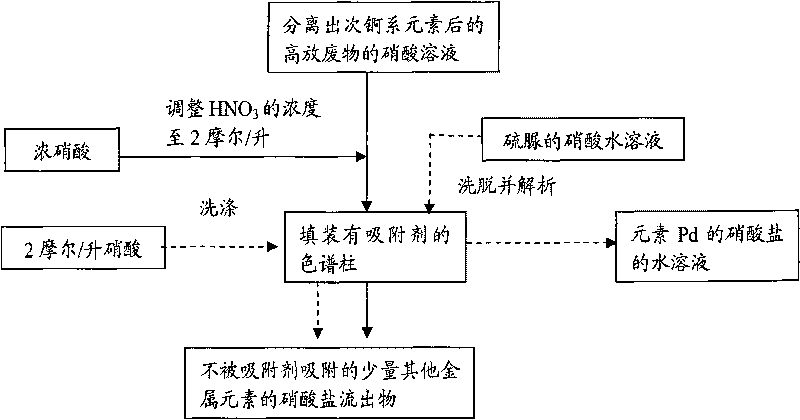
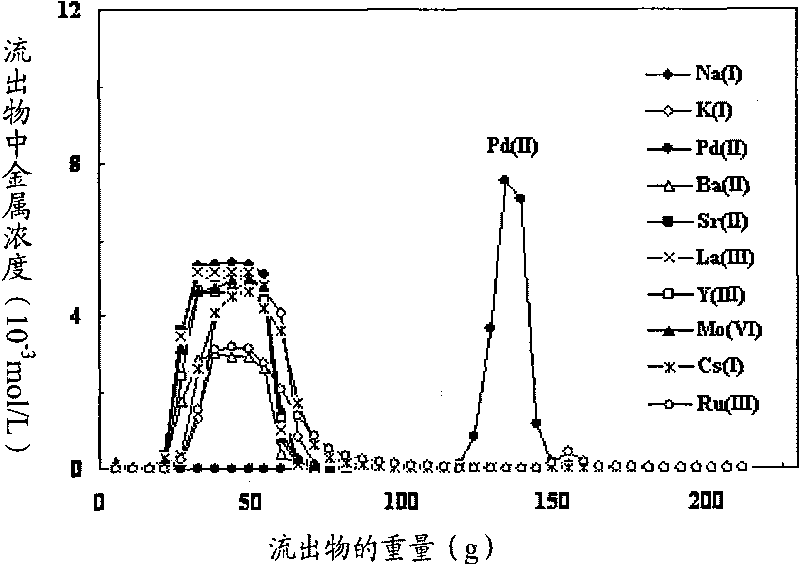
Method for separating element Pd from high-level radioactive waste
A technology of high-level radioactive waste and elements, which is applied in the field of reprocessing of high-level radioactive waste in the nuclear industry, to achieve the effect of simple and efficient method, high selectivity and good separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The preparation of embodiment 1 adsorbent
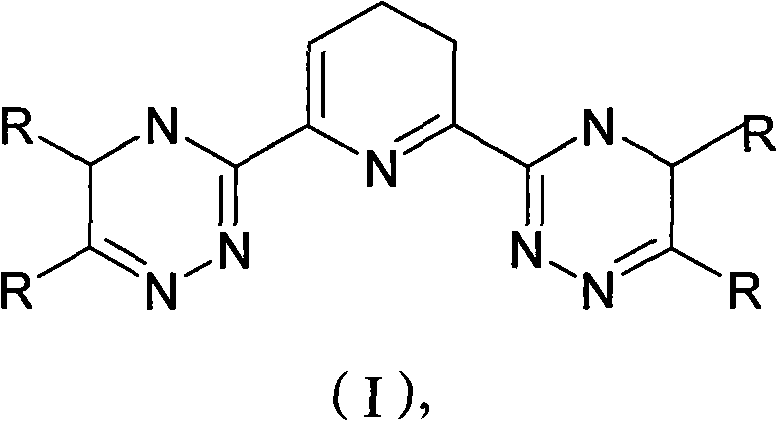
[0032] Dissolve 100 grams of 2,6-bis-(5,6-di-n-butyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-pyridine in 1000 mL of dichloromethane and mix well; add 300 grams of coating polymer macroporous SiO 2 (SiO 2 -P) Stir evenly to volatilize most of the dichloromethane until the material is in a nearly dry state, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45° C. for 24 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0033] The preparation of embodiment 2 adsorbent
[0034] Dissolve 100 g of 2,6-bis-(5,6-dimethyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-pyridine in 1500 mL of dichloromethane and mix well; add 600 g of coating polymer macroporous SiO 2 (SiO 2 -P) Stir evenly to volatilize most of the dichloromethane until the material is in a nearly dry state, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45° C. for 24 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Preparation of Adsorbent
[0036] Dissolve 100 grams of 2,6-bis-(5,6-diethyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)-pyridine in 3000 mL of dichloromethane and mix well; add 1500 grams of coating polymer macroporous SiO 2 (SiO 2 -P) Stir evenly to volatilize most of the dichloromethane until the material is in a nearly dry state, and then vacuum-dry the nearly dry material at 45° C. for 24 hours.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com