Vacuum insulated panel core material and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of vacuum insulation panels and core materials, which is applied to heat exchange equipment, protected pipes through thermal insulation, thermal insulation, etc., can solve the problems of high manufacturing cost, low manufacturing cost, and inability to achieve ideal thermal insulation performance, and achieves a reduction in manufacturing costs. Cost and thermal insulation improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
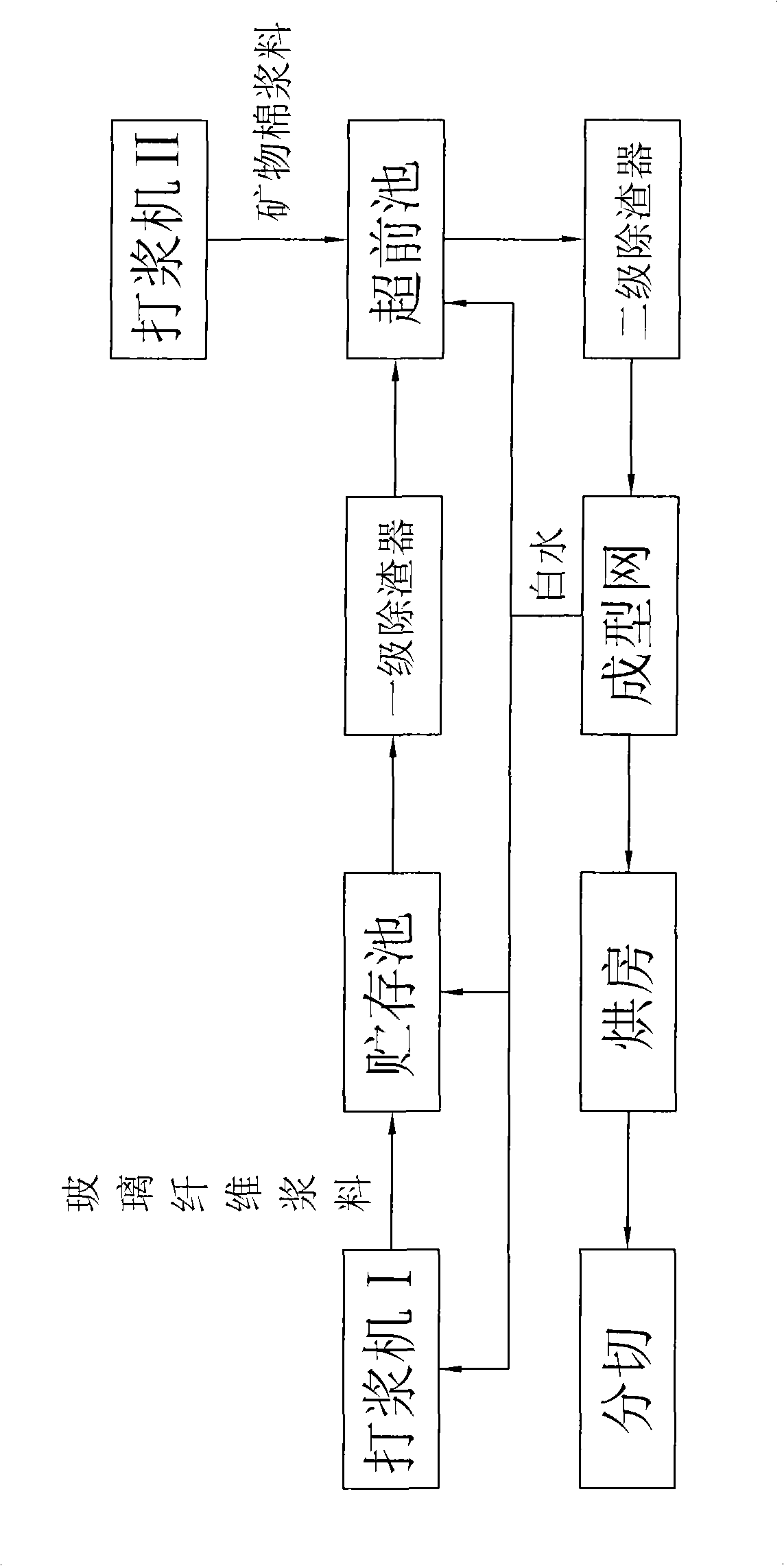
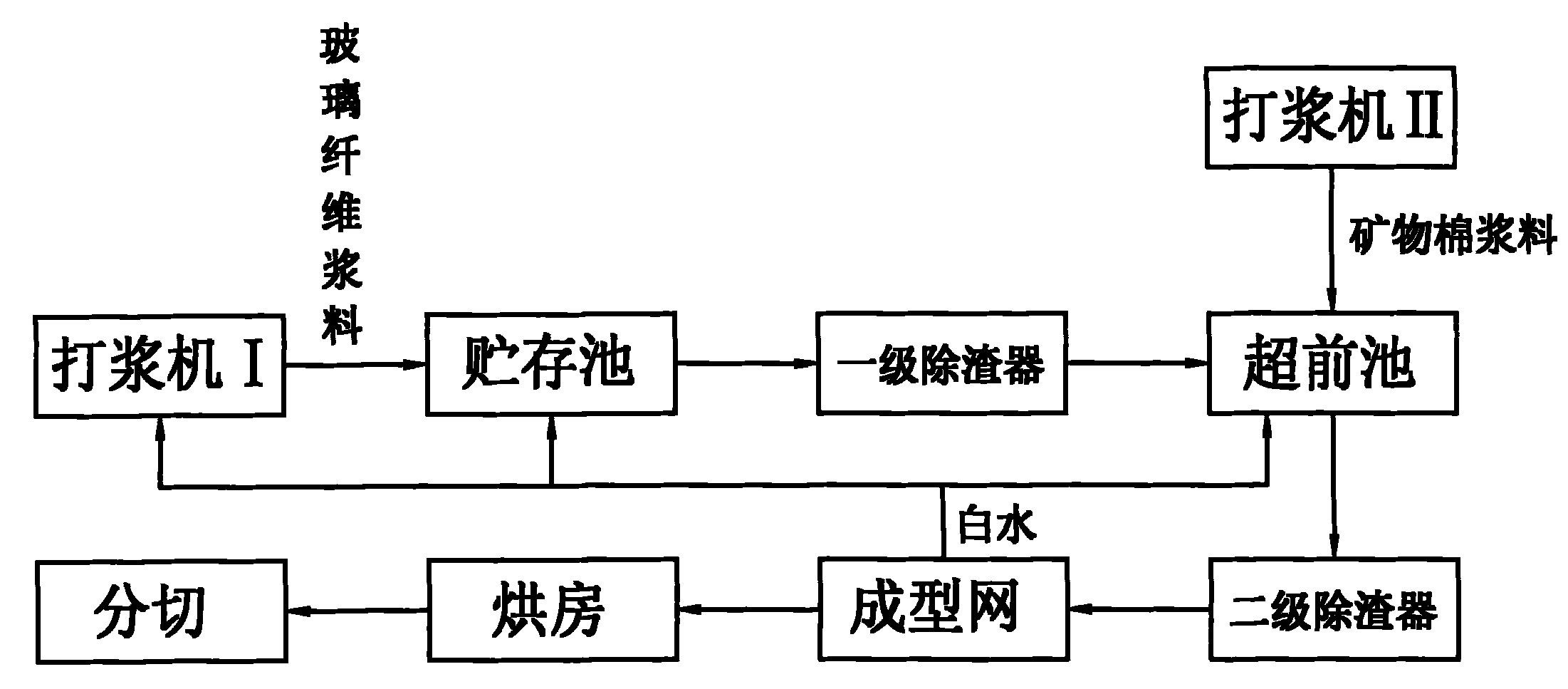
[0021] The core material of the vacuum insulation panel in this embodiment includes the following raw materials: 48Kg mineral wool, 45Kg glass fiber wool 27°SR, 35Kg glass fiber wool 18°SR, where "°SR" refers to the degree of beating, also known as beating The degree reflects the effect of fiber cutting, splitting, swelling, and hydration after the pulp passes through the refiner. The mineral wool is rock wool and / or slag wool. After melting natural rock or metallurgical slag in equipment such as a cupola or a pool kiln, the fiber diameter is 4-6 μm and the length is 1.0-6 μm by blowing or centrifugation. 4.0mm, mineral wool with a moisture content of 20%, the raw material cost is low, which is beneficial to reduce the production cost.
[0022] The accompanying drawing is a process flow chart of the present invention, as shown in the figure: the method for manufacturing the core material of a vacuum insulation panel in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0023] a)...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The raw material of the core material of the vacuum insulation panel in this embodiment is replaced by "45Kg glass fiber cotton 29 ° SR" in Example 1, and the rest are the same as in Example 1, and the method of Example 1 is adopted. In the manufacturing method, in step d, the pH value of the mixed slurry is adjusted to 2.9, and the core material of the vacuum insulation board is prepared, and a sampling inspection is carried out to measure its thermal conductivity, and compared with the sampled detection values of thermal conductivity of other core materials, and the comparison results are as follows surface:
[0035] name
Embodiment 3
[0037] The raw material of the core material of the vacuum insulation panel in this embodiment is "45Kg glass fiber cotton 31°SR" in Example 1 replaced with "45Kg glass fiber cotton 29°SR". In the manufacturing method, in step d, the pH value of the mixed slurry is adjusted to 2.8, and the core material of the vacuum insulation board is prepared, and a sampling inspection is carried out to measure its thermal conductivity, and compare it with the thermal conductivity sampling detection values of other core materials, and the comparison results are as follows surface:
[0038] name
[0039] From Examples 1 to 3, it can be known that the thermal conductivity of mineral wool and glass fiber cotton core materials is slightly lower than that of pure glass fiber wool, and is also lower than other heat preservation core materials. From the perspective of production cost, the manufacturing cost of the synthetic core material of mineral wool and glass fiber wool is also low...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com