Processing method for waste water
A treatment method and technology for waste liquid, applied in water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment equipment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., which can solve the problems of difficult reaction control, disordered decomposition reaction, and difficulty in oxidant treatment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
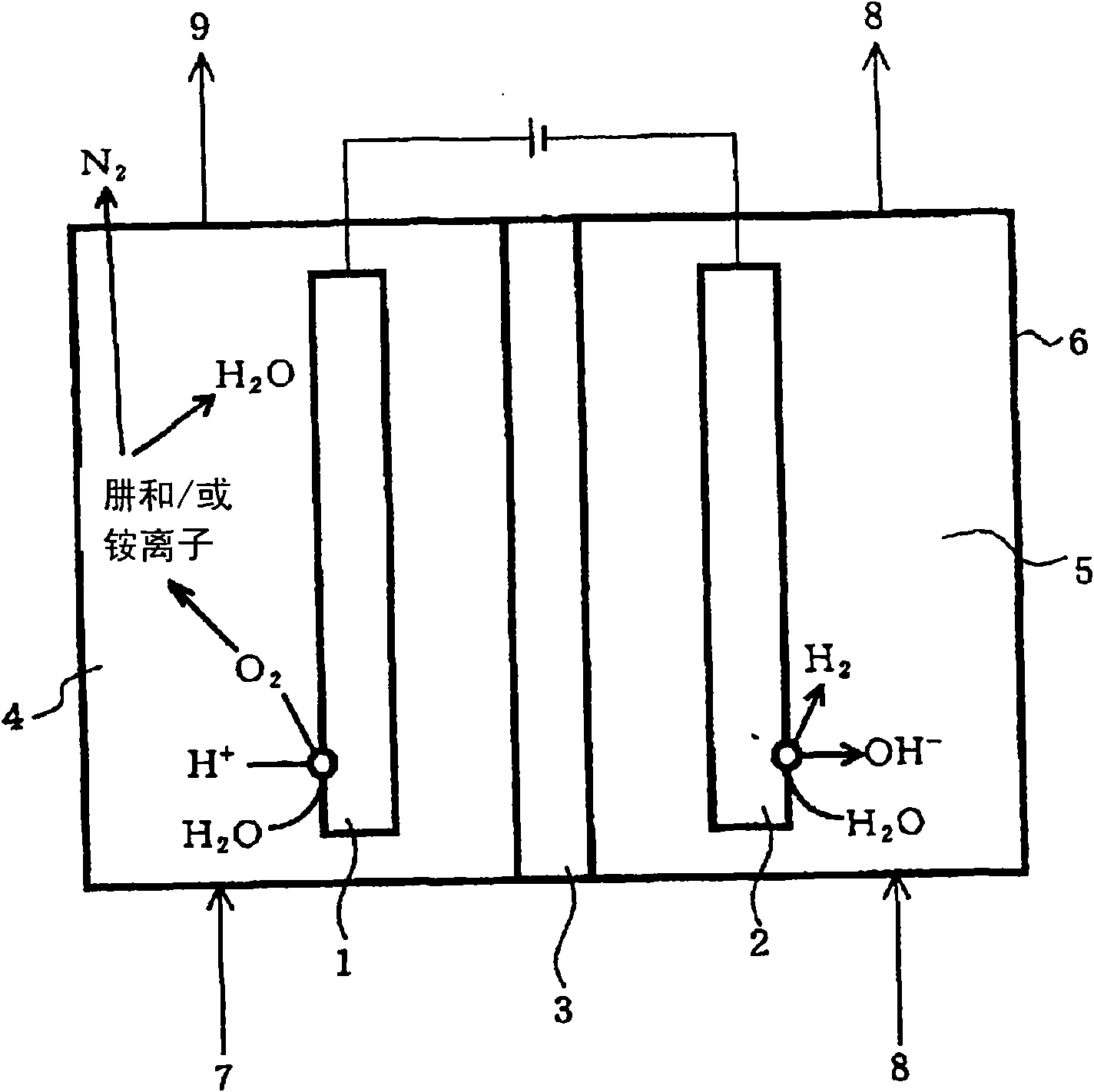
[0071] In Example 2, since the meshed anode 1 and cathode 2 are used, the contact interface area between the electrode and the electrolyte is significantly increased compared with the case of using a solid rod or plate electrode. Furthermore, since the anion exchange membrane 3a is arranged closely between the mesh-like anode 1 and cathode 2, the distance between the electrodes is shortened. Therefore, it is easy to cause an electrode reaction, so that the nitrogen reducing substances such as hydrazine and ammonium ions in the waste liquid 7 are efficiently oxidized in a short time.
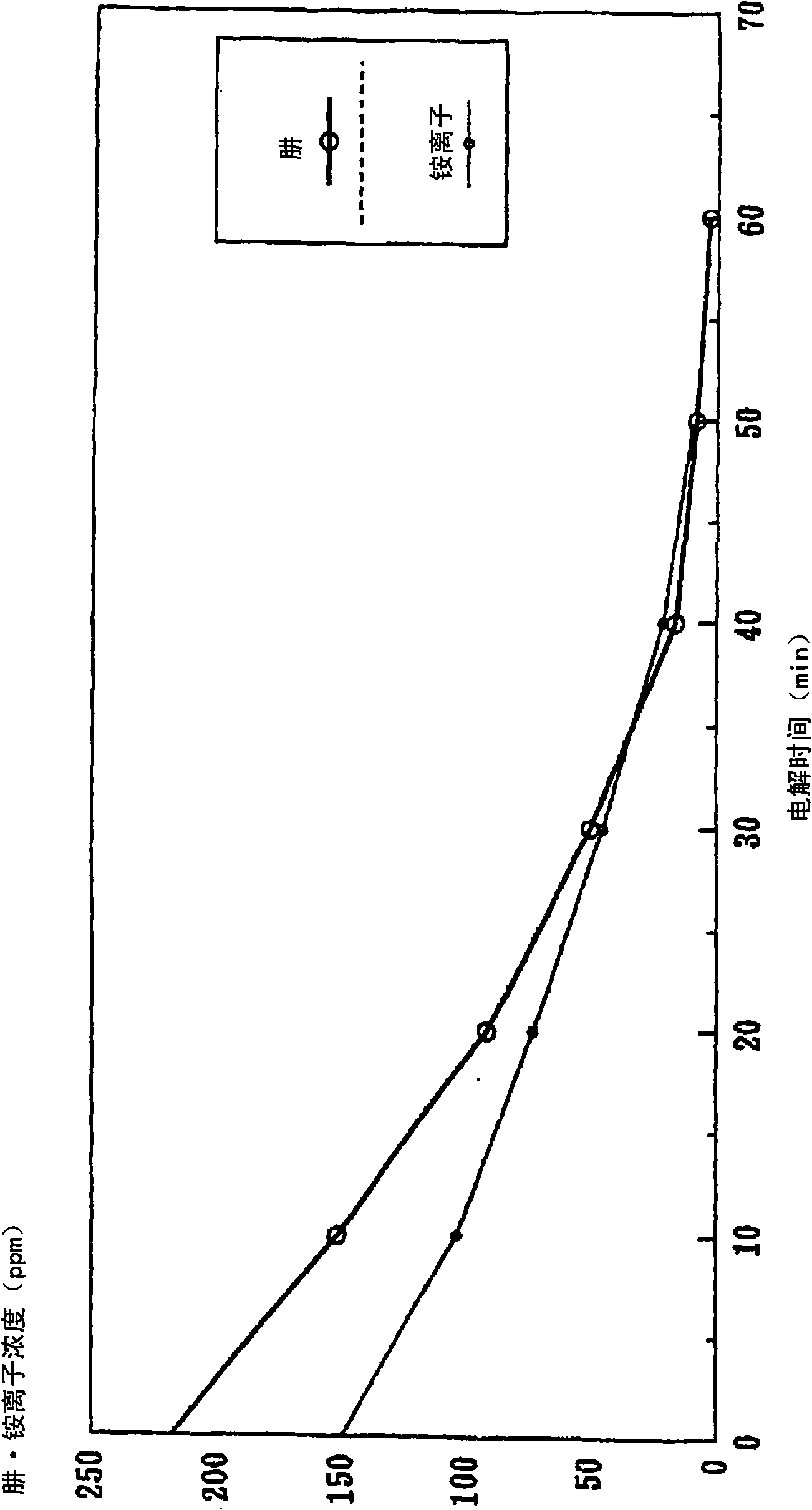
[0072] Figure 7 In the electrolytic cell 6 in which the anion exchange membrane 3a is arranged closely between the meshed anode 1 and the cathode 2, pure water is injected into the anode chamber 4 and the cathode chamber 5 for electrolysis, and the measured current changes with time. Graph. In addition, the electrolysis is in the electrolysis area of 0.75dm 2 , Applied voltage 10V (constant...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3, such as Figure 8 As shown, a cation exchange membrane 3b is set between the anode 1 and the cathode 2, and the electrolytic cell 6, which is divided into the anode chamber 4 and the cathode chamber 5 by the cation exchange membrane 3b, will contain medium like nitrate ions and nitrite ions. Nitrogen oxide waste liquid 7 is injected into the cathode chamber 5, and pure water 8 is injected into the anode chamber 4 for electrolysis. Here, the anode 1 is composed of a material in which self-gold plating is performed on the surface of an iron base material, and has a mesh shape. The cathode 2 is made of SUS, and like the anode 1, has a mesh shape. A cation-exchange membrane (strongly acidic cation-exchange membrane) is loosely interposed between these electrodes, and the ion-exchange membrane is placed in close contact with each other.
[0075] The water in the waste liquid 7 injected into the cathode chamber 5 is reduced on the cathode 2 according to the follo...
Embodiment 4
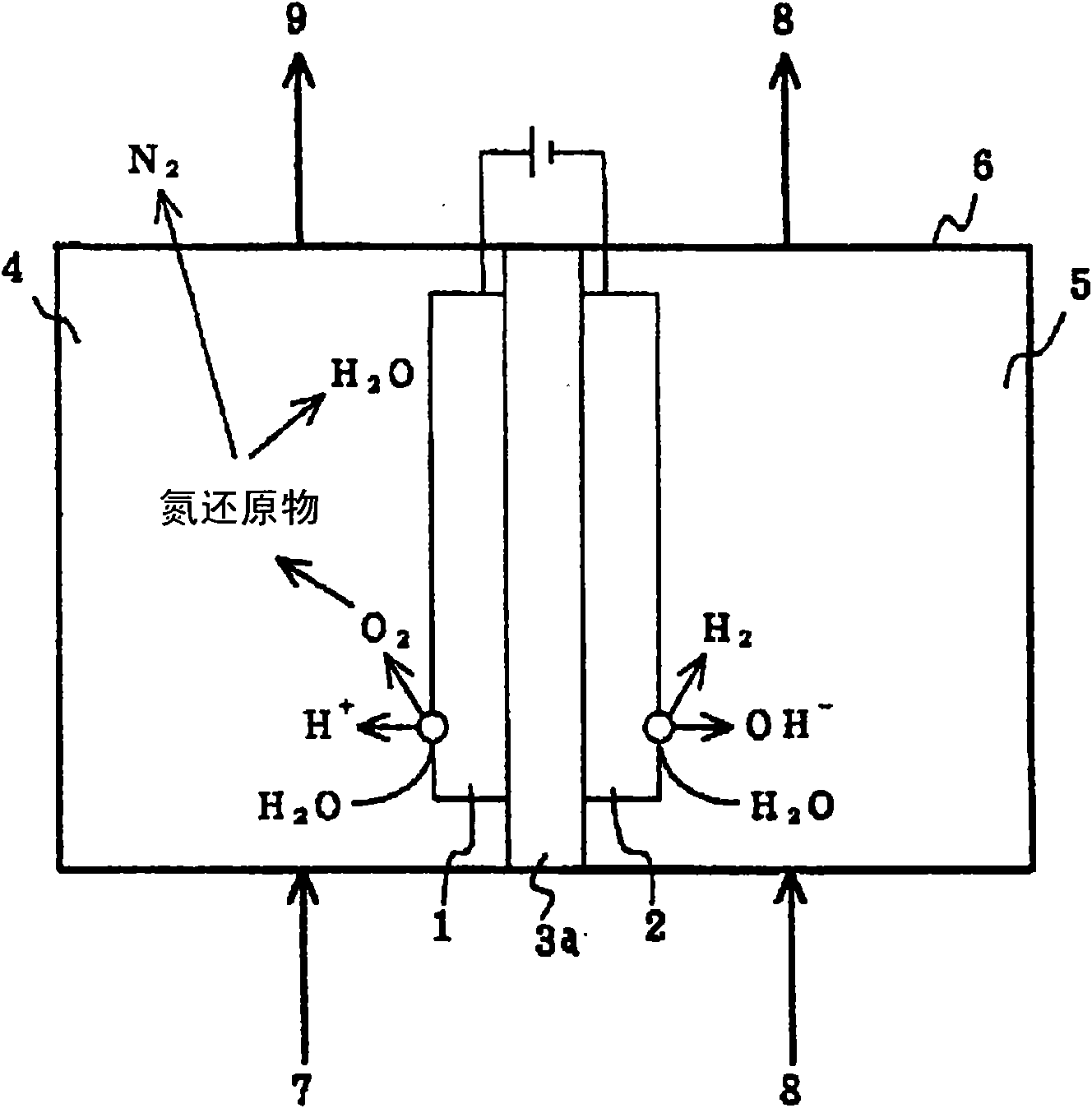
[0085] Example 4, such as Figure 11 As shown, a diaphragm 3 formed of aluminum oxide is arranged between any plate-shaped anode 1 and cathode 2, and is separated into an electrolytic cell 6 of an anode chamber 4 and a cathode chamber 5 by the diaphragm 3, and the anode chamber 4 Inject the waste liquid 7 containing any one of hydrazine and forged ions, at first inject pure water into the cathode chamber 5, and carry out the 1st electrolysis, the nitrogen reduction product (hydrazine and / or ammonium ion) in the waste liquid 7, by Oxygen generated on the anode 1 is oxidized to generate nitrogen gas. Next, inject the liquid 9 of this oxidation treatment into the cathode chamber 5, inject pure water into the anode chamber 4, or inject the waste liquid 7 again, and perform the second electrolysis to reduce the oxidizing substances in the waste liquid 7 deal with. Here, as the waste liquid 7 containing at least one of hydrazine and ions, for example, a waste liquid generated in a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com