Method of producing a cidic-soluble soybean protein
A soybean protein and acid-soluble technology, which is applied in the preparation field of acid-soluble soybean protein, can solve the problems of not obtaining acid-soluble soybean protein and increase the bitterness, and achieve the effect of low viscosity and high solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
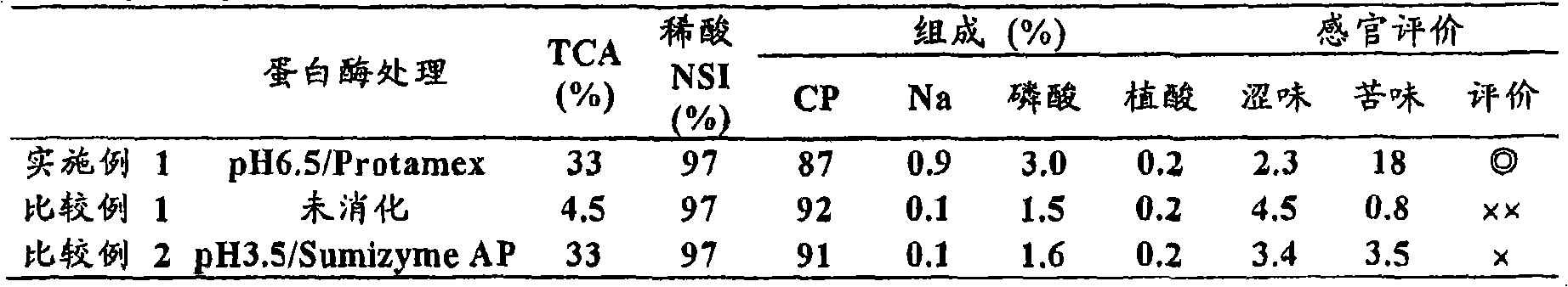
[0052] (embodiment 1) preparation of the acid-soluble soybean protein digested by neutral protease
[0053] Soybeans were flattened, extracted using n-hexane as an extraction solvent, separated and oil removed to obtain low-denatured defatted soybeans (NSI: 91). 7 parts by weight of water were added to 1 part by weight of the low-denatured defatted soybeans, and the pH was adjusted to 7 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution, and extracted while stirring at room temperature for 1 hour. Thereafter, the mixture was centrifuged at 4000×g to separate okara and insoluble components to obtain defatted soybean milk. The defatted soybean milk was adjusted to pH 4.5 with phosphoric acid, and then centrifuged at 2000 x g using a continuous centrifugal separator (decanter) to obtain an insoluble fraction (acid-precipitated curd) and a soluble fraction (whey). Water was added to this acid-precipitated curd to make the solid content 10% by weight, and acid-precipitated curd A was obtained....
experiment example 1
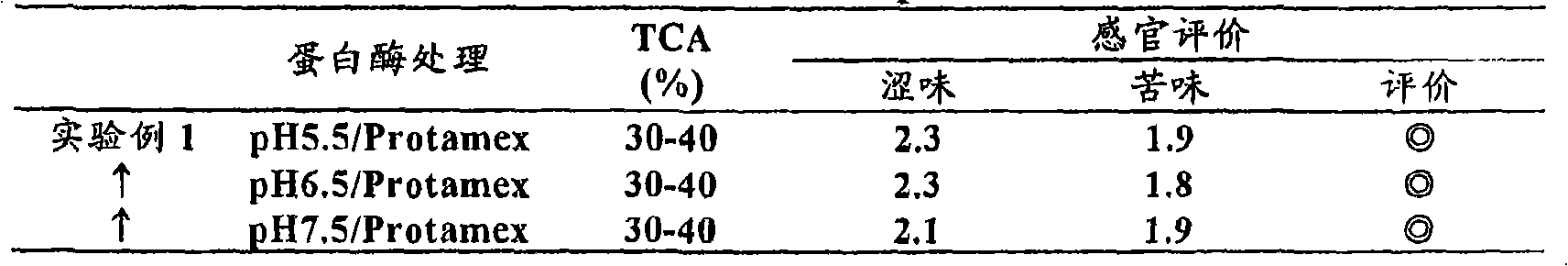
[0062] (Experimental Example 1) Research on Protease Reaction pH Value and Flavor
[0063] The acid precipitation slurry A of Example 1 was equally divided into three parts, adjusted to pH 5.5, 6.5 and 7.5 respectively with dilute sodium hydroxide solution, and then heated to 50°C. To these solutions, the protease described in Example 1 was added in an appropriately adjusted amount so that the TCA (0.22M) solubility of the hydrolyzate at each pH value was 30% to 40%, and hydrolysis was carried out for 60 minutes. After the reaction, heat at 85°C for 20 minutes to inactivate the enzyme. Subsequently, phosphoric acid was added to each hydrolyzate to adjust to pH 3.5, and then the phytase described in Example 1 was added in an amount corresponding to 8 units per 100 g of solid content, and the reaction was carried out for 30 minutes. A continuous direct heat sterilization device was used to heat at 140° C. for 7 seconds, and they were spray-dried to obtain various powdered acid-...
experiment example 2
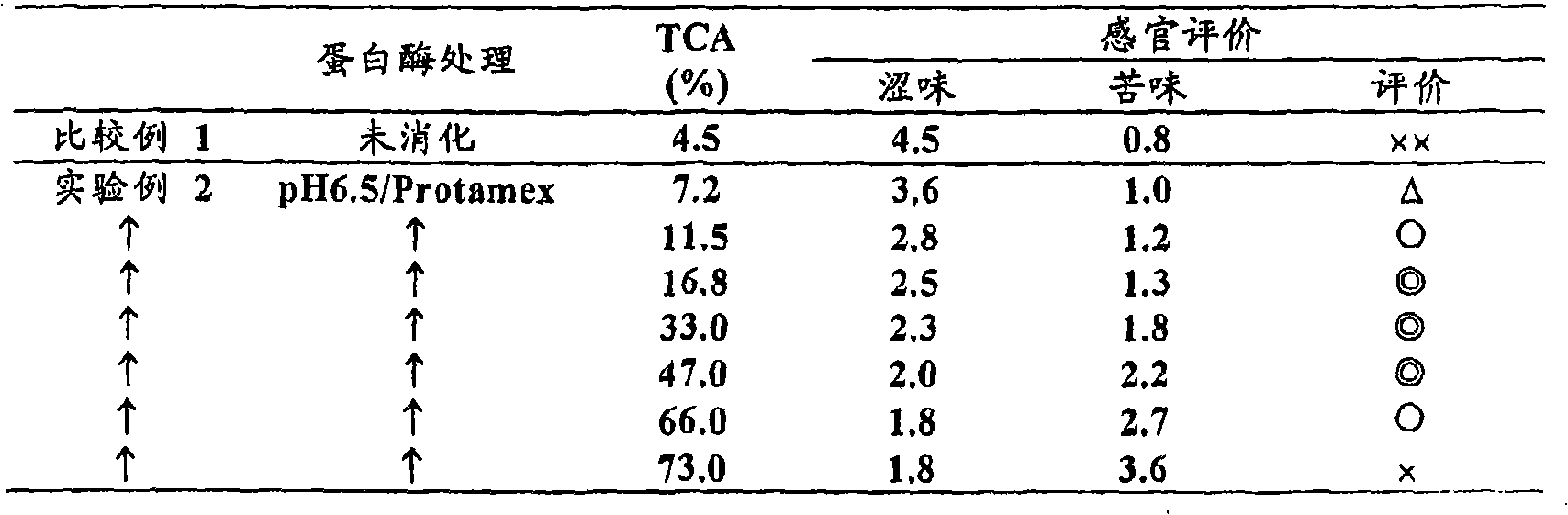
[0066] (Experimental Example 2) Study on Solubility and Flavor of TCA (0.22M)
[0067] The acid precipitation slurry A of Example 1 was adjusted to pH 6.5 with dilute sodium hydroxide solution and then heated to 50°C. To this solution, the protease described in Example 1 was added in different amounts, and hydrolysis was carried out for 60 minutes. After the reaction, heat at 85°C for 20 minutes to inactivate the enzyme. Subsequently, phosphoric acid was added to adjust to pH 3.5, and then the phytase described in Example 1 was added in an amount corresponding to 8 units per 100 g of solid content, and allowed to act for 30 minutes. Use a continuous direct heat sterilizer to heat at 140°C for 7 seconds. They are spray-dried to obtain powdery acid-soluble soybean protein. The obtained powdery acid-soluble soybean protein had TCA (0.22M) solubility of 7.2%, 11.5%, 16.8%, 33.0%, 47.0%, 66.0%, 73.0%.
[0068] As the results of sensory evaluation (Table 3), it shows that the de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com