Method for recovering and recycling sodium bromide from diethylbutylmalonate waste water
A technology of diethyl n-butylmalonate and sodium bromide, which is applied in the field of sodium bromide recovery and recycling, can solve the problems of increased recovery cost, lower recovery rate of sodium bromide, increased recovery cost and use cost, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
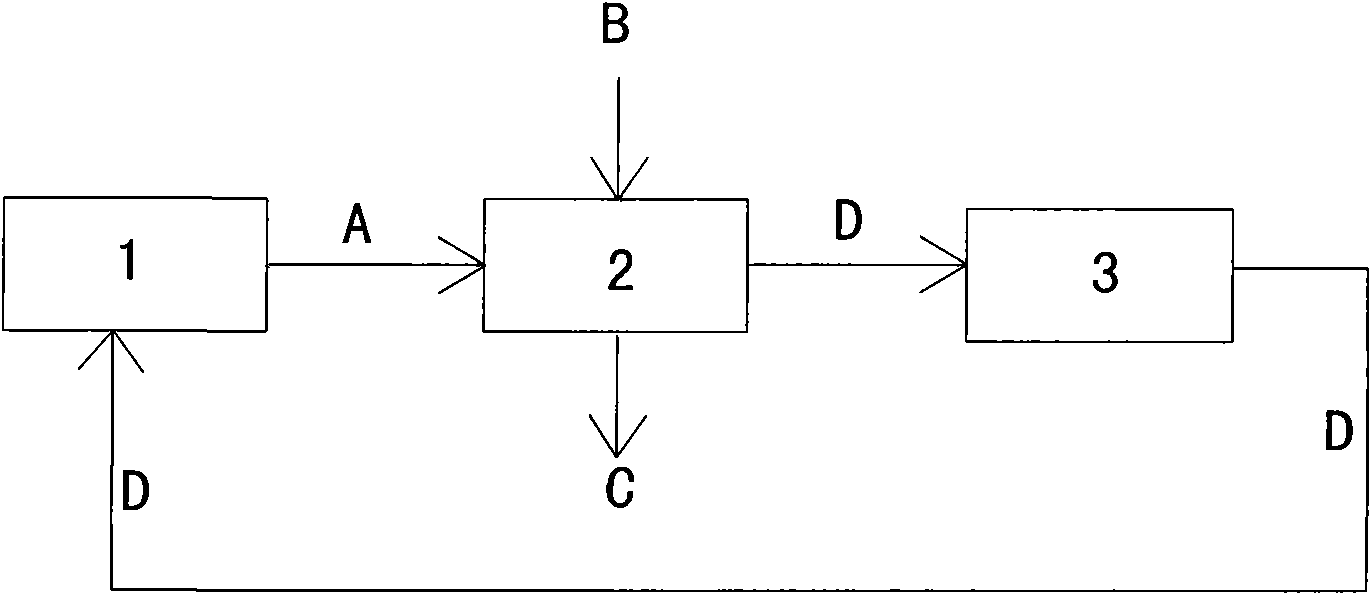
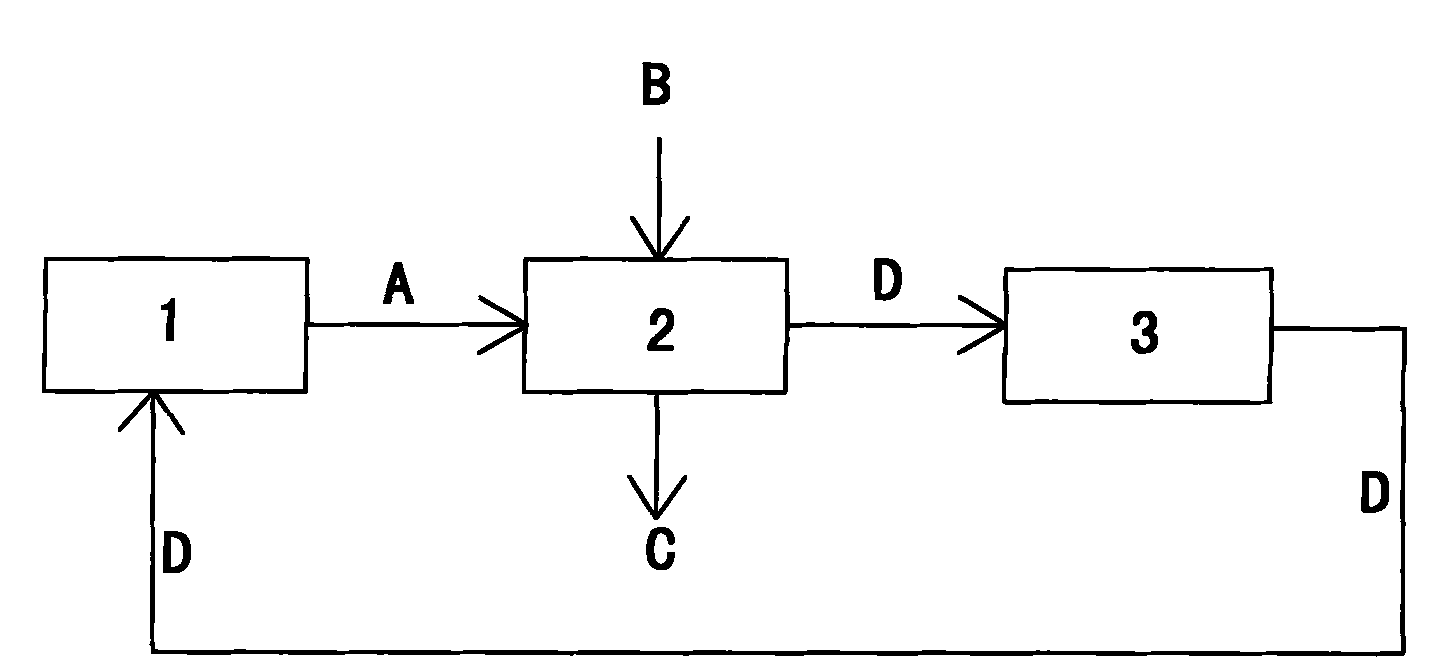
[0009] As shown in the accompanying drawings: from the method for recycling sodium bromide from n-butyl diethyl malonate waste water, it comprises the following process steps: from the production line 1 of n-butyl diethyl malonate Take 1000 grams of wastewater A. The above-mentioned waste water A is sent to the evaporator 2, steam B is passed into the evaporator 2, and the waste water A is heated with the steam B to steam the water C in the waste water, and the steamed water is discharged out of the evaporator 2. When 550 grams of water C is removed by evaporation, the waste water A becomes the concentrated solution D containing 400 grams of sodium bromide and 50 grams of water, and the concentrated solution D is sent into the cooling tank 3 to be naturally cooled to normal temperature. The concentrated solution D self-crystallized into 450 g of solid sodium bromide crystalline hydrate E during cooling. The above-mentioned solid sodium bromide crystalline hydrate E is sent to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com