 2
100g / L
water
to the desired volume
pH
1
[0075] 2. Lugalvan TM IZE, obtained from BASF (IZE contains 48-50 wt% copolymer)
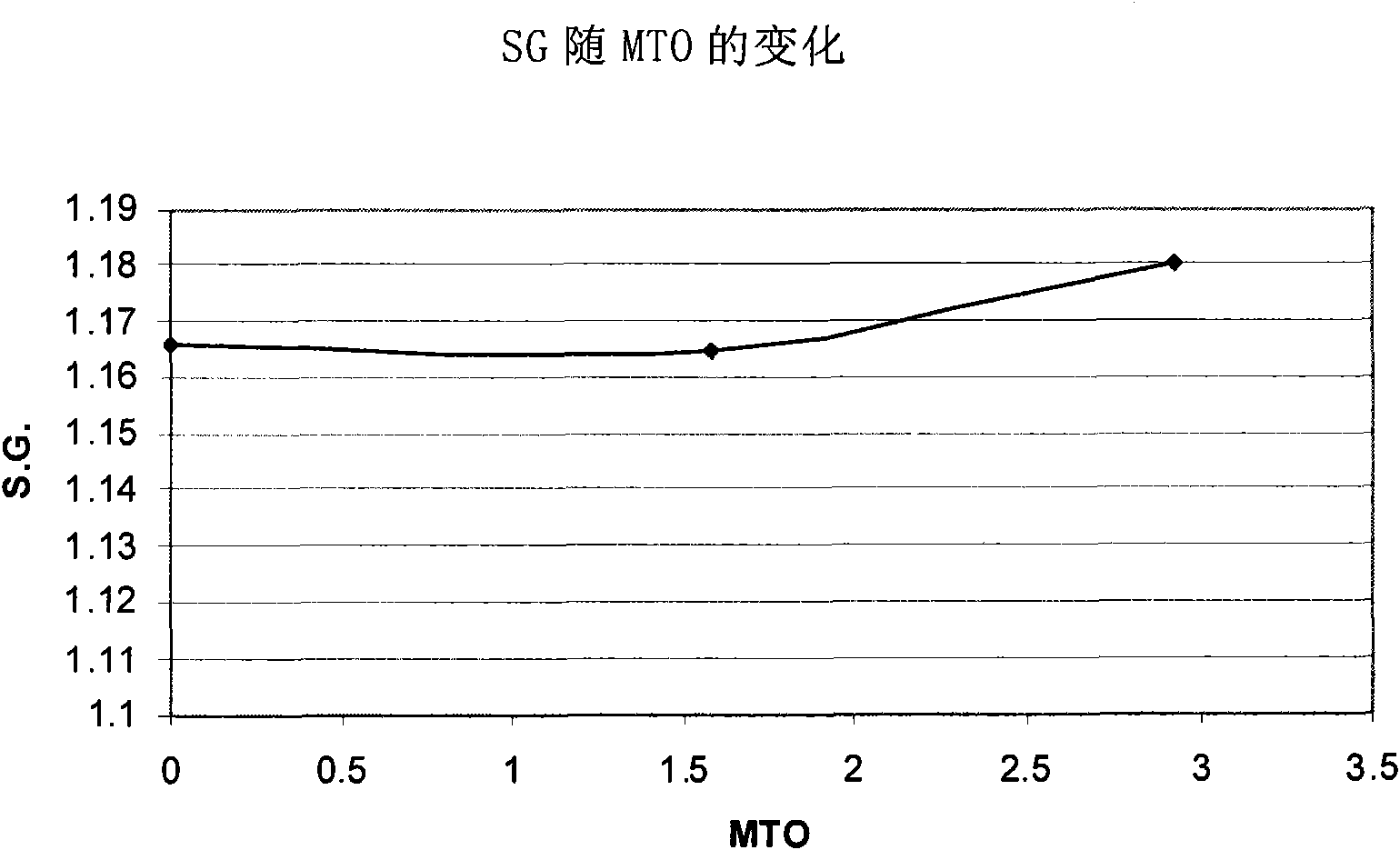
[0076] The indium composition was used to deposit an indium layer on a copper plate. The indium electroplating composition was maintained at a pH of 1 and a temperature of 60°C. The initial S.G. was measured to be 1.165. The composition was continuously stirred during indium metal plating. The cathode current density is maintained at 10A / dm 2 , and the indium deposition rate was 1 μm in 20 seconds. A copper plate served as the cathode, and the anode was a Metakem shielded insoluble anode of titanium and mixed oxides. During the depos...
Embodiment III
[0079] The following aqueous indium electroplating compositions were prepared:
[0080] table 3
[0081] components
content
Indium ion ( 3+ ) (from indium sulfate)
30g / L
30g / L
Imidazole-epichlorohydrin copolymer 3
100g / L
water
to the desired volume
pH
1
[0082] 3. Lugalvan TM IZE, obtained from BASF (IZE contains 48-50 wt% copolymer)
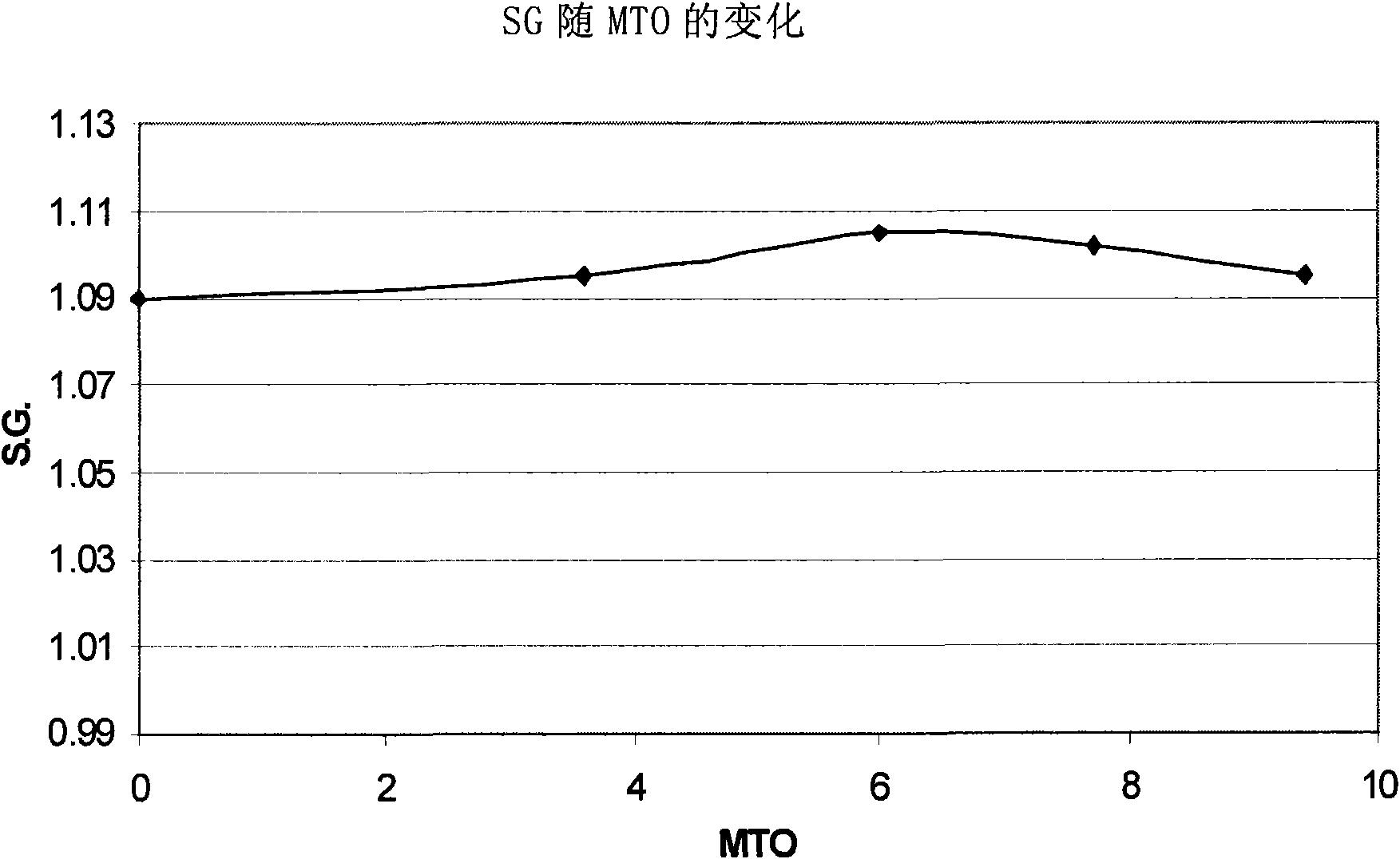
[0083] The indium composition was used to deposit an indium layer on a copper plate. The indium electroplating composition was maintained at a pH of 1 and a temperature of 60°C. The initial S.G. was measured to be 1.09. The composition was continuously stirred during indium metal plating. The cathode current density is maintained at 2A / dm 2 , and the indium deposition rate is 0.6 μm in 1 minute. A copper plate served as the cathode, and the anode was a Metakem shielded insoluble anode of titanium and mixed oxides. During deposition o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com