Method for immobilizing microorganisms and repairing defects of cement-based materials by adopting sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
A technology of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and microbial repair, applied in the field of surface defect repair and protection of cement-based materials, can solve problems such as poor compatibility of substrates, and achieve good weather resistance, significant protective effect of film coating, and tight bonding. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
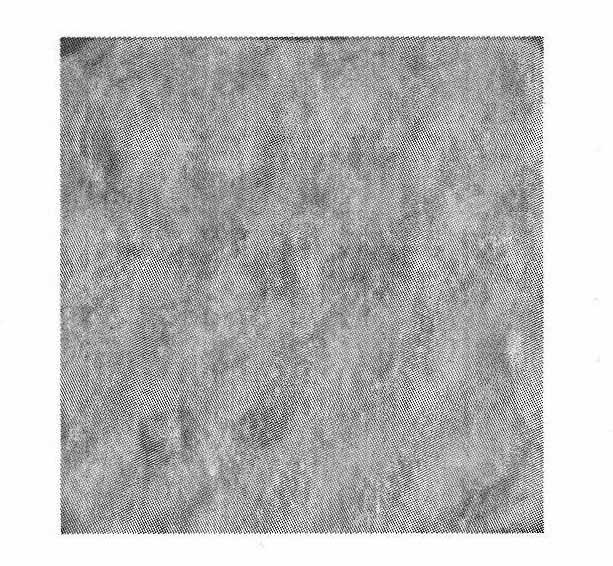
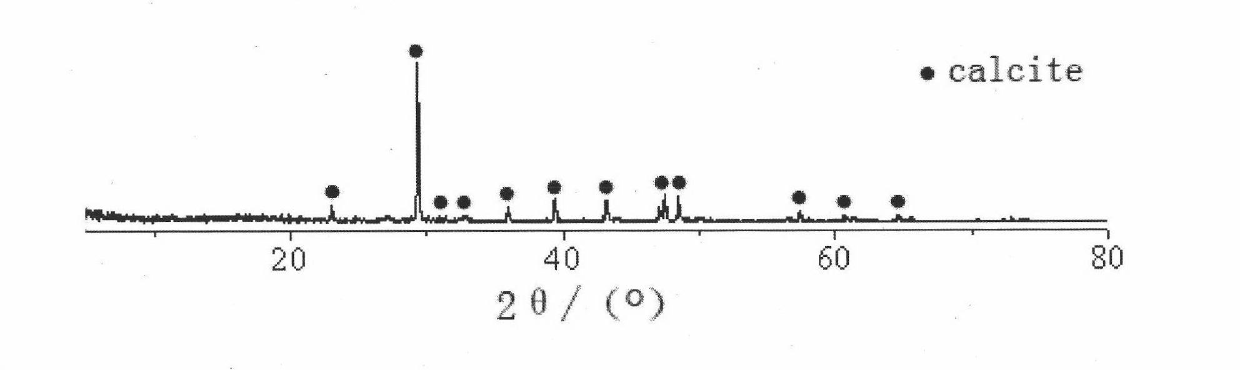
[0038] Inoculate the strain Bacillus pasteurii on the medium containing the substrate containing urea, and carry out shaking culture at 25-37°C. After 16-24 hours, when the concentration of the strain reaches 5×10 8 When cell / mL, the bacterial liquid was centrifuged at 5000-8000rpm for 5-8min to obtain a highly concentrated bacterial liquid concentration of 9.8×10 10 cell / mL, spread on the surface of the sample, then add 2% mass fraction sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution, and 1.0mol / L urea and Ca(NO 3 ) 2 The mixed solutions were applied successively on the surface of the specimens for the coating experiment. After 7 days, there were obvious continuous white deposition adhesion layers on the surface of the cement stone specimens (such as figure 2As shown), it is closely combined with the surface of cement stone, and the sample is confirmed to be calcite by XRD analysis, as shown in image 3 shown. Since carboxymethyl cellulose sodium is used to immobilize bacterial s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com