Non-Gauss noise-against blind equalization method
A non-Gaussian noise and blind equalization technology, which is applied to the shaping network, electrical components, and network topology in the transmitter/receiver, can solve the problems of relying on Gaussian noise assumptions, slow convergence speed, and large data volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The idea of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
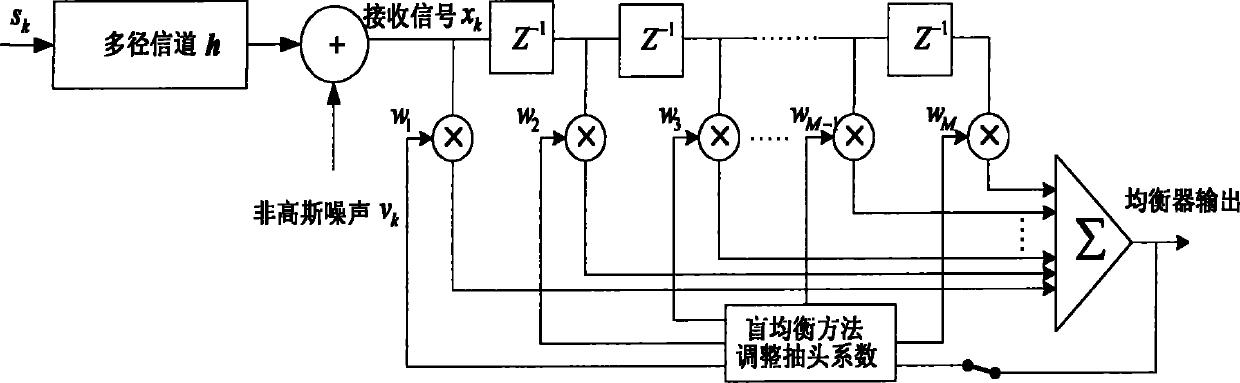
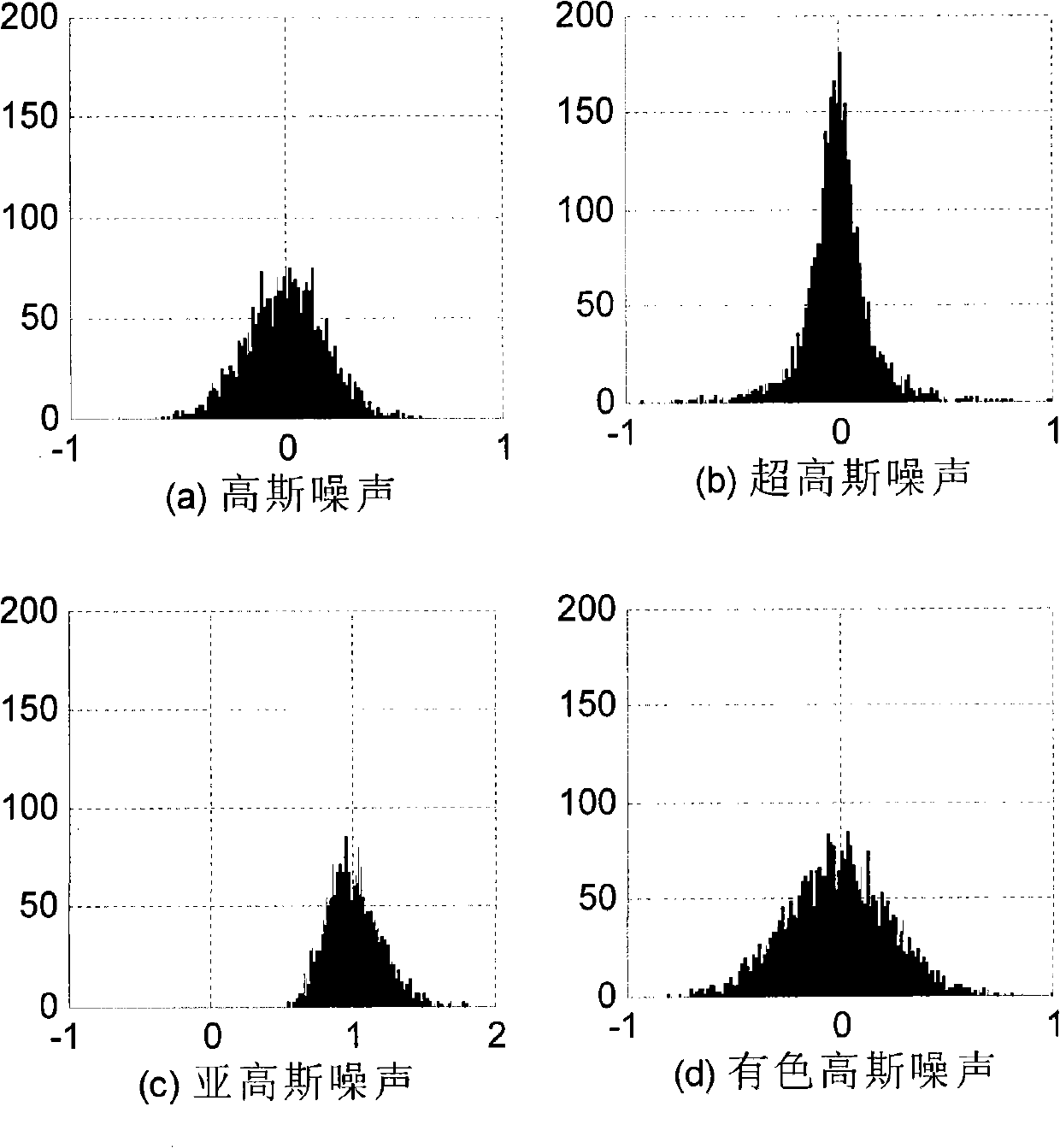
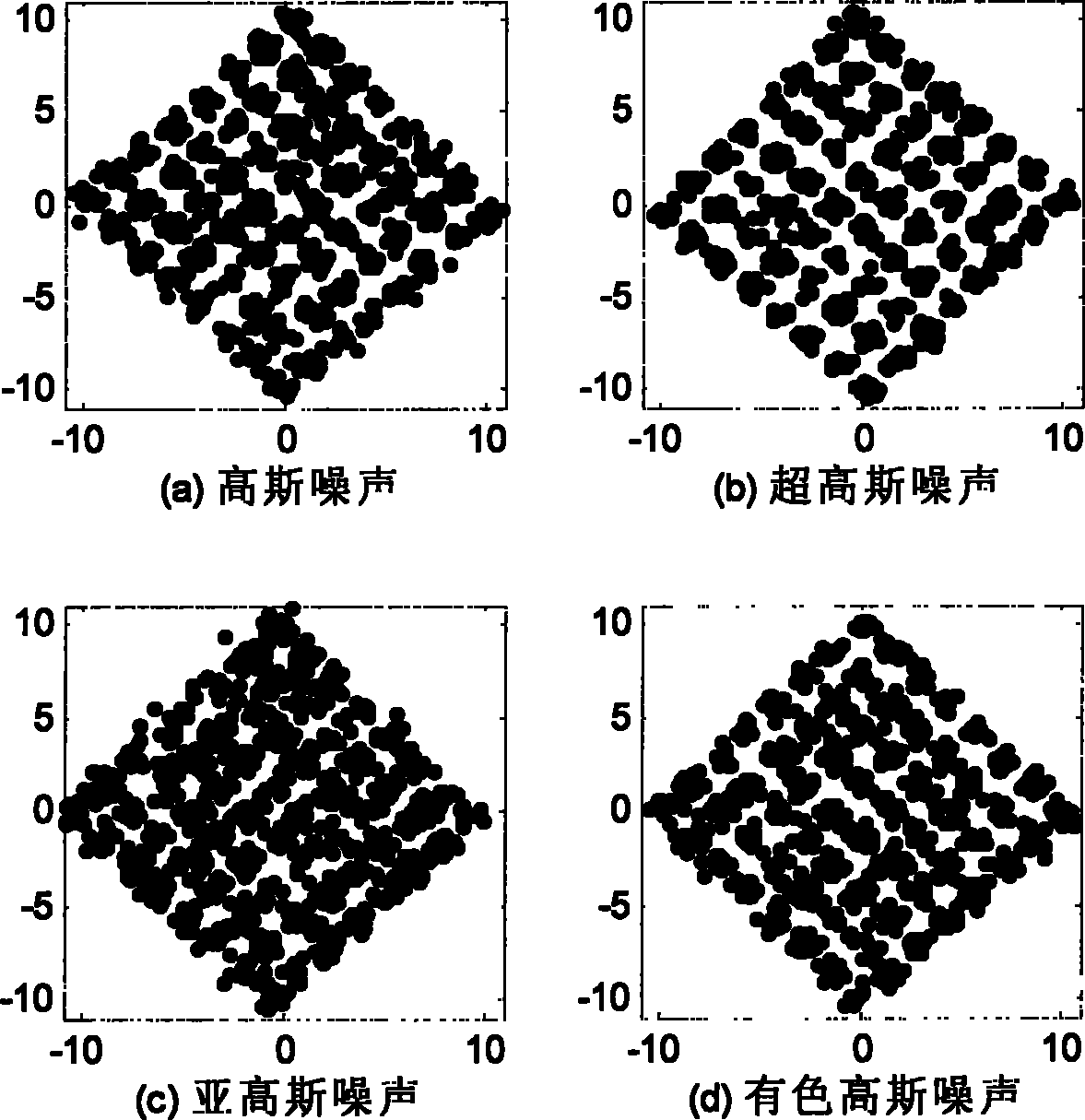
[0047] figure 1 is the system and equalizer model of the present invention. The equalizer input and output signals of the wireless sensor target node have the following relationship: x k = Σ i = 0 M - 1 h i s k - i + v k , y k = Σ i = 0 L - 1 w i x k - i , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com