Self-adaption on-board computer based on FPGA and method thereby for realizing dynamic allocation of internal resource
A technology of on-board computer and internal resources, applied in the field of aerospace data processing, can solve problems such as the inability to effectively manage reconfigurable FPGA resources, and achieve the effect of reducing hardware overhead, increasing flexibility, and simplifying the design process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
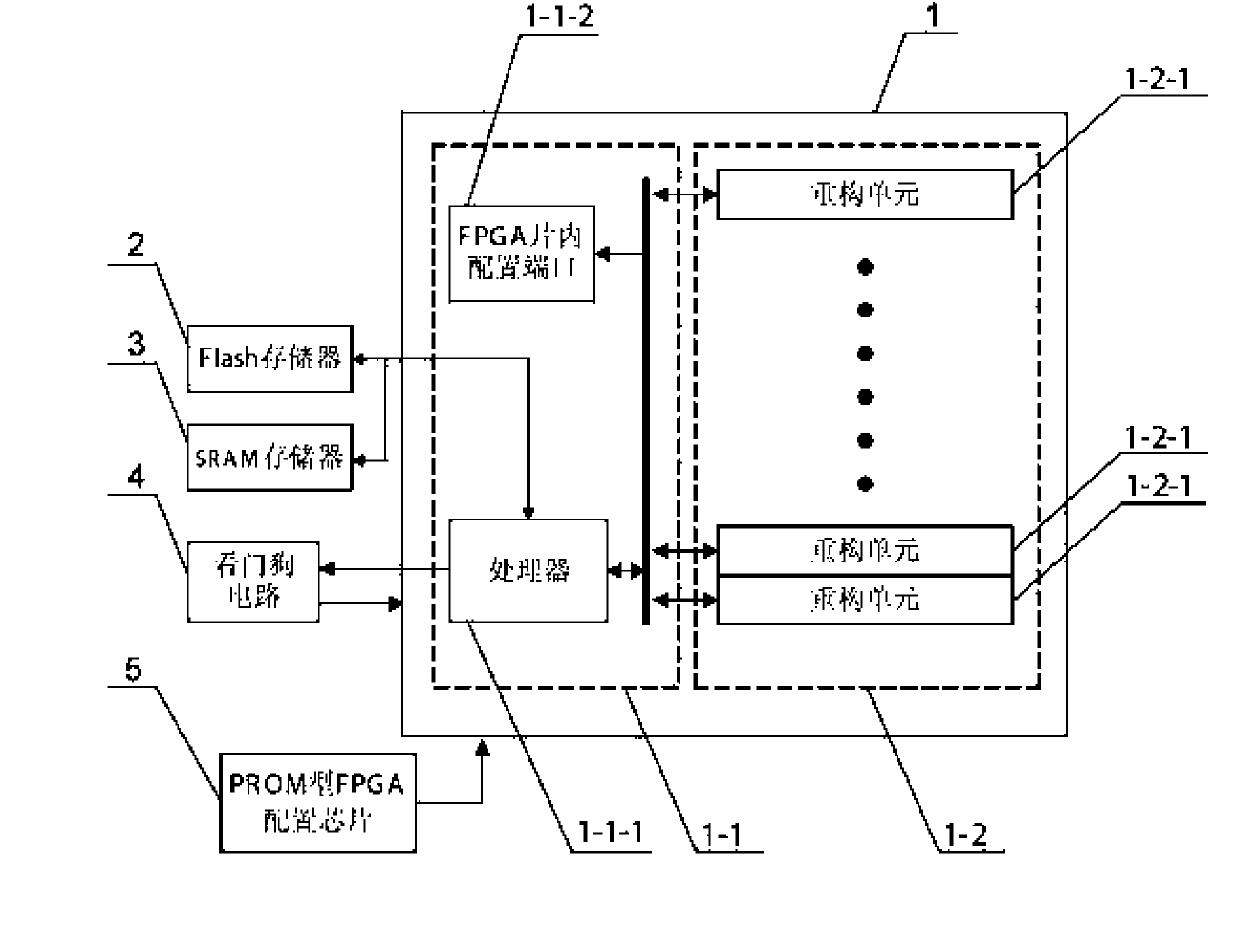
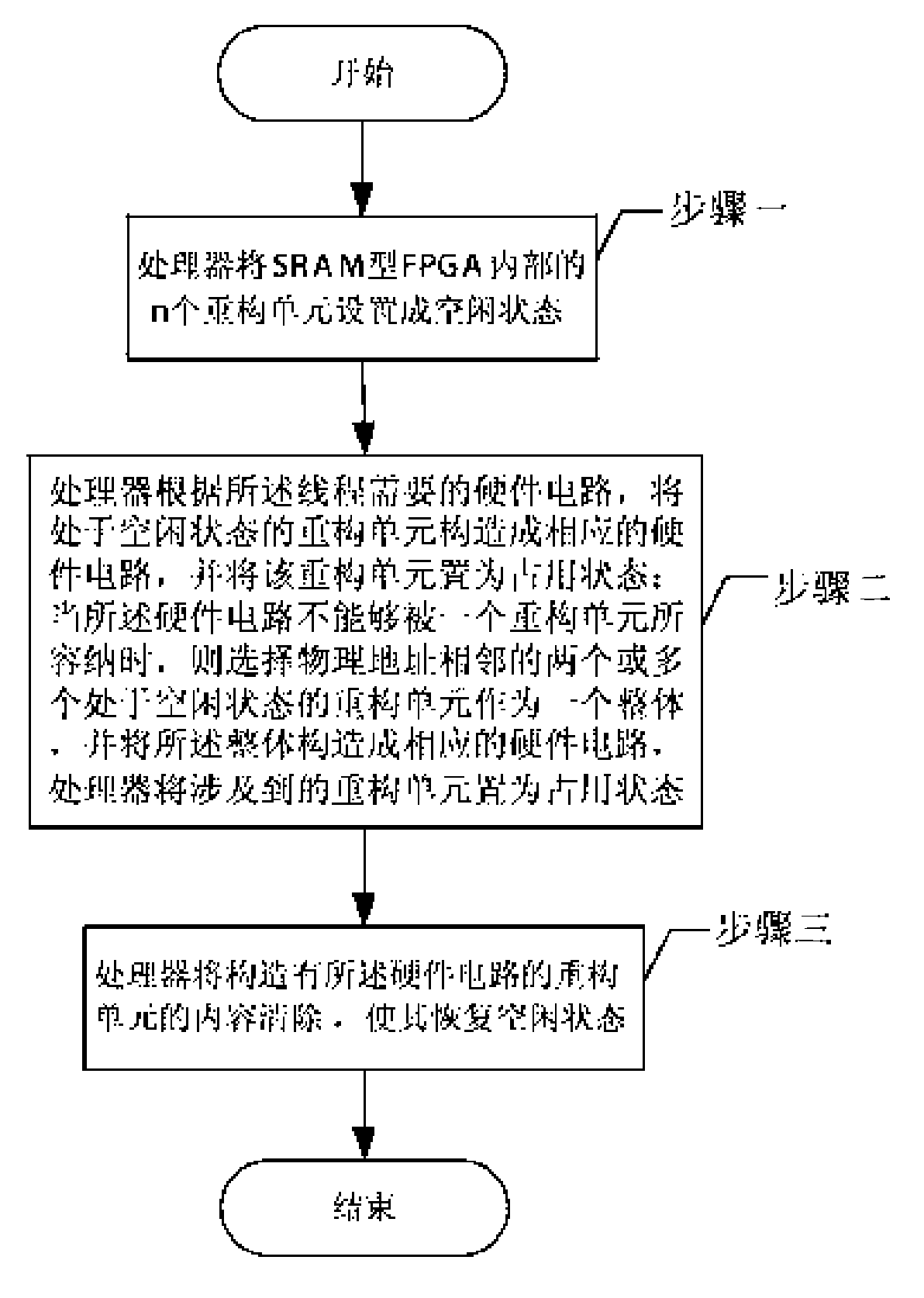
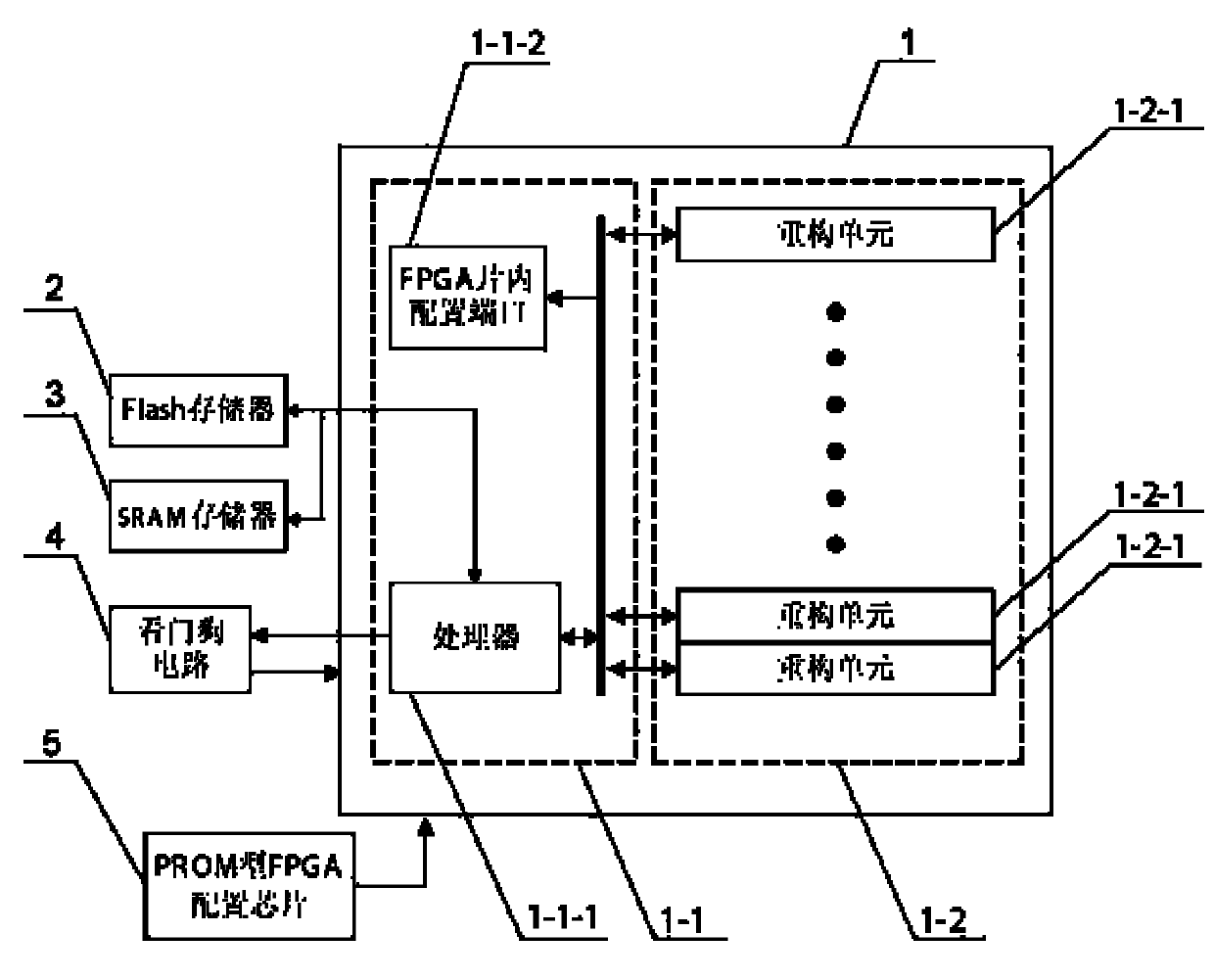
[0012] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment will be specifically described. An FPGA-based self-adaptive on-board computer includes a SRAM type FPGA1, a PROM type FPGA configuration chip 5 and a Flash memory 2, and the internal resources of the SRAM type FPGA1 include two parts, a master control unit 1-1 and a reconfiguration unit array 1-2, Wherein the main control unit 1-1 includes a processor 1-1-1 and an FPGA on-chip configuration port 1-1-2, and the reconstruction unit array 1-2 consists of n reconstruction units 1-2-1 of exactly equal size Composition, the configuration output port of PROM type FPGA configuration chip 5 is connected with the off-chip configuration input port of SRAM type FPGA1, and the control input and output port of Flash memory 2 is connected with the external memory control input and output port of processor 1-1-1, wherein , n is an integer greater than 0.
[0013] When the reconfiguration port of SRAM...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0014] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment will be specifically described. The difference between this embodiment and the FPGA-based self-adaptive onboard computer described in Embodiment 1 is that the Flash memory 2 is used to store user application program execution codes and configuration files of functional circuits, and the configuration files of each functional circuit The configuration file can call any reconfiguration unit 1-2-1 to construct the hardware circuit.
[0015] Flash memory 2 is a new type of non-volatile memory developed in recent years. It has the characteristics of no loss of data when power off, fast data access speed, electrical erasability, large capacity, online programmable, low price, and up to ten There are many advantages such as the erasing and writing times of 10,000 times and high reliability.
[0016] The FPGA-based self-adaptive onboard computer described in this embodiment can adopt the foll...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0018] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment will be specifically described. The difference between this embodiment and the adaptive onboard computer based on FPGA described in Embodiment 1 is that it also includes a watchdog circuit 4, and the watchdog circuit 4 is realized by a watchdog chip, and the processor 1 The dog feeding signal output port of -1-1 is connected with the dog feeding signal input port of the watchdog circuit 4, and the reset signal output port of the watchdog circuit 4 is connected with the reset signal input port of the SRAM type FPGA1.
[0019] An FPGA-based self-adaptive on-board computer, in addition to adopting configuration file readback and flashing mechanisms, can also use a watchdog circuit to implement fault-tolerant design. The FPGA-based self-adaptive on-board computer described in this embodiment uses The watchdog circuit realizes the fault-tolerant design. The circuit periodically receives t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com