Transverse flux permanent-magnet planar motor
A permanent magnet planar and transverse magnetic flux technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of low current control accuracy, complex motor structure, limited mover stroke, etc., to improve current and electromagnetic force control High precision, elimination of mutual inductance between phases, high thrust density and power density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
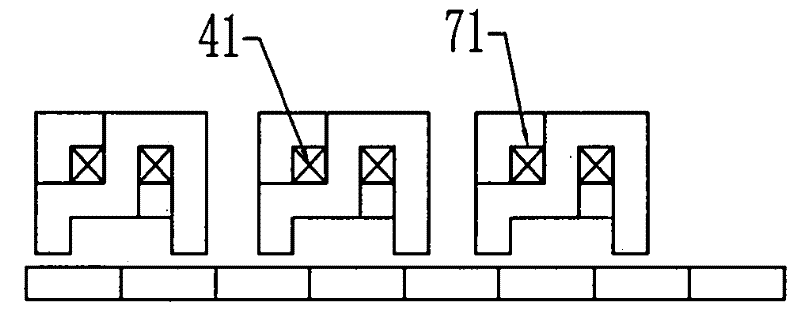
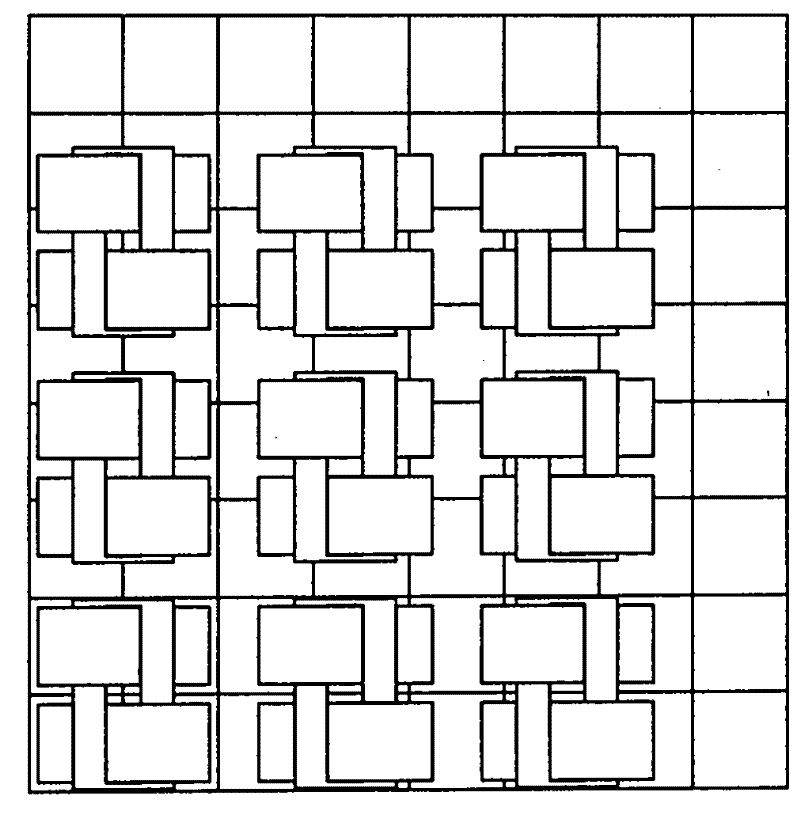
[0009] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment, this embodiment is made up of primary and secondary; secondary is made up of permanent magnet array; primary is made up of several motor units, each motor unit is made up of m 2 Composed of phase armature units, m 2 Phase armature units form a phase armature unit array with m rows and m columns, and the row spacing of the phase armature unit array is equal to the column spacing; each phase armature unit is composed of a phase unit core and a phase unit winding Each phase unit core is composed of two core units and has a phase unit core with a tooth hole 71, and the tooth hole 71 is formed by superimposing the tooth grooves 72 of the two core units, and each core unit is composed of two teeth and a magnetic The two teeth are arranged along the horizontal direction of the cross section, and a yoke section is connected between the two teeth; the two core units are arranged along ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0010] Specific embodiment two, combine Figure 3 to Figure 7 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment is that each core unit in the phase unit core consists of a long tooth 51, a short tooth 52, a high-level yoke segment 53, a low-level magnetic The yoke section 54 and a vertical yoke section 55 are composed; the long teeth 51 and short teeth 52 are arranged along the horizontal direction of the cross section, and the long teeth 51 and the short teeth 52 are sequentially connected with high-level magnets. Yoke segment 53 , vertical yoke segment 55 and low horizontal yoke segment 54 , the side root of the long tooth 51 is connected to the side of one end of the high horizontal yoke segment 53 , and the high horizontal yoke segment 53 The other end of the vertical yoke section 55 is connected to the root of one side of the vertical yoke section 55, and the other side of the vertical yoke section 55 is connected to one end of t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
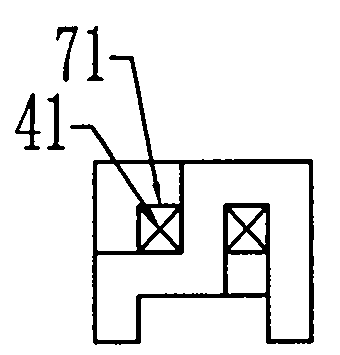
[0011] Specific embodiment three, combine Figure 3 to Figure 5 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is that the coil 41 is circularly wound on the upper part of the long tooth 51 or on the high horizontal yoke segment 53 or the vertical yoke segment 55 through the two tooth holes 71 to form a Phase-to-phase unit windings. Other compositions and connection methods are the same as those in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com