Breeding method of feeding non-protective amino acid to early-weaning lambs, feedstuff and preparation method thereof
An early weaning and protective technology, which is applied in the direction of animal feed, animal feed, additional food elements, etc., can solve the problems of research materials or data public reporting, high age requirements for research animals, and inability to be absorbed and utilized by animals, so as to improve Effects on reproductive rate, improved performance, lean mass and increased lean percentage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
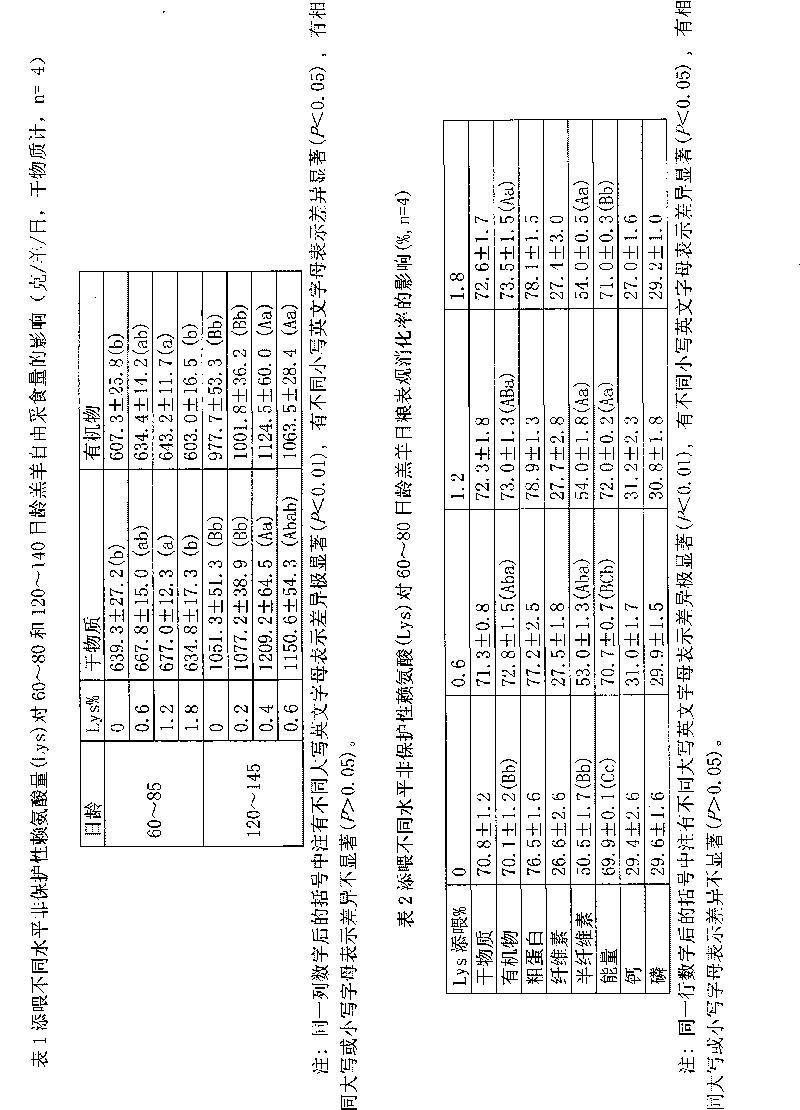
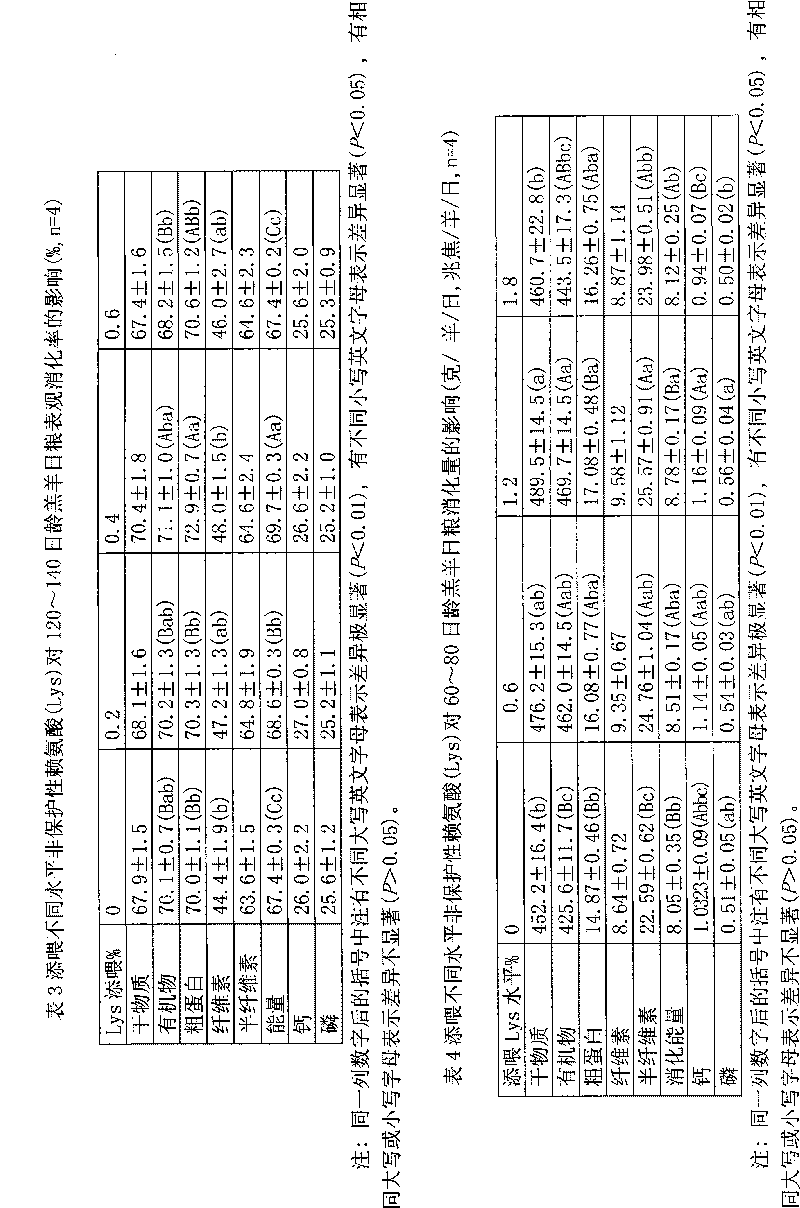
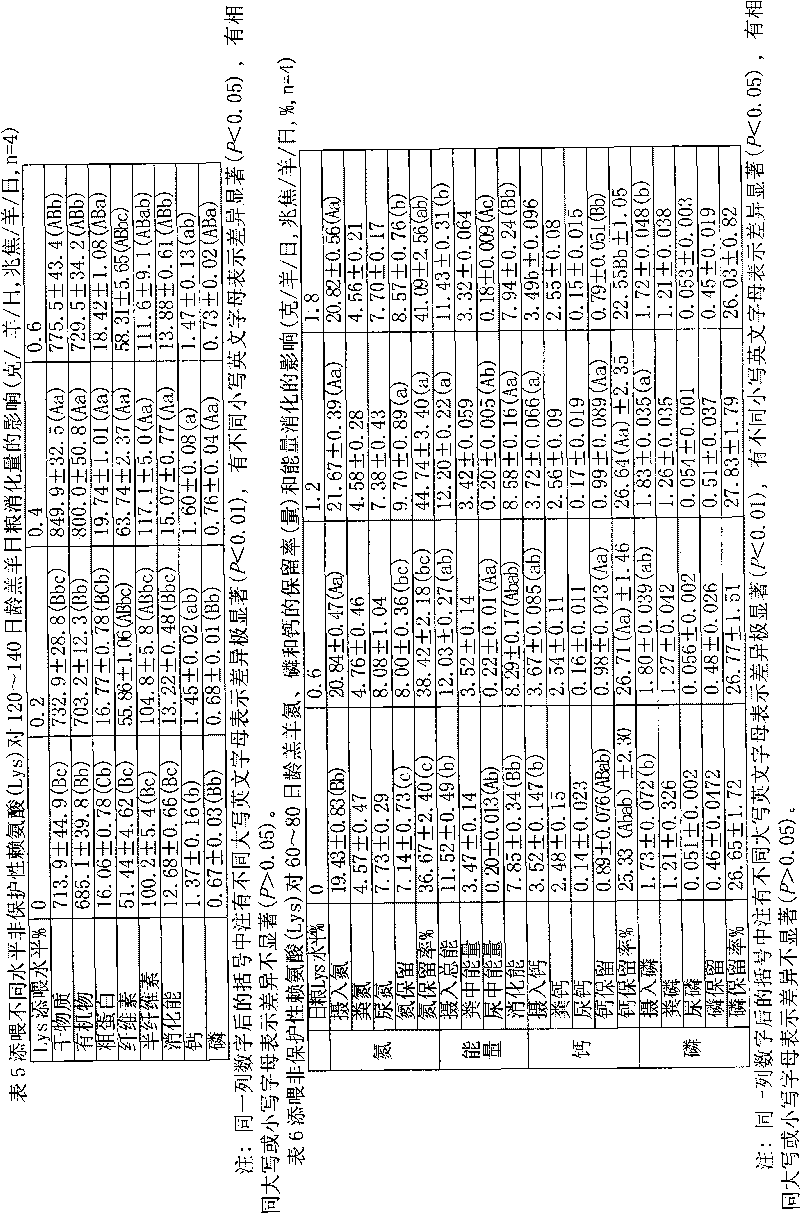
[0017] Example 1, the early weaned lambs are fed with non-protective amino acid feed (i.e. the ration of the present invention) by weight of raw materials from 4.5 parts to 5.5 parts of milk powder, 60 parts to 75 parts of corn flour, 20 parts of cottonseed meal to 30 parts, expanded soybean powder 6.5 to 8.5 parts, stone powder 2.5 to 3.5 parts, fish meal 0.09 to 0.11 parts, large salt 0.4 to 0.5 parts, vitamin / trace element additives 0.02 to 0.03 parts, sodium sulfate 0.3 parts to 0.5 parts, 1.1 to 1.3 parts of non-protected lysine, 0.03 to 0.04 parts of non-protected methionine, and 0.7 to 0.9 parts of betaine to form the first feeding feed for early weaned lambs fed with non-protected amino acids (i.e. the diet of the present invention).
Embodiment 2
[0018] Embodiment 2, this early weaned lamb is fed with non-protective amino acid feeding feed (i.e. the ration of the present invention) by weight of raw materials by 4.5 parts or 5.5 parts of milk powder, 60 parts or 75 parts of corn flour, 20 parts of cottonseed meal Or 30 parts, 6.5 parts or 8.5 parts of expanded soybean powder, 2.5 parts or 3.5 parts of stone powder, 0.09 or 0.11 parts of fish meal, 0.4 or 0.5 parts of large salt, 0.02 or 0.03 parts of vitamin / trace element additives, 0.3 parts of sodium sulfate or 0.5 parts, 1.1 or 1.3 parts of non-protected lysine, 0.03 or 0.04 parts of non-protected methionine, 0.7 or 0.9 parts of betaine, which is the first feed for early weaned lambs fed with non-protected amino acids (i.e. the diet of the present invention).
Embodiment 3
[0019]Embodiment 3, this early weaned lamb is fed with non-protective amino acid feeding feed (i.e. the ration of the present invention) by weight of raw materials from 60 parts to 75 parts of corn flour, 20 parts to 30 parts of cottonseed meal, expanded soybean meal 6.5 to 8.5 parts, 4.5 to 5.5 parts of corn stalks crushed into 2 cm to 4 cm, 2.5 to 3.5 parts of stone powder, 0.09 to 0.11 parts of fish meal, 0.4 to 0.5 parts of large salt, 0.02 parts of vitamin / trace element additives 0.03 to 0.03 parts, 0.3 to 0.5 parts of sodium sulfate, 1.1 to 1.3 parts of non-protected lysine, 0.03 to 0.04 parts of non-protected methionine, and 0.5 to 0.7 parts of betaine to form the second early weaned lamb Add the feedstuff (ie the diet of the present invention) of non-protective amino acid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com