Process for producing a glyceride composition
A technology of composition and glyceride, which is applied in the field of preparation of glyceride composition, and can solve problems such as unsaturation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
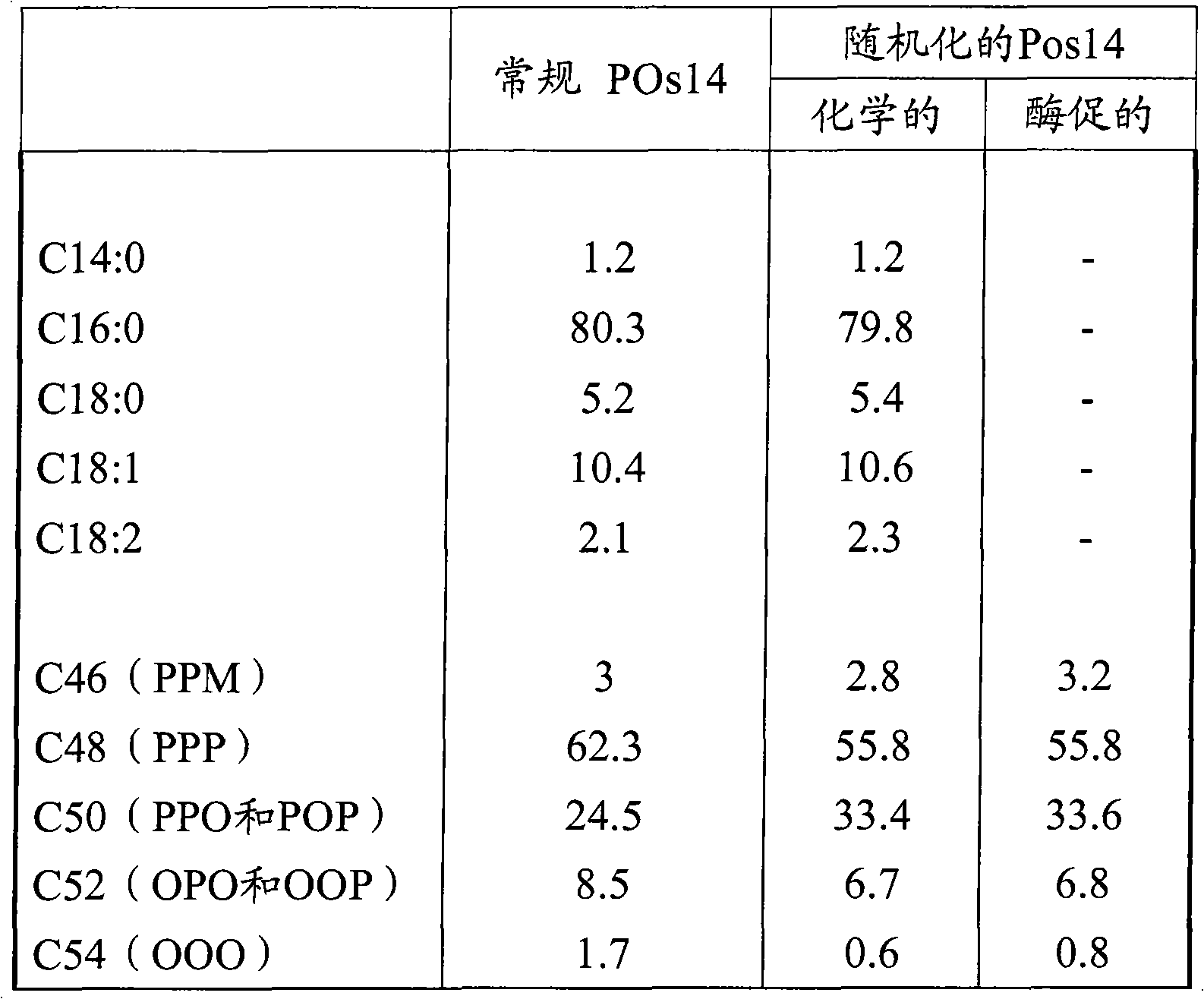
[0048] Randomization of Palm Olein Stearin Components by Chemical Methods
[0049] Performing chemical randomization reactions provides a reference for enzyme-catalyzed randomization reactions. 1 kg of palm oil stearin fraction with an iodine value of 14 (POs 14) was heated under vacuum at 110° C. for 15 minutes to remove all moisture. The vacuum was interrupted, 0.15% sodium ethoxide was added and the reaction was continued under vacuum at 110° C. for 30 minutes. The reaction was terminated by washing the oil several times with demineralized water at 95°C.
Embodiment 2
[0052] Enzymatic Randomization of Palm Olein Stearin Fractions in a Batch Reaction
[0053] The following three parameters were used for the randomization of the palm stearin fraction and for the production of structured lipids generally comprising OPO (1,3-dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglyceride).
[0054] ●Total fatty acid composition: name
[0055] ●Carbon number of triglyceride: C48 tripalmitoyl glyceride
[0056] C50 Monooleoyl Dipalmitoyl Glyceride
[0057] C52 Dioleoyl Monopalmitoyl Glyceride
[0058] C54 Trioleoyl Glyceride
[0059] ●The relative position of palmitic acid: Sn-2C16:0
[0060] Sn-2, as defined above, refers to the number of moles (or weights) of palmitoyl residues present at the 2-position of glycerides divided by the total number of moles (or weights) of palmitoyl residues present in triglycerides.
[0061] POs14 (palm oil glyceryl stearate with an iodine number of 14) was randomized in a ba...
Embodiment 3
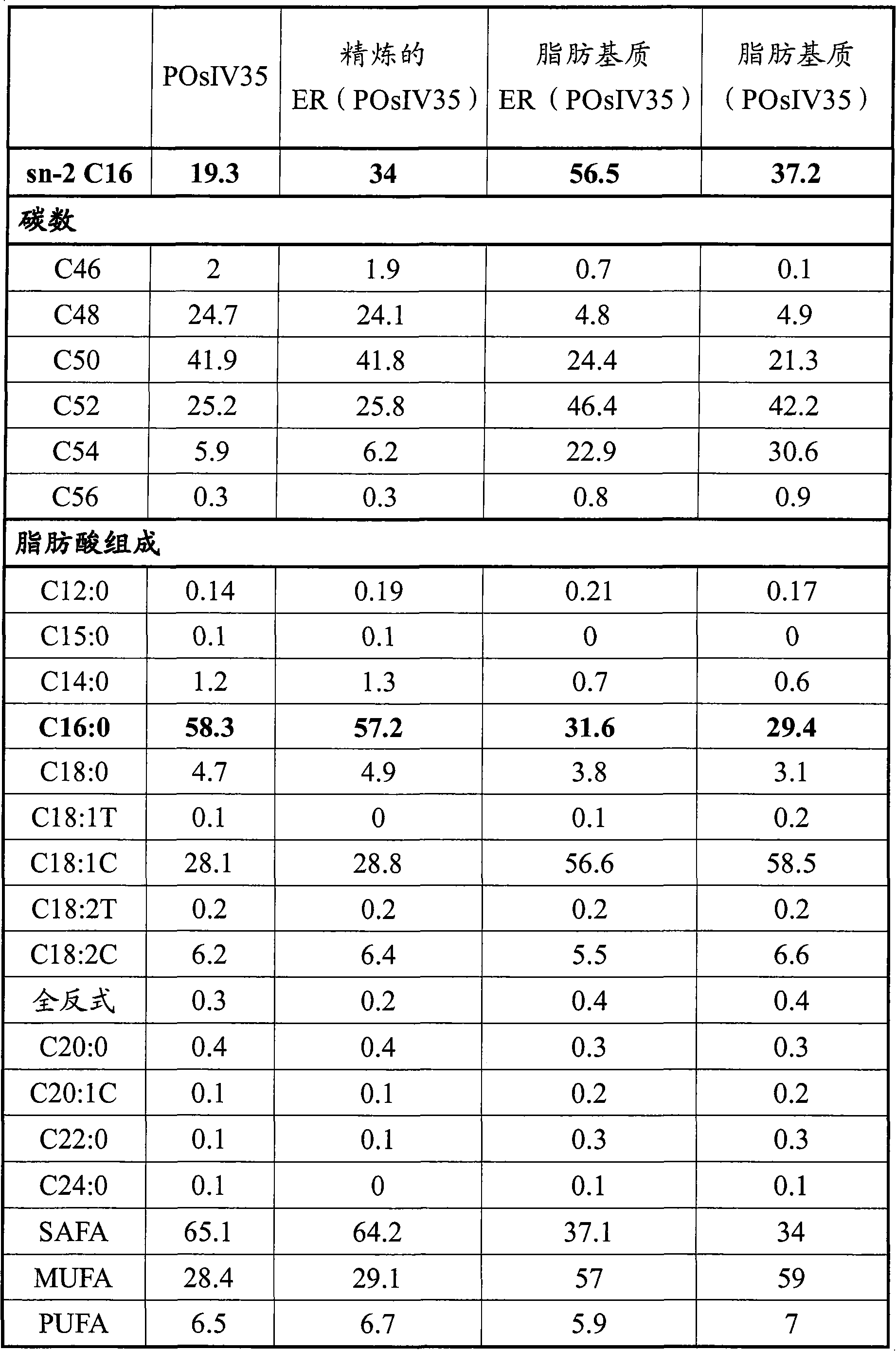
[0070] Produced with conventional and randomized palm stearin fraction (POs14) containing 1,3- Structural lipids of dioleoyl-2-palmitoylglyceride (OPO)
[0071] Structural lipids containing OPO are produced by enzymatic 1,3-specific acid hydrolysis between oleic acid and POs14. A continuous packed bed reactor containing the enzyme was used. The enzyme was lipase D (Rhizopsis delbrueckii, Amano) immobilized on microporous polypropylene microspheres (Accurel).
[0072] The feed oil consisted of a mixture of POs14 and oleic acid in a gram / gram ratio of 1:1.4. The mixture was slowly pumped through the column containing the immobilized enzyme. During the passage of the oil / fatty acid mixture, an acidolysis reaction occurs, the degree of conversion of which is proportional to the retention time in the column. The retention time is the void volume of the enzyme bed divided by the flow rate. The retention time used in this example was 53 minutes.
[0073] Water is added to ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com